- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-CUL7
CUL7 Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2a
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
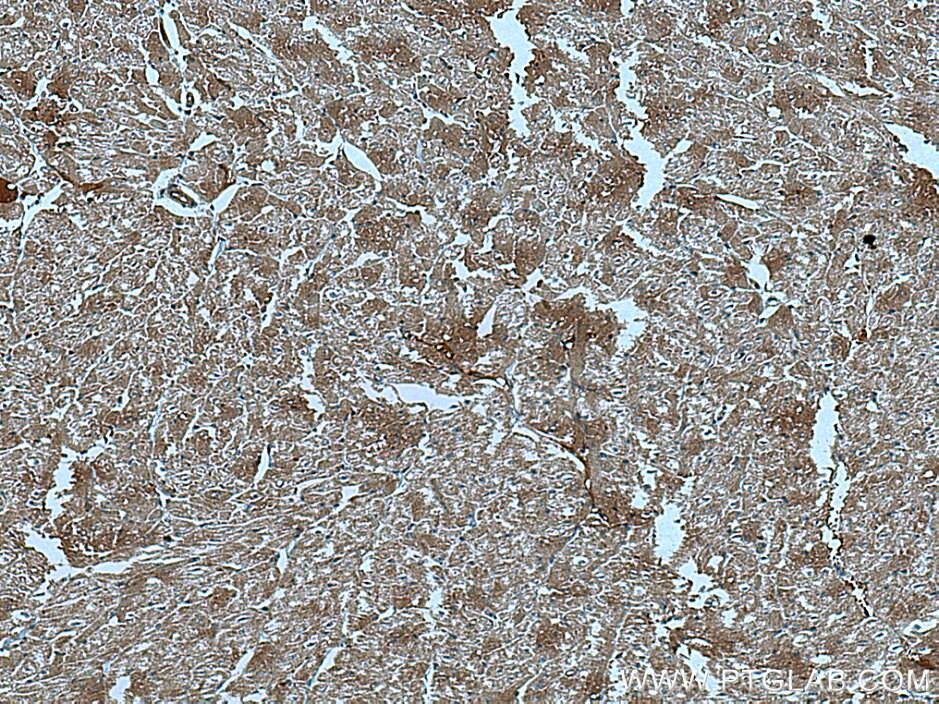
WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
2E3G9
N° de cat : 67034-1-PBS
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
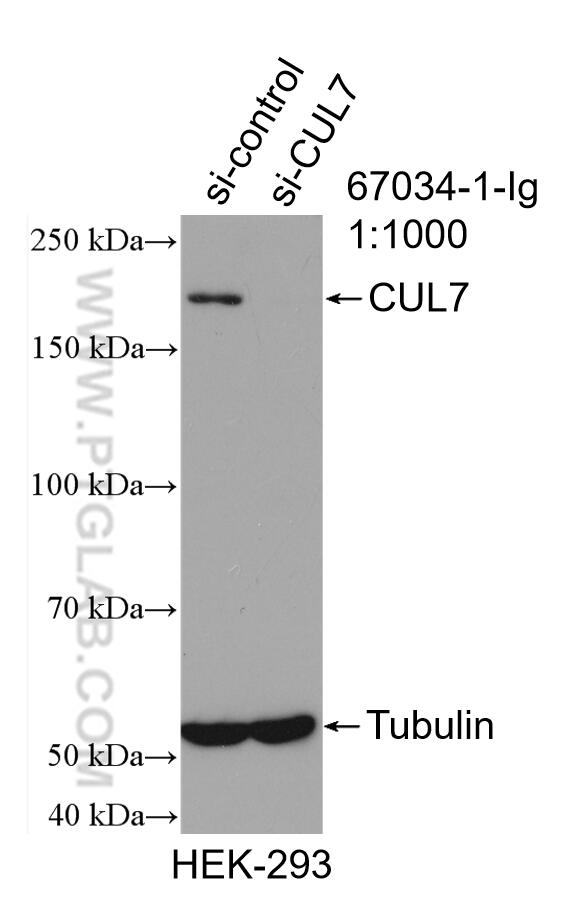
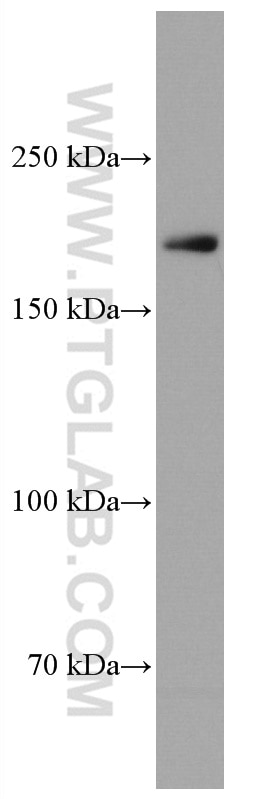
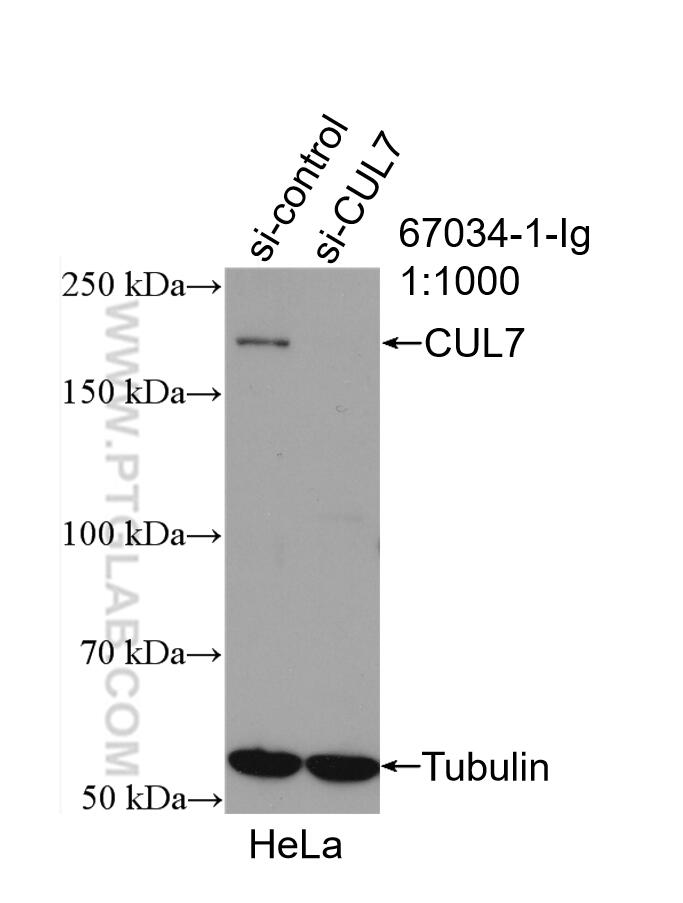
67034-1-PBS cible CUL7 dans les applications de WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | CUL7 Protéine recombinante Ag6943 |
| Nom complet | cullin 7 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 1698 aa, 191 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 185 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC033647 |
| Symbole du gène | CUL7 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 9820 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
he cullin family proteins are scaffold proteins for the Ring finger type E3 ligases, participating in the proteolysis through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Humans express seven cullin proeins: CUL1-3, CUL4A, CUL4B, CUL5, and CUL7. Each cullin protein can form an E3 ligase similar to the prototype Ring-type E3 ligase Skp1-CUL1-F-box complex. The Cullin-RING-finger type E3 ligases are important regulators in early embryonic development, as highlighted by genetic studies demonstrating that knock-out of CUL1, CUL3, or CUL4A in mice results in early embryonic lethality. CUL7 was originally discovered as 185-kDa protein associated with the large T antigen of simian virus 40 (SV40). CUL7-deficient mice exhibit neonatal lethality with reduced size and vascular defects. CUL7 presumably plays a role in the DNA damage response by limiting p53 activity. CUL7 mutations have also been identified in 3-Msyndrome and the Yakuts short stature syndrome, both of which are characterized by pre- and post-natal growth retardation but with relatively normal mental and endocrine functions, suggesting that CUL7 may also be crucial for human placental development.