- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-CXCL16
CXCL16 Monoclonal Antibody for WB, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2a
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris
Applications
WB, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
2H7B3
N° de cat : 60123-1-PBS
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
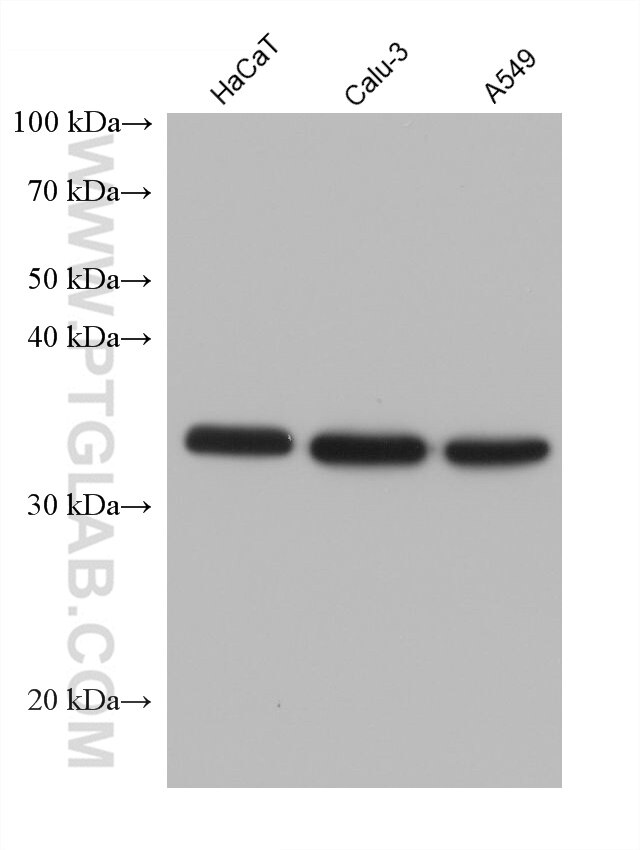
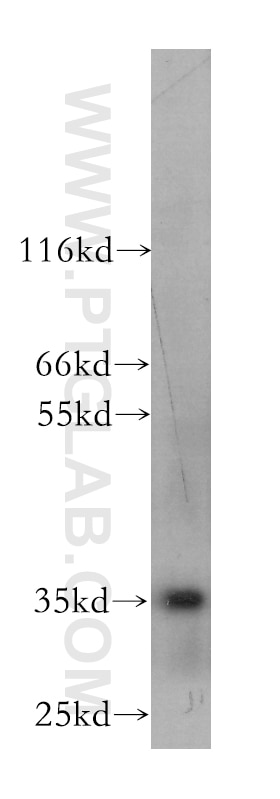
60123-1-PBS cible CXCL16 dans les applications de WB, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | CXCL16 Protéine recombinante Ag4883 |
| Nom complet | chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 16 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 273 aa, 30 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 35 kDa, 60 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC017588 |
| Symbole du gène | CXCL16 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 58191 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
CXCL16 is a recently discovered cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family, which is synthesised in plasmacytoid dendritic cell as a transmembrane molecule. It exists in a transmembrane and soluble form. The transmembrane form of CXCL16 functions as an adhesion molecule for CXCR6-expressing cells, whereas the soluble form of CXCL16 mediates infiltration of circulating cells into sites of injury. CXCL16, has been proposed as an important pathogenic mediator in inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, glomerulonephritis, or prostate cancer. CXCL16 has been implicated in some forms of renal disease such as lupus nephritis and antiglomerular basement membrane nephritis. CXCL16 also plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of angiotensin II-induced renal injury and fibrosis through regulation of macrophage and T cell infiltration and bone marrow-derived fibroblast accumulation.