- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-EXOC1
EXOC1 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IP, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 11690-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
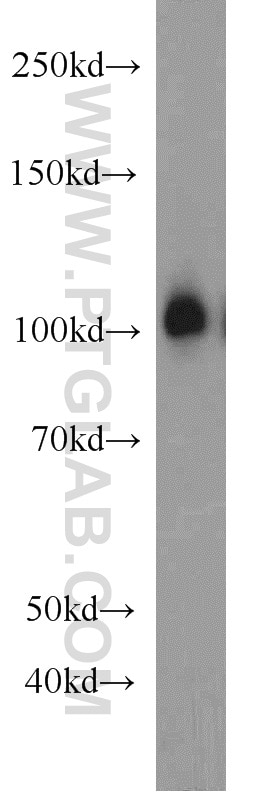
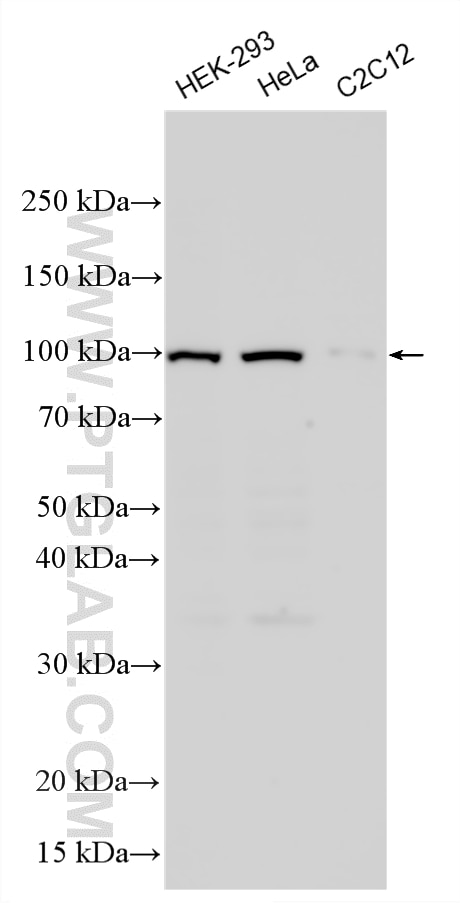
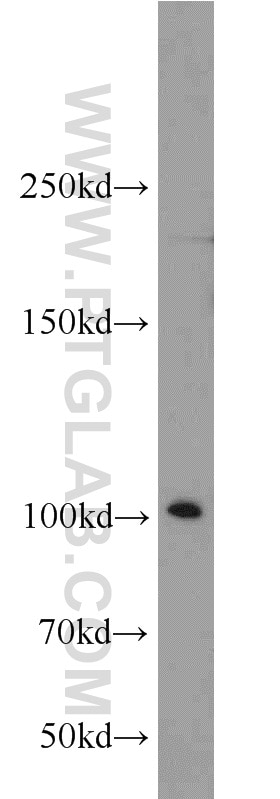
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HEK-293, cellules C2C12, cellules HeLa, tissu cérébral de rat, tissu cérébral de souris, tissu cérébral humain |
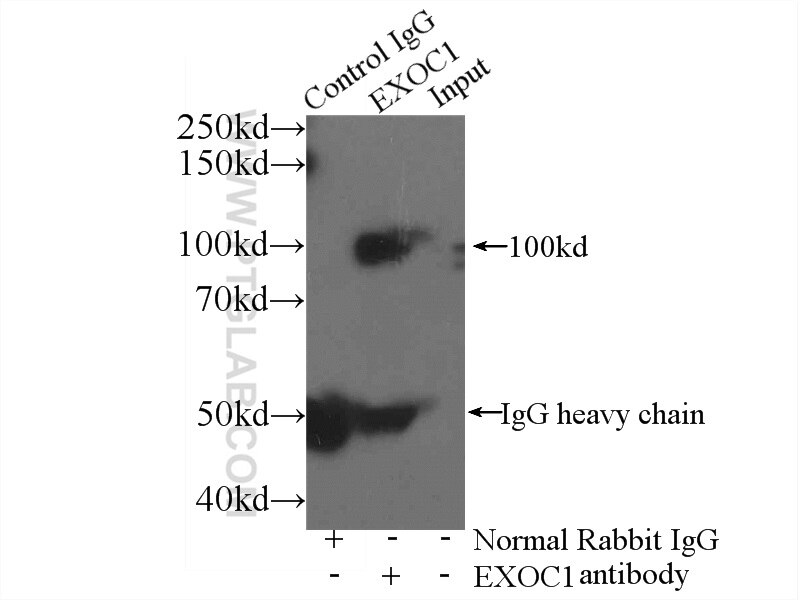
| Résultats positifs en IP | tissu cérébral de souris |
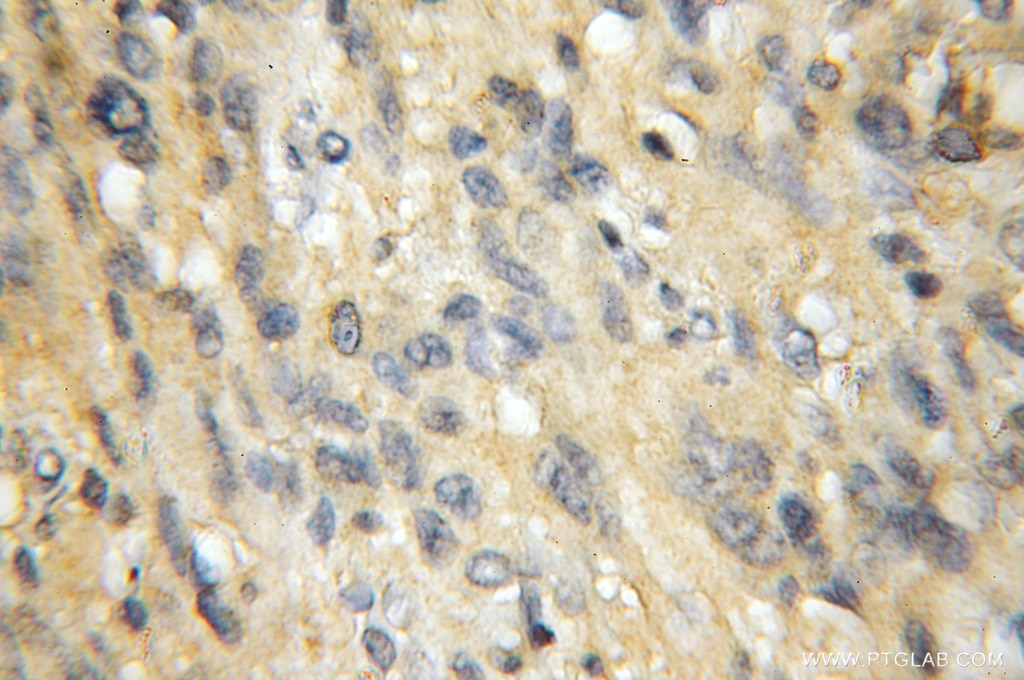
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de gliome humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
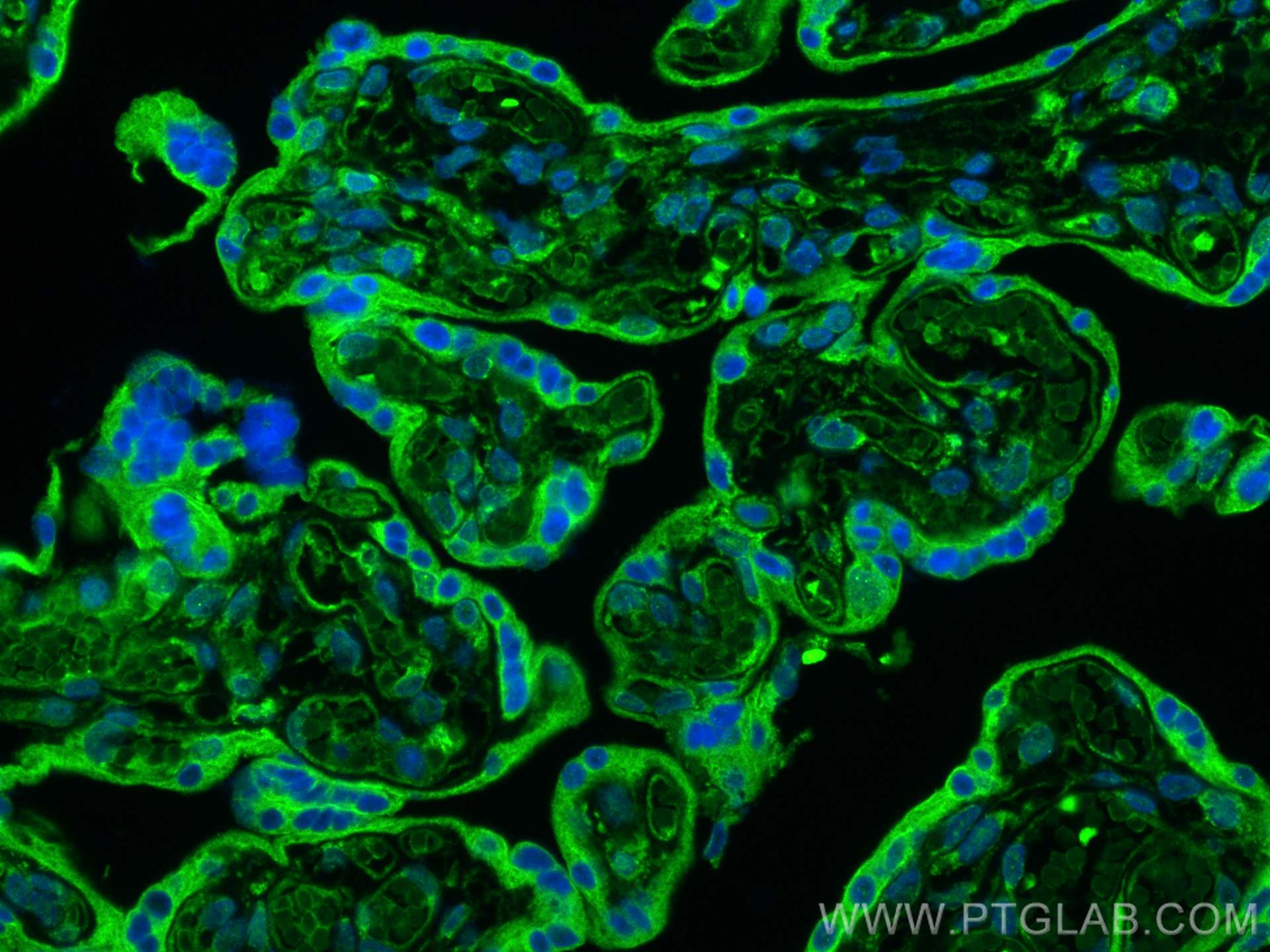
| Résultats positifs en IF-P | tissu placentaire humain, |
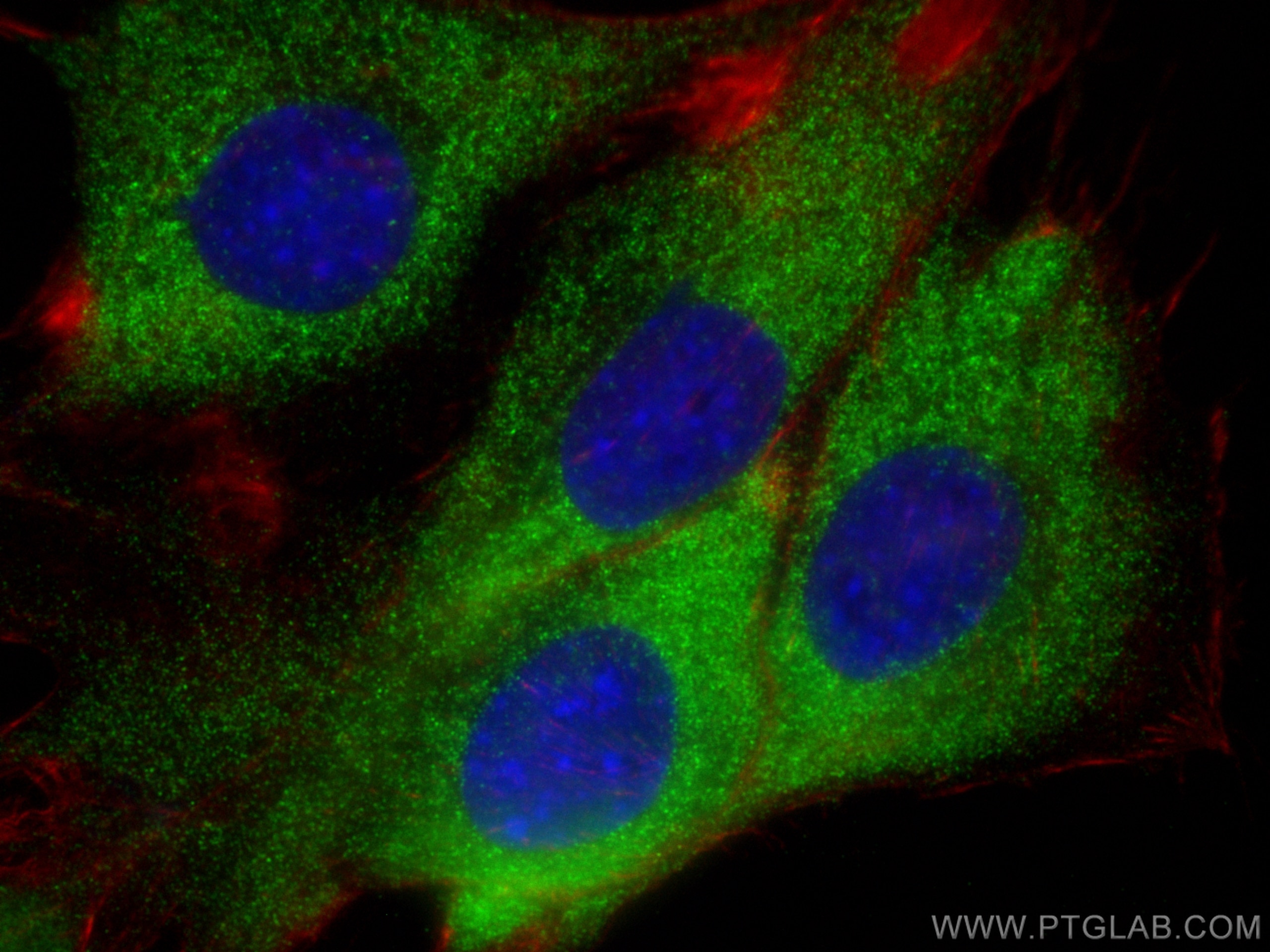
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules C2C12, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 10 publications below |
| IF | See 9 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
11690-1-AP cible EXOC1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | EXOC1 Protéine recombinante Ag2303 |
| Nom complet | exocyst complex component 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 894 aa, 102 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 102 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC020650 |
| Symbole du gène | EXOC1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 55763 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
EXOC1 (exocyst complex component 1), also known as SEC3, is a component of the exocyst complex which is essential for the targeting of exocytic vesicles to specific docking sites on the plasma membrane. The exocyst complex is an octameric complex that tethers vesicles at the plasma membrane, regulates polarized exocytosis, and recruits membranes and proteins required for nanotube formation.Recently it has been reported that exocyst complex proteins are likely a key effector of Nef-mediated enhancement of nanotube formation, and possibly microvesicle secretion, which suggests a new paradigm of exocyst involvement in polarized targeting for intercellular transfer of viral proteins and viruses.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for EXOC1 antibody 11690-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for EXOC1 antibody 11690-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for EXOC1 antibody 11690-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for EXOC1 antibody 11690-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Nanotechnol Intercellular nanotubes mediate mitochondrial trafficking between cancer and immune cells.
| ||
J Cell Biol The exocyst controls lysosome secretion and antigen extraction at the immune synapse of B cells. | ||
Elife EXOC1 plays an integral role in spermatogonia pseudopod elongation and spermatocyte stable syncytium formation in mice. | ||
PLoS Pathog Shigella hijacks the exocyst to cluster macropinosomes for efficient vacuolar escape. | ||
Retrovirology Proteomic analysis of HIV-1 Nef cellular binding partners reveals a role for exocyst complex proteins in mediating enhancement of intercellular nanotube formation. |