Anticorps Monoclonal anti-FABP4
FABP4 Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2b
Réactivité testée
Humain, porc, rat, souris
Applications
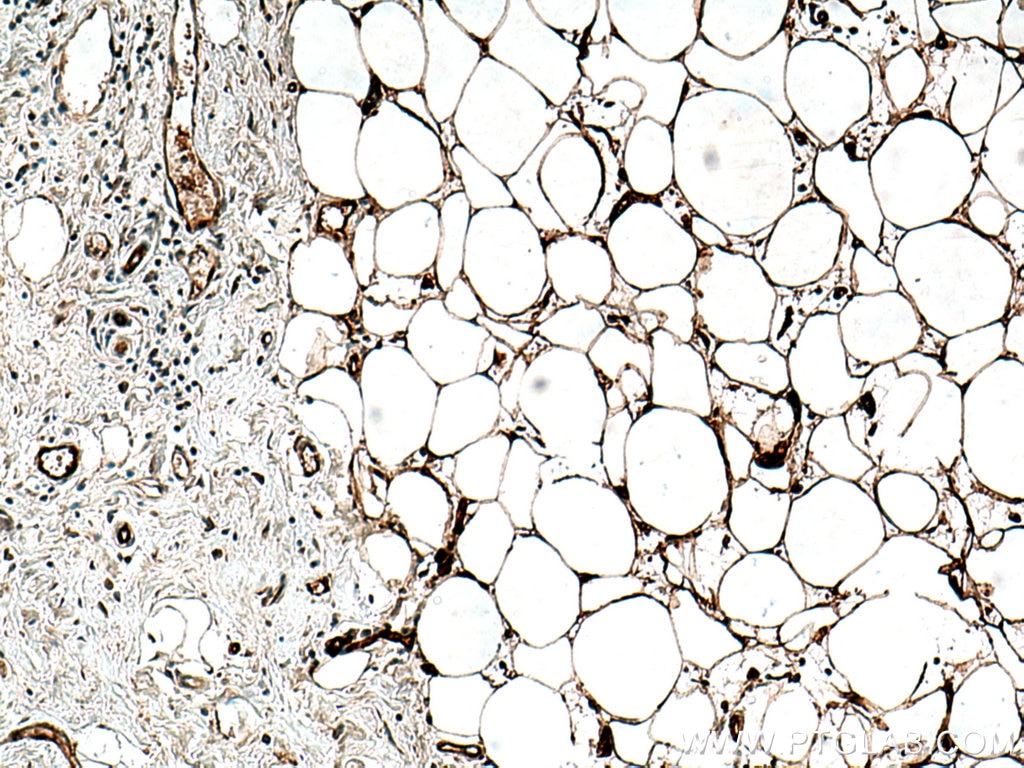
WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
3E7E1
N° de cat : 67167-1-PBS
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
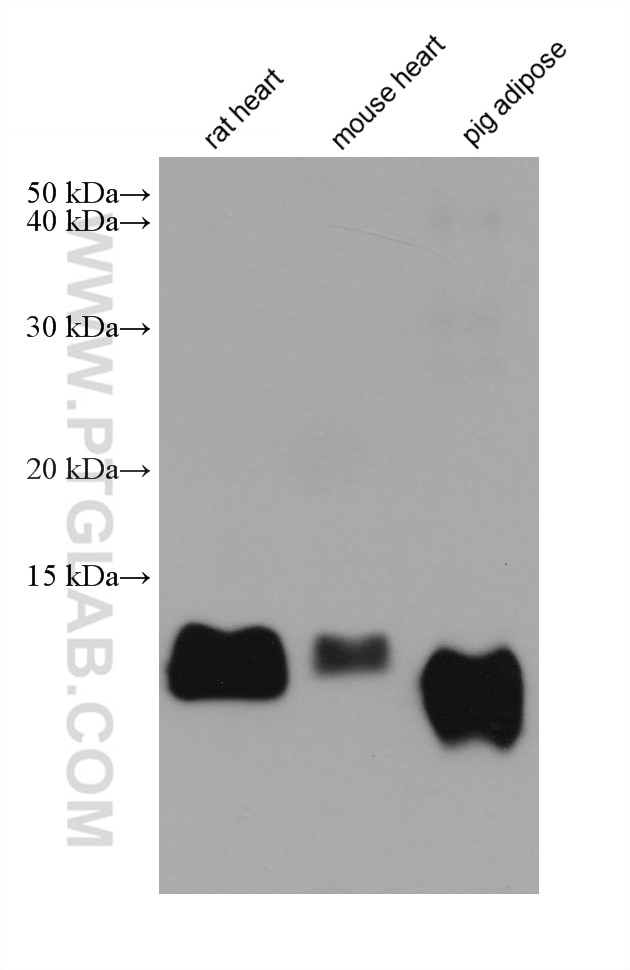
67167-1-PBS cible FABP4 dans les applications de WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, porc, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, porc, rat, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | FABP4 Protéine recombinante Ag8565 |
| Nom complet | fatty acid binding protein 4, adipocyte |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 132 aa, 15 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 14 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC003672 |
| Symbole du gène | FABP4 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 2167 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Fatty acid binding protein (FABP) 4 is a member of the FABP family which abundantly expressed, fatty acid carrier proteins. FABPs are capable of binding a variety of hydrophobic molecules such as long-chain fatty acids and are important for their uptake and intracellular trafficking. It was first identified as an adipocyte-specific protein, important for the maintenance of lipid and glucose metabolism. It is also detected in macrophages, where it participates in regulating inflammation and cholesterol trafficking via NFκB and PPAR. In more recent studies, FABP4 has been found in a variety of endothelial cells, where it has been identified as a target of VEGF and a regulator of cell proliferation and possibly angiogenesis. Pathologically, FABP4 has been associated with the development of metabolic syndrome, diabetes and cancer and vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaques. FABP4 has been identified as a novel prognostic factor for both adverse cardiovascular events and breast cancer.