- Phare
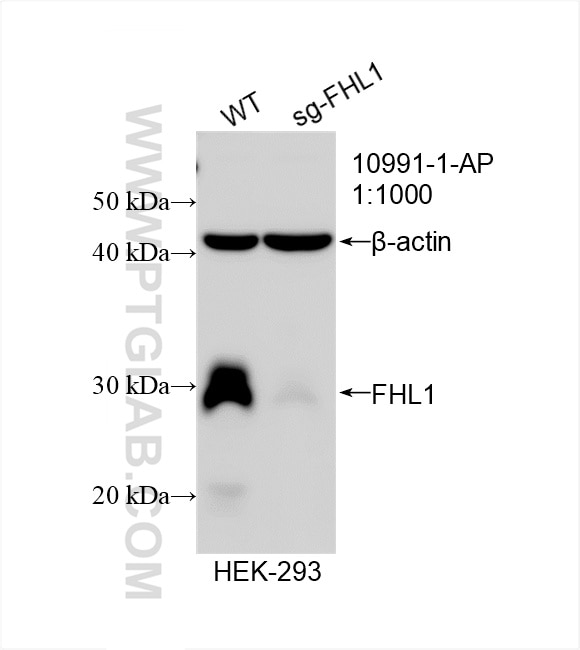
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-FHL1
FHL1 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IP, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, poisson-zèbre, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF, IP, CoIP, ChIP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 10991-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
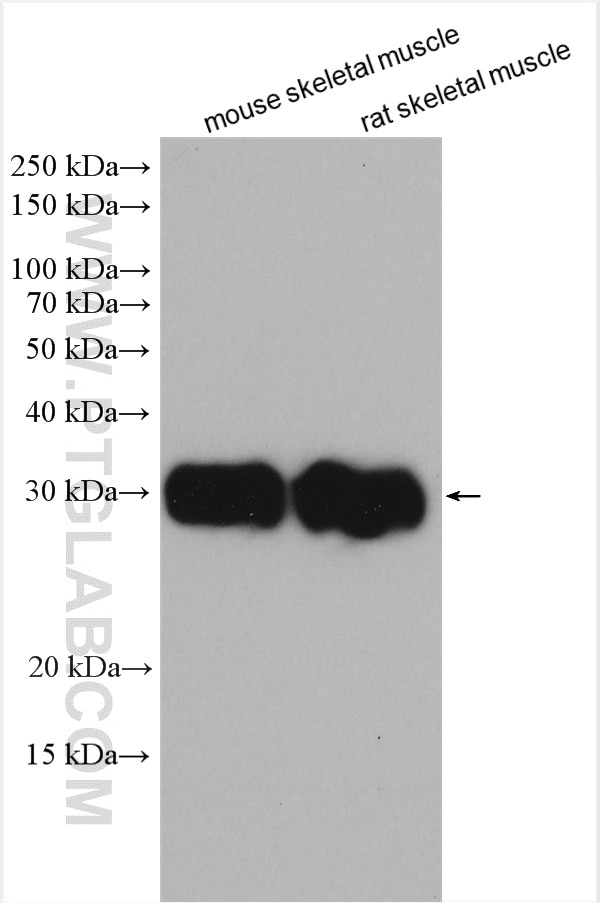
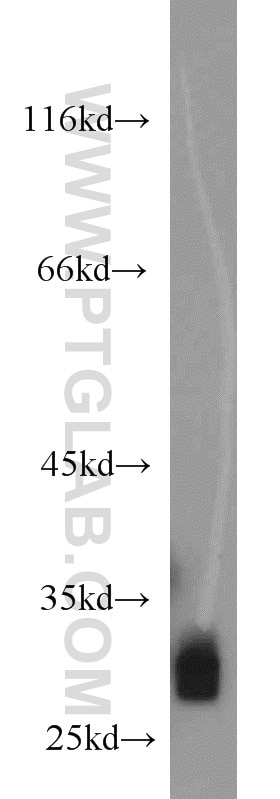
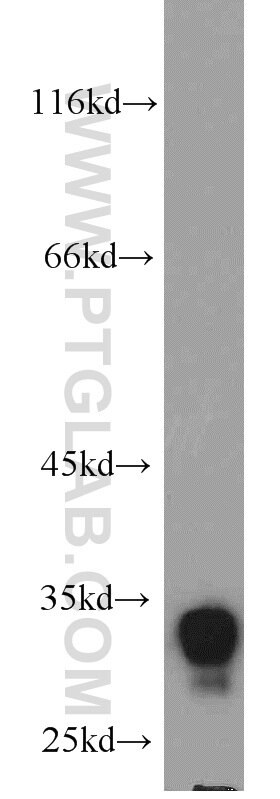
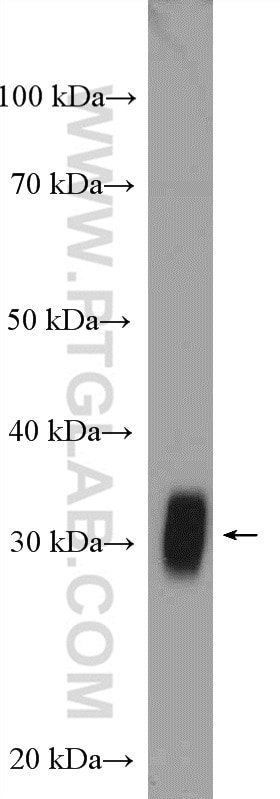
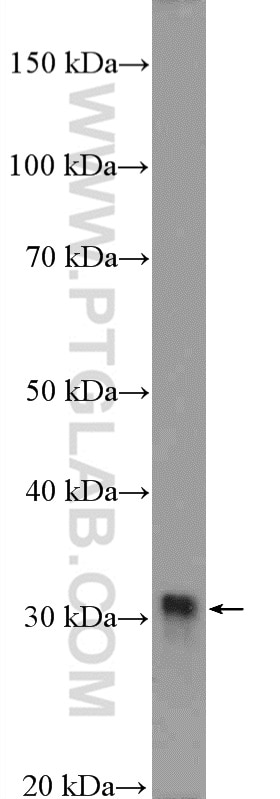
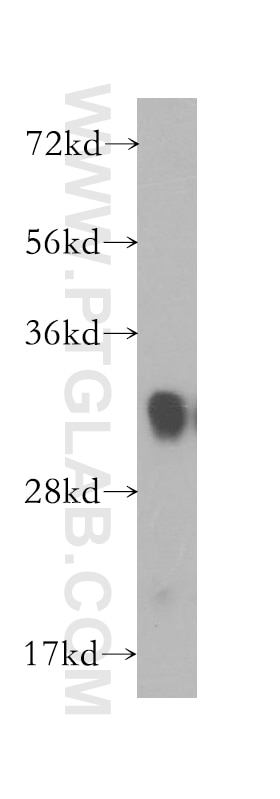
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu de muscle squelettique de souris, cellules HEK-293, tissu cérébral humain, tissu de côlon de souris, tissu de muscle squelettique de rat |
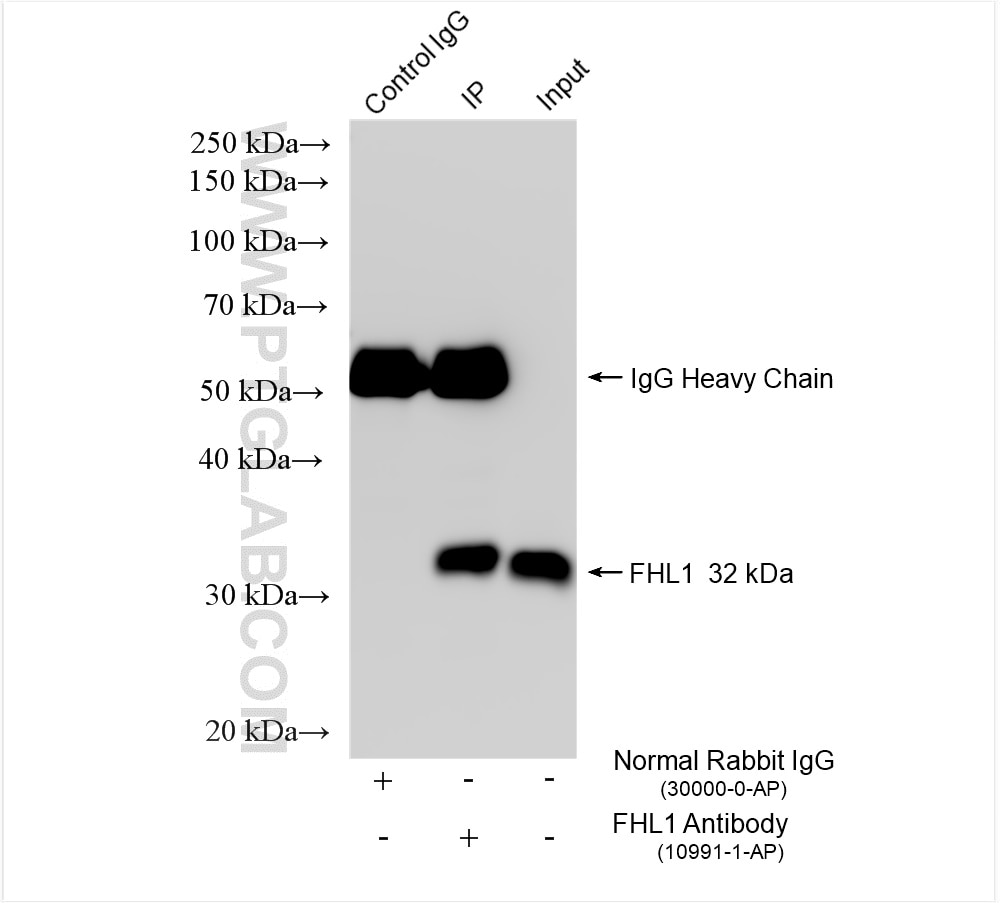
| Résultats positifs en IP | tissu de muscle squelettique de souris, |
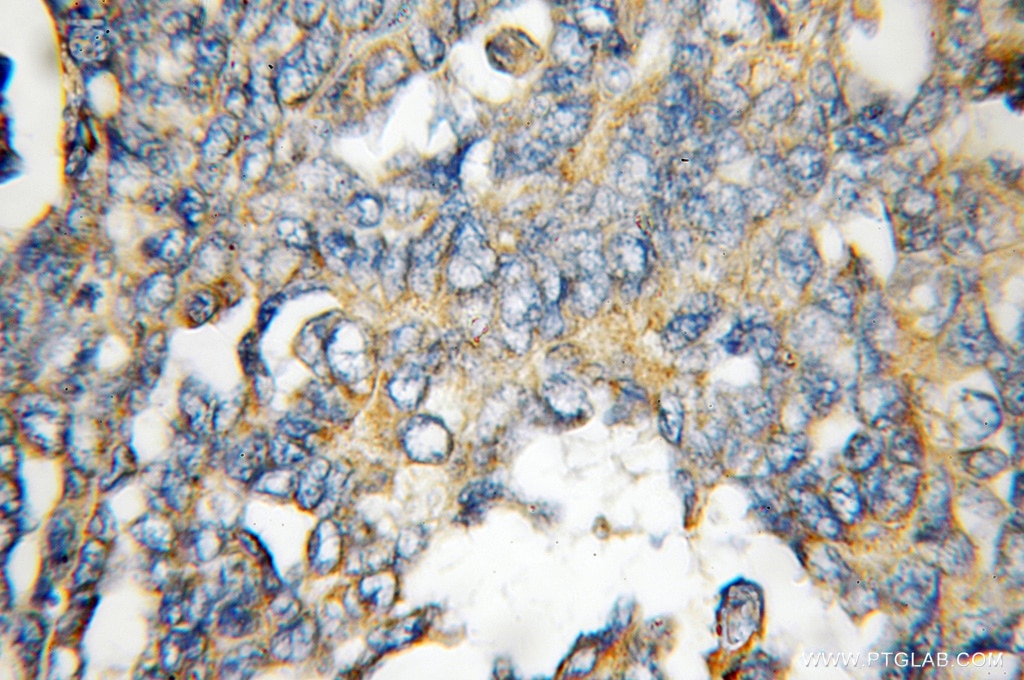
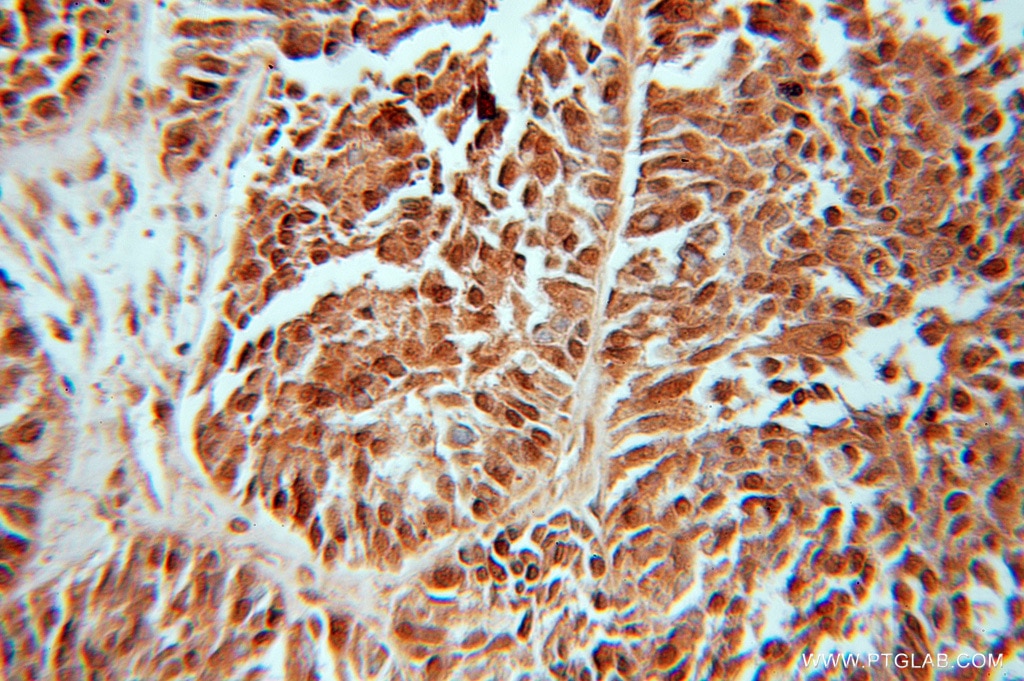
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de tumeur ovarienne humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:8000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 4 publications below |
| WB | See 27 publications below |
| IHC | See 10 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
| CoIP | See 2 publications below |
| ChIP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
10991-1-AP cible FHL1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF, IP, CoIP, ChIP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, poisson-zèbre, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, poisson-zèbre, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, poisson-zèbre, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | FHL1 Protéine recombinante Ag1448 |
| Nom complet | four and a half LIM domains 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 32 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 32 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC010998 |
| Symbole du gène | FHL1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 2273 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Four-and-a-half LIM domains 1 (FHL1), a member of the FHL protein family, which composed of FHL 1, 2, 3, 4 and ACT (activator of CREM), and characterized by an N-terminal half LIM domain followed by four complete LIM domains. FHL1 may contribute to sarcomere synthesis, assembly and biomechanical stress sensing. FHL1 is also a methylation-silenced tumor-suppressor gene on chromosome X in gastrointestinal cancers, which contributes to the formation of an epigenetic field for cancerization. FHL1(10991-1-AP) is highly expressed in skeletal muscle and to a lesser extent in heart, placenta, ovary, prostate, testis, small intestine, colon and spleen. This is a rabbit polyantibody raised against full length of human FHL1.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for FHL1 antibody 10991-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for FHL1 antibody 10991-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for FHL1 antibody 10991-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Clin Invest Human four-and-a-half LIM family members suppress tumor cell growth through a TGF-beta-like signaling pathway.
| ||
Genes Dev Browning of human adipocytes requires KLF11 and reprogramming of PPARγ superenhancers.
| ||
Nat Commun A signature motif in LIM proteins mediates binding to checkpoint proteins and increases tumour radiosensitivity.
| ||
J Cell Biol Src-mediated phosphorylation converts FHL1 from tumor suppressor to tumor promoter. | ||
J Cell Sci MAL/MRTF-A controls migration of non-invasive cells by upregulation of cytoskeleton-associated proteins. |