- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
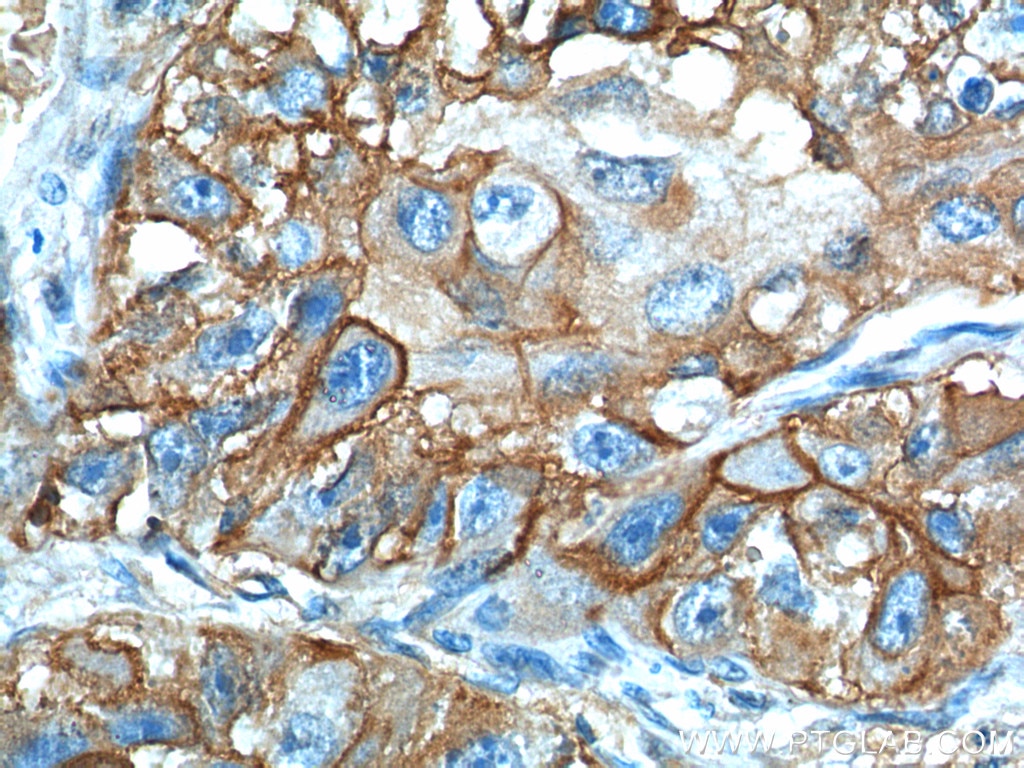
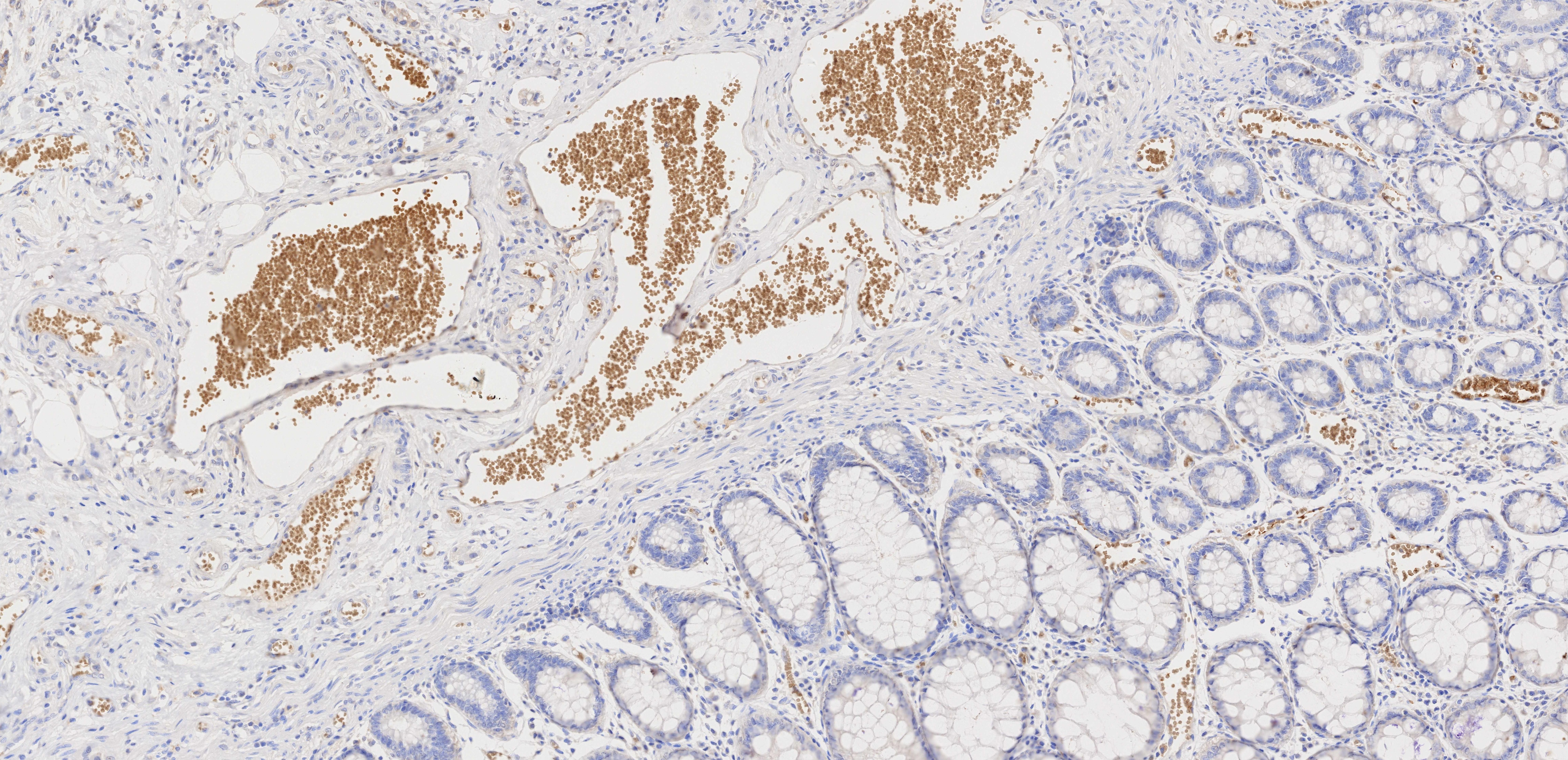
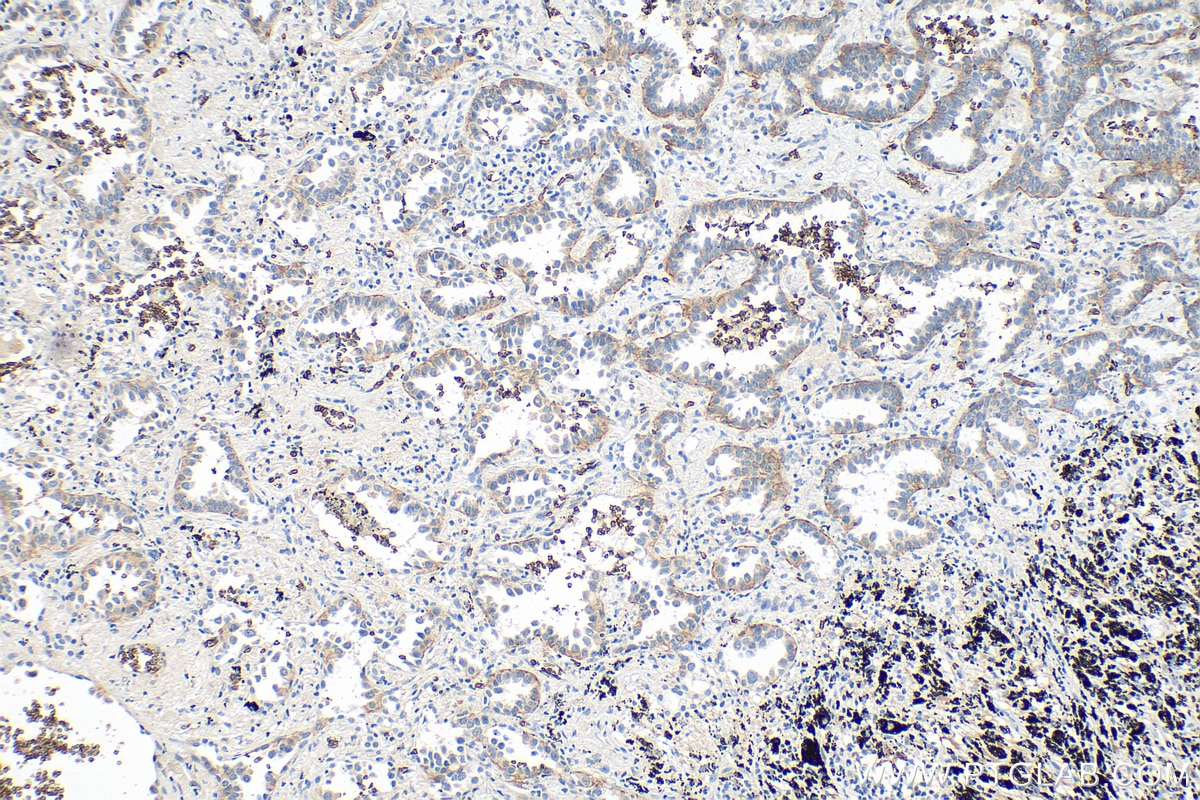
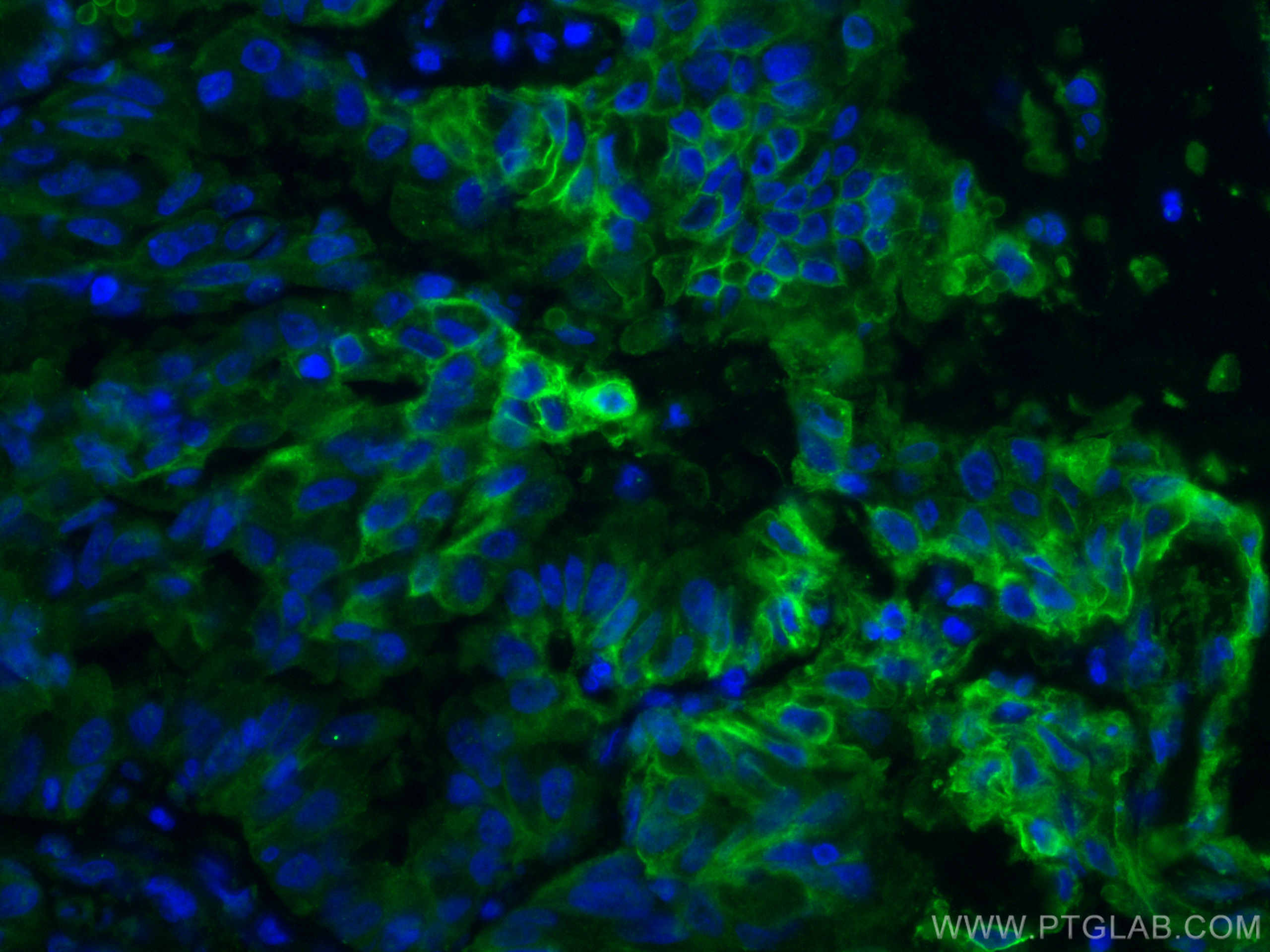
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-GLUT1
GLUT1 Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, FC (Intra), ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris
Applications
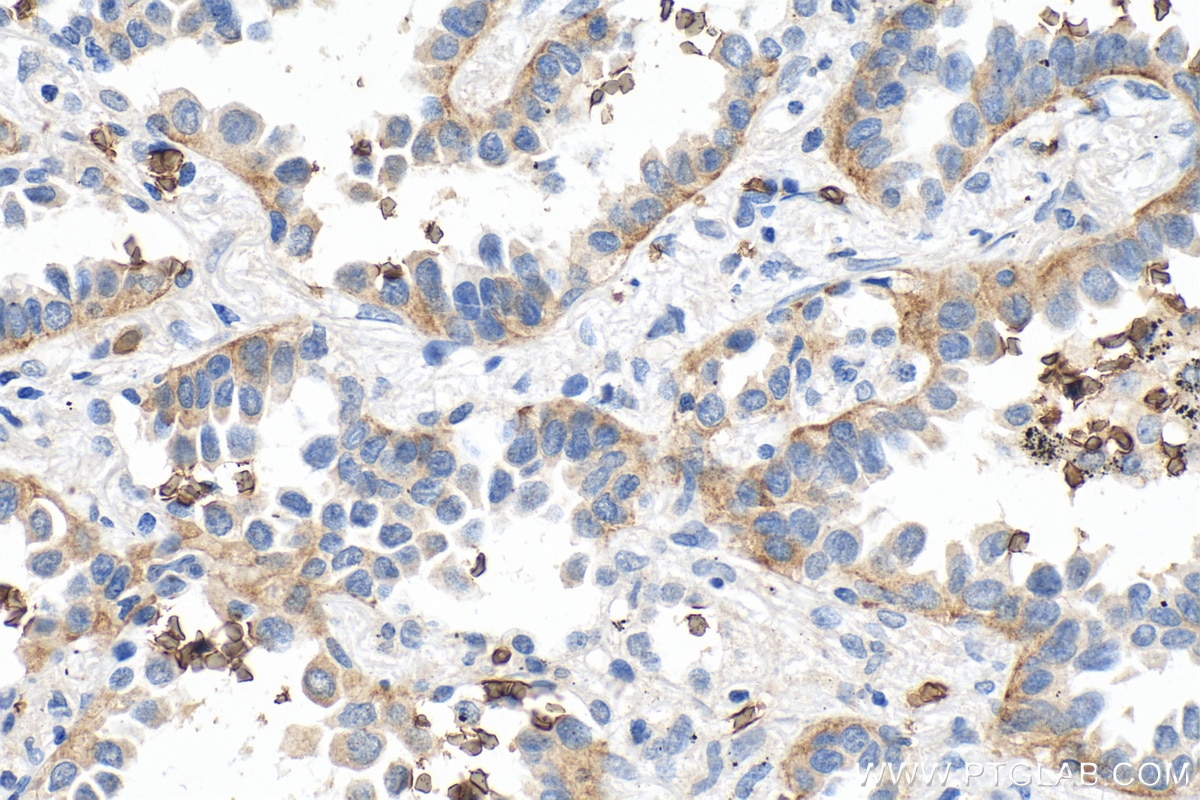
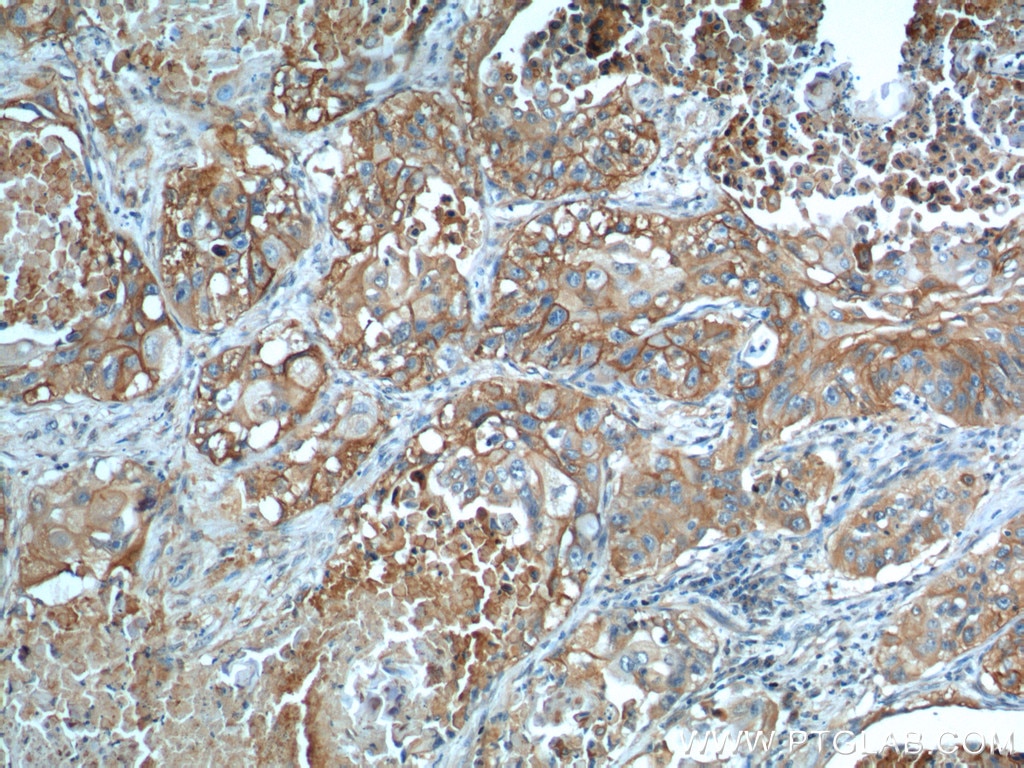
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, FC (Intra), ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
2A5A2
N° de cat : 66290-1-PBS
Synonymes
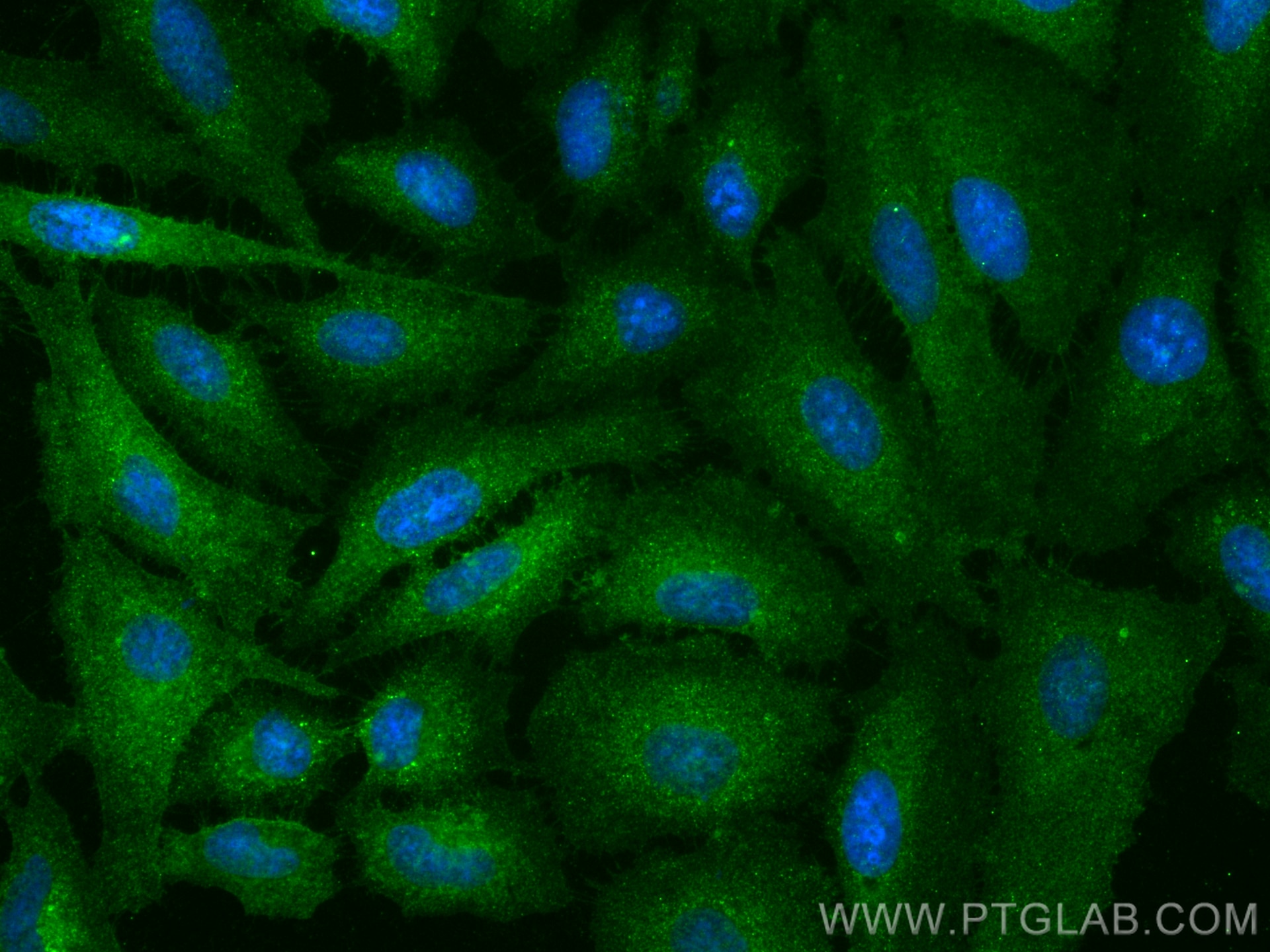
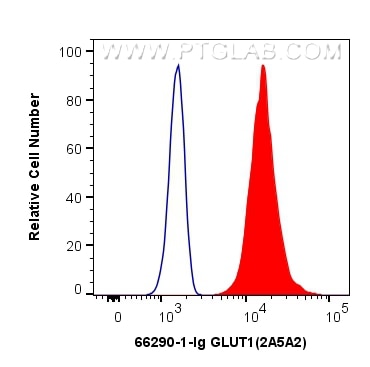
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
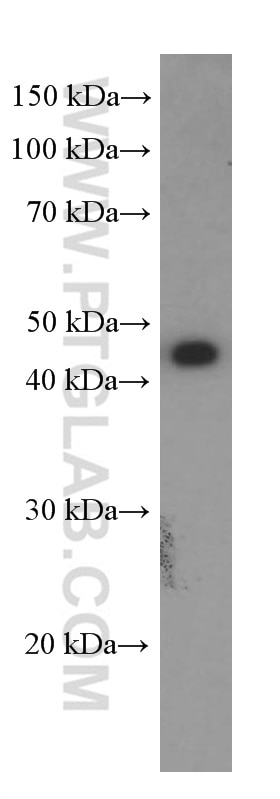
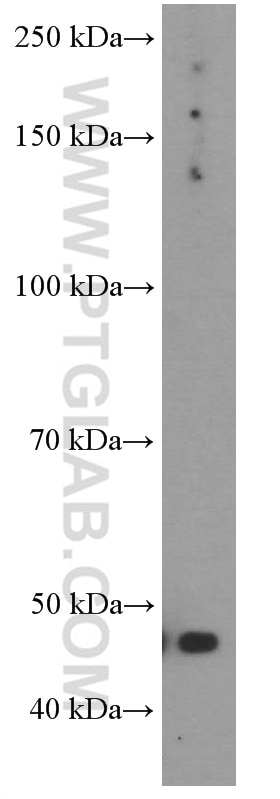
66290-1-PBS cible GLUT1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, FC (Intra), ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | GLUT1 Protéine recombinante Ag17108 |
| Nom complet | solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 492 aa, 54 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 45-55 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC121804 |
| Symbole du gène | GLUT1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 6513 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine G |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1), also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 (SLC2A1), is a uniporter protein responsible for the transport of glucose in many cell types and across the blood-brain barrier.
What is the molecular weight of GLUT1? Is GLUT1 post-translationally modified?
There are two forms of GLUT1 transporter that differ in their molecular weight. The 45-kDa form is found in glial cells, while the 55-kDa form is present in the endothelial cells regulating glucose transport over the blood-brain and blood-tissue barriers (PMID: 9630522). N-glycosylation of asparagine at position 42 is the only known post-translation modification of GLUT1 (PMID: 3839598).
What is the subcellular localization of GLUT1?
Glucose transporters, including GLUT1, are multiple-pass integral membrane proteins. GLUT1 is present at the plasma membrane but is also a subject of recycling between plasma membrane and endosomes.
What molecules can be transported by GLUT1?
The main substrate of GLUT1 transport is glucose, but it can also transport galactose, mannose, glucosamine, and reduced ascorbate.
What is the tissue expression pattern of GLUT1?
GLUT1 is expressed by many cell types but the highest levels are observed in erythrocytes and in the central nervous system (astrocytes). GLUT1 is responsible for glucose transfer across the blood-brain and blood-tissue barriers, including placental transport.