Anticorps Recombinant de lapin anti-NMDAR2A/GRIN2A
NMDAR2A/GRIN2A Recombinant Antibody for WB, IF-P, FC (Intra), Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
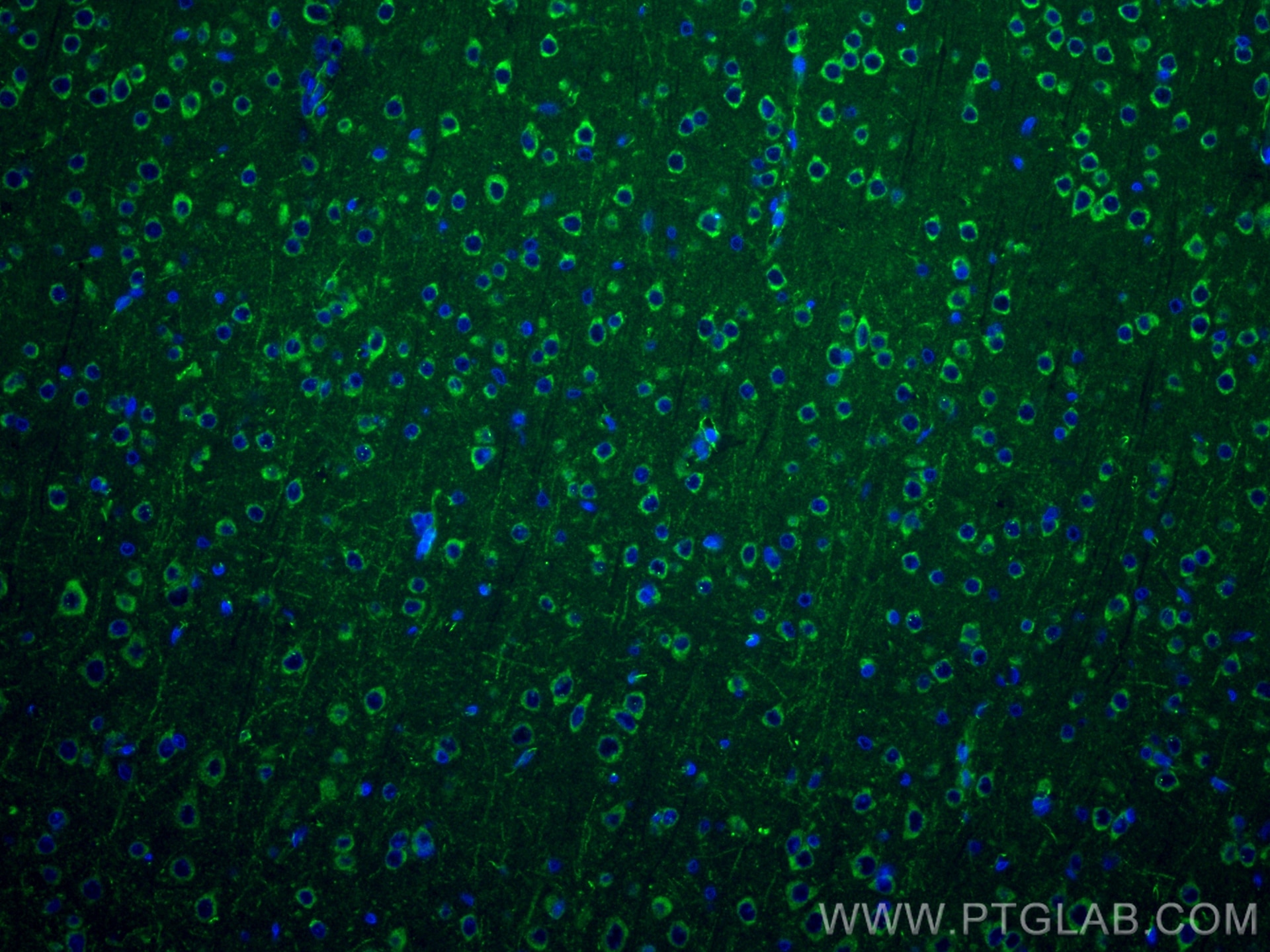
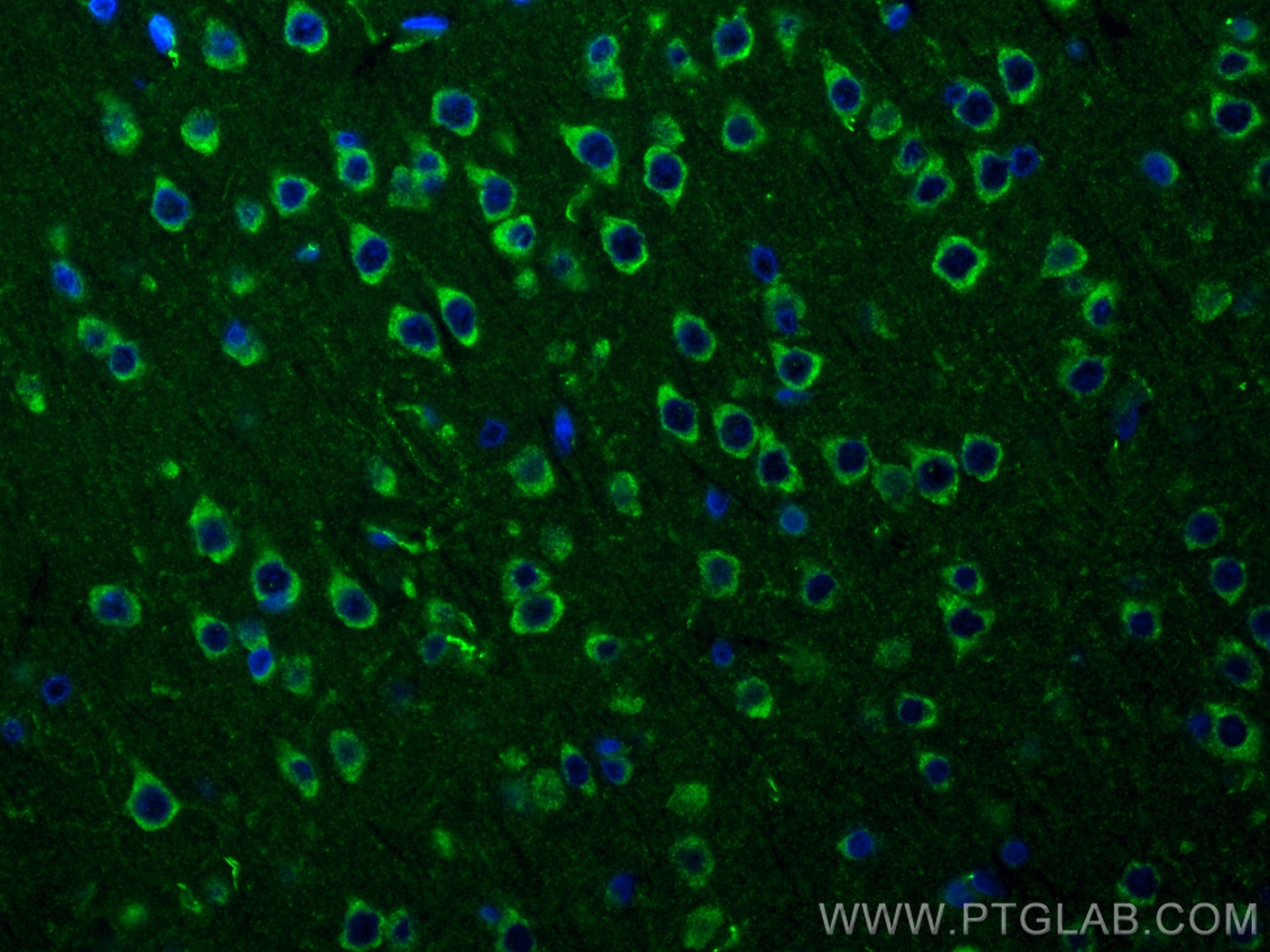
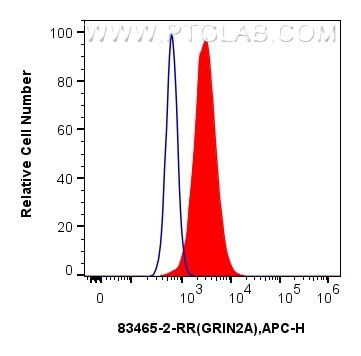
WB, IF-P, FC (Intra), Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
240445D4
N° de cat : 83465-2-PBS
Synonymes
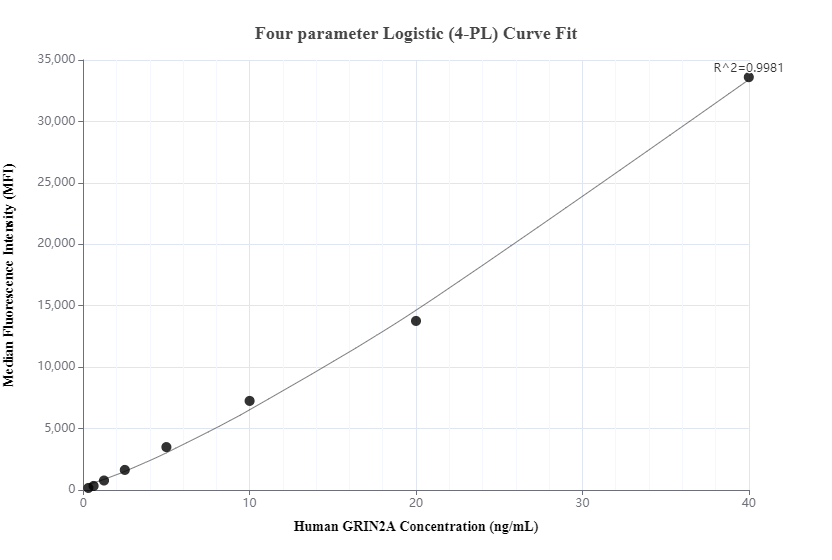
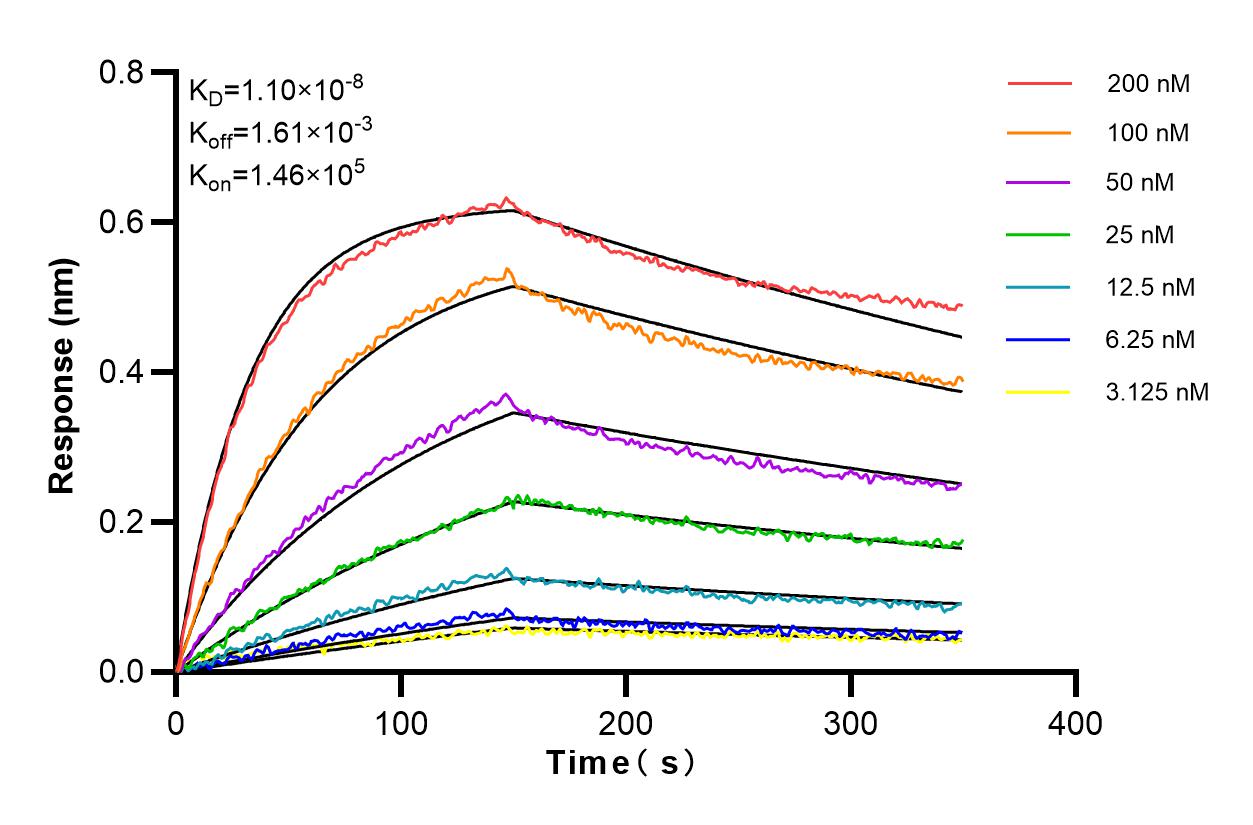
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
83465-2-PBS cible NMDAR2A/GRIN2A dans les applications de WB, IF-P, FC (Intra), Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Recombinant |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | NMDAR2A/GRIN2A Protéine recombinante Ag29101 |
| Nom complet | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2A |
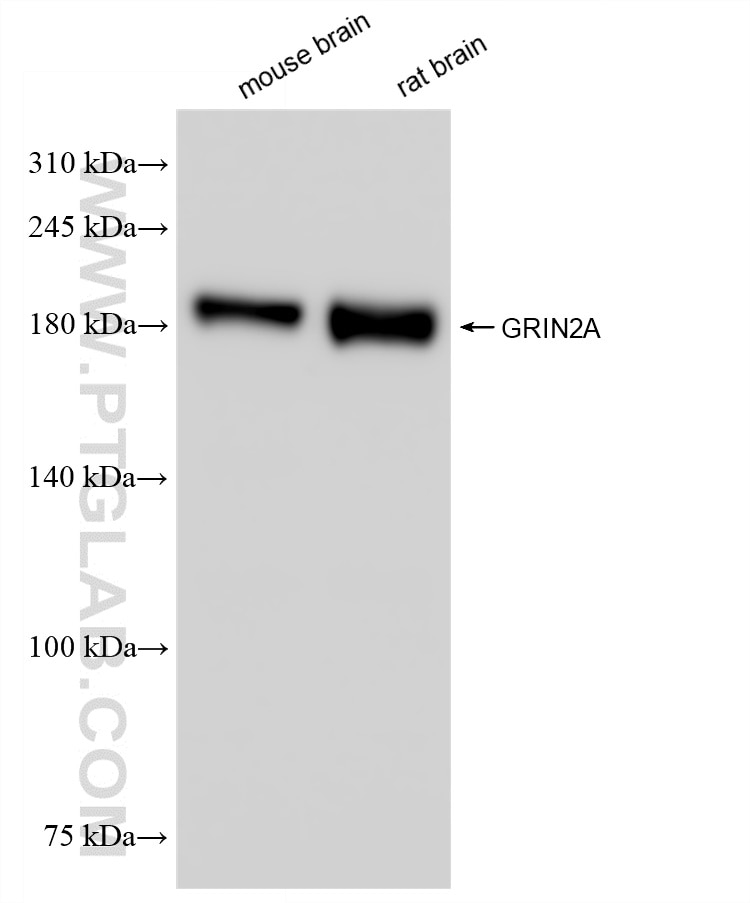
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 165 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 160-180 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | NM_000833 |
| Symbole du gène | GRIN2A |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 2903 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
GRIN2A (glutamate ionotropic receptor NMDA type subunit 2A), also known as NMDAR2A. And its molecular weight is 165 kDa. GRIN2A is located in cell projection, dendritic spine, cell membrane, synapse, postsynaptic cell membrae, cytolamic vesicle membrane, which is expressed in many tissues, highest expression in brain and heart. This gene encodes a member of the glutamate-gated ion channel protein family. The encoded protein is an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunit. NMDA receptors are both ligand-gated and voltage-dependent, and are involved in long-term potentiation, an activity-dependent increase in the efficiency of synaptic transmission thought to underlie certain kinds of memory and learning. These receptors are permeable to calcium ions, and activation results in a calcium influx into post-synaptic cells, which results in the activation of several signaling cascades. Disruption of this gene is associated with focal epilepsy and speech disorder with or without cognitive disability. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.