- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-HDAC5-specific
HDAC5-specific Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris et plus (1)
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, CoIP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 16166-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
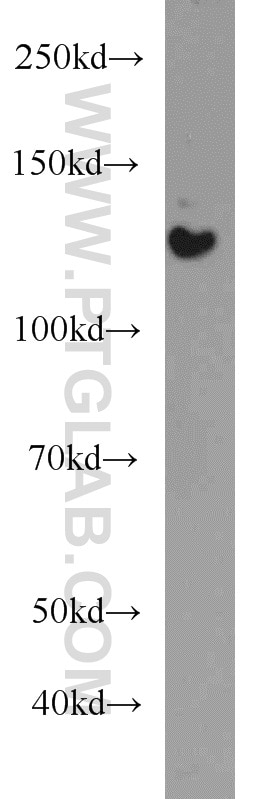
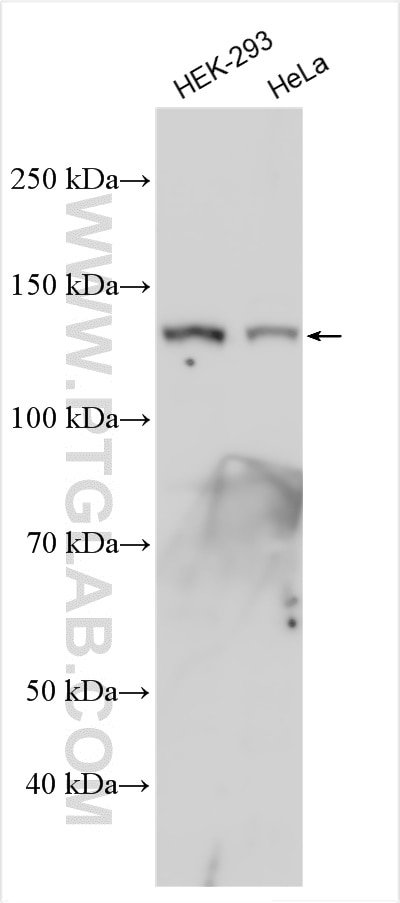
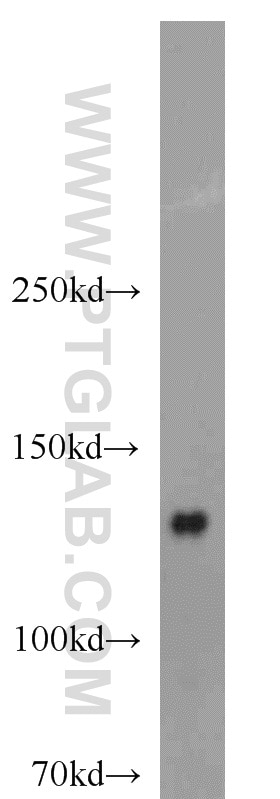
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HeLa, cellules HEK-293, tissu cérébral humain fœtal |
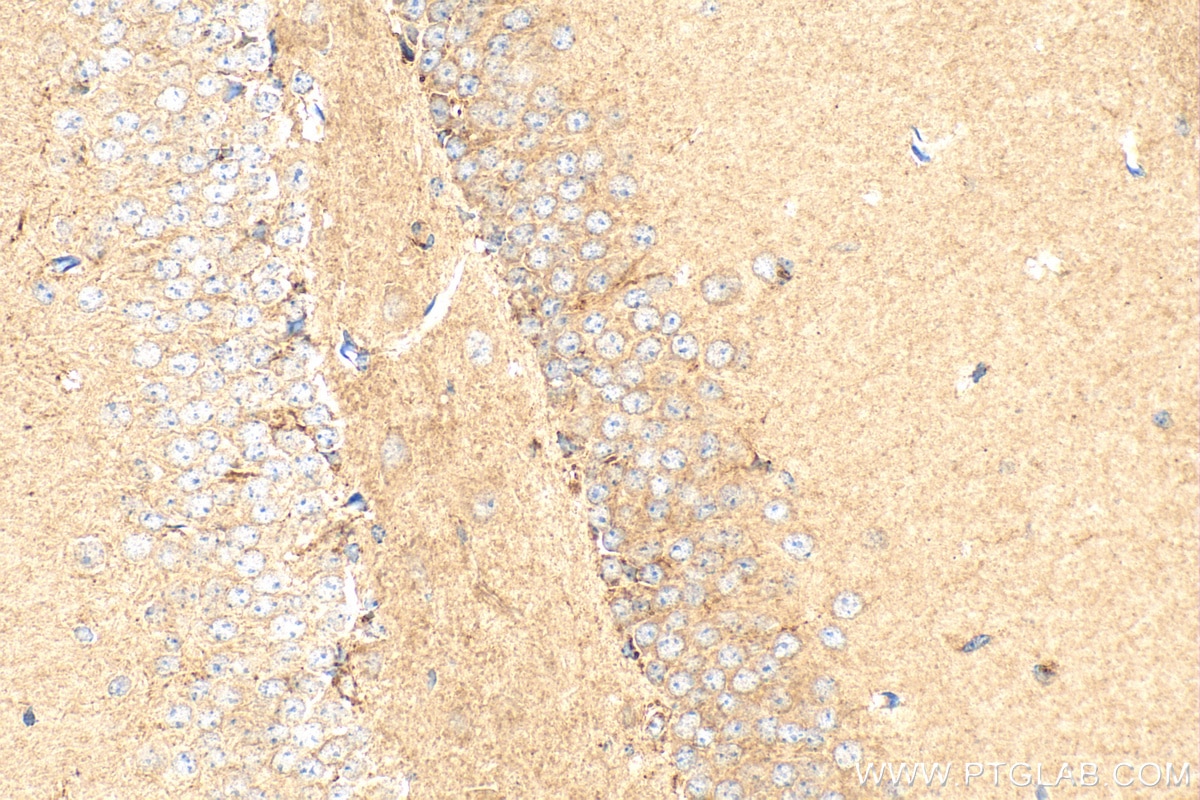
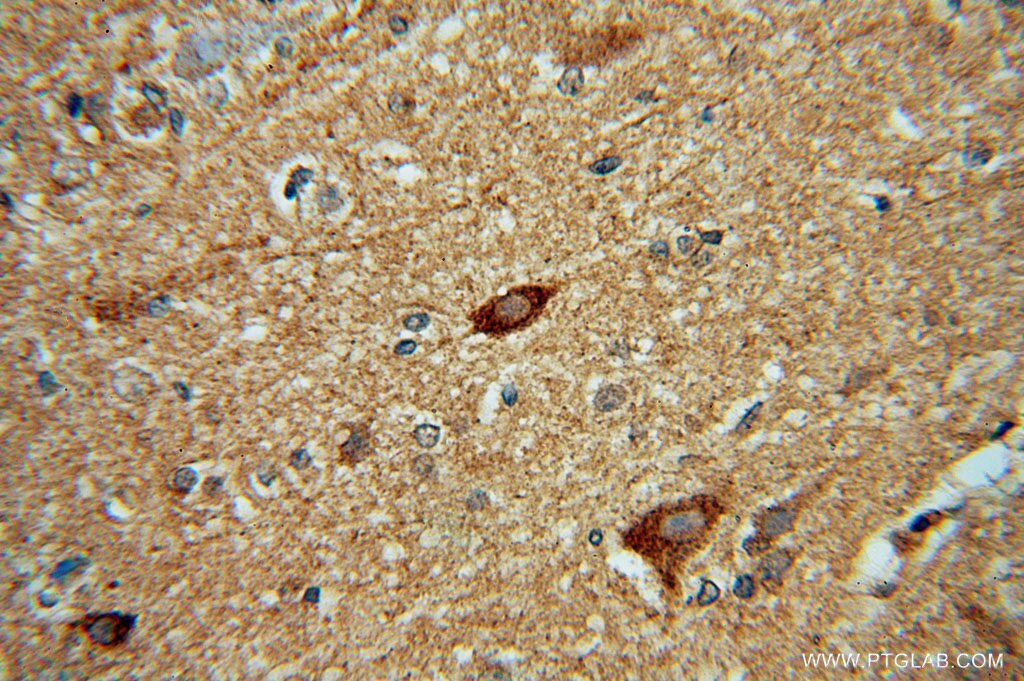
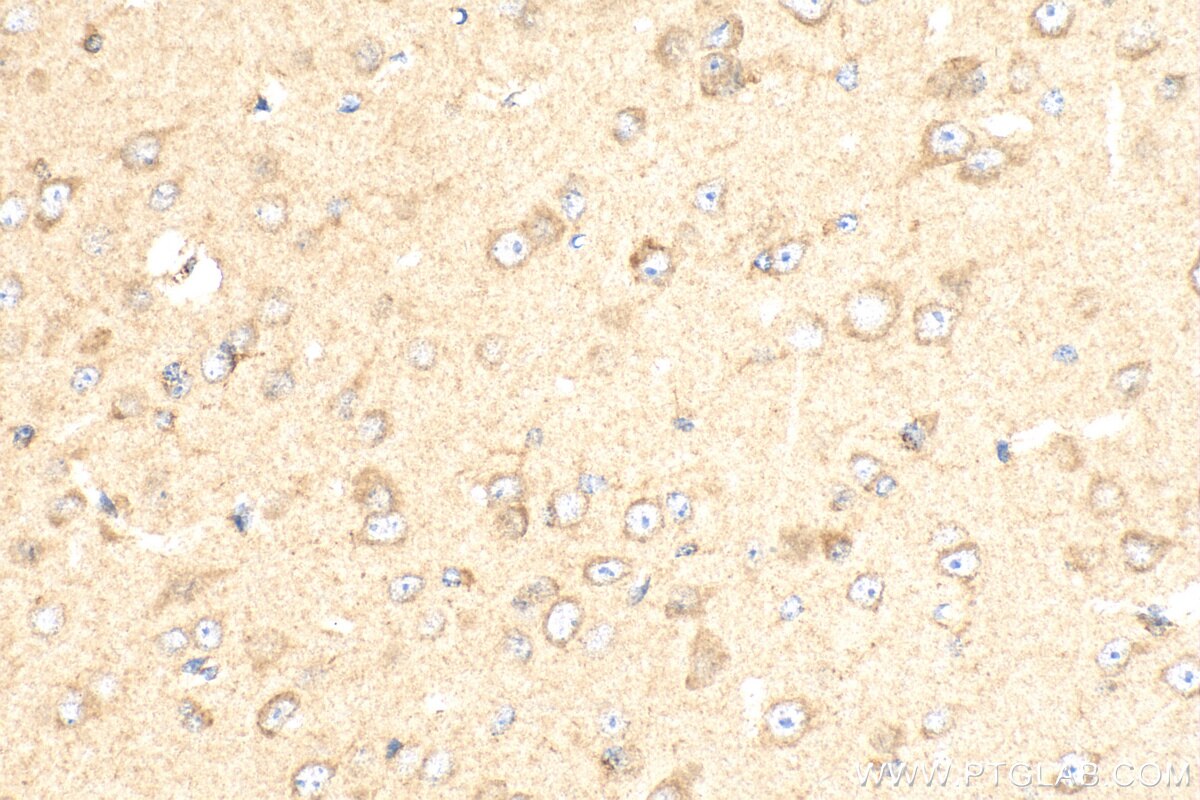
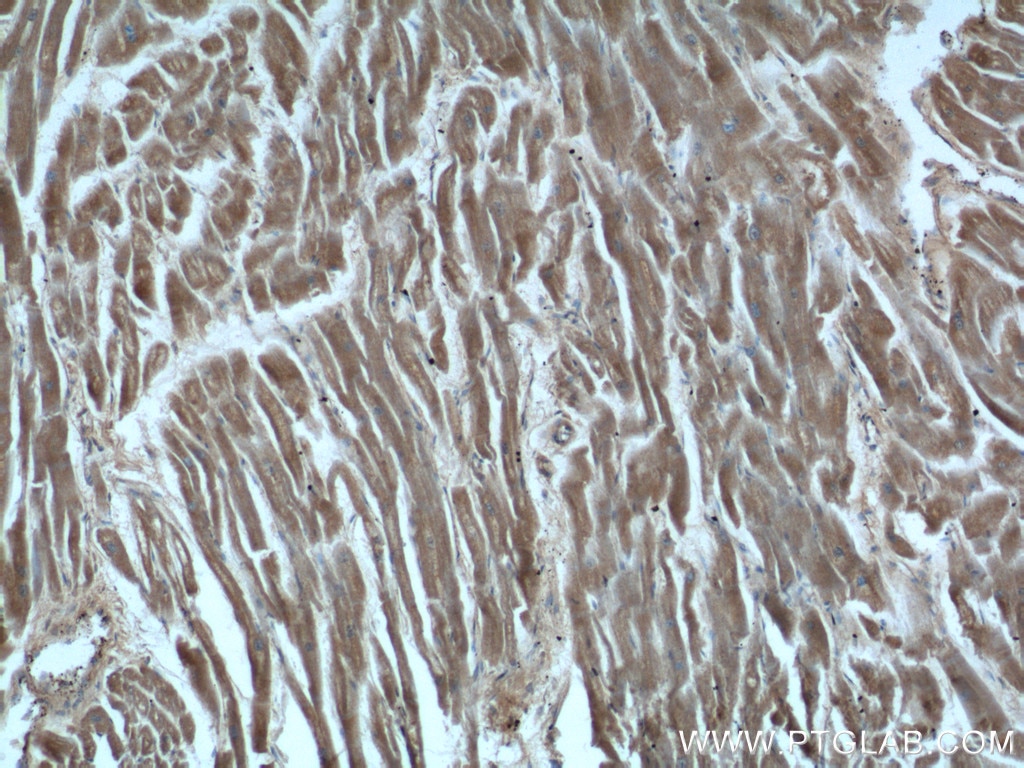
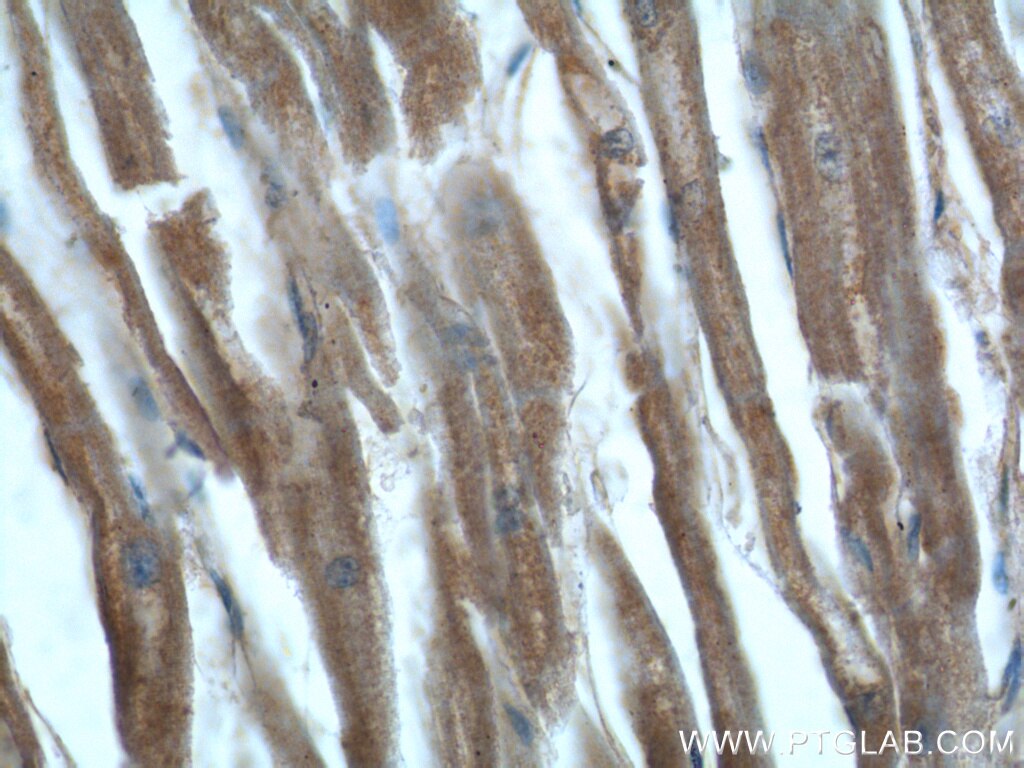
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu cérébral de souris, tissu cardiaque humain, tissu cérébral humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
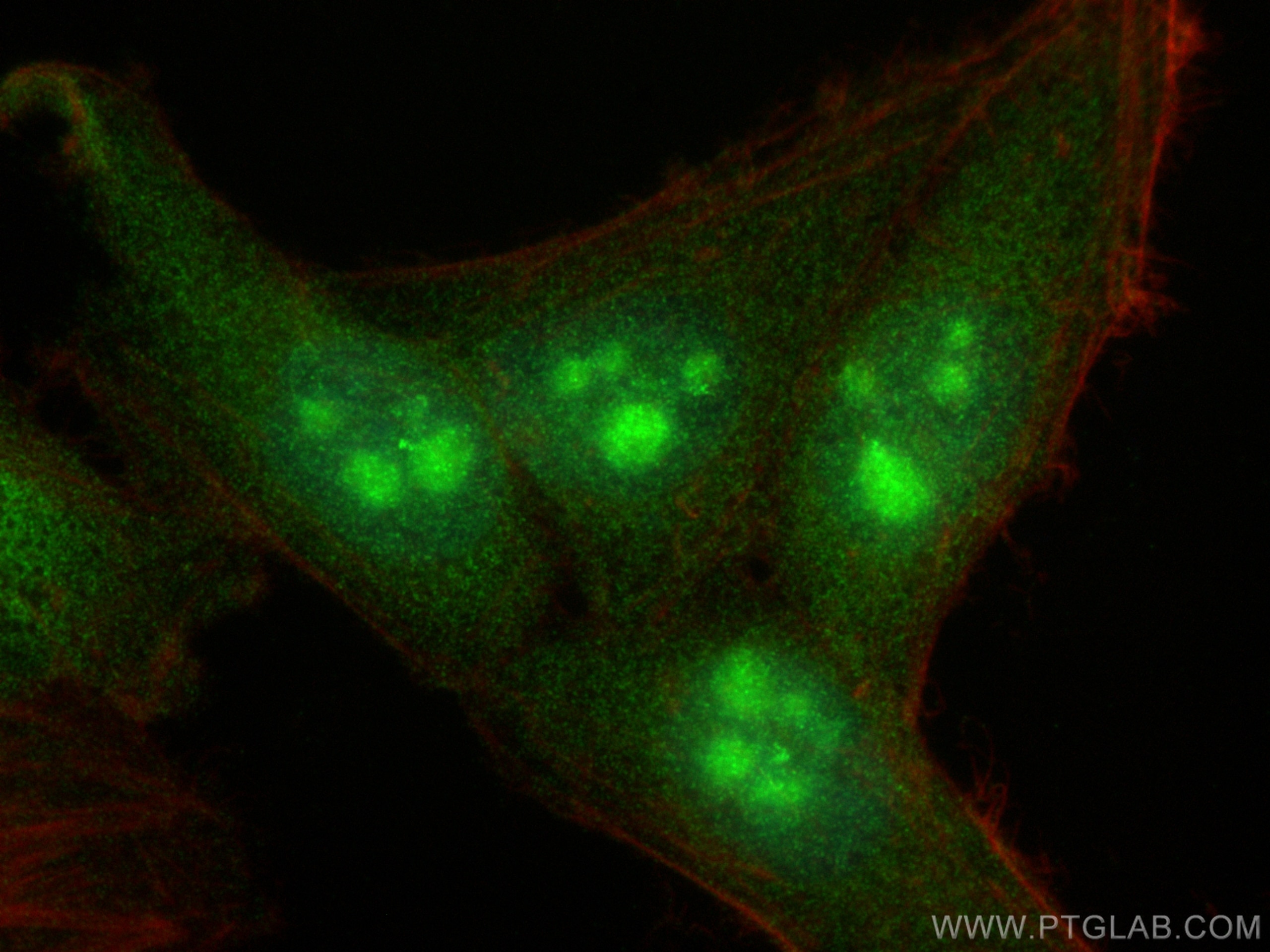
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules HepG2, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:100-1:1000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 5 publications below |
| WB | See 26 publications below |
| IHC | See 4 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
| CoIP | See 3 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
16166-1-AP cible HDAC5-specific dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, CoIP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Peptide |
| Nom complet | histone deacetylase 5 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 122 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 120-140 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC051824 |
| Symbole du gène | HDAC5 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 10014 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Histone acetylation and deacetylation alternately expose and occlude DNA to transcription factors. At least 4 classes of HDAC were identified. HDAC5 is a class II HDAC. HDAC5 is responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). Histone deacetylation gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression, and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. HDAC5 is involved in muscle maturation by repressing transcription of myocyte enhancer MEF2C. During muscle differentiation, HDAC5 shuttles into the cytoplasm, allowing the expression of myocyte enhancer factors. This antibody only binds HDAC5. It does not cross-react with other HDACs.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for HDAC5-specific antibody 16166-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for HDAC5-specific antibody 16166-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for HDAC5-specific antibody 16166-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Targeting Epigenetic Crosstalk as a Therapeutic Strategy for EZH2-Aberrant Solid Tumors. | ||
Sci Transl Med ATP citrate lyase drives vascular remodeling in systemic and pulmonary vascular diseases through metabolic and epigenetic changes | ||
Biomaterials Myocardial delivery of miR30d with peptide-functionalized milk-derived extracellular vesicles for targeted treatment of hypertrophic heart failure | ||
Kidney Int Histone deacetylase 4 selectively contributes to podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy. | ||
Cancer Lett ITGA2 overexpression inhibits DNA repair and confers sensitivity to radiotherapies in pancreatic cancer | ||
J Cell Mol Med Low levels of AMPK promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer primarily through HDAC4- and HDAC5-mediated metabolic reprogramming.
|