- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-HORMAD1
HORMAD1 Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris
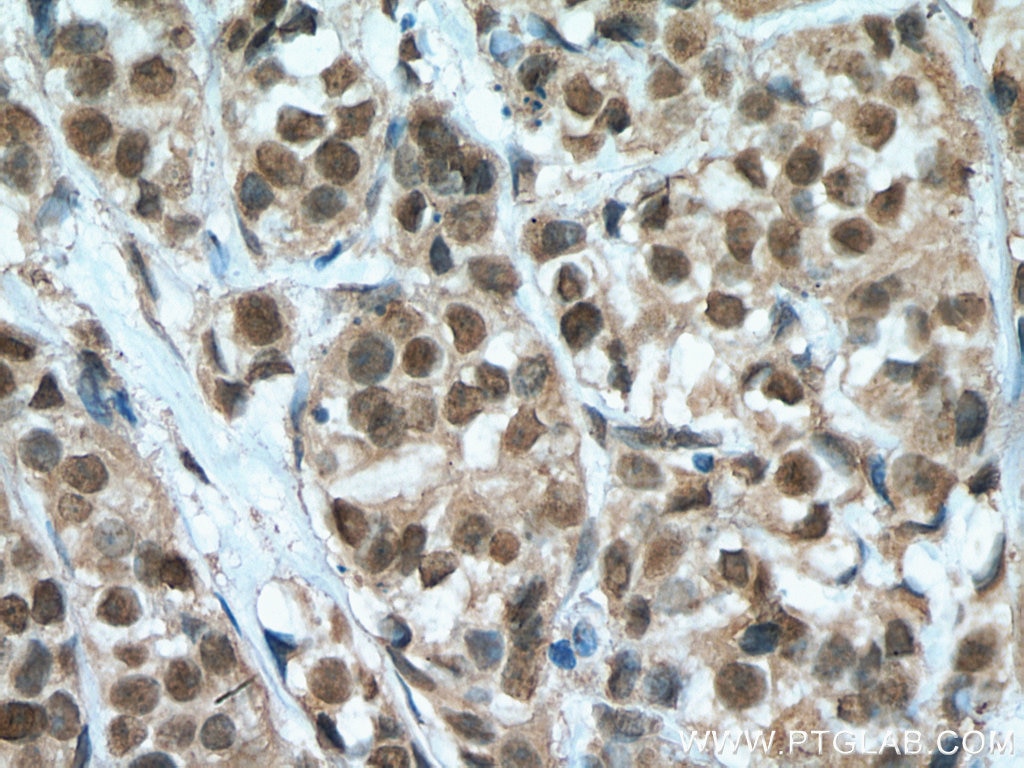
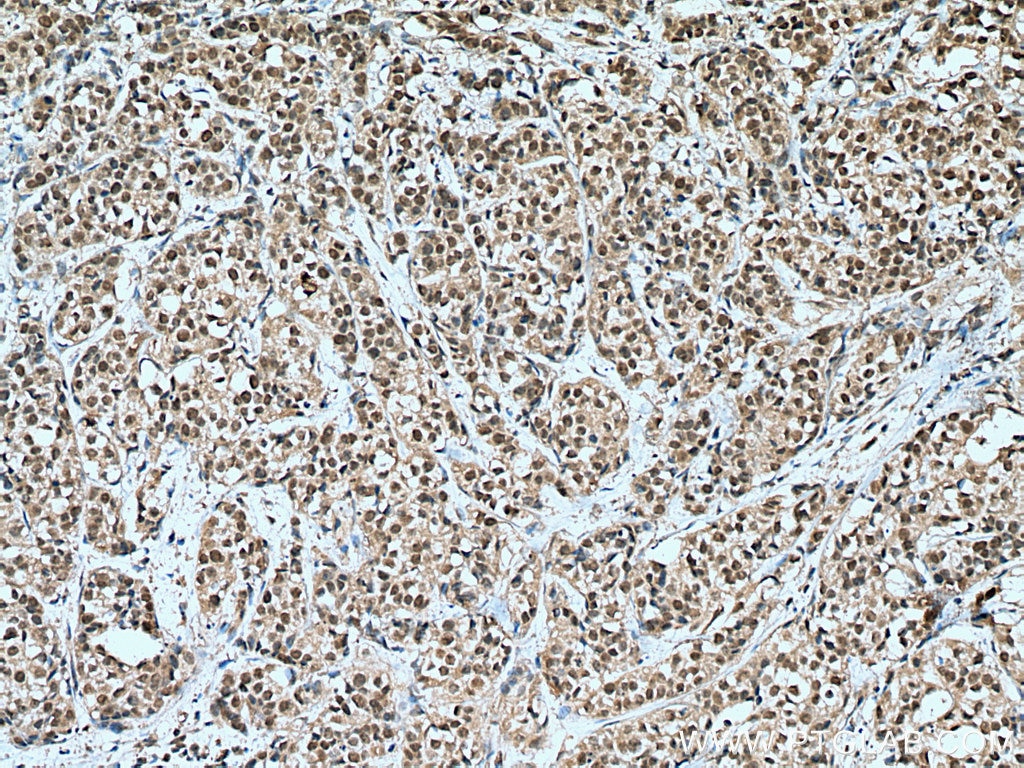
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
2D7E12
N° de cat : 67091-1-PBS
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
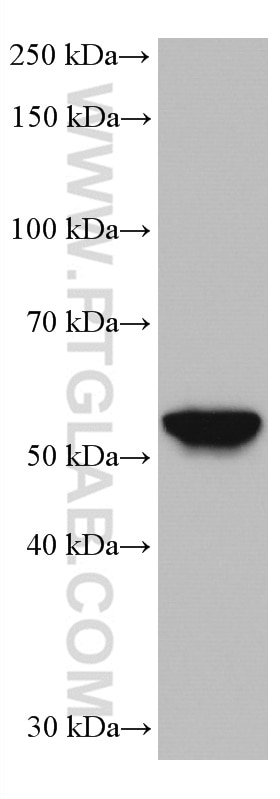
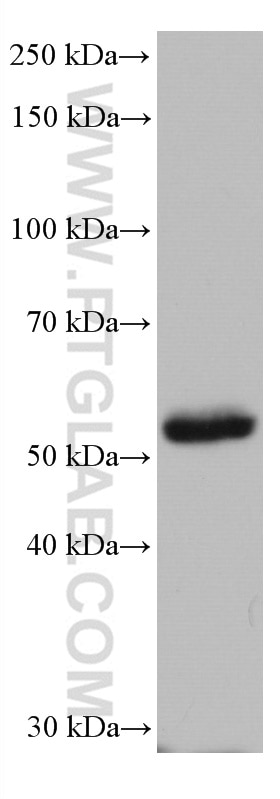
67091-1-PBS cible HORMAD1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | HORMAD1 Protéine recombinante Ag28316 |
| Nom complet | HORMA domain containing 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 45 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 50-55 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC047406 |
| Symbole du gène | HORMAD1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 84072 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine G |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
HORMA domain-containing proteins regulate interactions between homologous chromosomes (homologs) during meiosis in a wide range of eukaryotes [PMID:21079677]. They also implicated in other processes related to crossover formation, including DSB formation, inhibition of promiscuous formation of the synaptonemal complex (SC), and the meiotic prophase checkpoint that monitors both DSB processing and SCs [PMID:19851446]. HORMAD1 first accumulates on the chromosomes during the leptotene to zygotene stages of meiotic prophase I. As germ cells progress into the pachytene stage, HORMAD1 disappears from the synapsed chromosomal regions. However, once the chromosomes desynapse during the diplotene stage, HORMAD1 again accumulates on the chromosome axis of the desynapsed homologs [PMID:19686734].