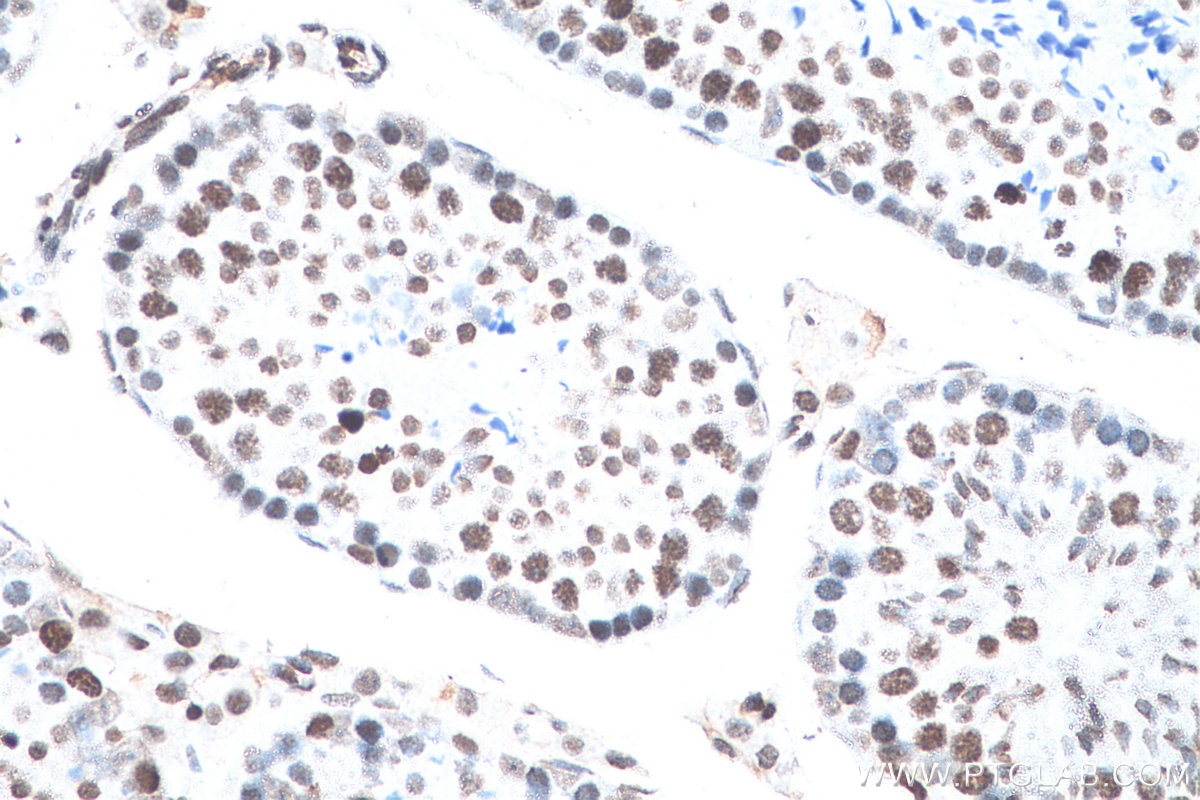
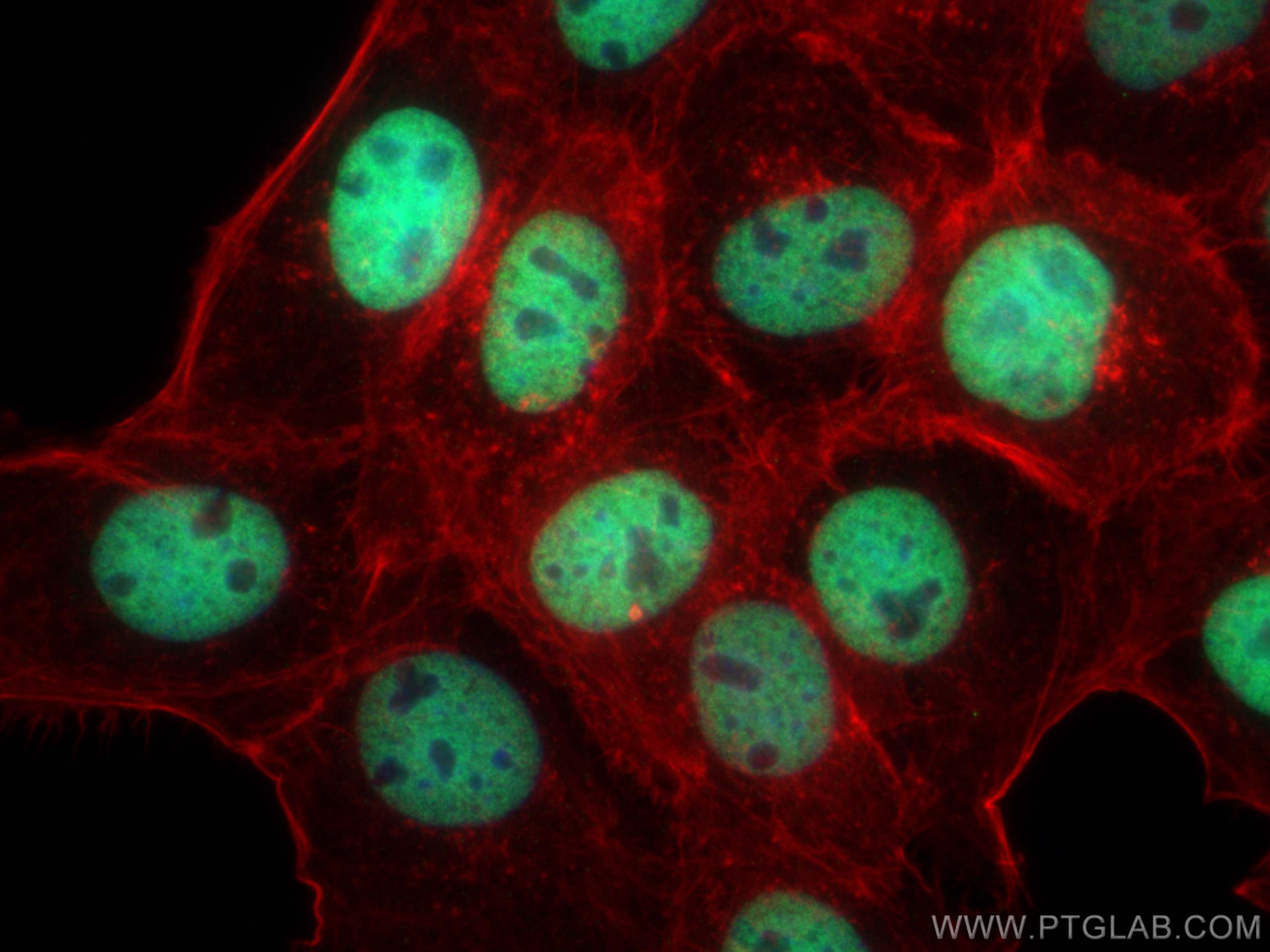
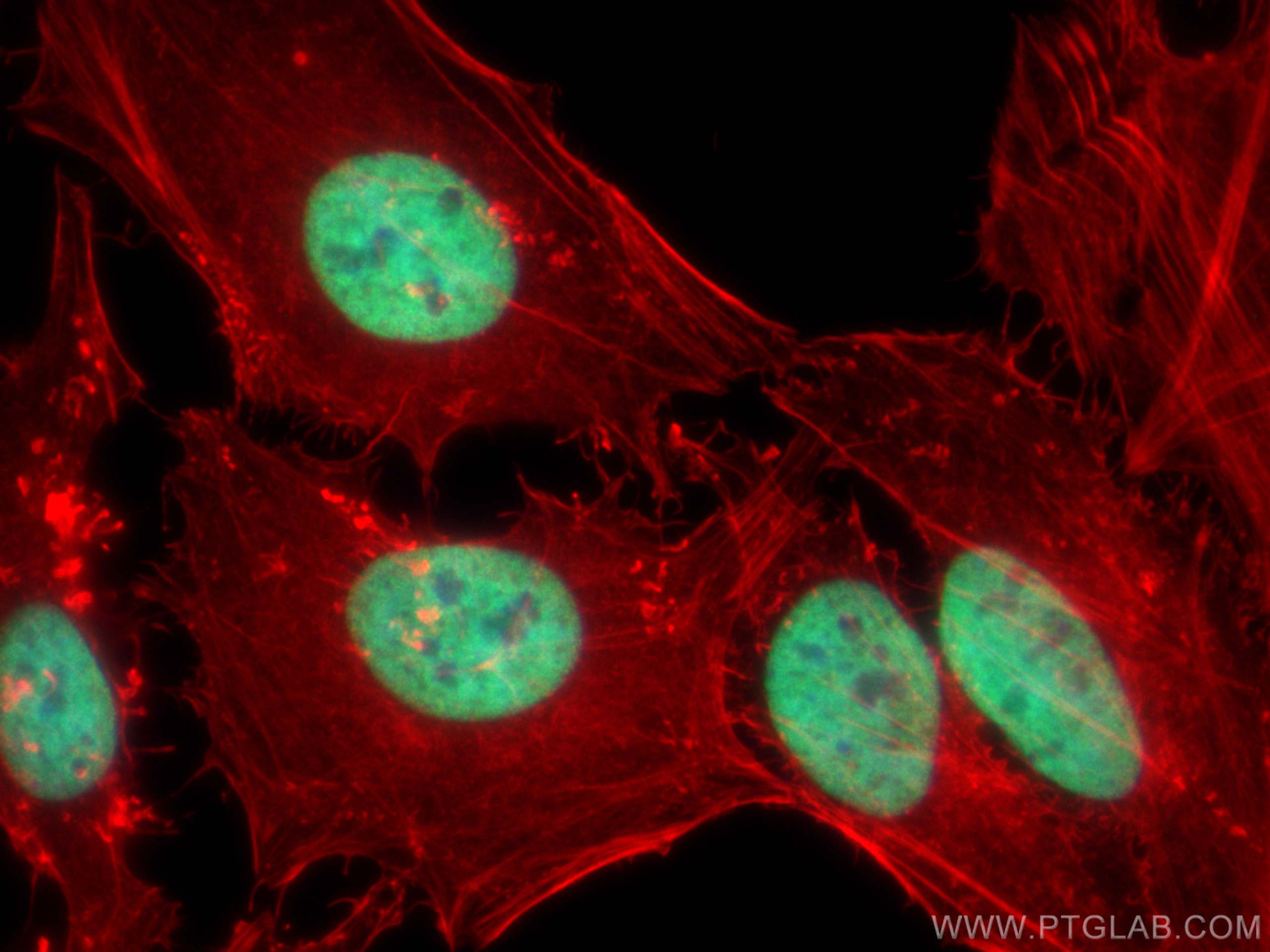
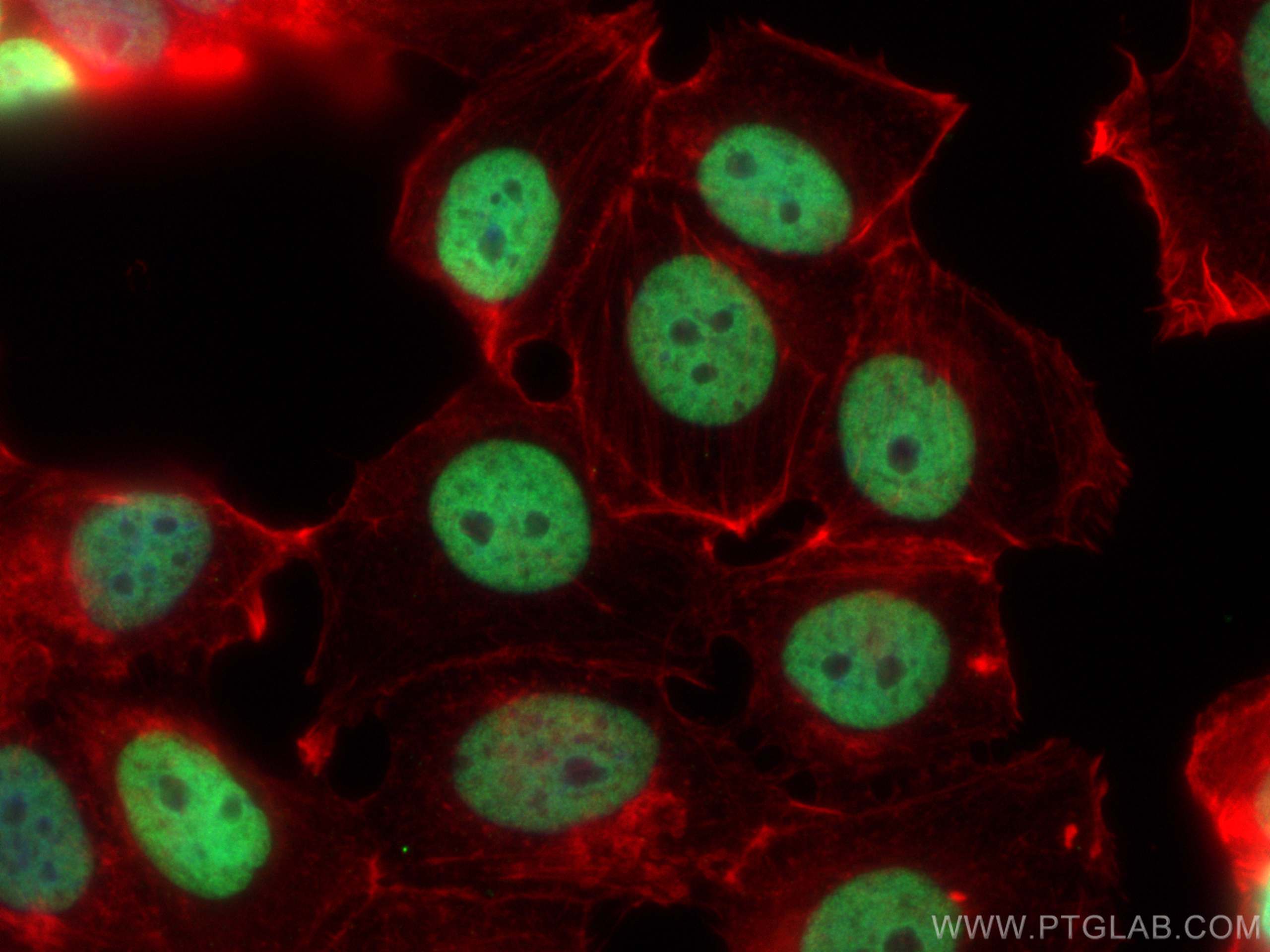
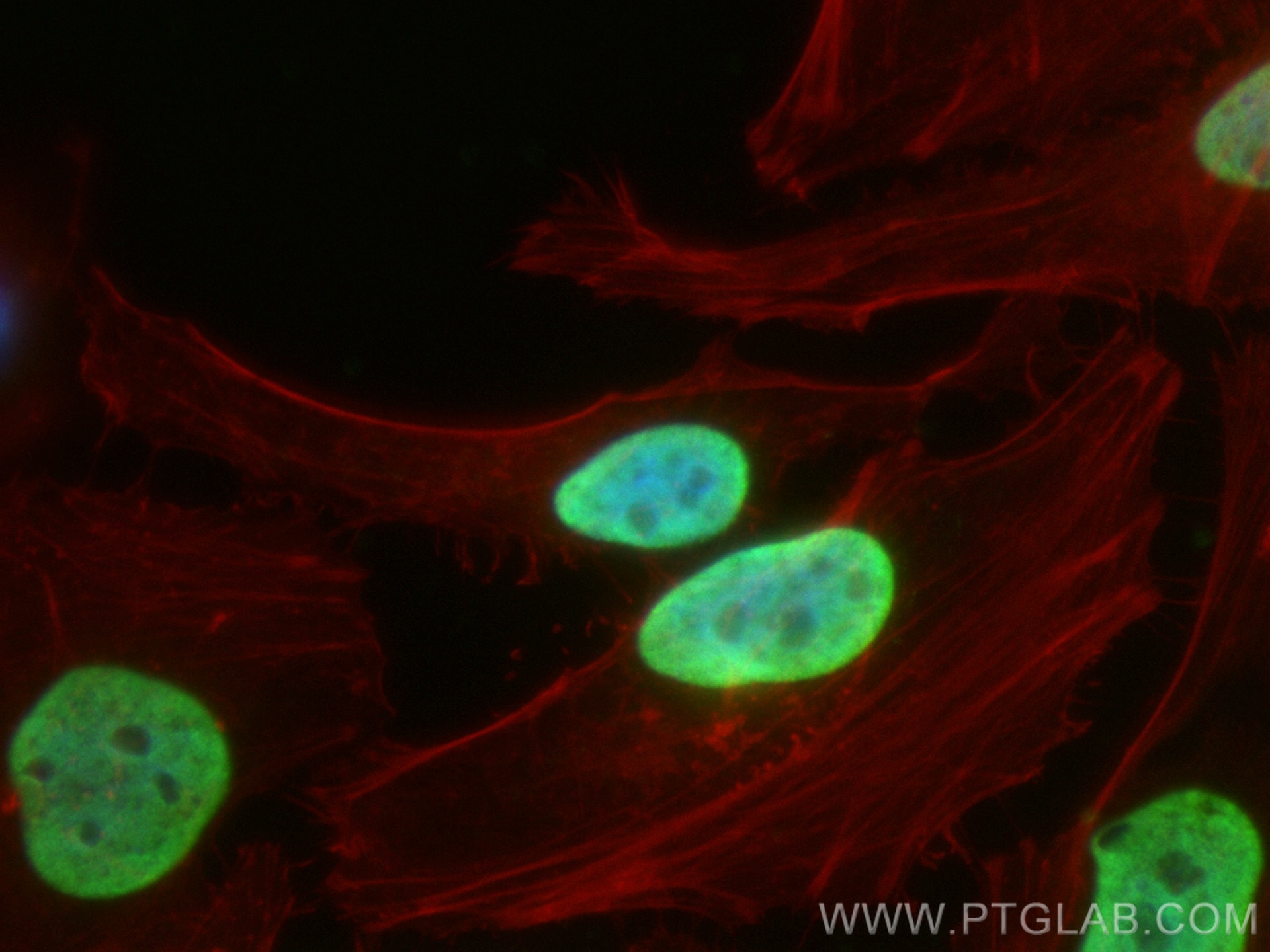
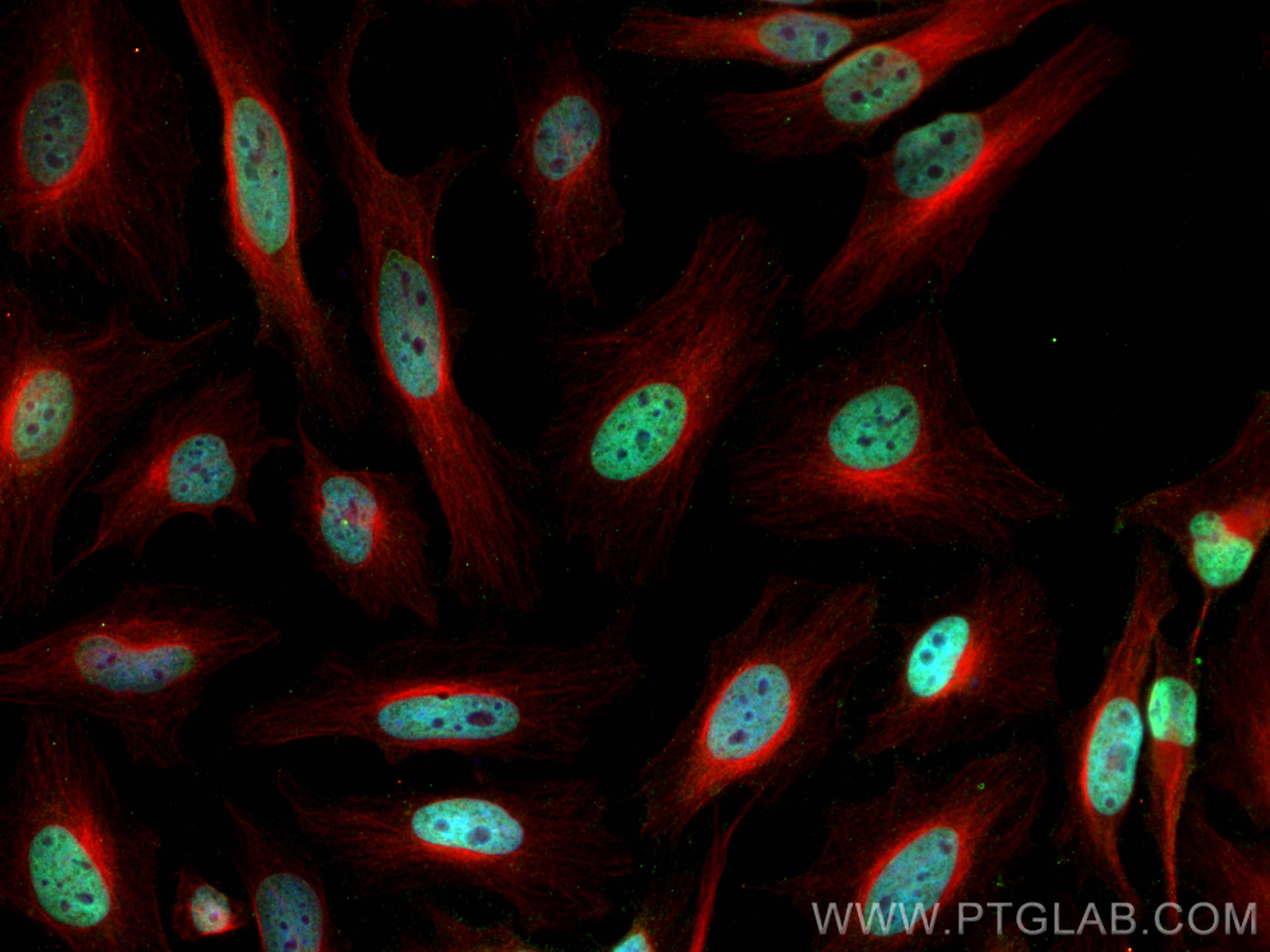
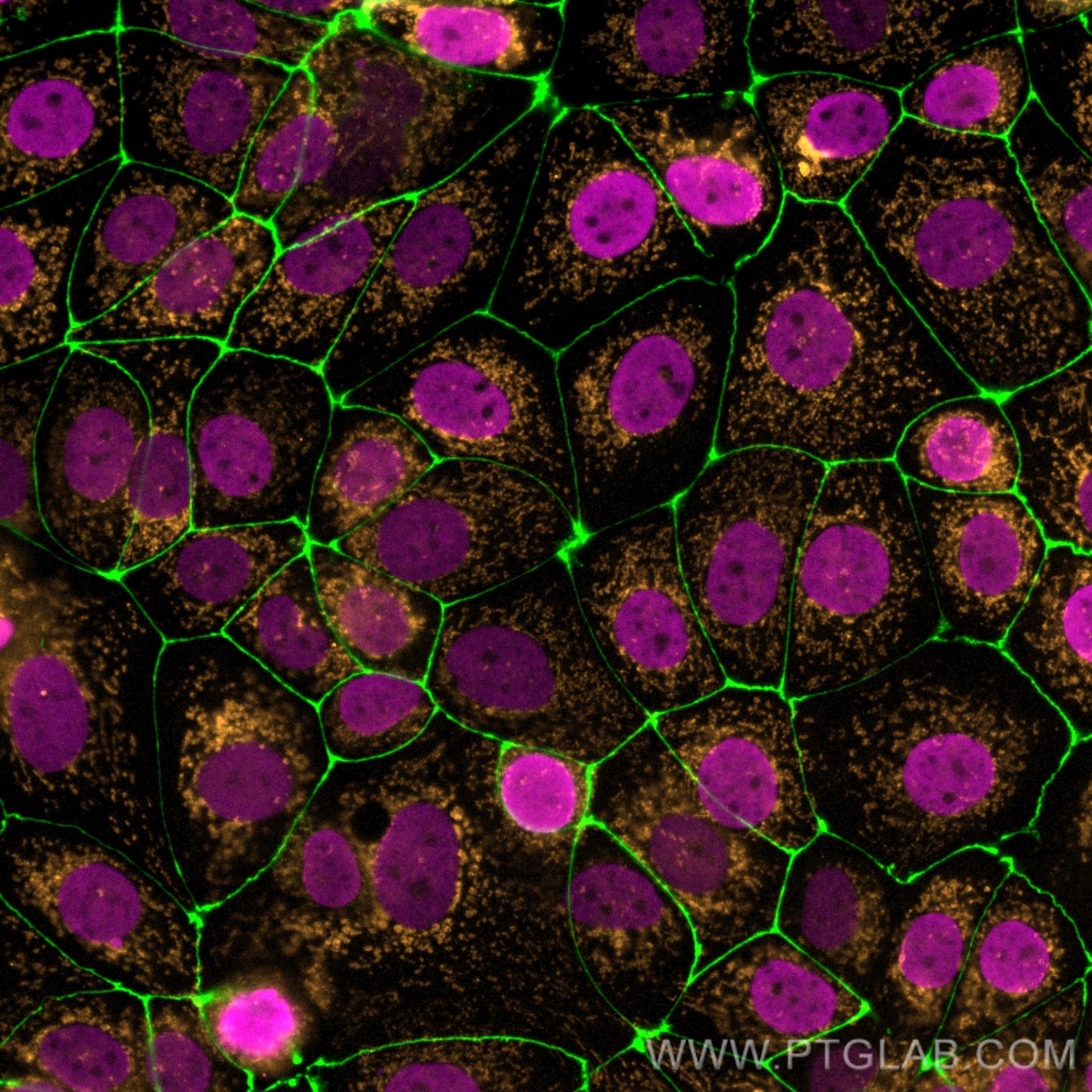
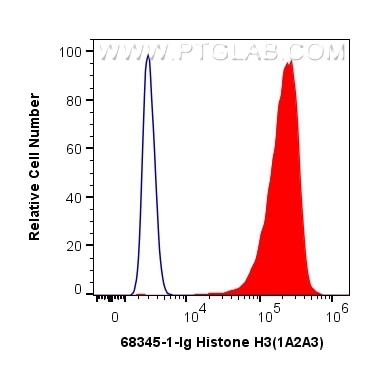
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-Histone H3
Histone H3 Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2b
Réactivité testée
canin, chien, Humain, Lapin, poisson-zèbre, porc, poulet, rat, souris, Hamster, wheat
Applications
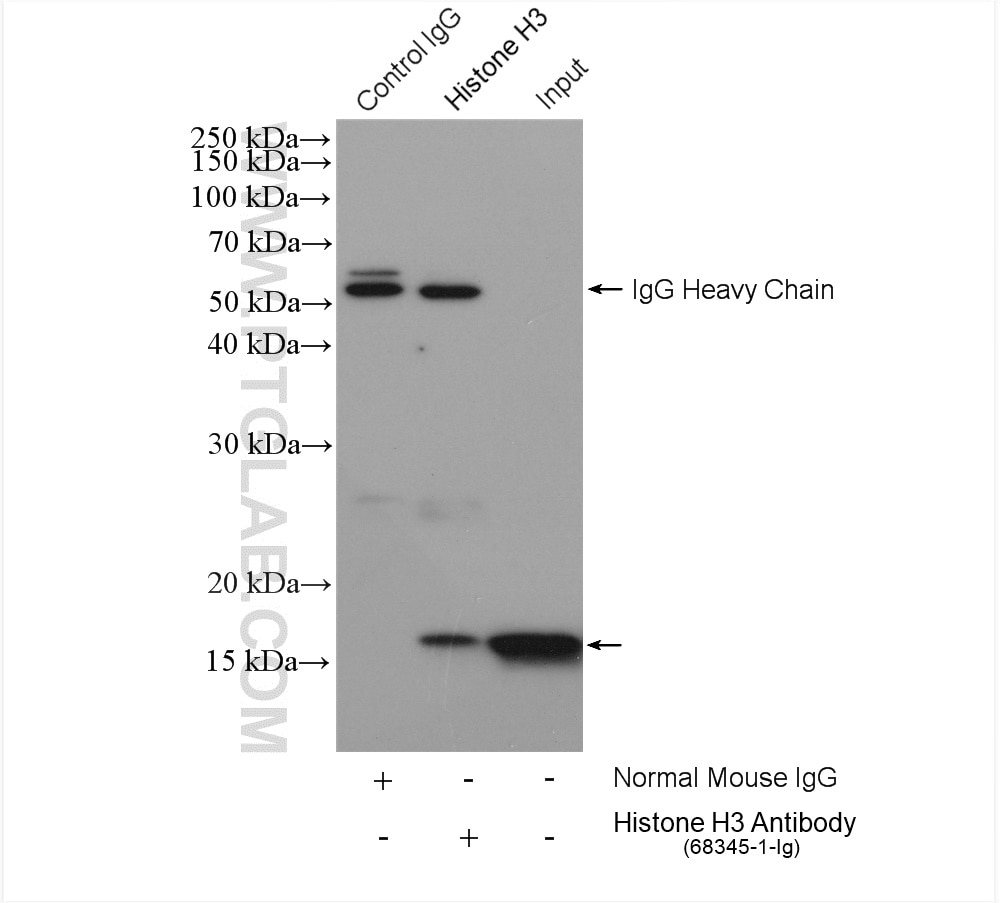
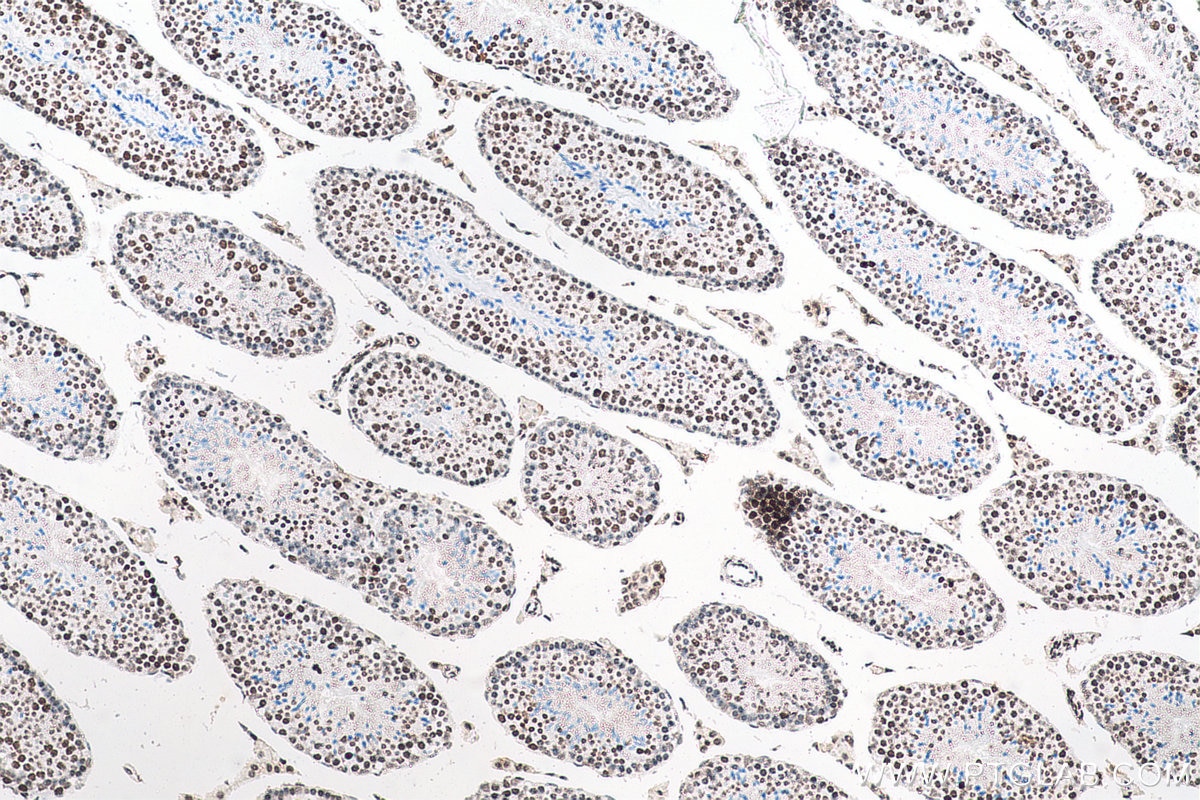
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
1A2A3
N° de cat : 68345-1-PBS
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
68345-1-PBS cible Histone H3 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons canin, chien, Humain, Lapin, poisson-zèbre, porc, poulet, rat, souris, Hamster, wheat
| Réactivité | canin, chien, Humain, Lapin, poisson-zèbre, porc, poulet, rat, souris, Hamster, wheat |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Peptide |
| Nom complet | histone cluster 1, H3a |
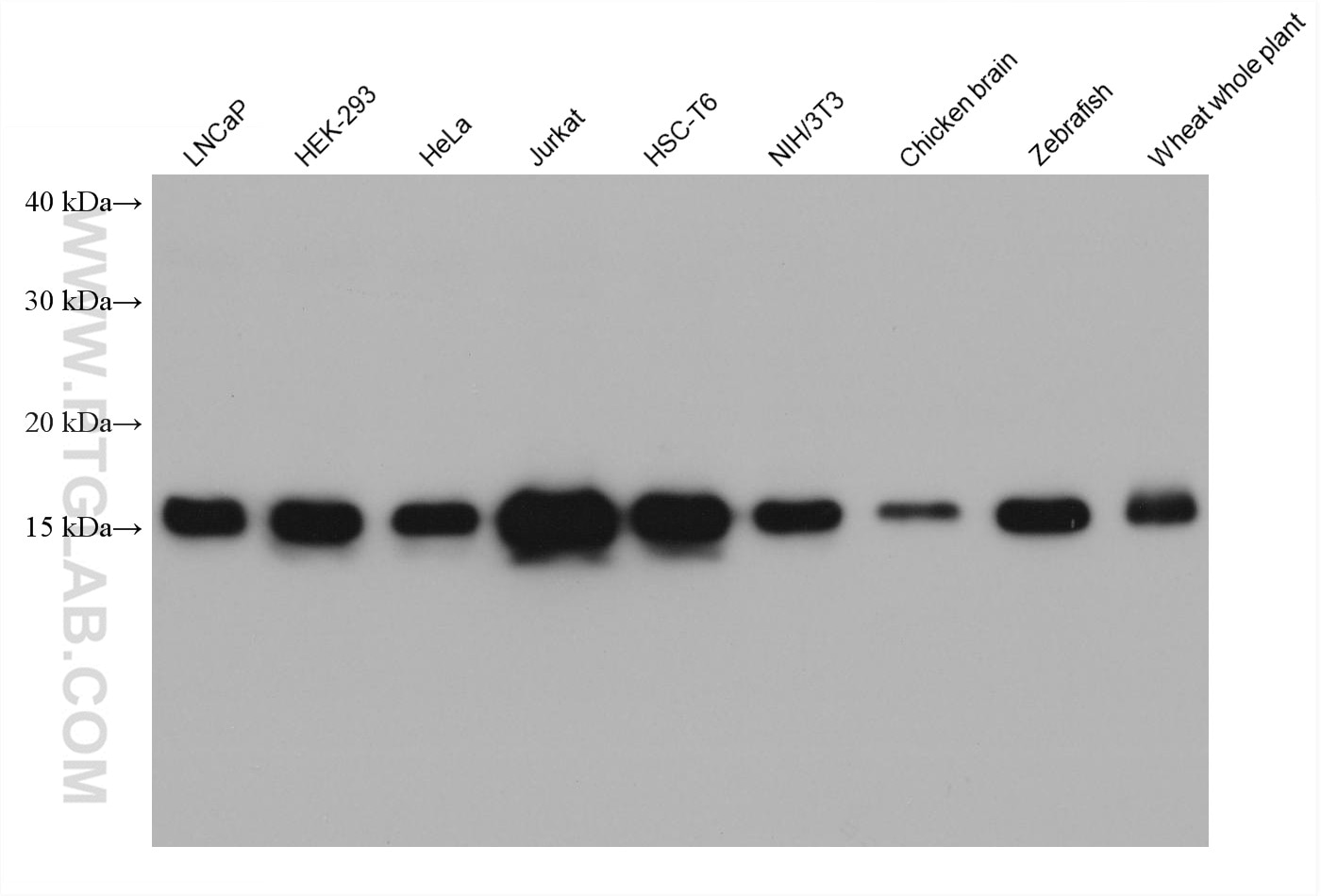
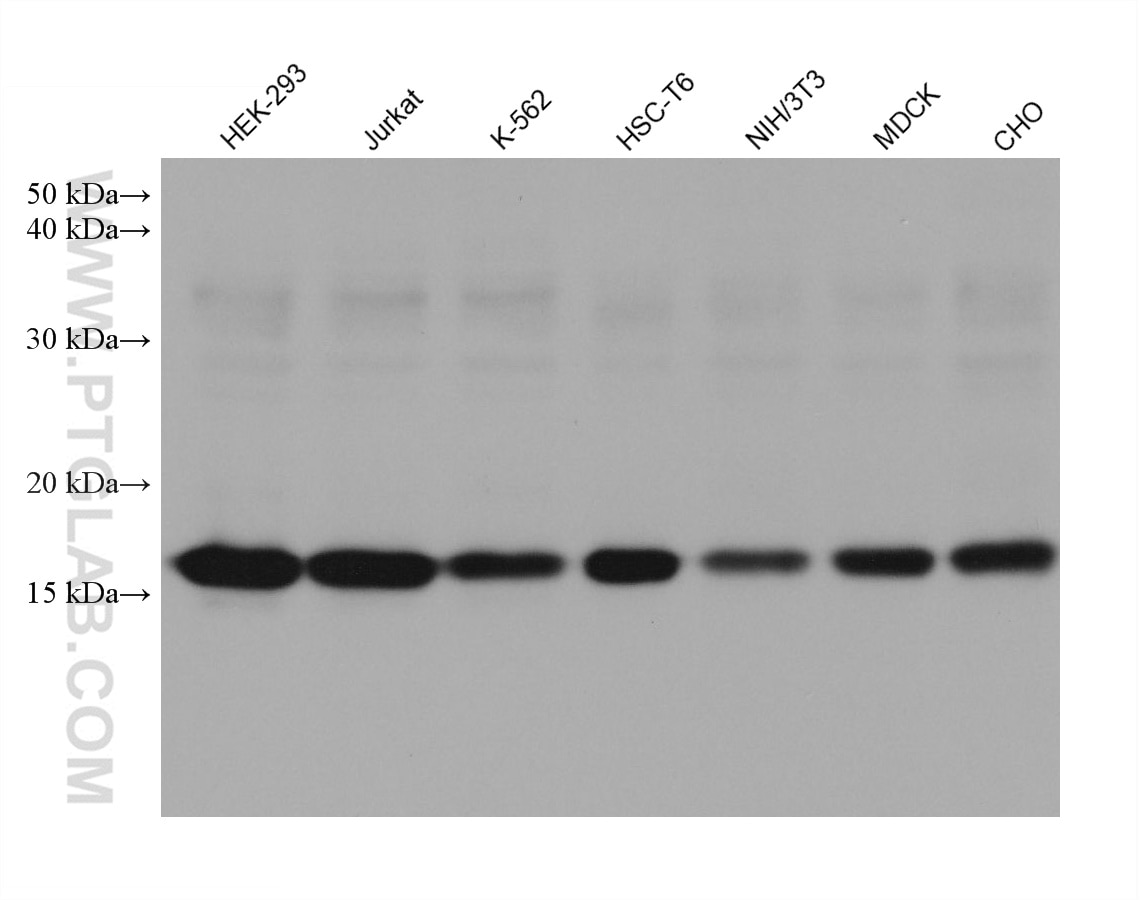
| Poids moléculaire observé | 15-17 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC066245 |
| Symbole du gène | HIST1H3A |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 8350 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Histones are small, highly basic proteins that consist of a globular domain with unstructured N- and C-terminal tails protruding from the main structure. Histone H3 is one of the five main histones that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Two molecules of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) form an octamer, around which approximately 146 bp of DNA is wrapped in repeating units, called nucleosomes. In addition to their role in DNA compartmentalization, histones also play crucial roles in various biologic processes, including gene expression and regulation, DNA repair, chromatin condensation, cell cycle progression, chromosome segregation, and apoptosis. The ability of histones to regulate chromatin dynamics primarily originates from various posttranslational modifications carried out by histone-modifying enzymes.