Anticorps Recombinant de lapin anti-IFITM3
IFITM3 Recombinant Antibody for WB, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain
Applications
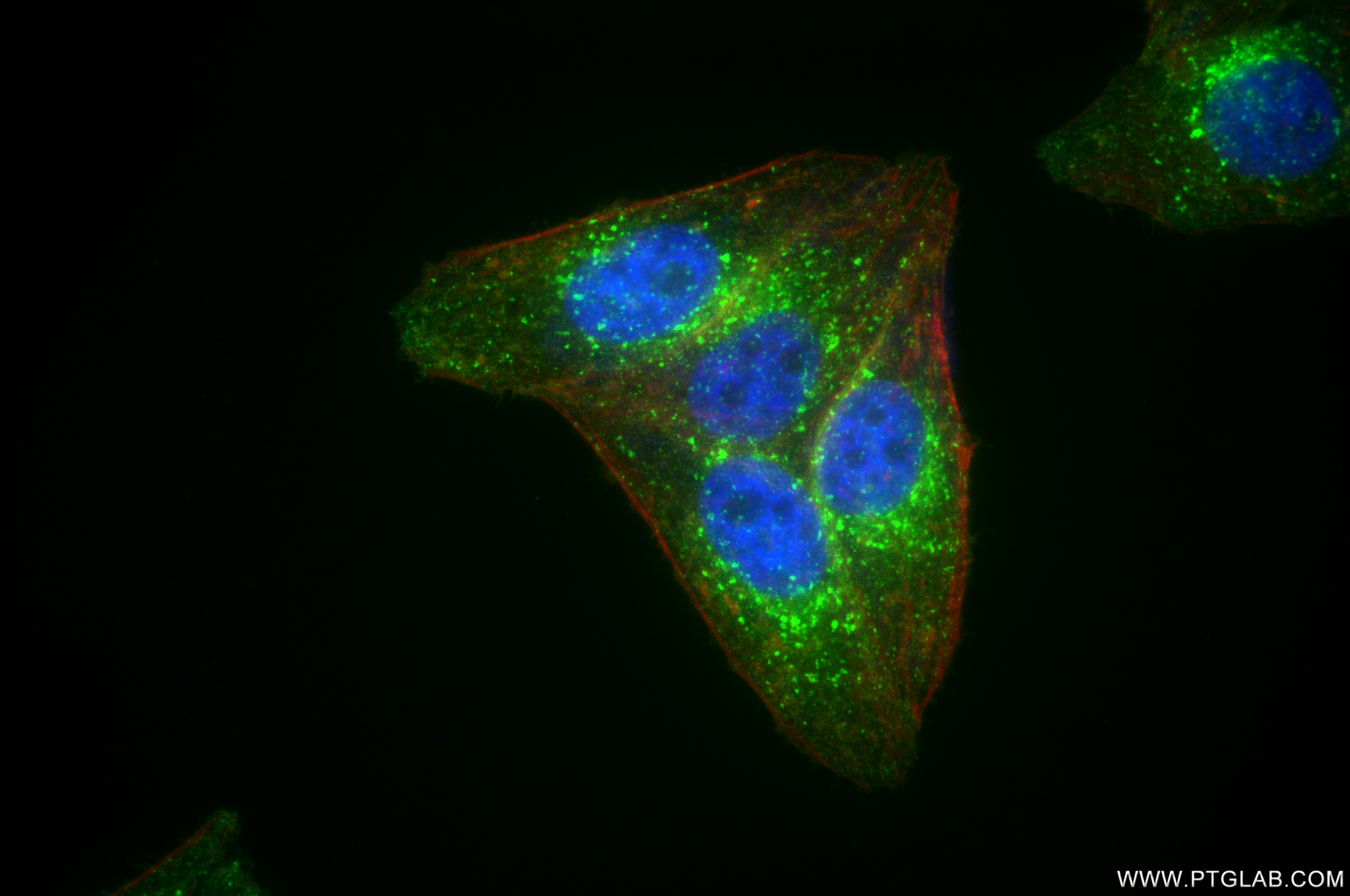
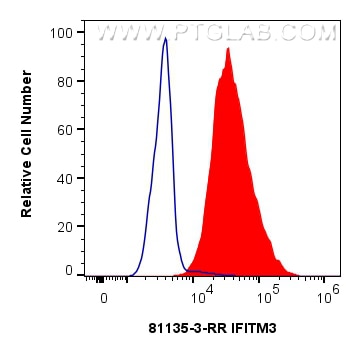
WB, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
242056C9
N° de cat : 81135-3-PBS
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
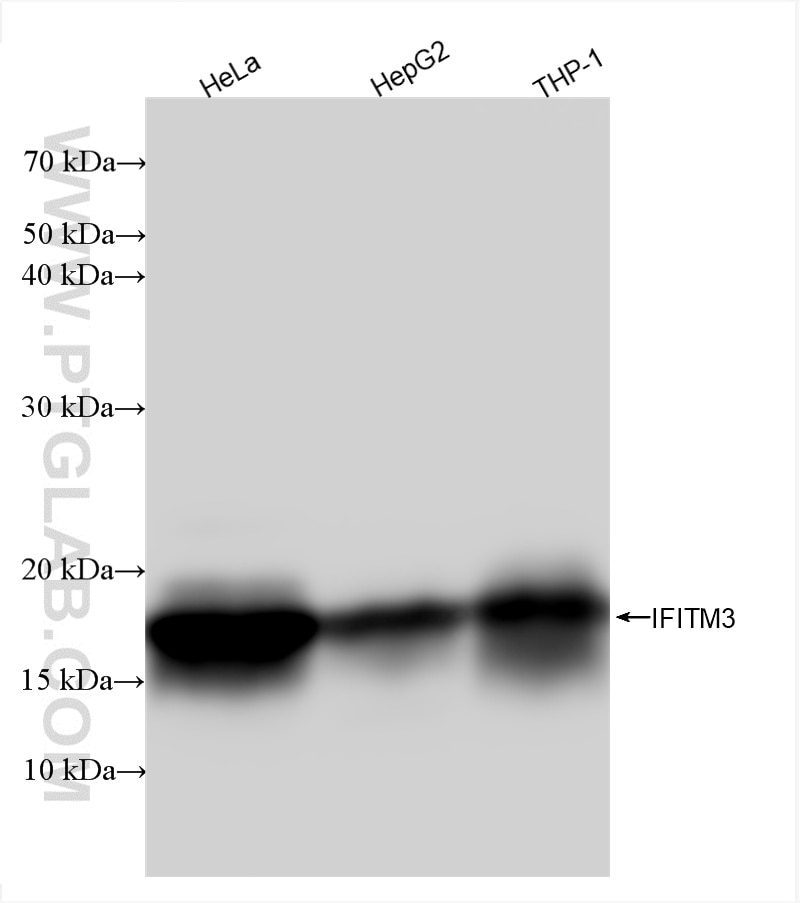
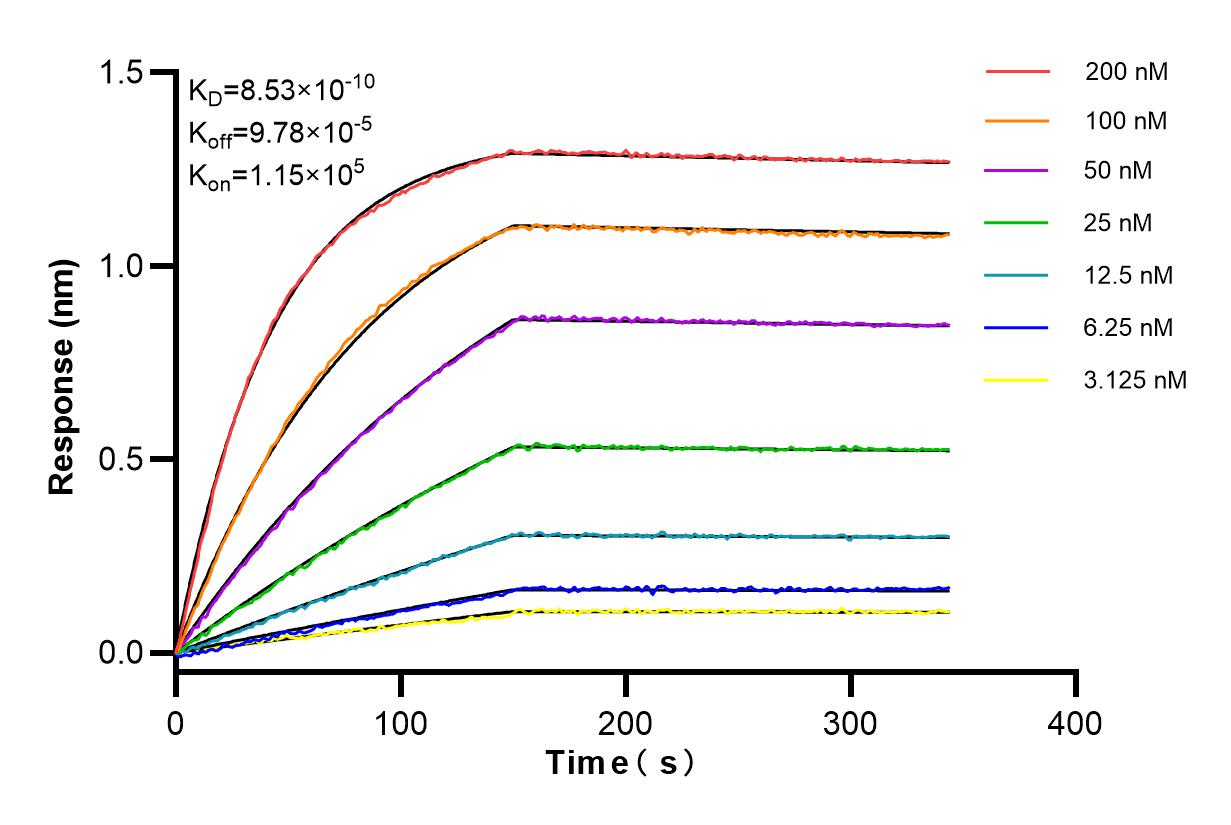
81135-3-PBS cible IFITM3 dans les applications de WB, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain
| Réactivité | Humain |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Recombinant |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | IFITM3 Protéine recombinante Ag2285 |
| Nom complet | interferon induced transmembrane protein 3 (1-8U) |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 133 aa, 15 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 15-20 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC006794 |
| Symbole du gène | IFITM3 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 10410 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
IFITM3, also named as interferon-inducible protein 1-8U, belongs to the CD225 family. It is IFN-induced antiviral protein that mediates cellular innate immunity to at least three major human pathogens, namely influenza A H1N1 virus, West Nile virus (WNV), and dengue virus, by inhibiting the early steps of replication. IFITM3 is identified as interferon-induced cellular proteins that restrict infections by retroviruses and filoviruses and of influenza virus and flaviviruses, respectively. IFITM3, the most potent antiviral IFITM, was found to inhibit an uncharacterized early infectious event after VSV endocytosis, but before primary transcription of its viral genome. IFITM proteins are viral restriction factors that can inhibit infection mediated by the influenza A virus (IAV) hemagglutinin (HA) protein. They differentially restrict the entry of a broad range of enveloped viruses, and modulate cellular tropism independently of viral receptor expression.