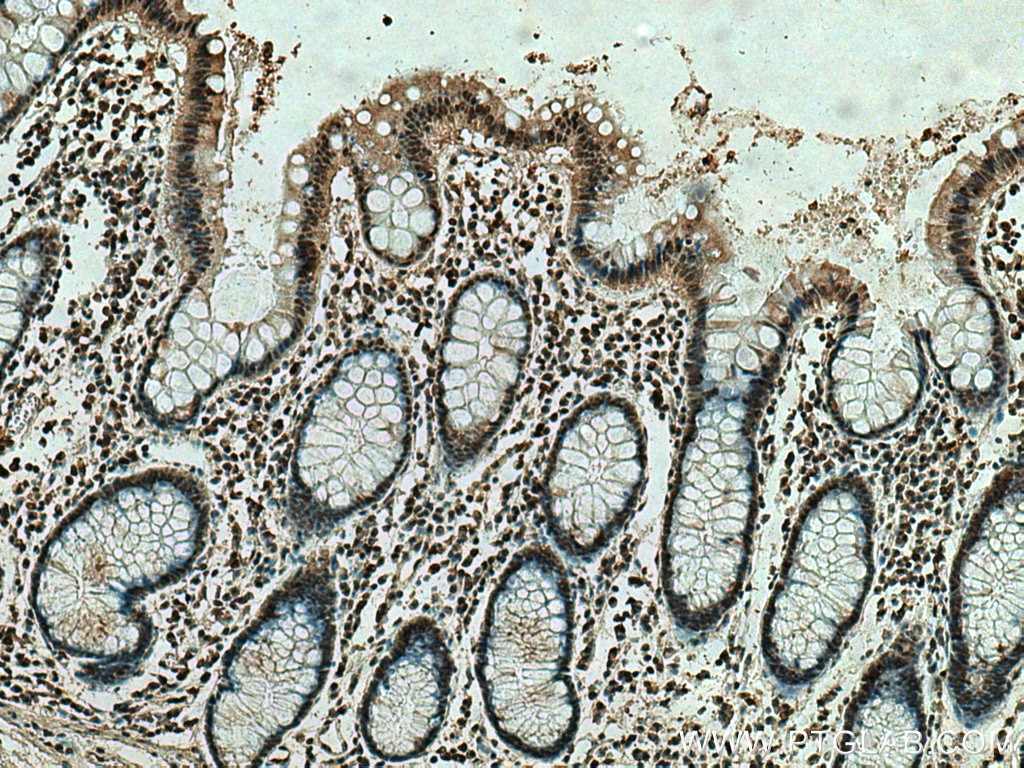
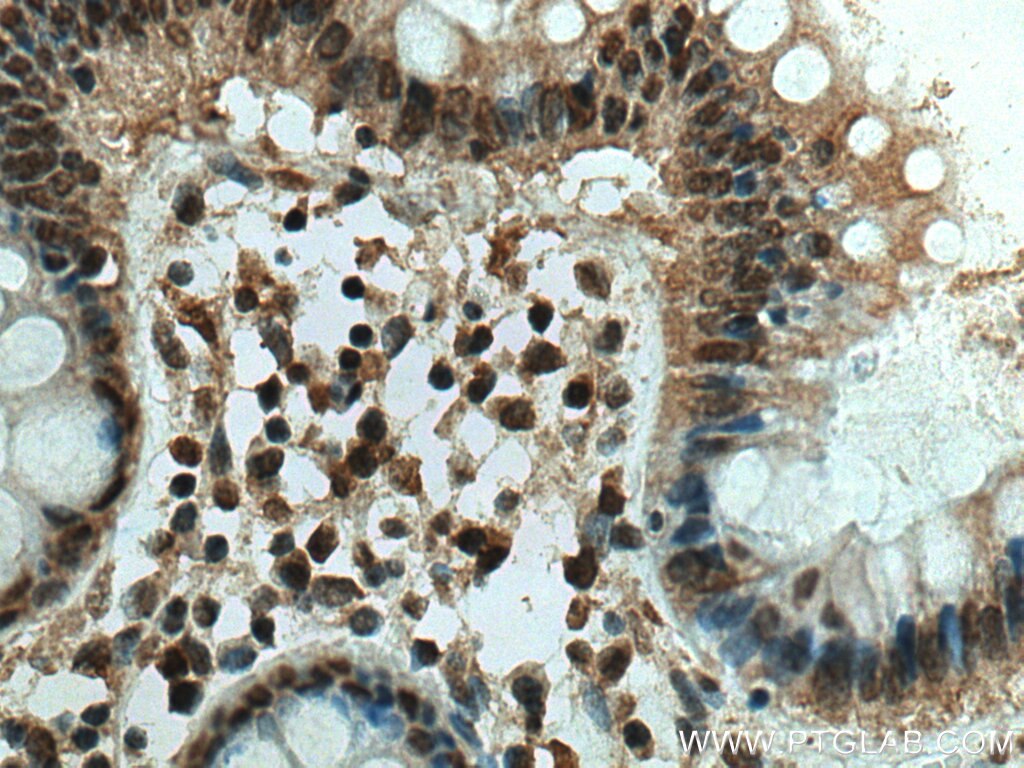
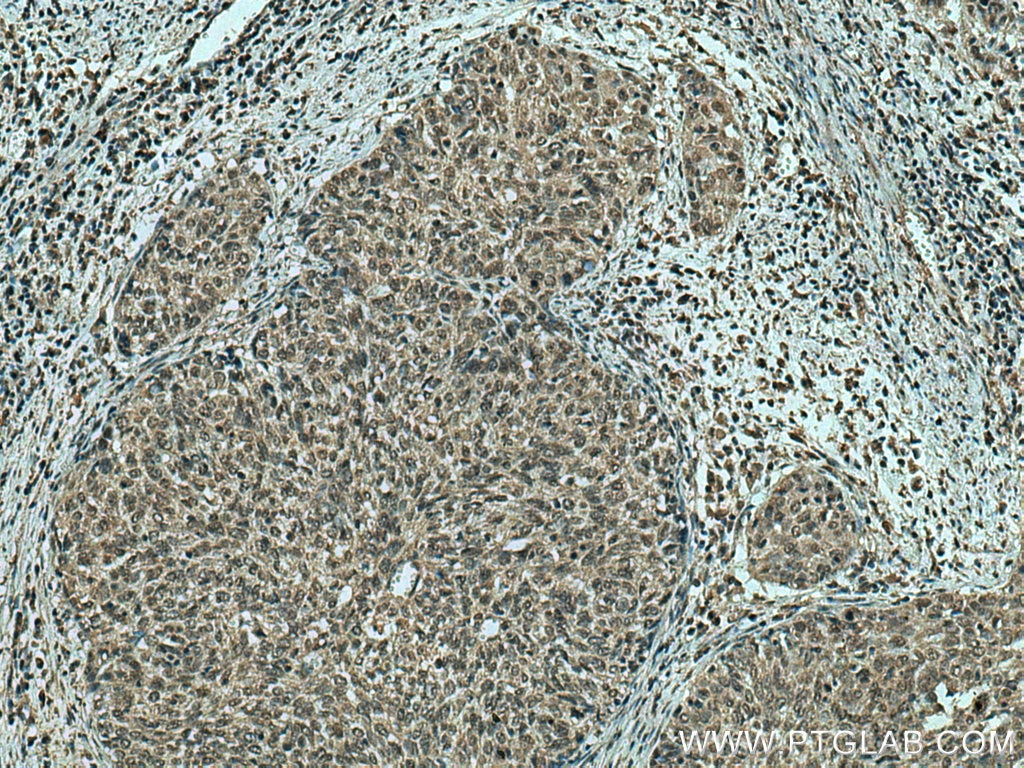
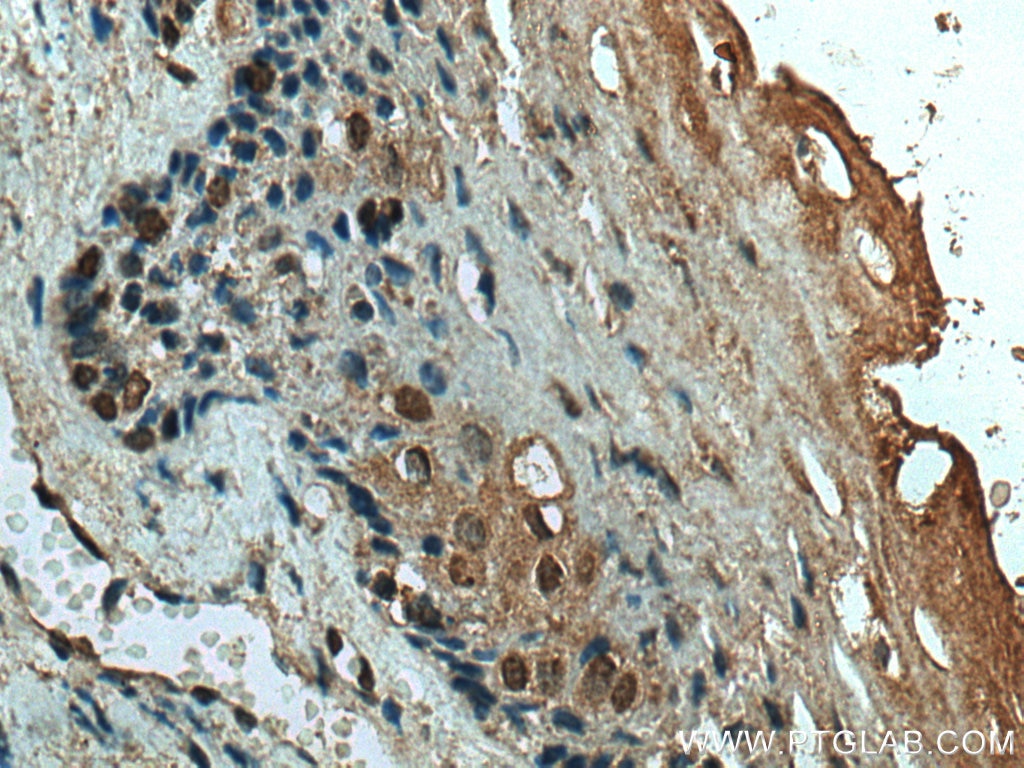
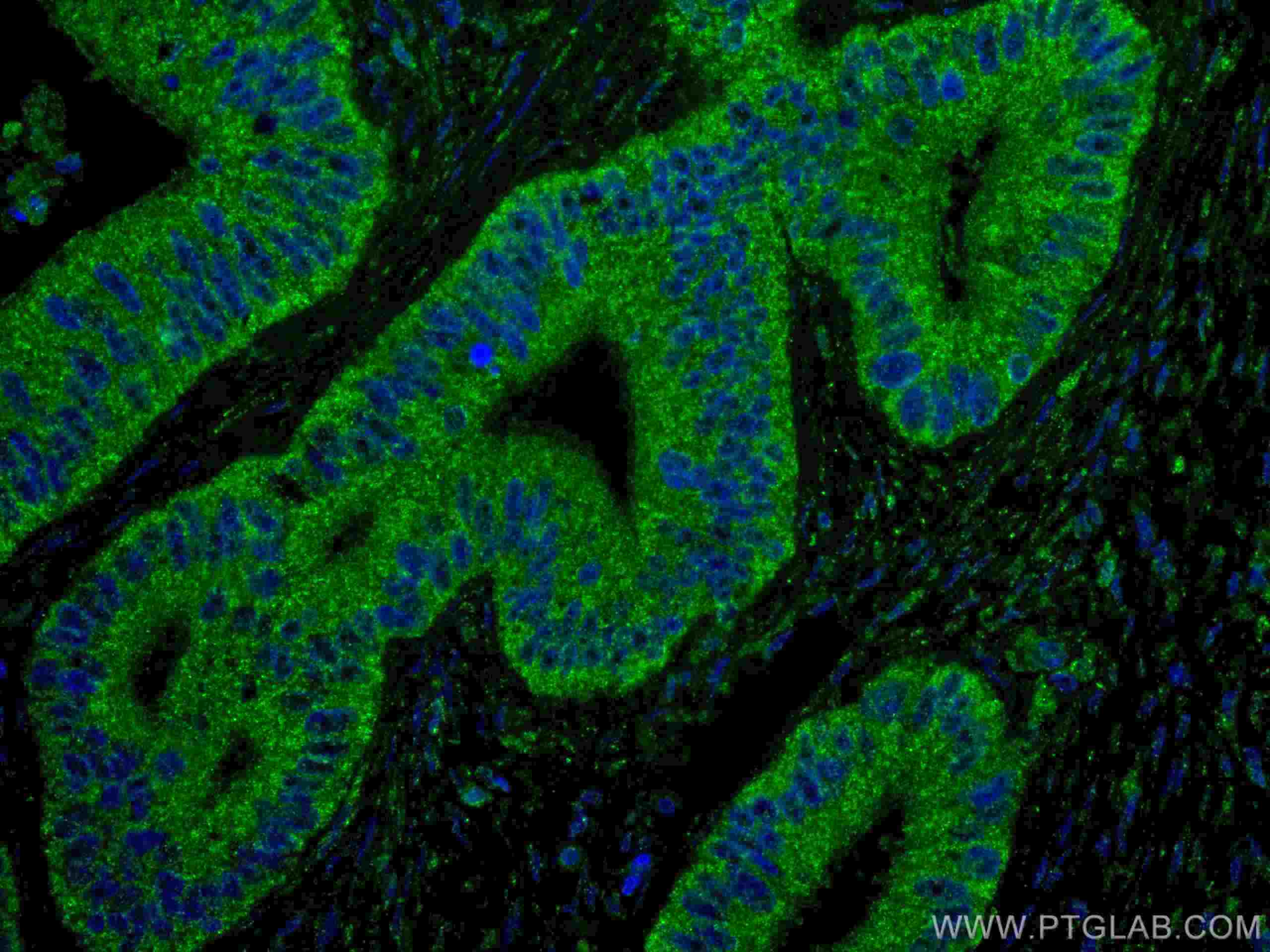
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-ING4
ING4 Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Réactivité testée
Humain, Lapin, porc, rat
Applications
WB, IHC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
1A12A3
N° de cat : 67754-1-PBS
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
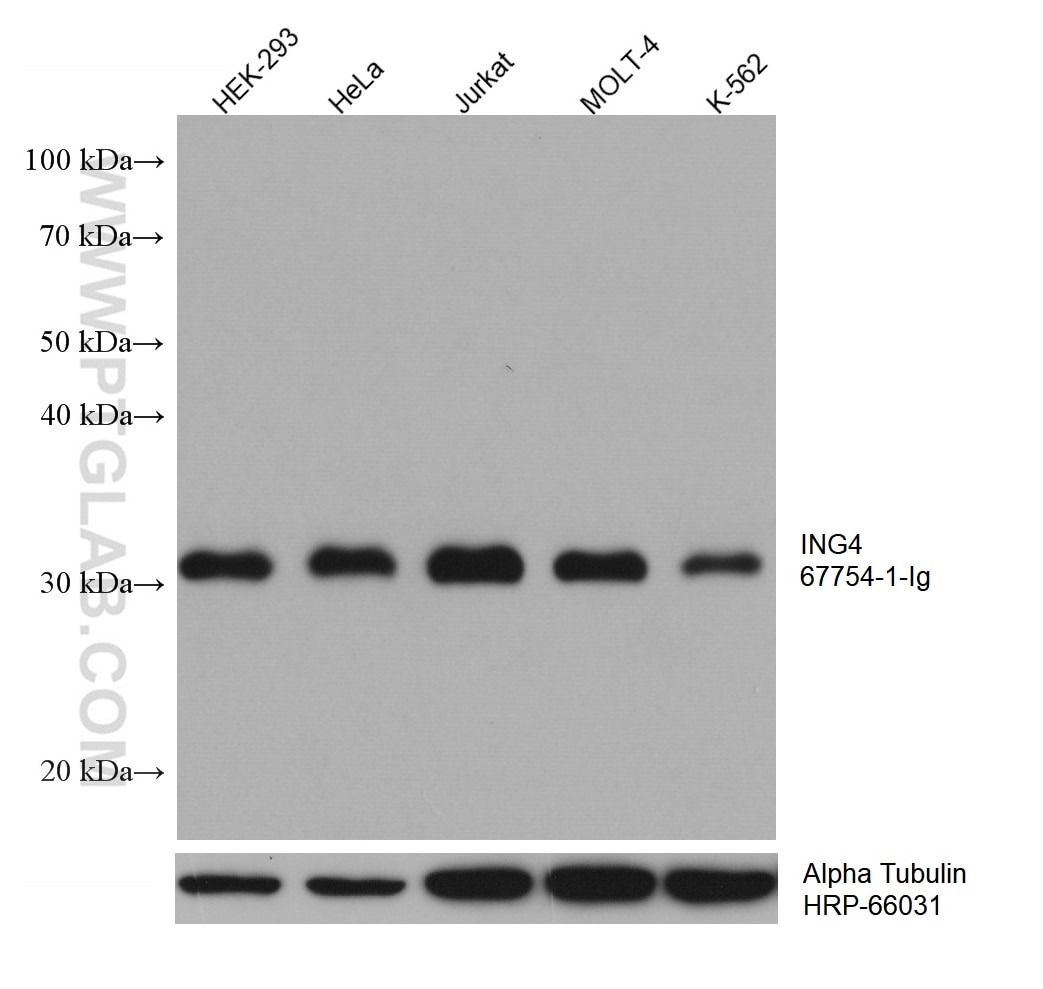
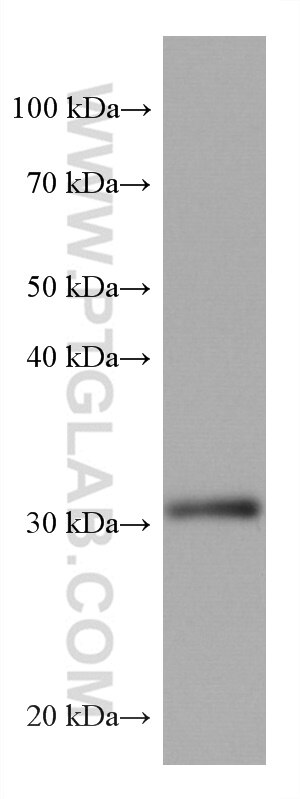
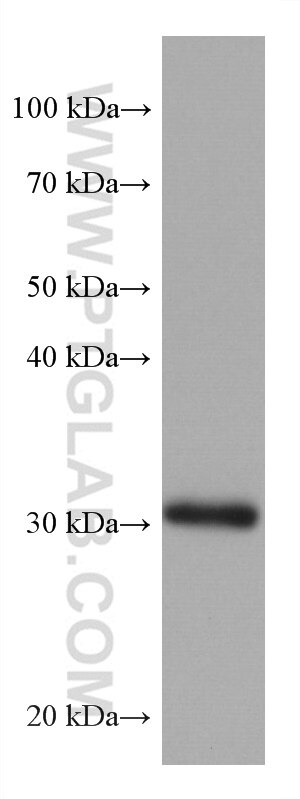
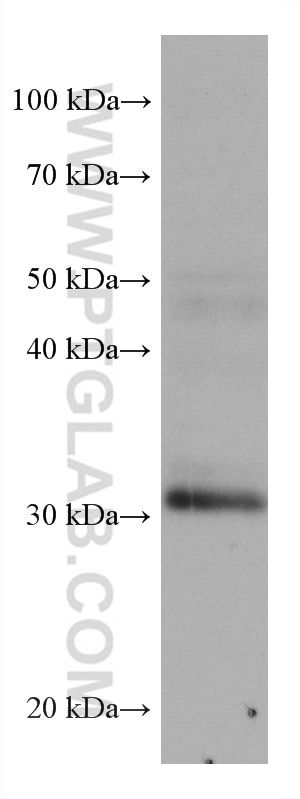
67754-1-PBS cible ING4 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, Lapin, porc, rat
| Réactivité | Humain, Lapin, porc, rat |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | ING4 Protéine recombinante Ag4610 |
| Nom complet | inhibitor of growth family, member 4 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 29 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 29 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC007781 |
| Symbole du gène | ING4 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 51147 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine G |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
ING4, also named as p29ING4, belongs to the ING family. It is a component of the HBO1 complex which has a histone H4-specific acetyltransferase activity, a reduced activity toward histone H3 and is responsible for the bulk of histone H4 acetylation in vivo. It may inhibit tumor progression by modulating the transcriptional output of signaling pathways which regulate cell proliferation. ING4 can suppress brain tumor angiogenesis through transcriptional repression of RELA/NFKB3 target genes when complexed with RELA. It may also specifically suppress loss of contact inhibition elicited by activated oncogenes such as MYC. Represses hypoxia inducible factor's (HIF) activity by interacting with HIF prolyl hydroxylase 2 (EGLN1). ING4 is a tumor suppressor gene that interacts with NFkB and represses its transcriptional activity. Several lines of evidence suggest that the tumor suppressor gene ING4, NFkB and its target genes matrix metalloproteases MMP-2, MMP-9 and u-PA are critically involved in tumor invasion.