- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal)
PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF-P, IP, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF-P, IP, CoIP, ChIP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 28076-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
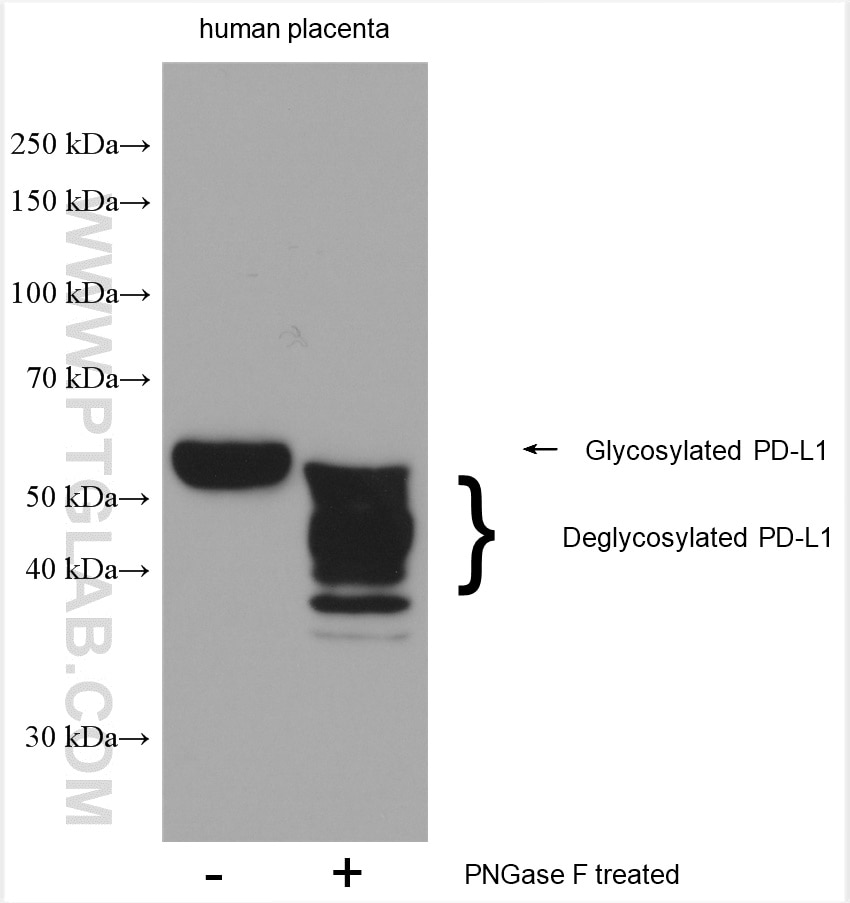
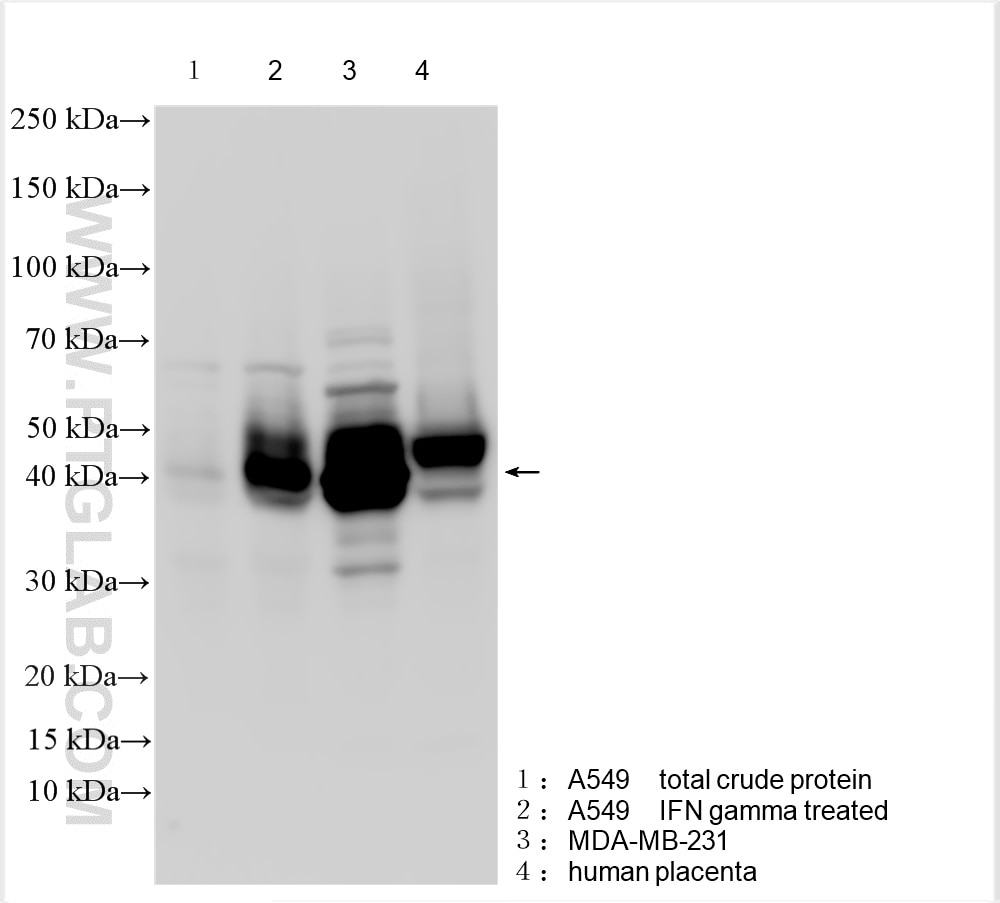
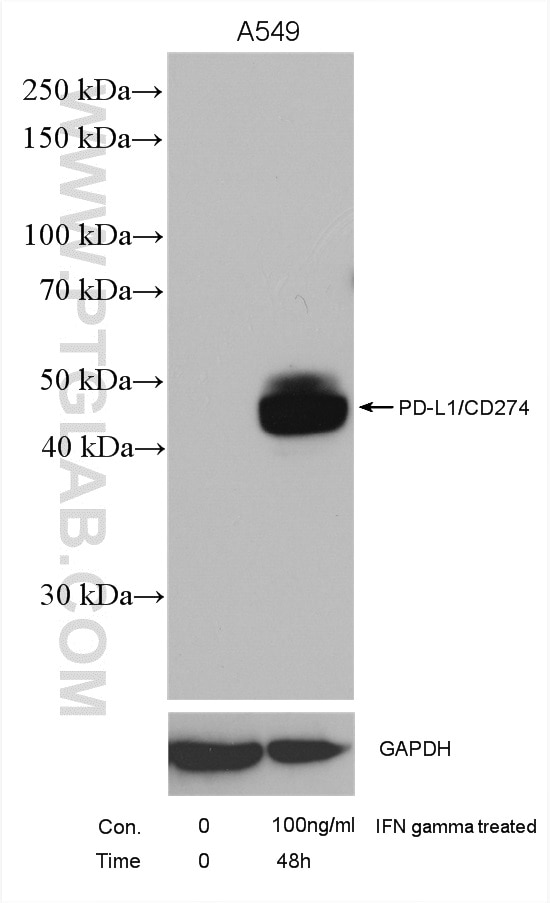
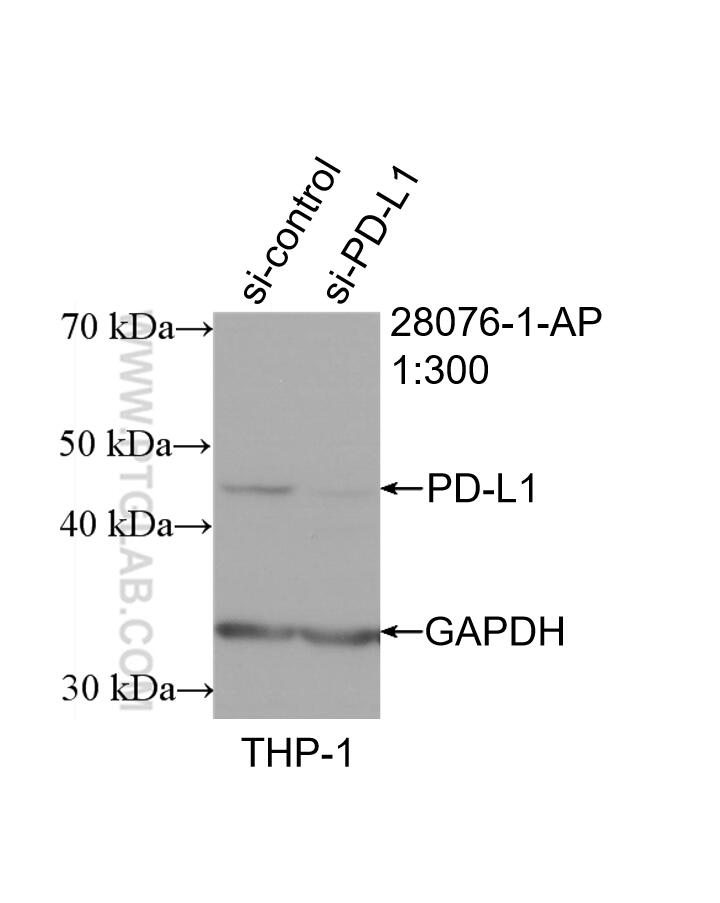
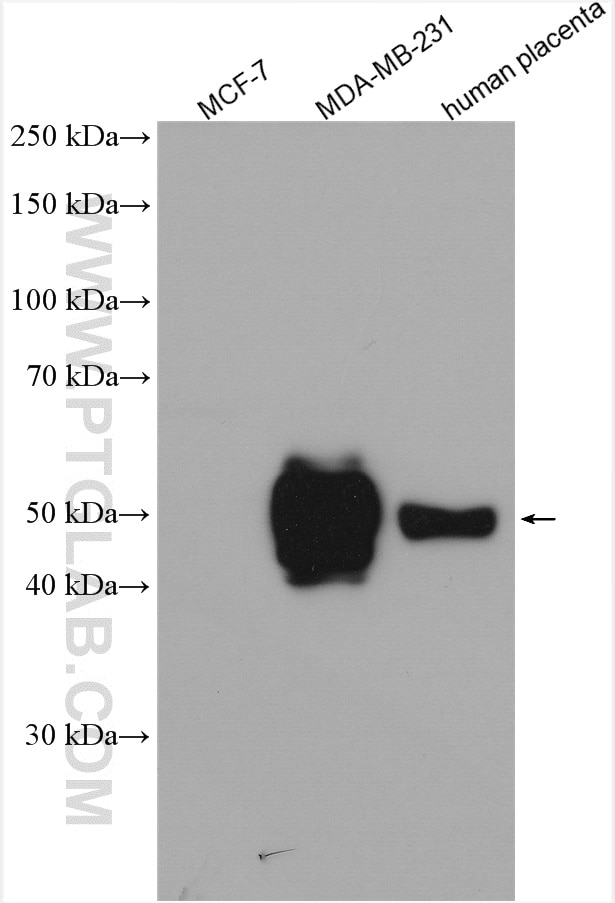
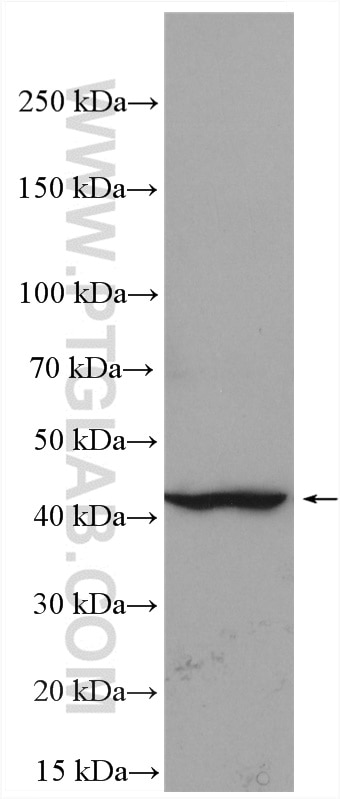
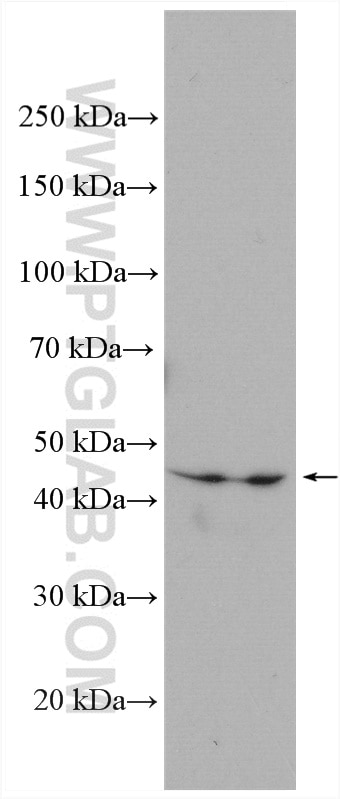
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules A549 traitées par IFN gamma, cellules MDA-MB-231, cellules THP-1, tissu cardiaque de rat, tissu cardiaque de souris, tissu placentaire humain |
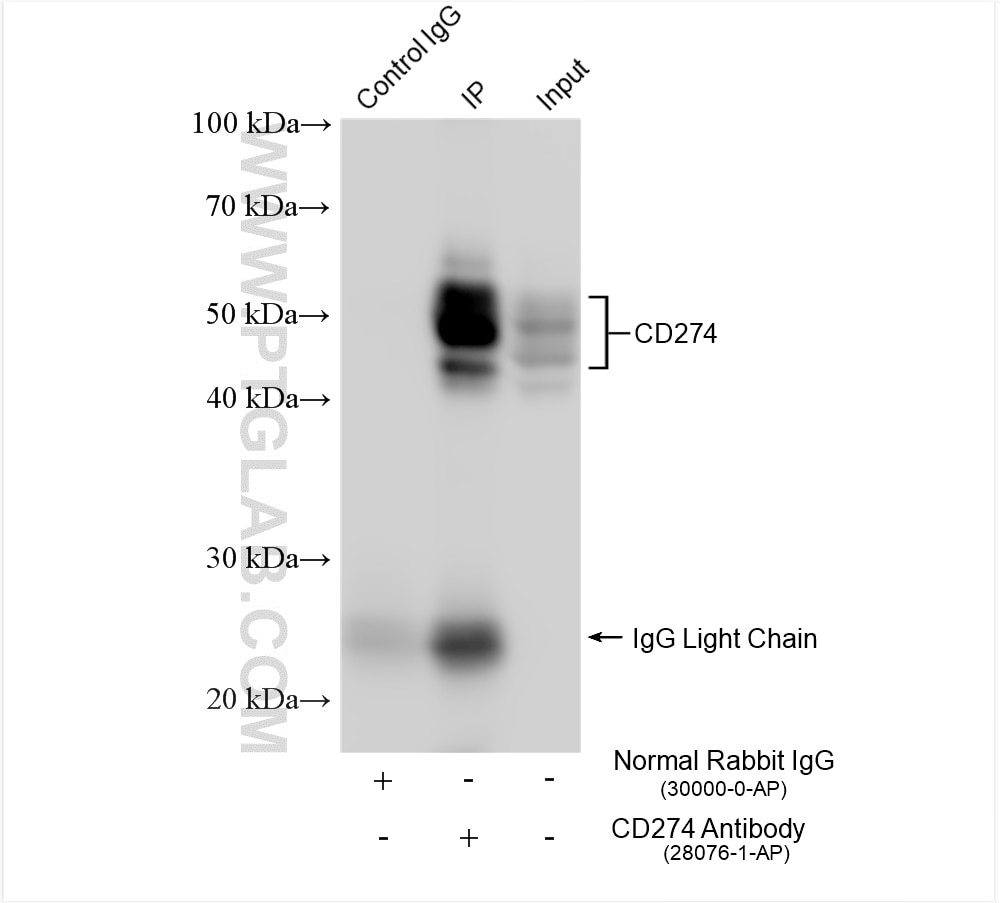
| Résultats positifs en IP | cellules MDA-MB-231, |
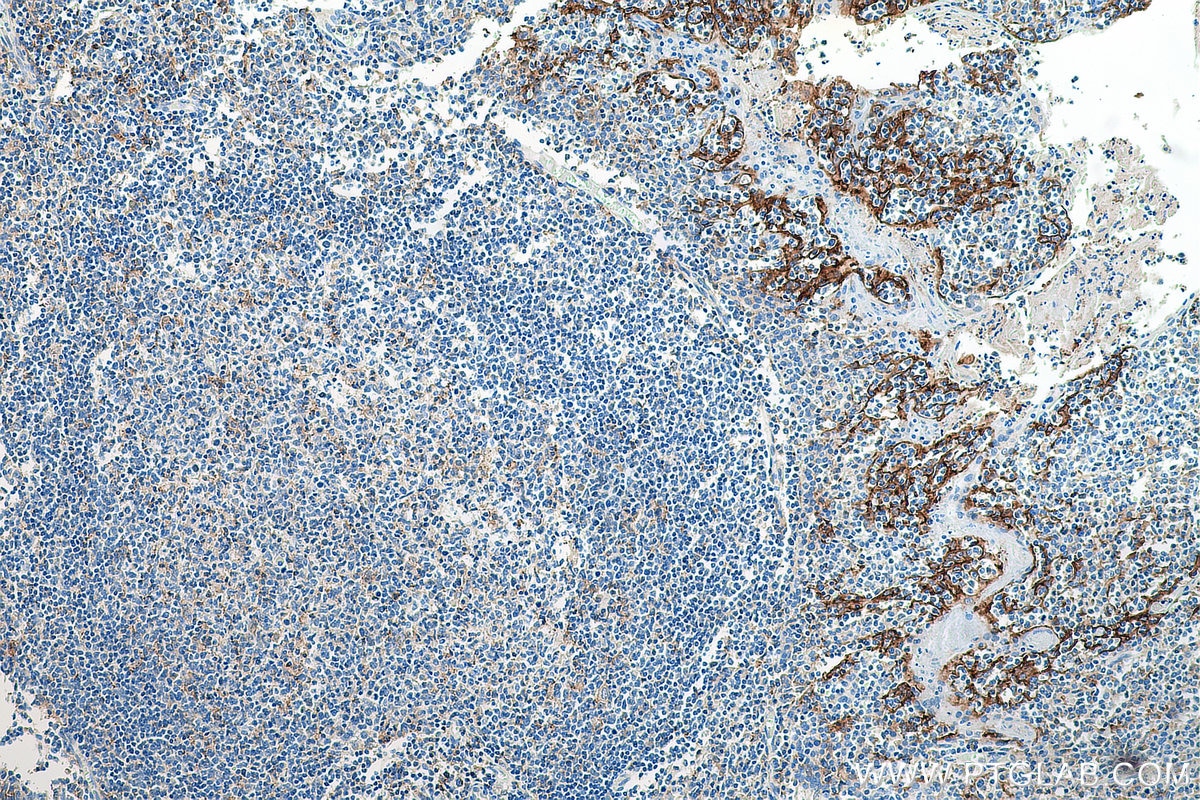
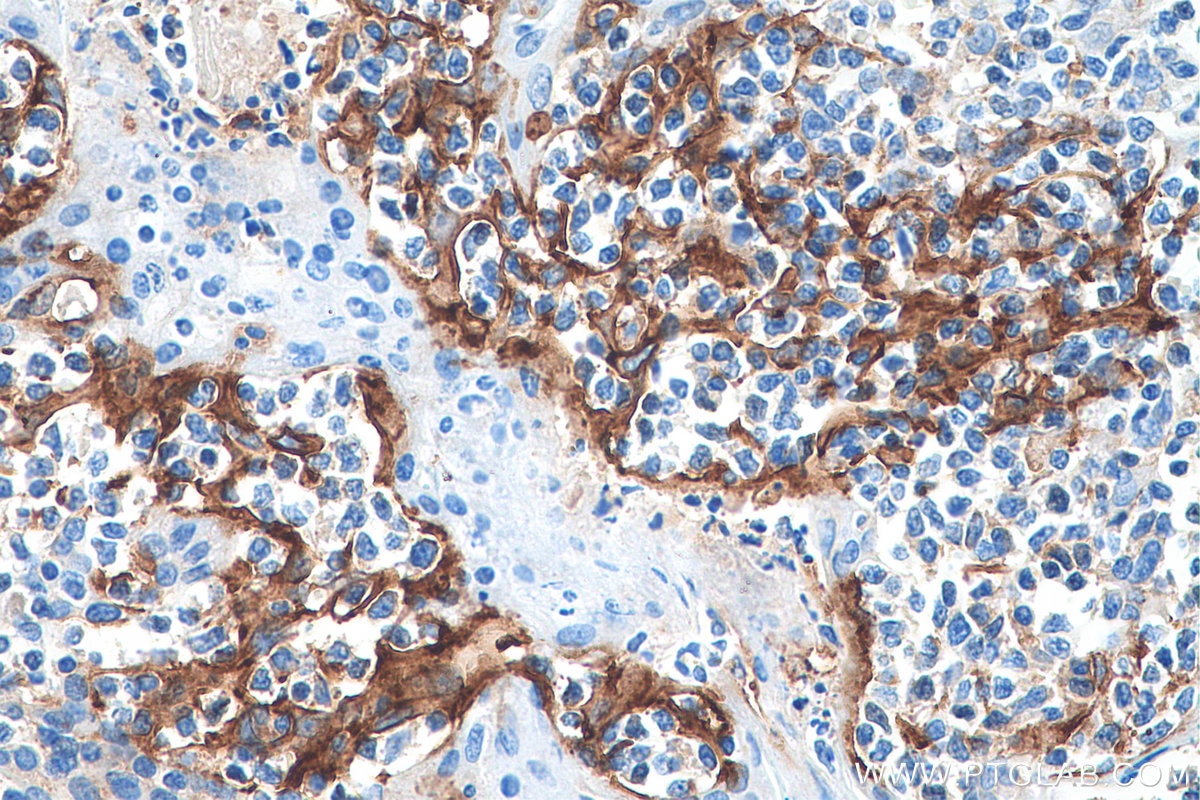
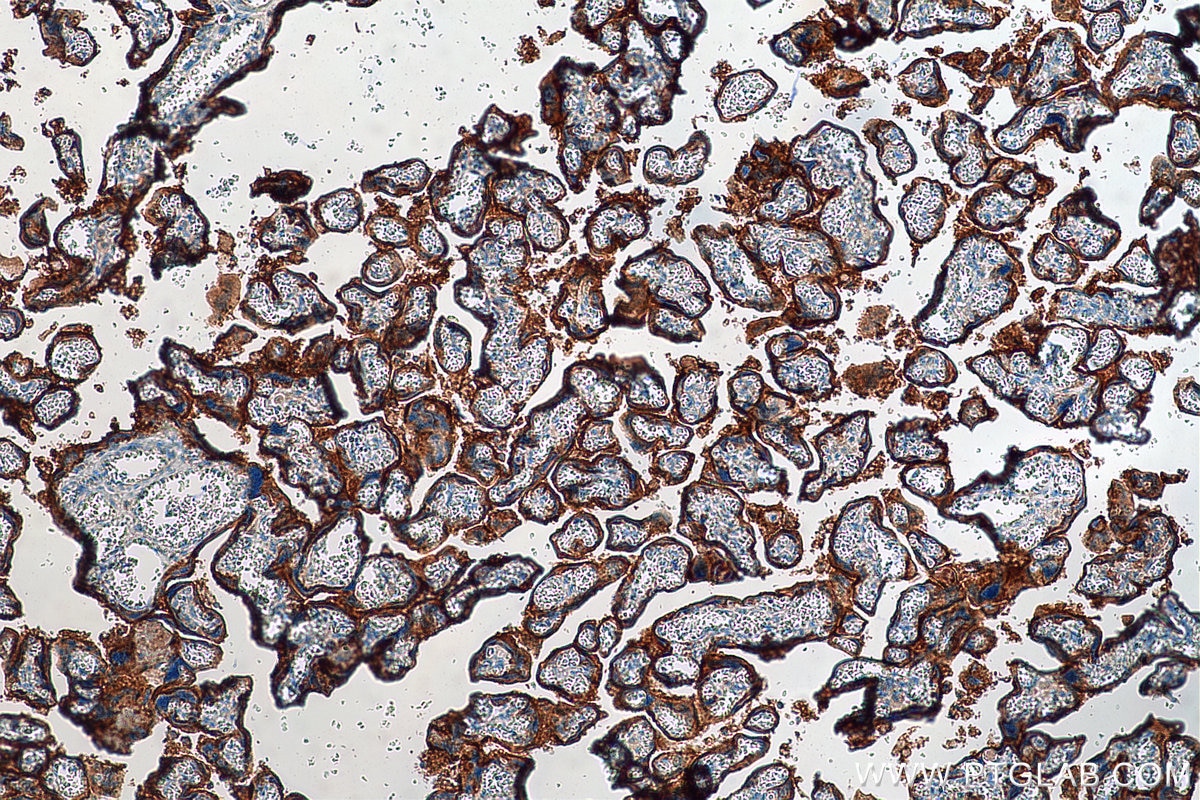
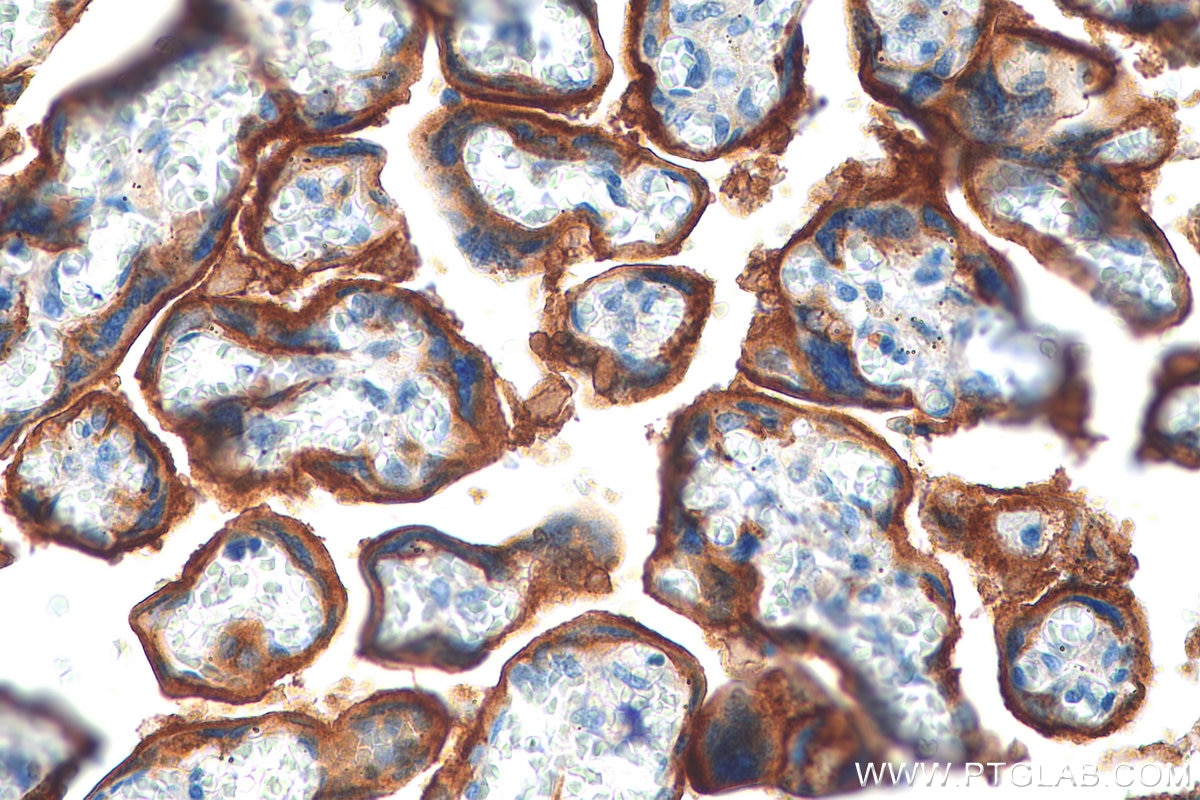
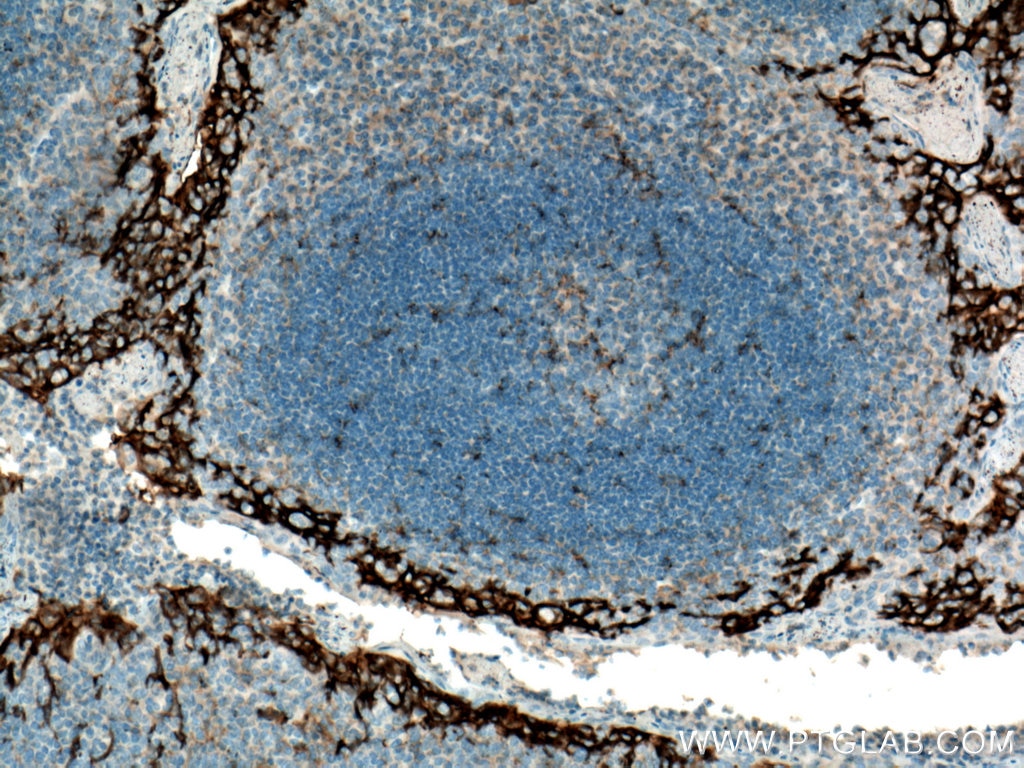
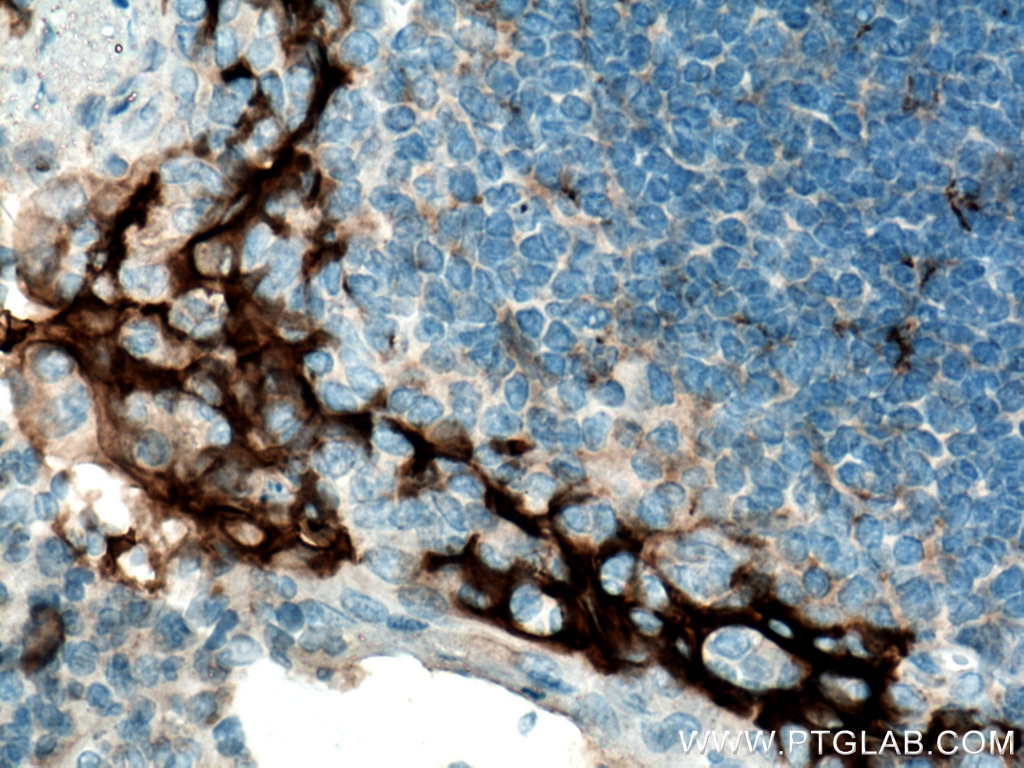
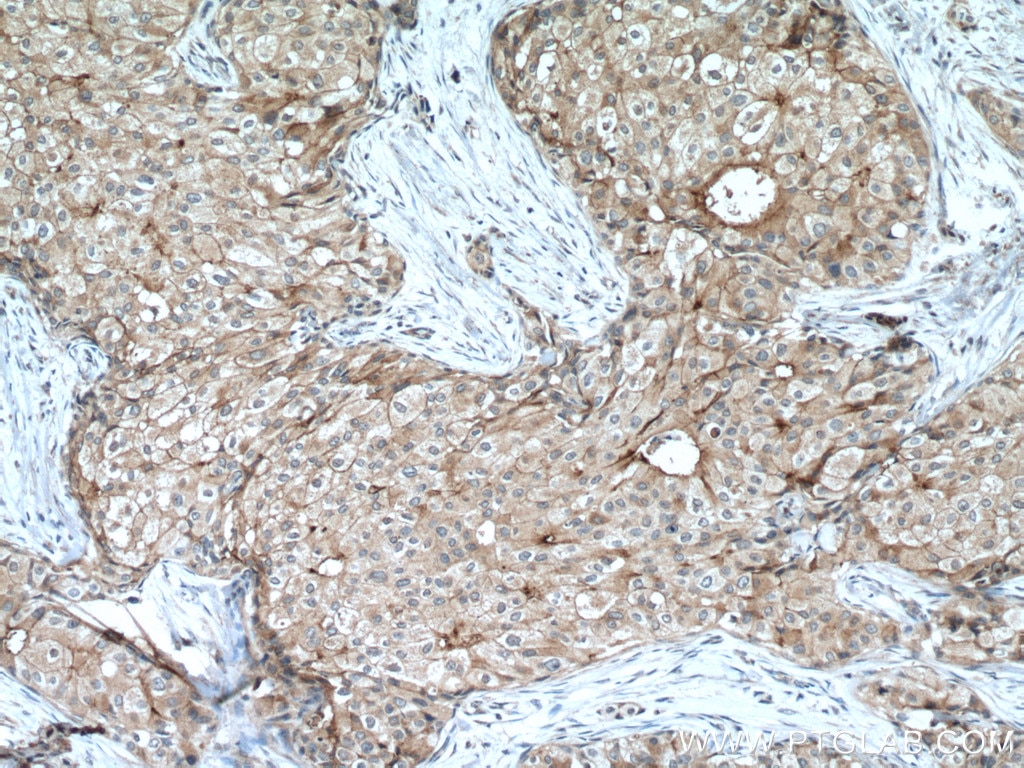
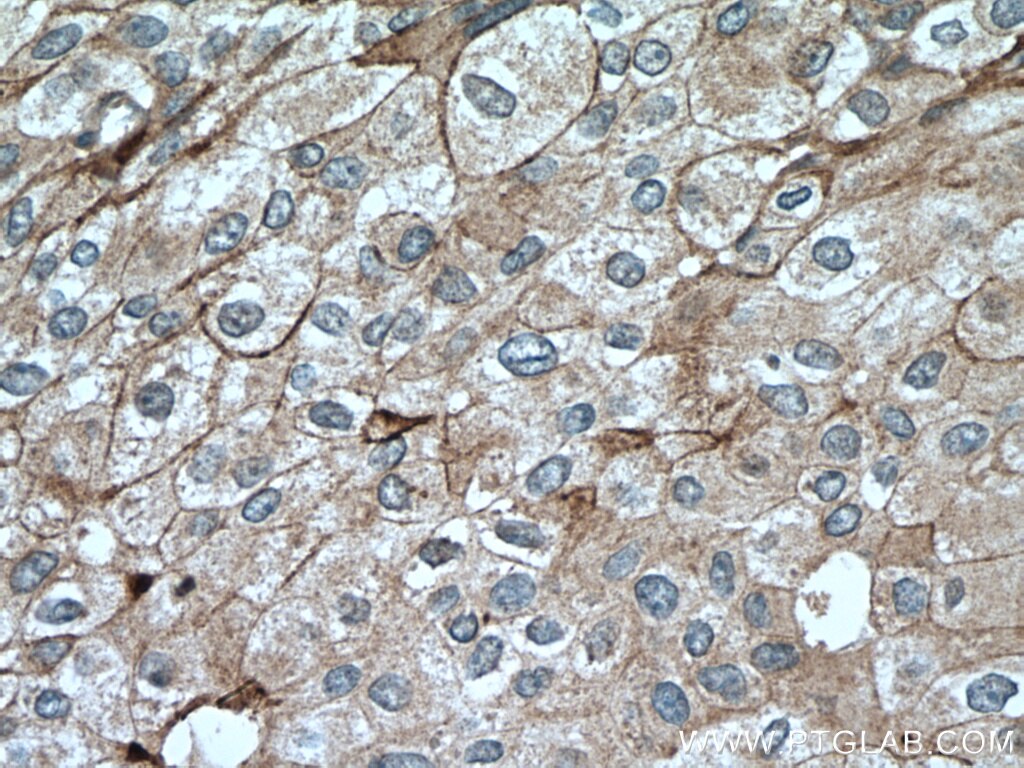
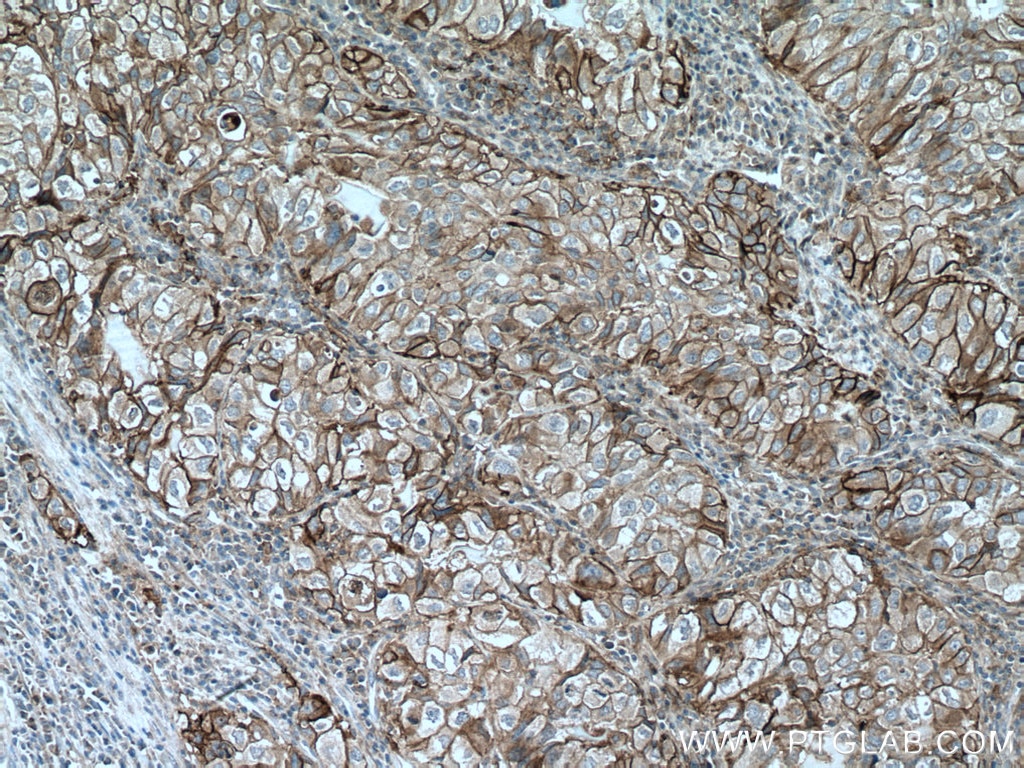
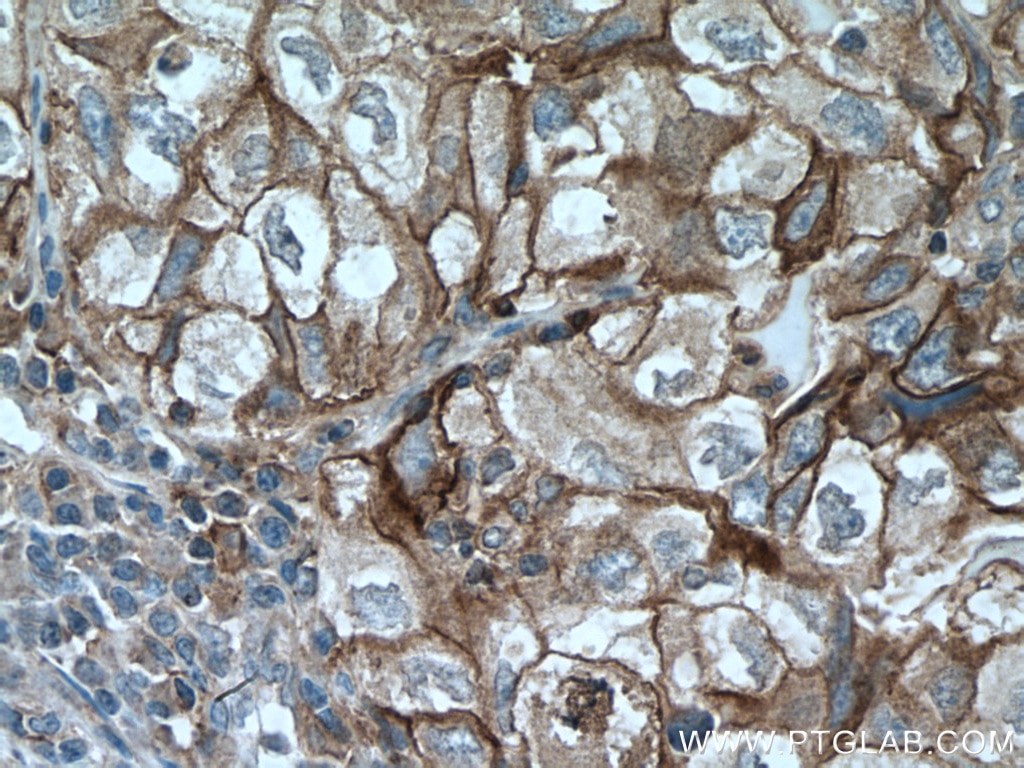
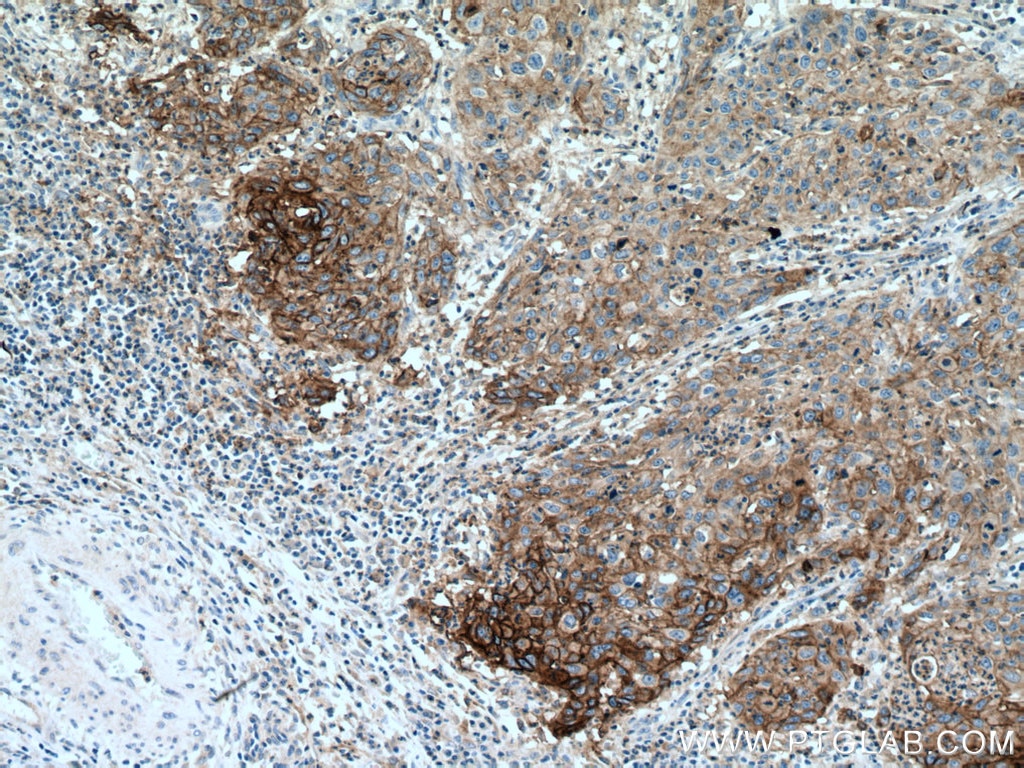
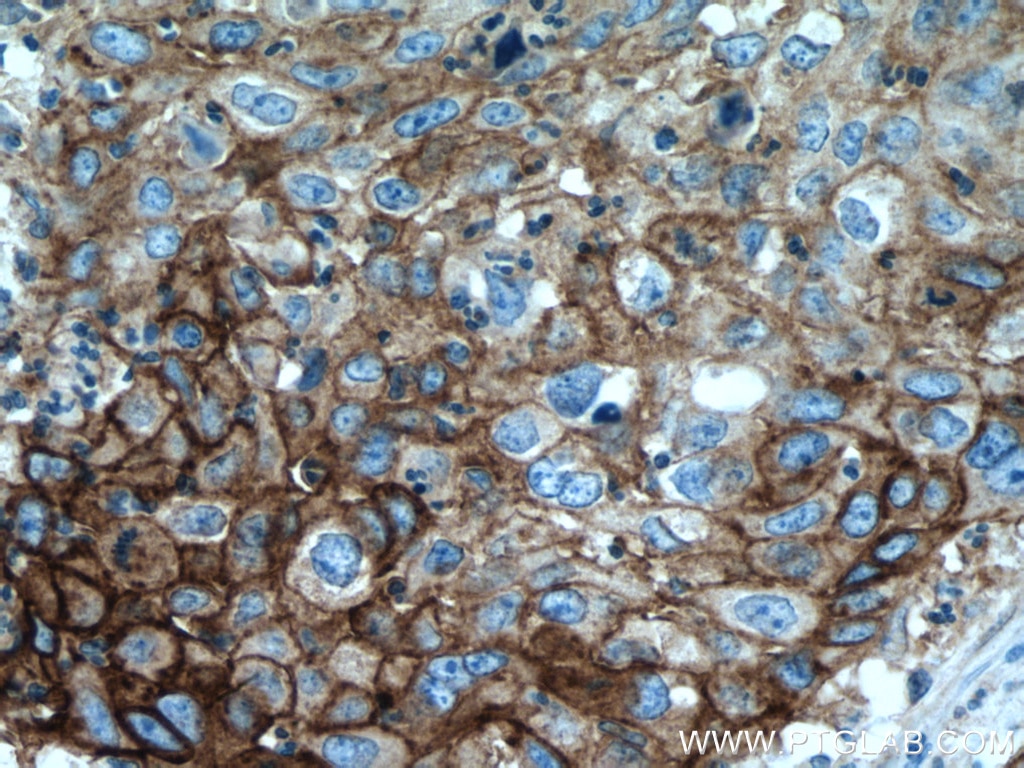
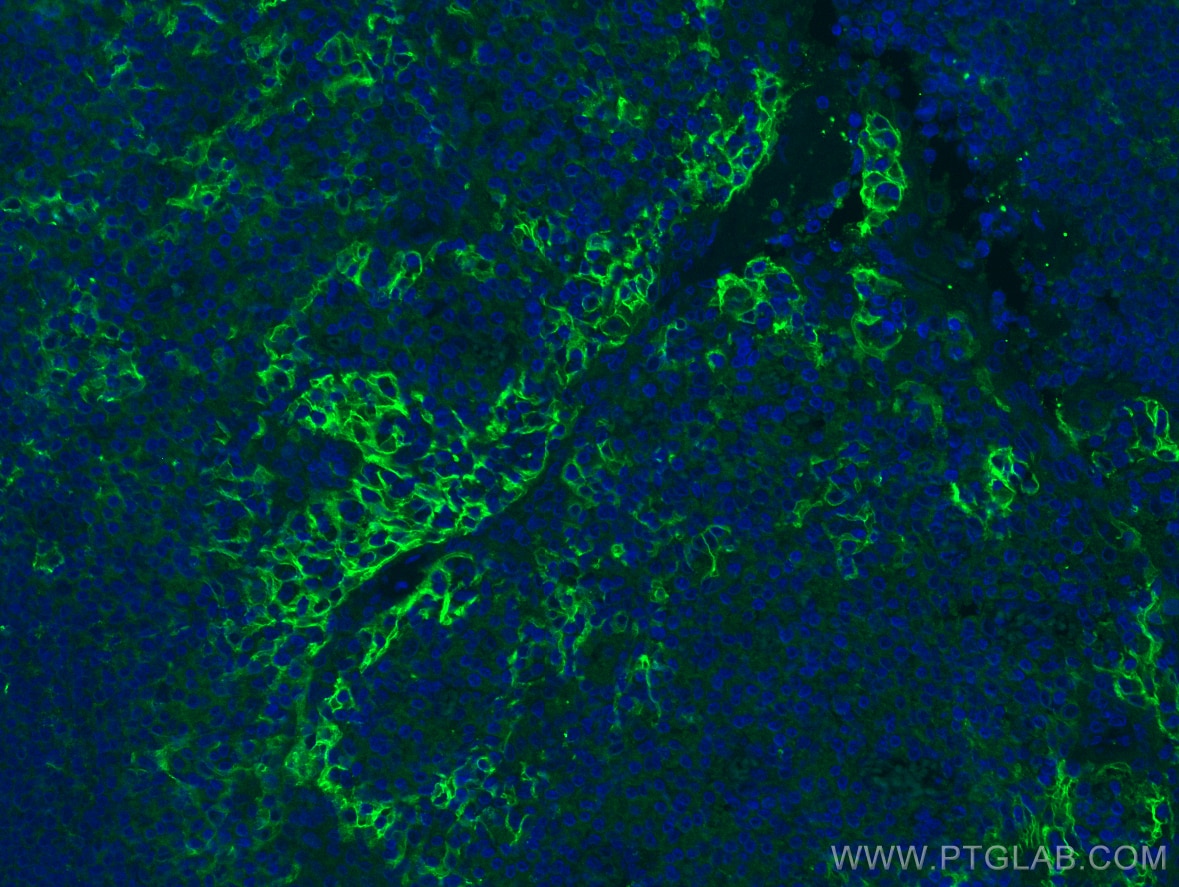
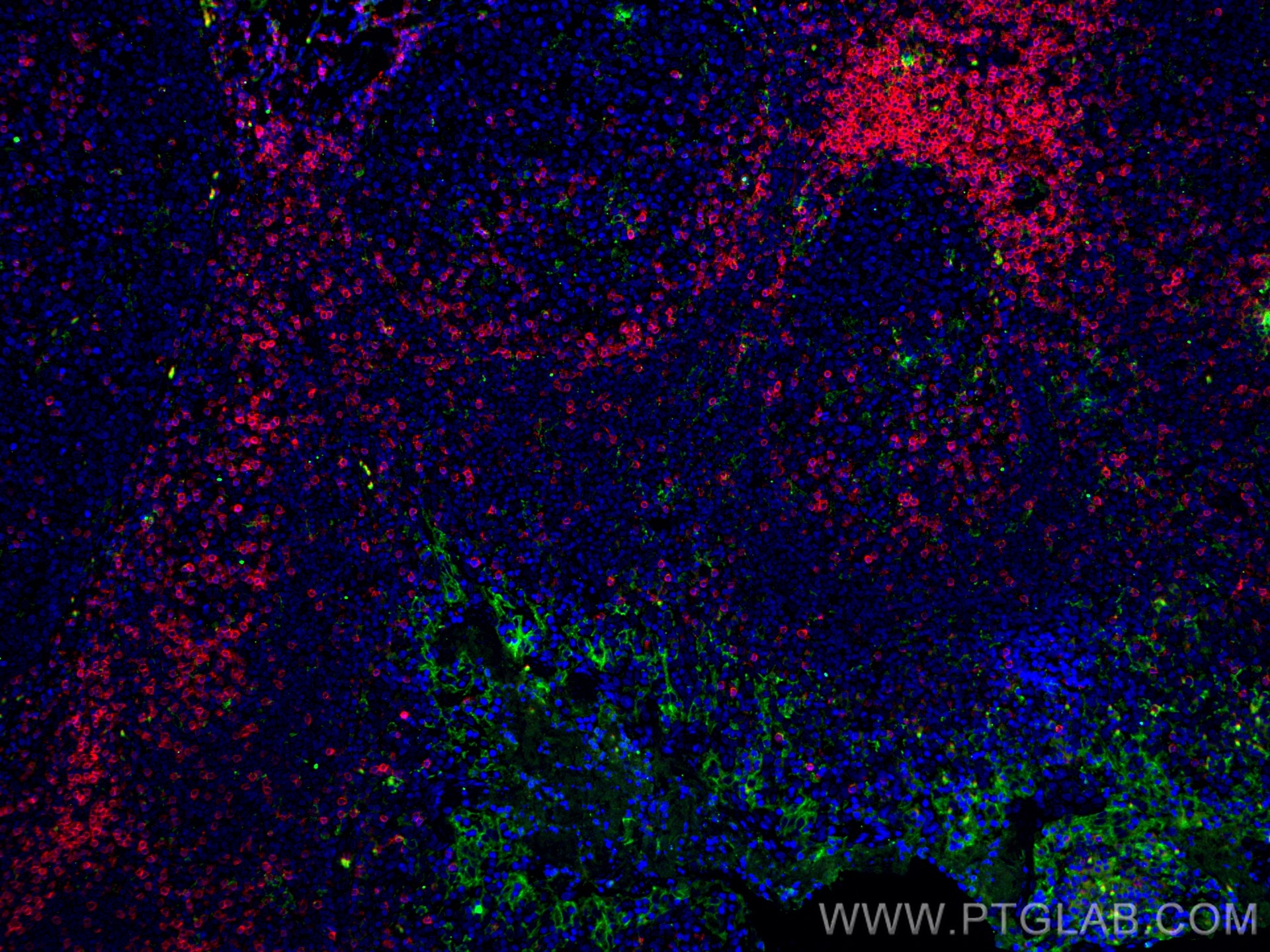
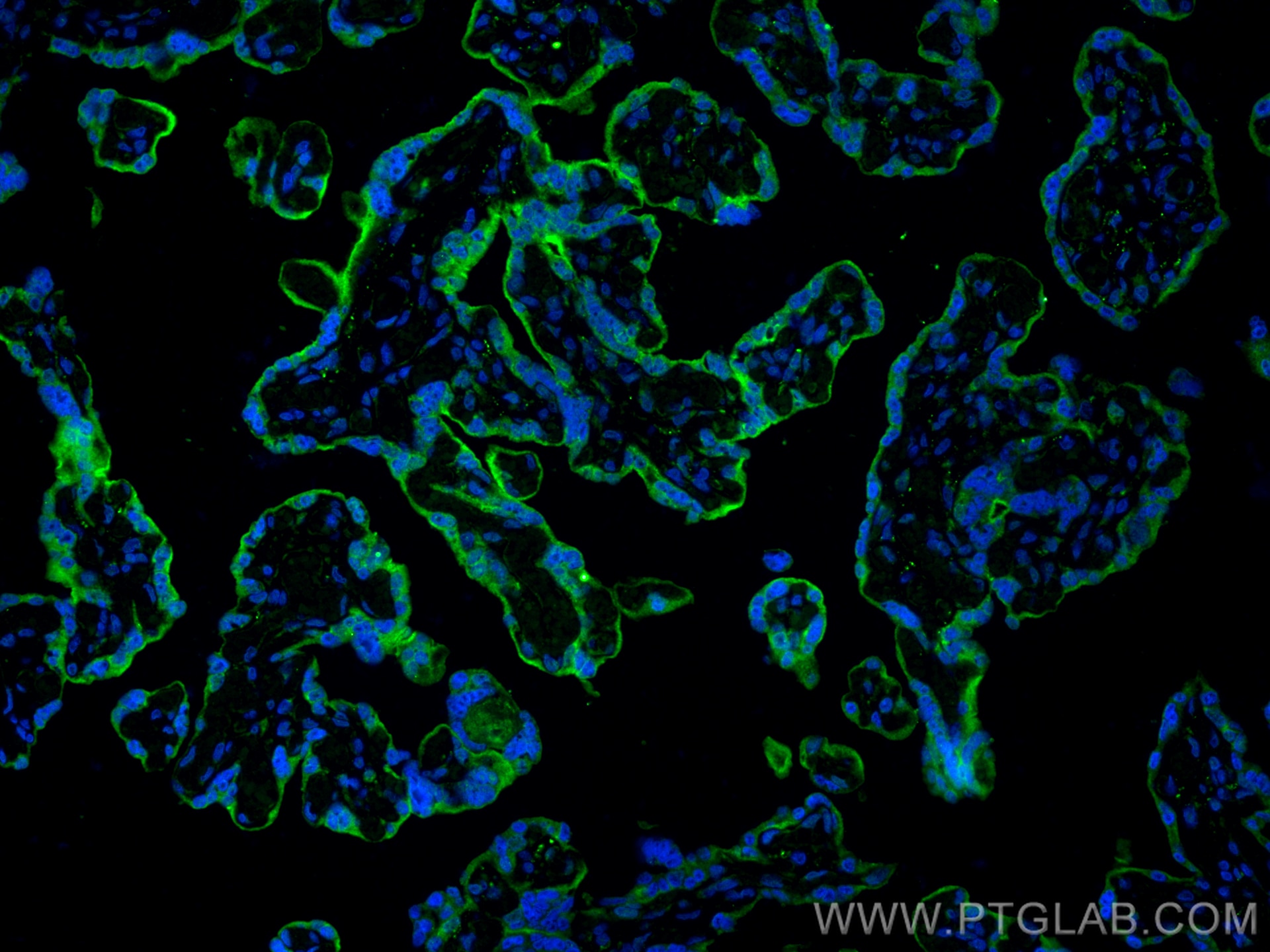
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu d'amygdalite humain, tissu de cancer du col de l'utérus humain, tissu de cancer du poumon humain, tissu de cancer du sein humain, tissu placentaire humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
| Résultats positifs en IF-P | tissu d'amygdalite humain, tissu placentaire humain |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Informations sur le produit
28076-1-AP cible PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF-P, IP, CoIP, ChIP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) Protéine recombinante Ag27557 |
| Nom complet | CD274 molecule |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 290 aa, 33 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 45-50 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC074984 |
| Symbole du gène | PD-L1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 29126 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
PD-L1, also known as CD274 or B7H1, stands for programmed cell death ligand 1. It is a type I transmembrane protein that is thought to repress immune responses by binding to its receptor (PD1), thus inhibiting T-cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. It contains V-like and C-like immunoglobulin domains. PD-L1 expression is regulated by various cytokines, such as TNF-α or LPS (ISSN: 1848-7718). Increased expression of this protein in certain types of cancers, e.g., renal cell carcinoma or colon cancer, correlates with poor prognosis.
What is the molecular weight of PD-L1?
Depending on the isoform, the calculated molecular weight of the protein varies between 20 and 33 kDa (176-290 aa).
What are the isoforms of PD-L1?
According to NCBI, three different isoforms have been identified. There are significant differences in the untranslated and protein coding regions.
What is the subcellular localization and tissue specificity of PD-L1?
It is predicted to localize in the plasma membrane of various cell types, with a particularly high expression in placental trophoblast and subsets of immune cells. High levels of PD-L1 protein have also been detected in lung and colon tissues.
What is the function of PD-L1 in immune responses?
PD-L1 is critical for the induction and maintenance of immune self-tolerance during infection or inflammation in normal tissues. The interaction of PD-L1 and its receptors is responsible for preventing auto-immune phenotypes and balancing the overall immune response in situations such as pregnancy or tissue allografts. The interaction between PD-L1 and PD-1 or B7.1 starts an inhibitory signaling cascade, which results in the decreased proliferation of antigen-specific T-cells and increased survival of regulatory T-cells (PMID: 15240681).
How can PD-L1's implication in cancer be used as a drug target?
In certain tumors, high expression of PD-L1 serves as a stop-sign to inhibit the recognition of cancer cells by T-cells (PMID: 23087408). The interaction between PD-L1 and its receptors (PD1 and B7.1) is a mechanism for the tumor to evade the host immune response (PMID: 29357948). Several mAbs have been developed to target that interaction and thus prevent the inactivation of cytotoxic T-cells by the tumor (PMIDs: 23890059, 18173375).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) antibody 28076-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) antibody 28076-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) antibody 28076-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) antibody 28076-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Mol Cancer Targeting PERP promotes anti-tumor immunity in HNSCC by regulating tumor immune microenvironment and metabolic homeostasis | ||
Cell Metab Dual impacts of serine/glycine-free diet in enhancing antitumor immunity and promoting evasion via PD-L1 lactylation | ||
ACS Cent Sci Allosteric Regulation of IGF2BP1 as a Novel Strategy for the Activation of Tumor Immune Microenvironment | ||
Nat Commun A protease-cleavable liposome for co-delivery of anti-PD-L1 and doxorubicin for colon cancer therapy in mice | ||
Cell Rep Med Benzosceptrin C induces lysosomal degradation of PD-L1 and promotes antitumor immunity by targeting DHHC3 | ||
Sci Adv Inhibition of ACLY overcomes cancer immunotherapy resistance via polyunsaturated fatty acids peroxidation and cGAS-STING activation |