Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-Polycystin 2
Polycystin 2 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IP, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
canin, Humain, rat, souris
Applications
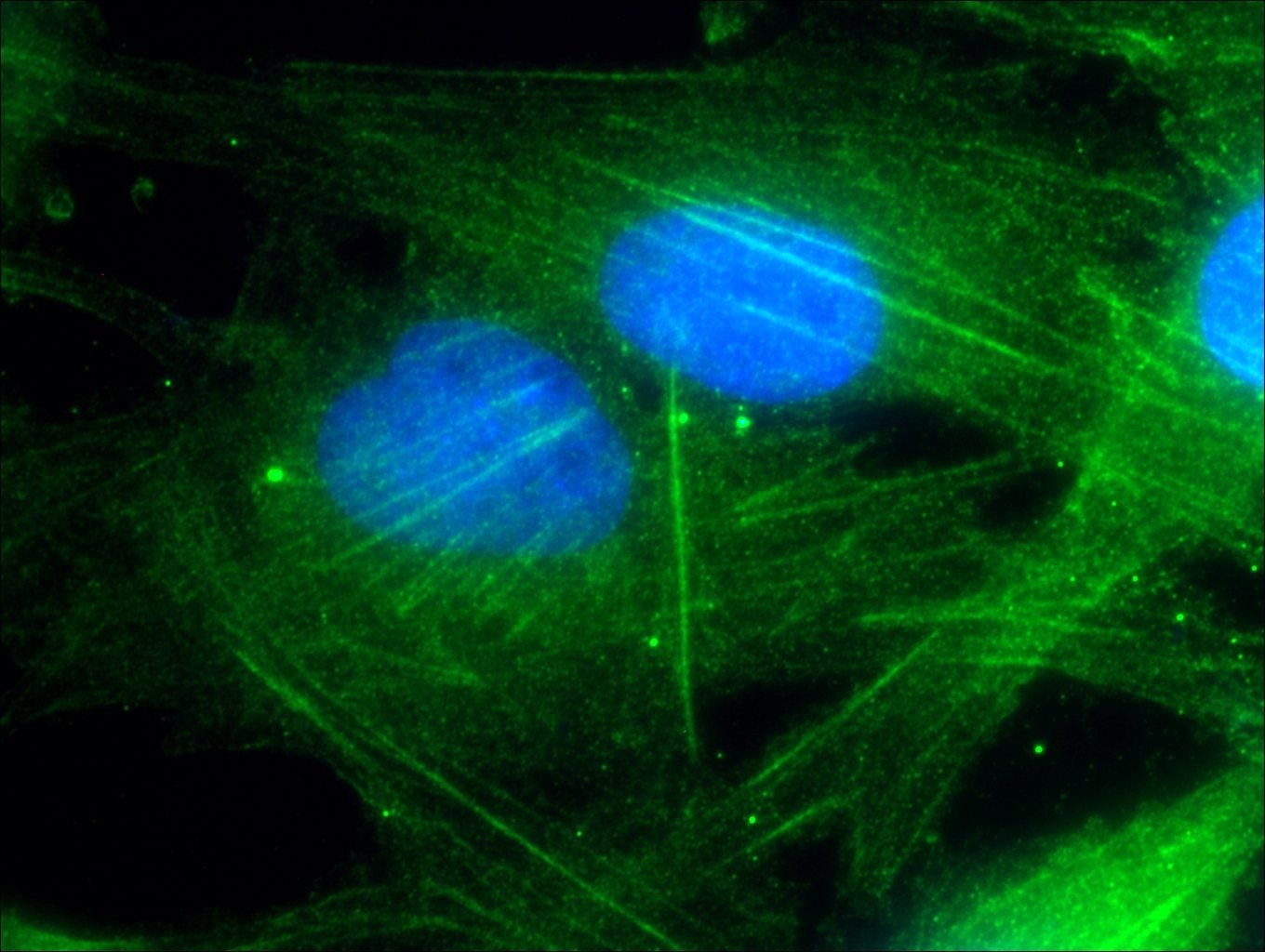
WB, IHC, IF, IP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 19126-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
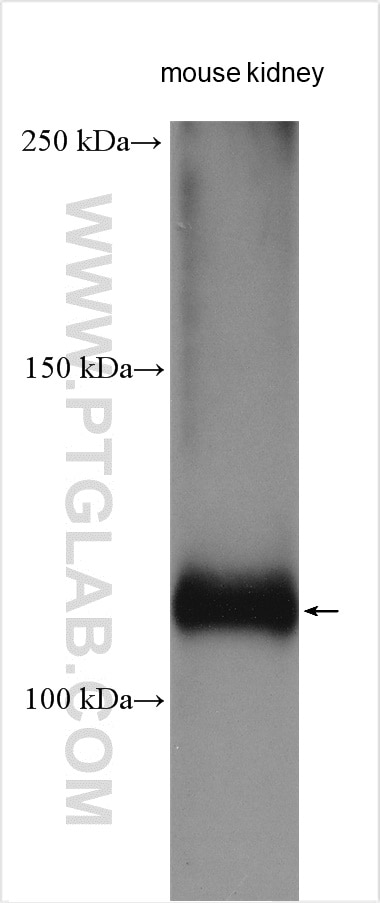
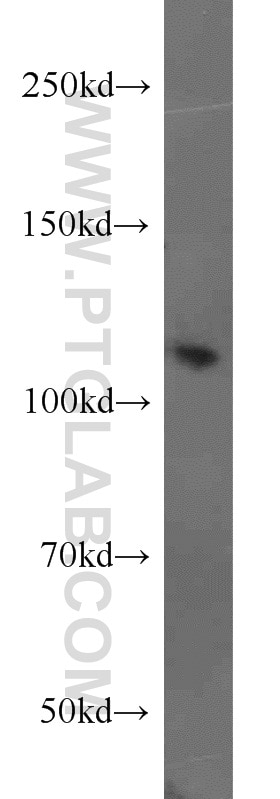
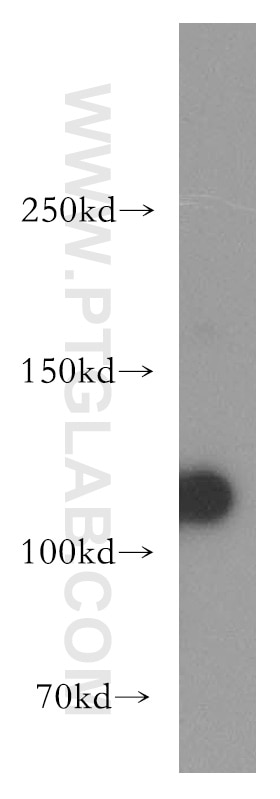
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu rénal de souris, cellules HEK-293, tissu rénal humain |
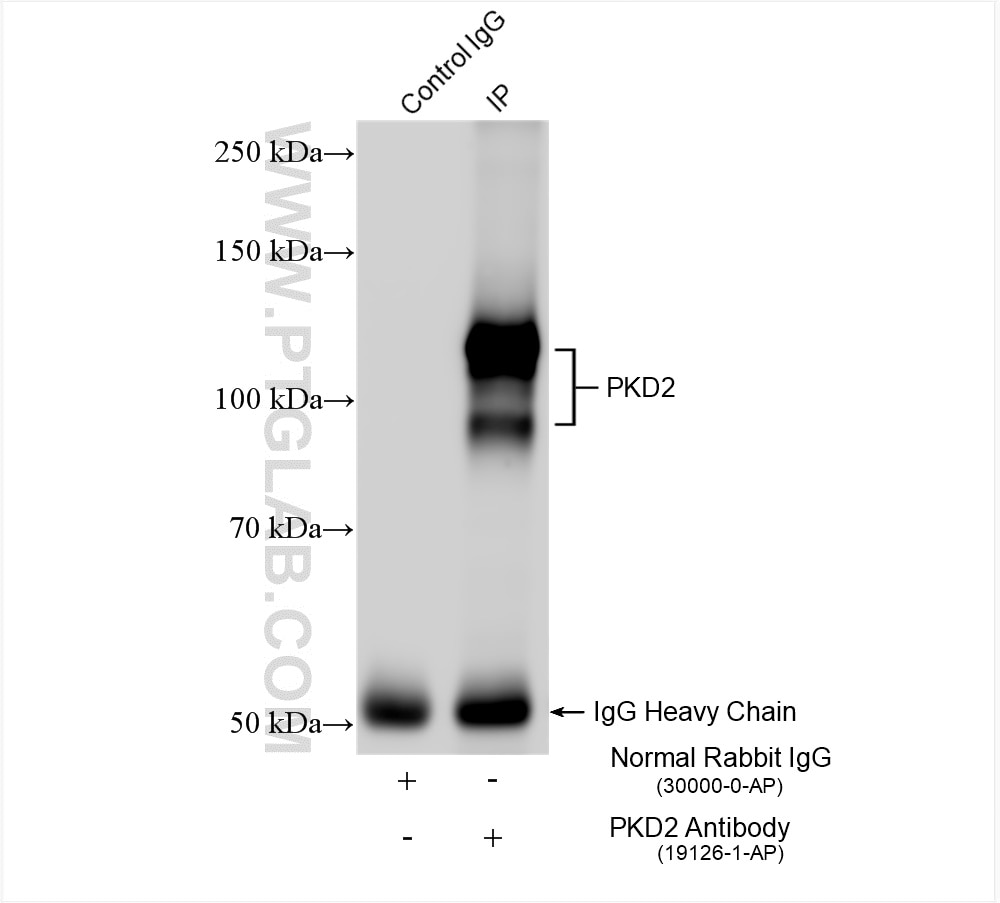
| Résultats positifs en IP | tissu testiculaire de souris, |
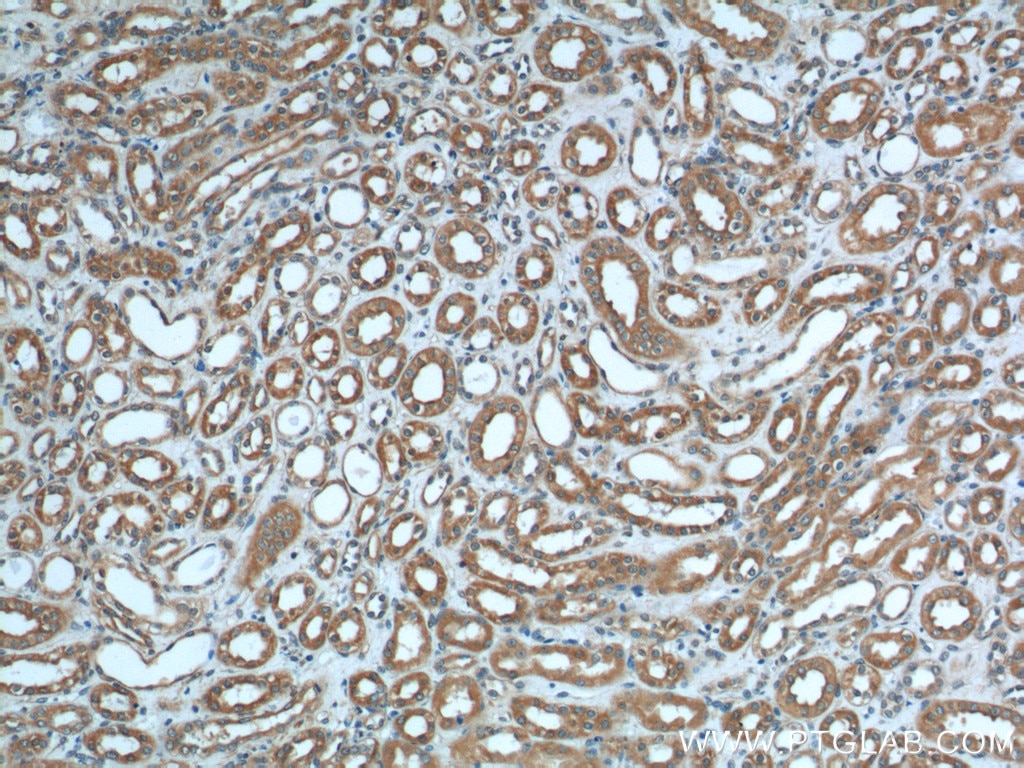
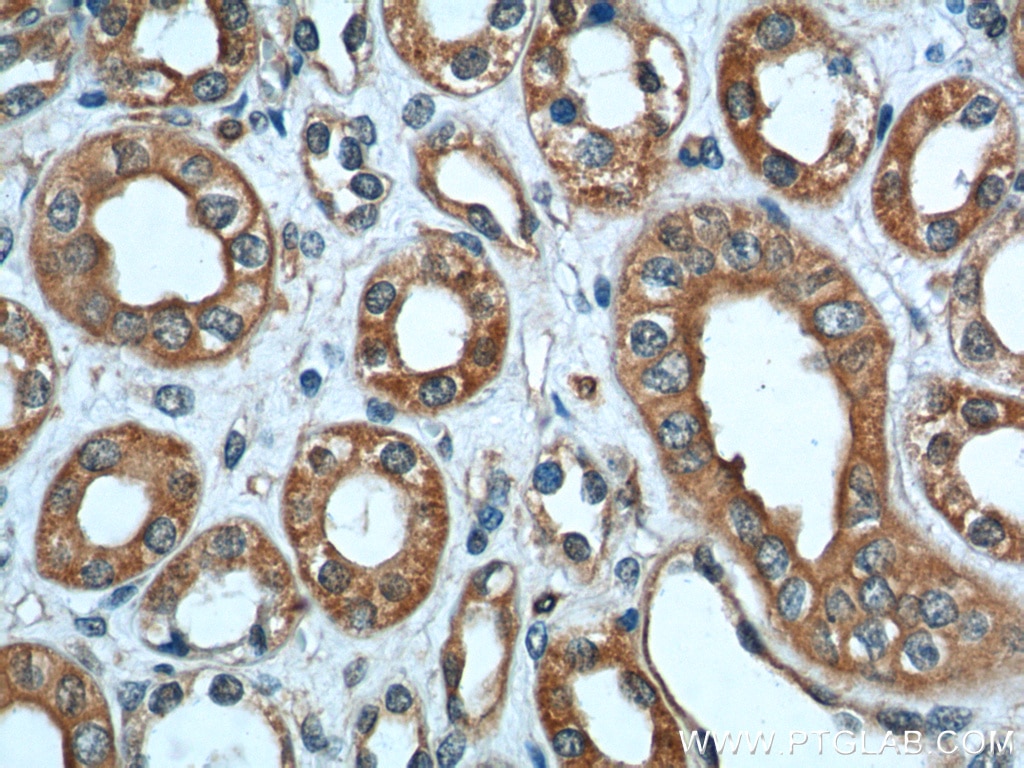
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu rénal humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:16000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 7 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
19126-1-AP cible Polycystin 2 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF, IP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons canin, Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | canin, Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Peptide |
| Nom complet | polycystic kidney disease 2 (autosomal dominant) |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 110 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 109 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | NM_000297 |
| Symbole du gène | PKD2 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 5311 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Polycystin 2 (PKD2), the product of the gene mutated in type 2 autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, belongs to the polycystin family. PKD2 is a ~110-kDa six-transmembrane channel protein with cytoplasmic N- and C-termini. This protein functions as a Ca2+-activated intracellular Ca2+ release channel in the endoplasmic reticulum. It is also present in the plasma membrane, where it functions as a nonselective cation channel. In addition, PKD2 expression has been documented in the primary cilium of kidney epithelial cells, where it is believed to have an essential role in mediating Ca2+ entry in response to flow rate changes, suggesting that it may be part of a mechanosensing machinery residing in the primary cilium. (PMID: 16135816; 10497221)
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Polycystin 2 antibody 19126-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Polycystin 2 antibody 19126-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for Polycystin 2 antibody 19126-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for Polycystin 2 antibody 19126-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Front Mol Biosci The Role of TRPC6 in Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion and Cellular Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injuries. | ||
Hum Pathol Down-regulation of polycystin in lymphatic malformations: Possible role in the proliferation of lymphatic endothelial cells. | ||
Cell Physiol Biochem iTRAQ-Based Proteomic Analysis of Neonatal Kidney from Offspring of Protein Restricted Rats Reveals Abnormalities in Intraflagellar Transport Proteins. | ||
Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol TRPP2 is located in the primary cilia of human non-pigmented ciliary epithelial cells | ||
Autophagy Rep Shear stress induces autophagy in Schlemm's canal cells via primary cilia-mediated SMAD2/3 signaling pathway | ||
J Am Soc Nephrol Pkd2 Deficiency in Embryonic Aqp2 + Progenitor Cells Is Sufficient to Cause Severe Polycystic Kidney Disease |