Anticorps Recombinant de lapin anti-PPAR Gamma
PPAR Gamma Recombinant Antibody for WB, IHC, IF-P, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
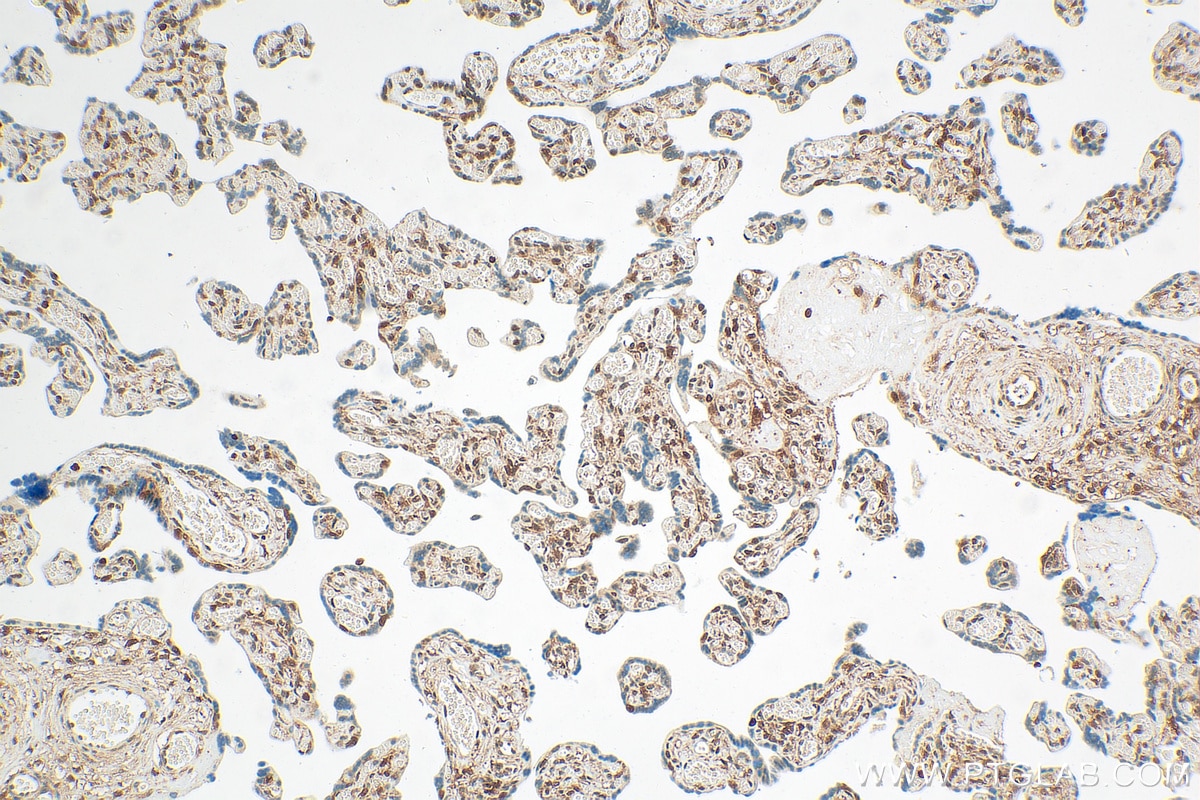
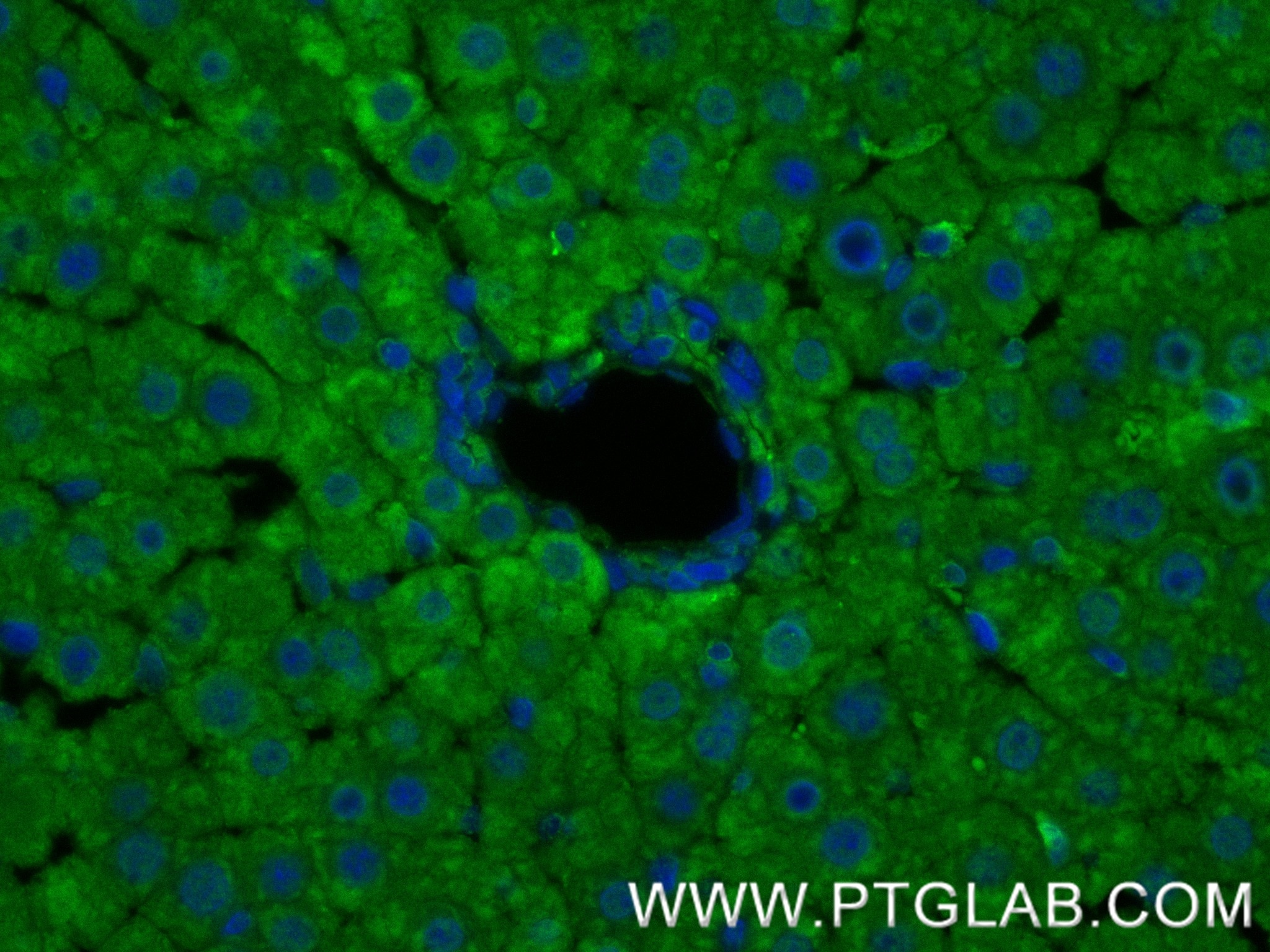
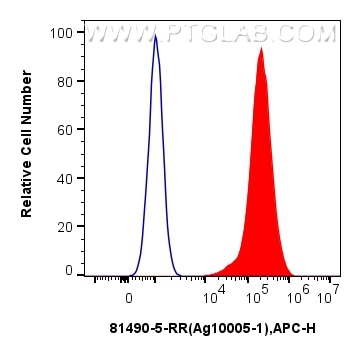
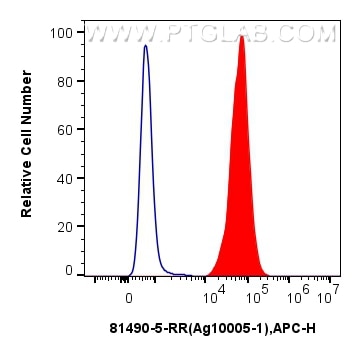
WB, IHC, IF-P, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
230374A3
N° de cat : 81490-5-PBS
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
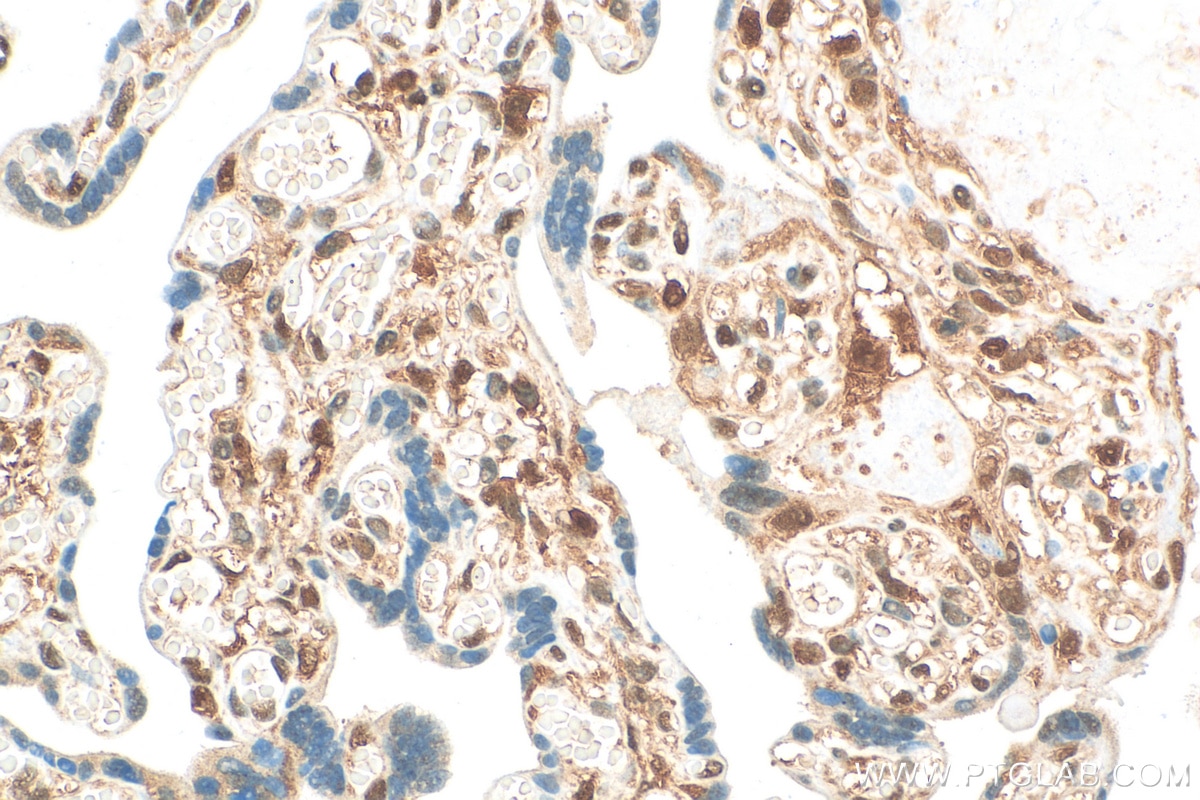
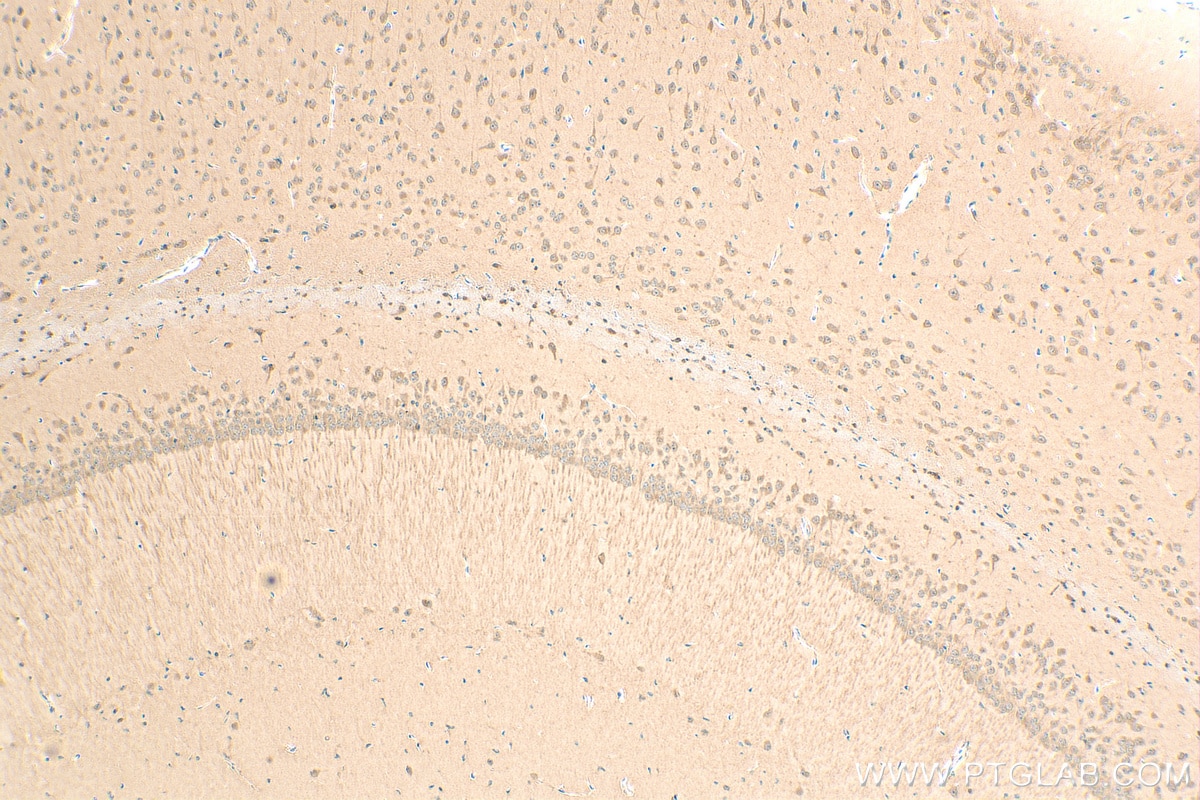
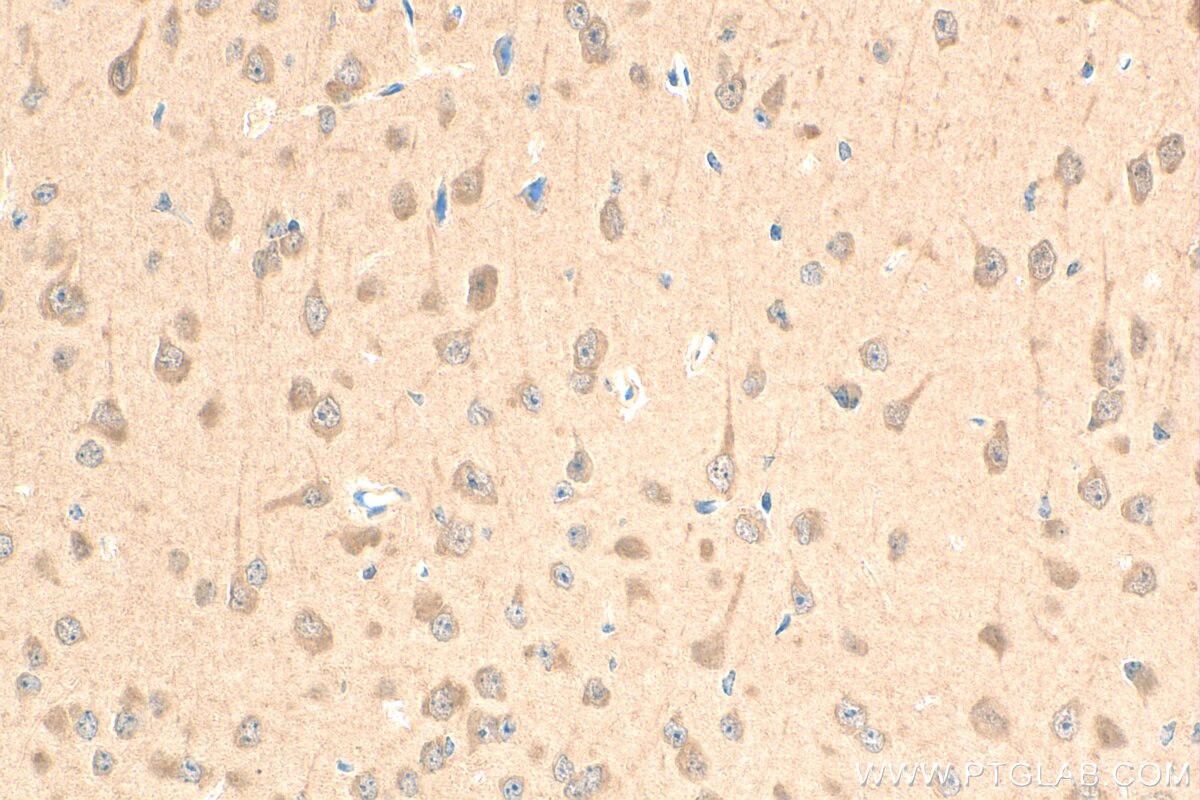
81490-5-PBS cible PPAR Gamma dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF-P, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Recombinant |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | PPAR Gamma Protéine recombinante Ag10005 |
| Nom complet | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
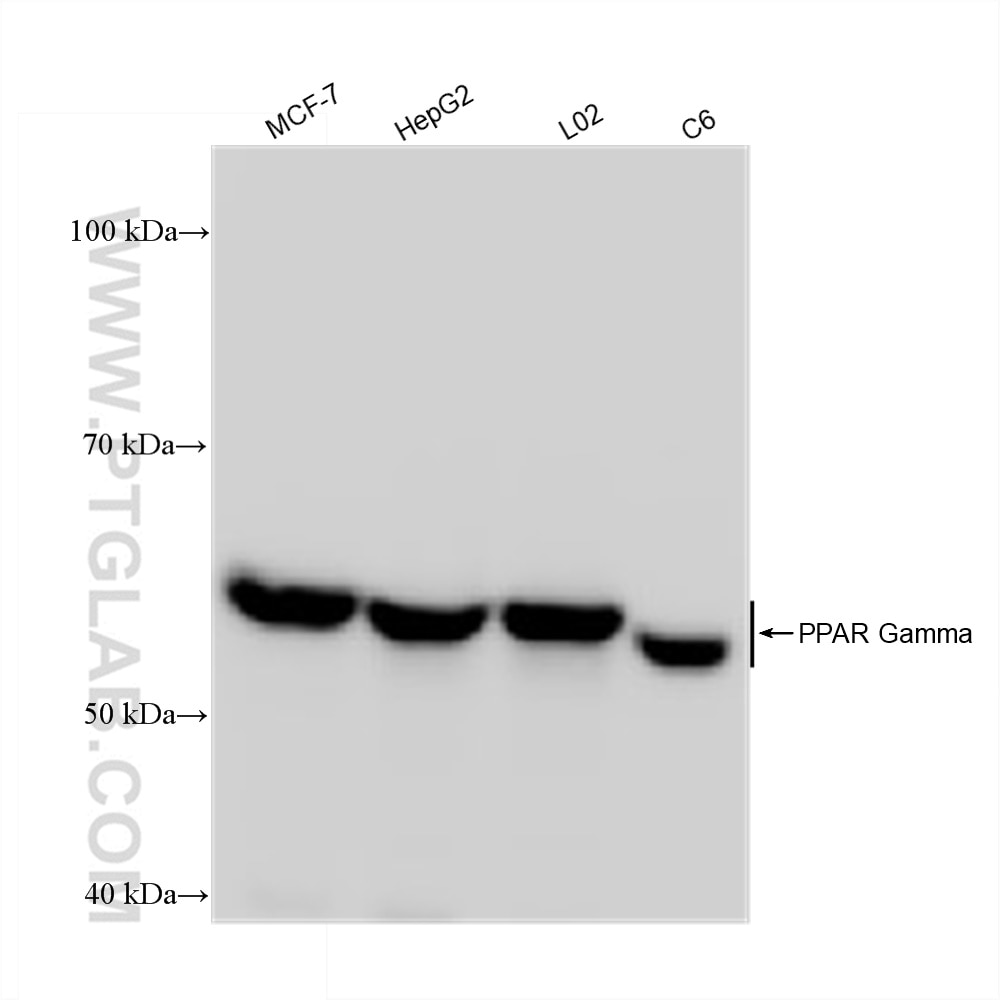
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 58 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 50-60 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC006811 |
| Symbole du gène | PPARG |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 5468 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Protein A purfication |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) are ligand-activated intracellular transcription factors, members of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily (NR), that includes estrogen, thyroid hormone receptors, retinoic acid, Vitamin D3 as well as retinoid X receptors (RXRs). The PPAR subfamily consists of three subtypes encoded by distinct genes denoted PPARα (NR1C1), PPARβ/δ (NR1C2) and PPARγ (NR1C3), which are activated by selective ligands. PPARγ, also named as PPARG, contains one nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain and is a receptor that binds peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. It plays an important role in the regulation of lipid homeostasis, adipogenesis, ins resistance, and development of various organs. Defects in PPARG are the cause of familial partial lipodystrophy type 3 (FPLD3) and may be associated with susceptibility to obesity. Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 ins-resistant diabetes and hypertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. Genetic variations in PPARG are associated with susceptibility to glioma type 1 (GLM1). PPARG has two isoforms with molecular weights of 57 kDa and 54 kDa (PMID: 9831621), but modified PPARG is about 67 KDa (PMID: 16809887). PPARG2 is a splice variant and has an additional 30 amino acids at the N-terminus (PMID: 15689403). Experimental data indicate that a 45 kDa protein displaying three different sequences immunologically related to the nuclear receptor PPARG2 is located in mitochondria (mt-PPAR). However, the molecular weight of this protein is clearly less when compared to that of PPARG2 (57 kDa) (PMID: 10922459). PPARG has been reported to be localized mainly (but not always) in the nucleus. PPARG can also be detected in the cytoplasm and was reported to possess extra-nuclear/non-genomic actions (PMID: 17611413; 19432669; 14681322).