Anticorps Monoclonal anti-Polyglutamine
Polyglutamine Monoclonal Antibody for WB, ELISA, Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2b, kappa
Réactivité testée
n/a
Applications
WB, ELISA, Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
MW1
N° de cat : 65239-1-PBS
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
65239-1-PBS cible Polyglutamine dans les applications de WB, ELISA, Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons n/a
| Réactivité | n/a |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b, kappa |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Protéine recombinante |
| Nom complet | Polyglutamine |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | N/A |
| Symbole du gène | |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
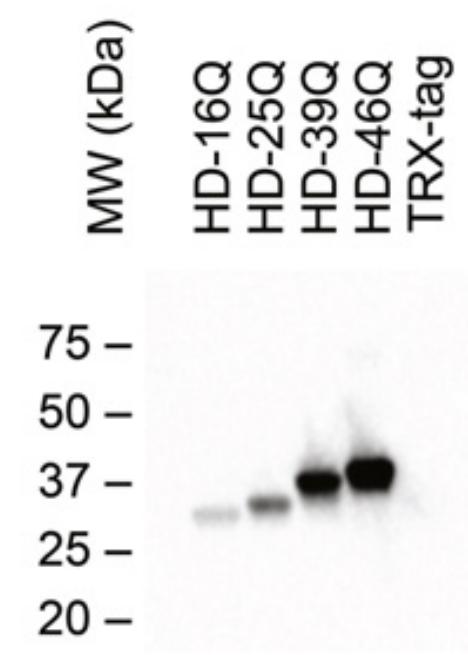
Huntington's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by the expansion of a polyglutamine (polyQ) repeat in the N-terminal portion of huntingtin protein to a length above 35-40 units (PMID: 26047735; 19507258). The mutational expansion of polyglutamine above a critical length causes a toxic gain of function in huntingtin and results in neuronal death. In the course of the disease, expanded huntingtin is proteolyzed, becomes abnormally folded, and accumulates in oligomers, fibrils, and microscopic inclusions (PMID: 25336039). The anti-polyglutamine (polyQ) antibody MW1 specifically binds the polyQ domain of huntingtin exon 1. On western blot, the MW1 clone strongly prefers to bind to the expanded polyQ repeat form of Htt, displaying no detectable binding to normal huntingtin (PMID: 11719267).