- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-TNFSF11/RANKL
TNFSF11/RANKL Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IF/ICC, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IF/ICC, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
3F2E1
N° de cat : 66610-1-PBS
Synonymes
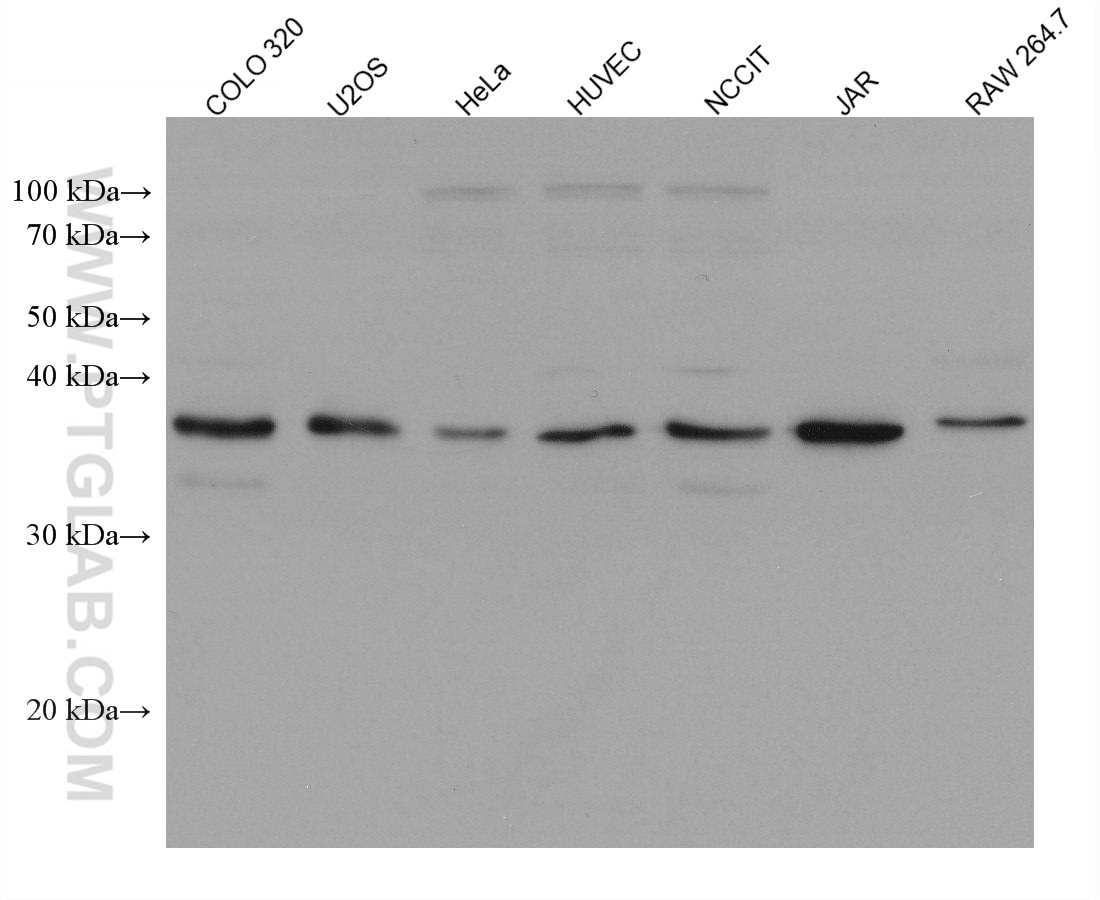
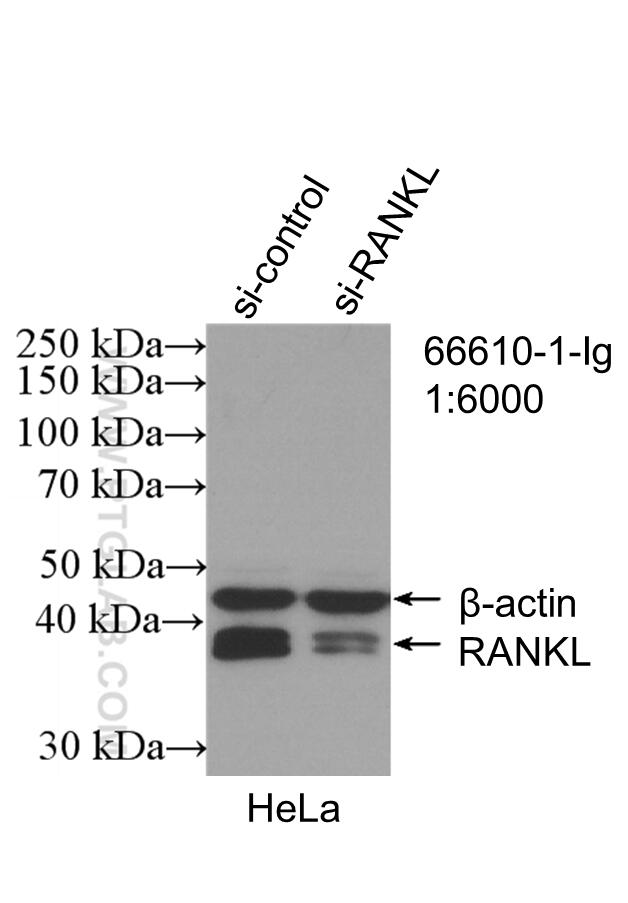
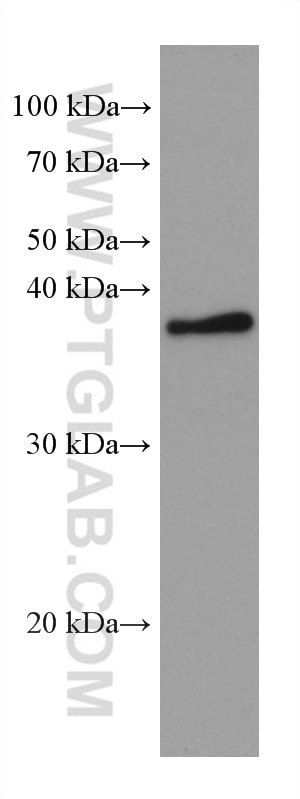
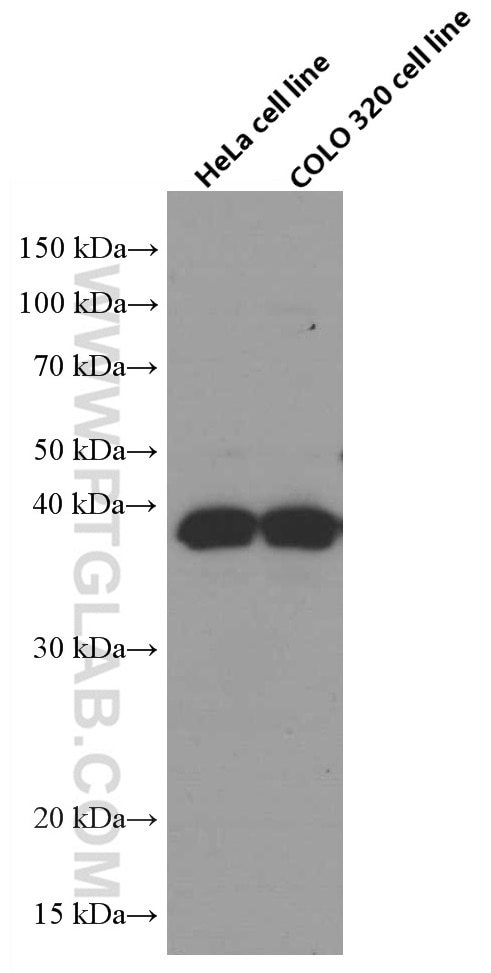
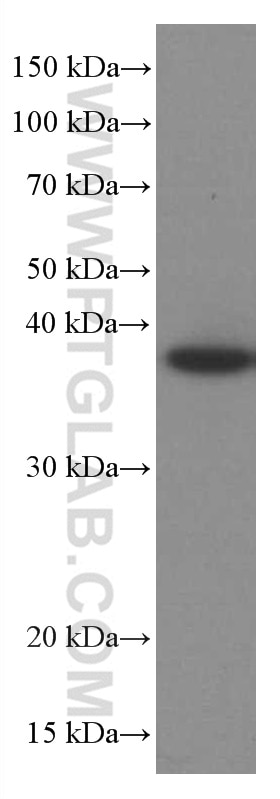
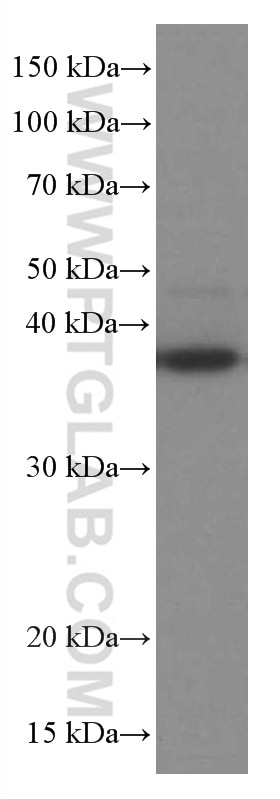
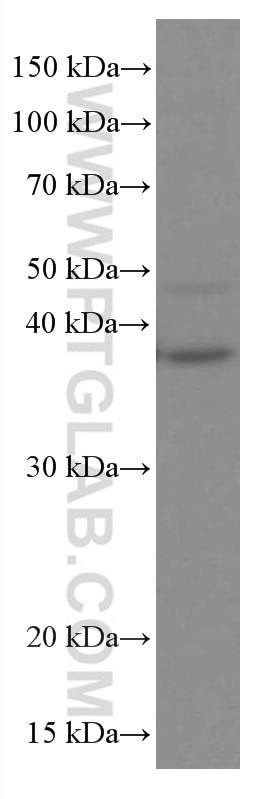
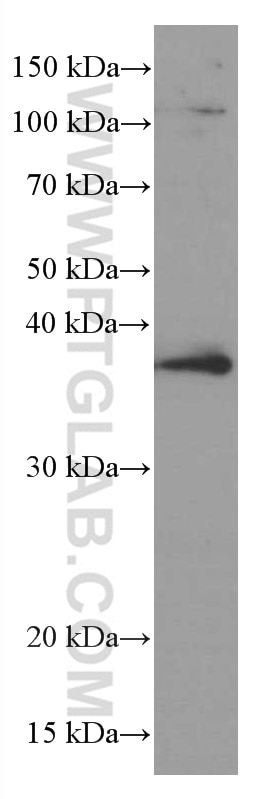
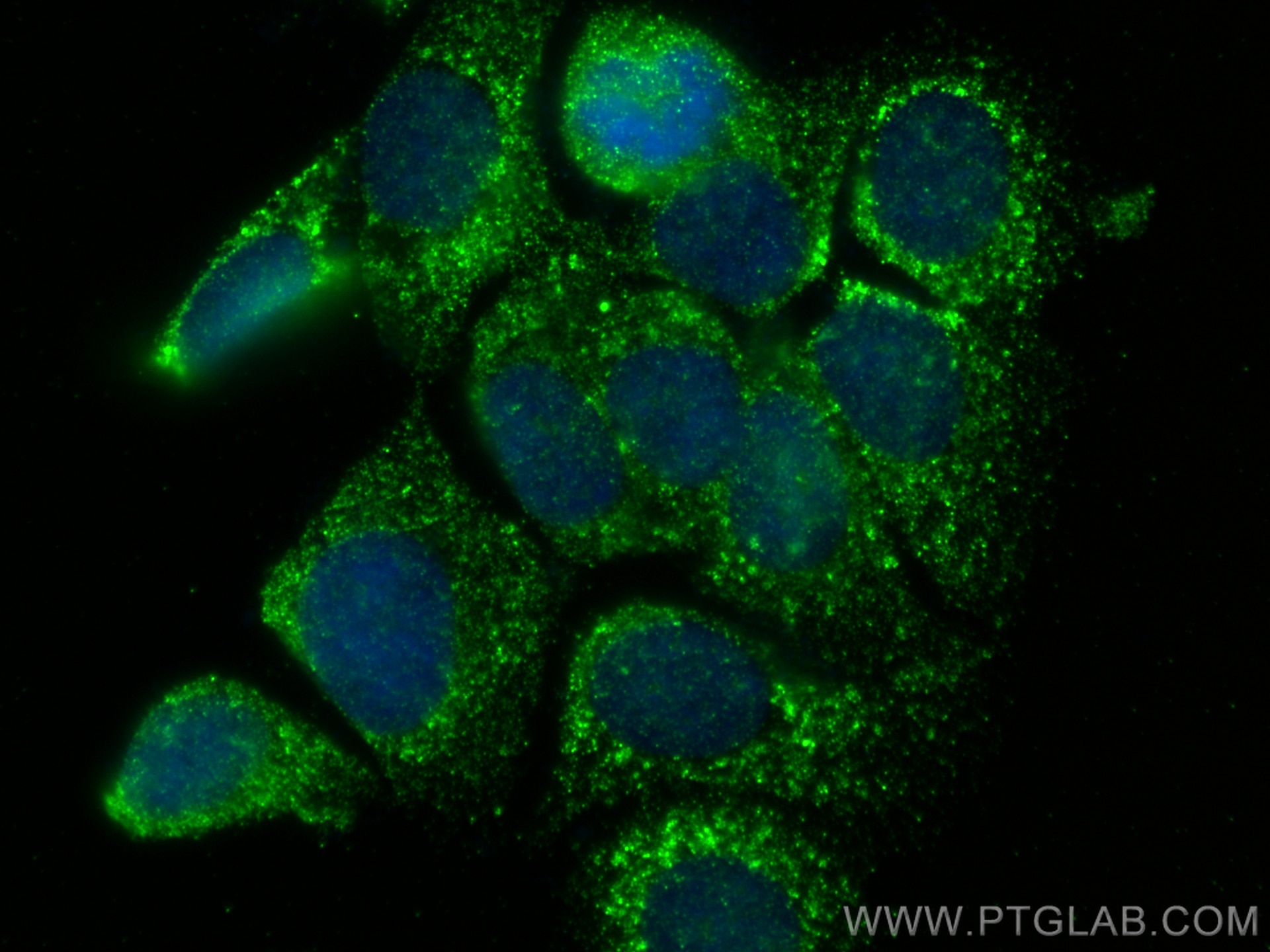
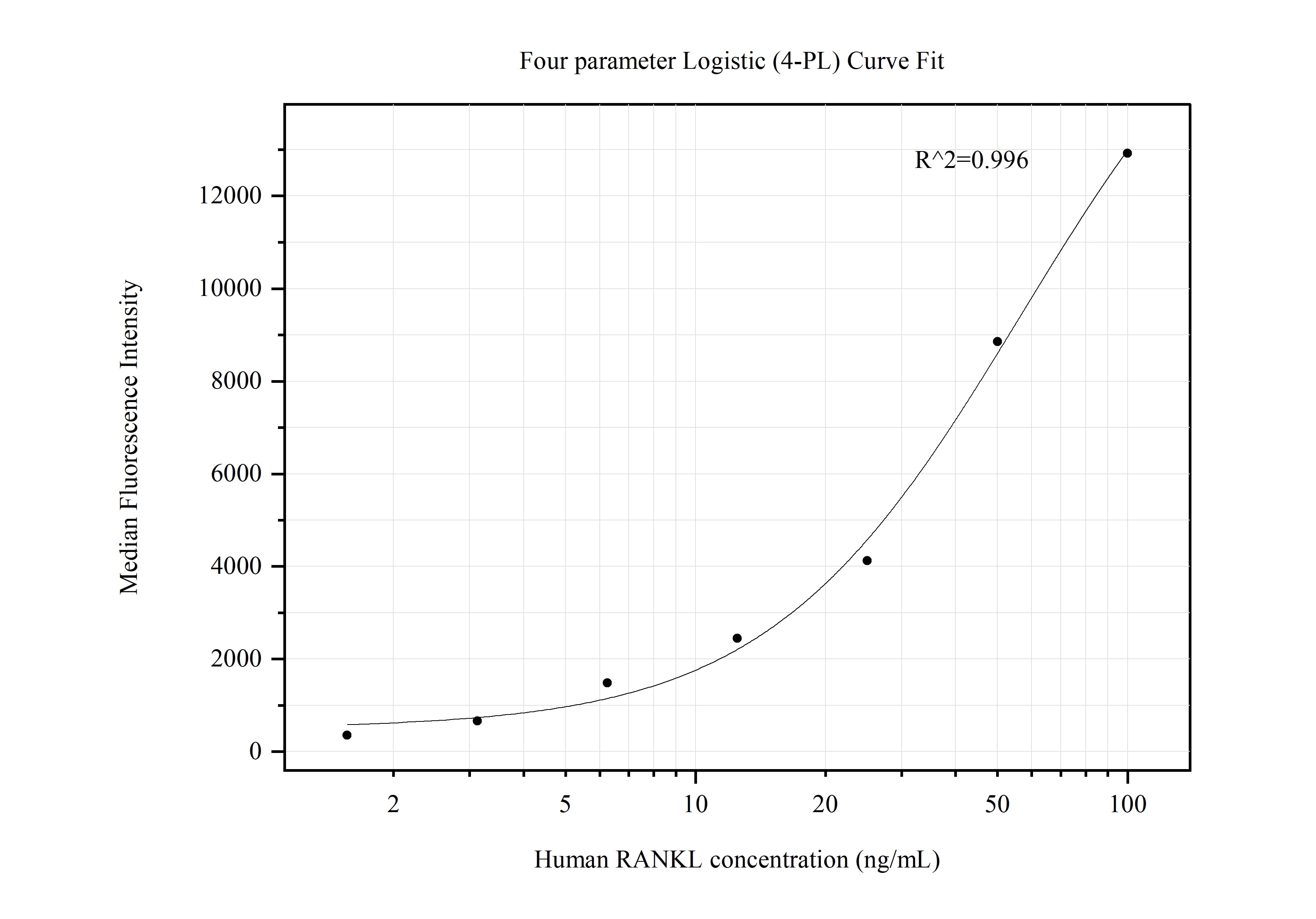
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
66610-1-PBS cible TNFSF11/RANKL dans les applications de WB, IF/ICC, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | TNFSF11/RANKL Protéine recombinante Ag19975 |
| Nom complet | tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 317 aa, 35 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 35-38 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC074890 |
| Symbole du gène | RANKL |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 8600 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine G |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
TNFSF11 also known as RANKL, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) cytokine family which is a ligand for osteoprotegerin and functions as a key factor for osteoclast differentiation and activation. RANKL is a polypeptide of 217 amino acids that exerts its biological activity both in a transmembrane form of about 40-45 kDa and in soluble one of 31 kDa (PMID: 15308315). The membrane-bound RANKL (mRANKL) is cleaved into a sRANKL by the metalloprotease-disintegrin TNF-alpha convertase (TACE) or a related metalloprotease (MP). RANKL induces osteoclast formation through its receptor, RANK, which transduces signals by recruiting adaptor molecules, such as the TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) family of proteins. RANKL was shown to be a dentritic cell survival factor and is involved in the regulation of T cell-dependent immune response. T cell activation was reported to induce expression of this gene and lead to an increase of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss. RANKL was shown to activate antiapoptotic kinase AKT/PKB through a signaling complex involving SRC kinase and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6, which indicated this protein may have a role in the regulation of cell apoptosis.