- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-RENALASE
RENALASE Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IP, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 15003-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
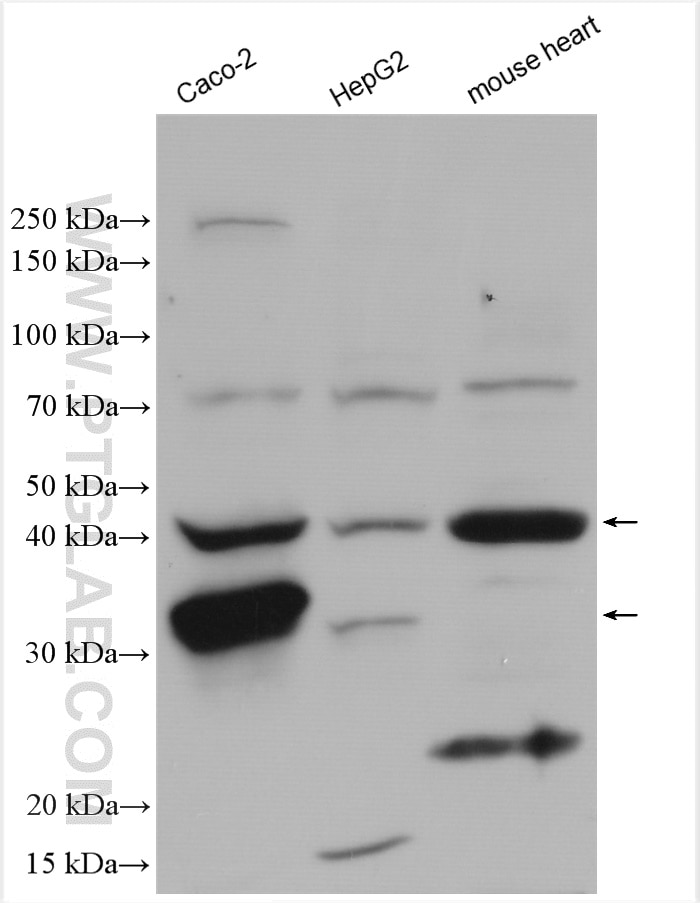
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules Caco-2, |
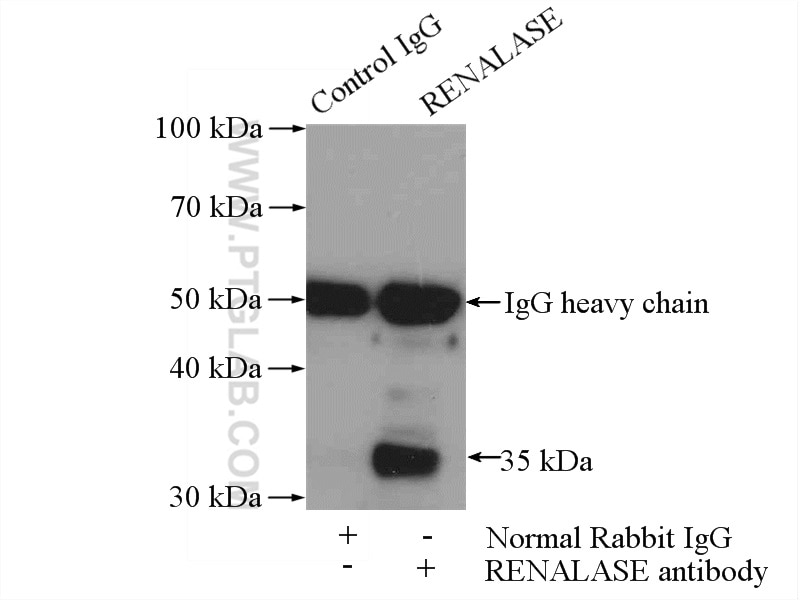
| Résultats positifs en IP | cellules HEK-293 |
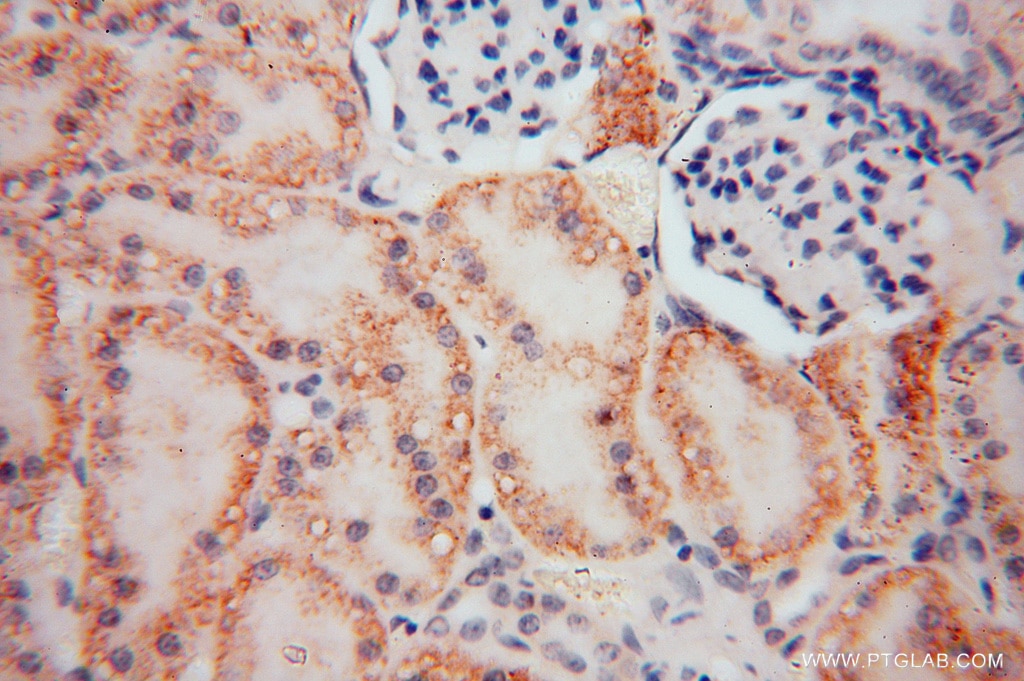
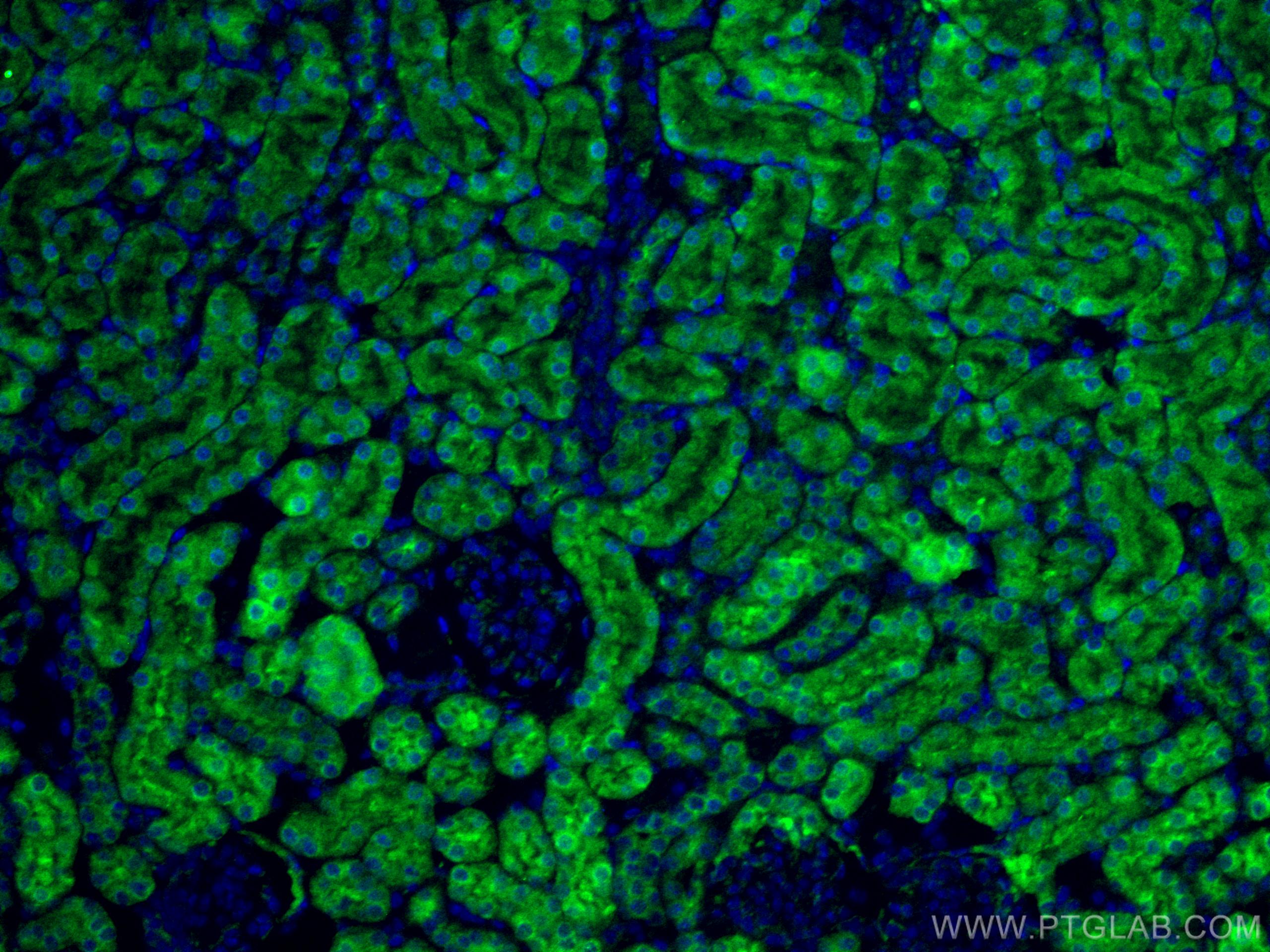
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu rénal humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
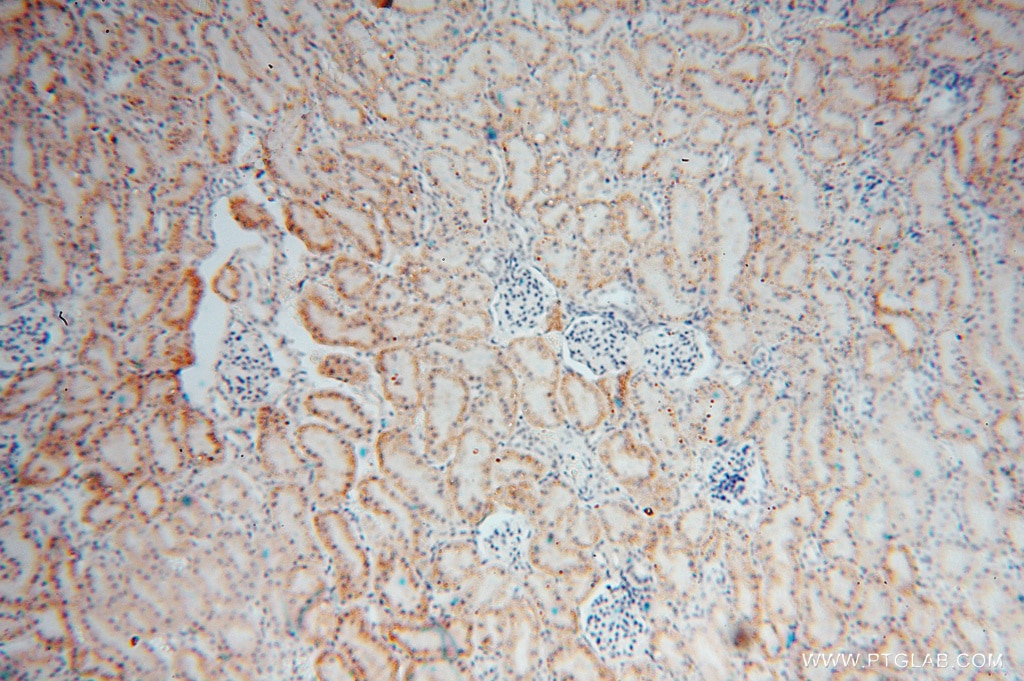
| Résultats positifs en IF-P | tissu rénal de souris, |
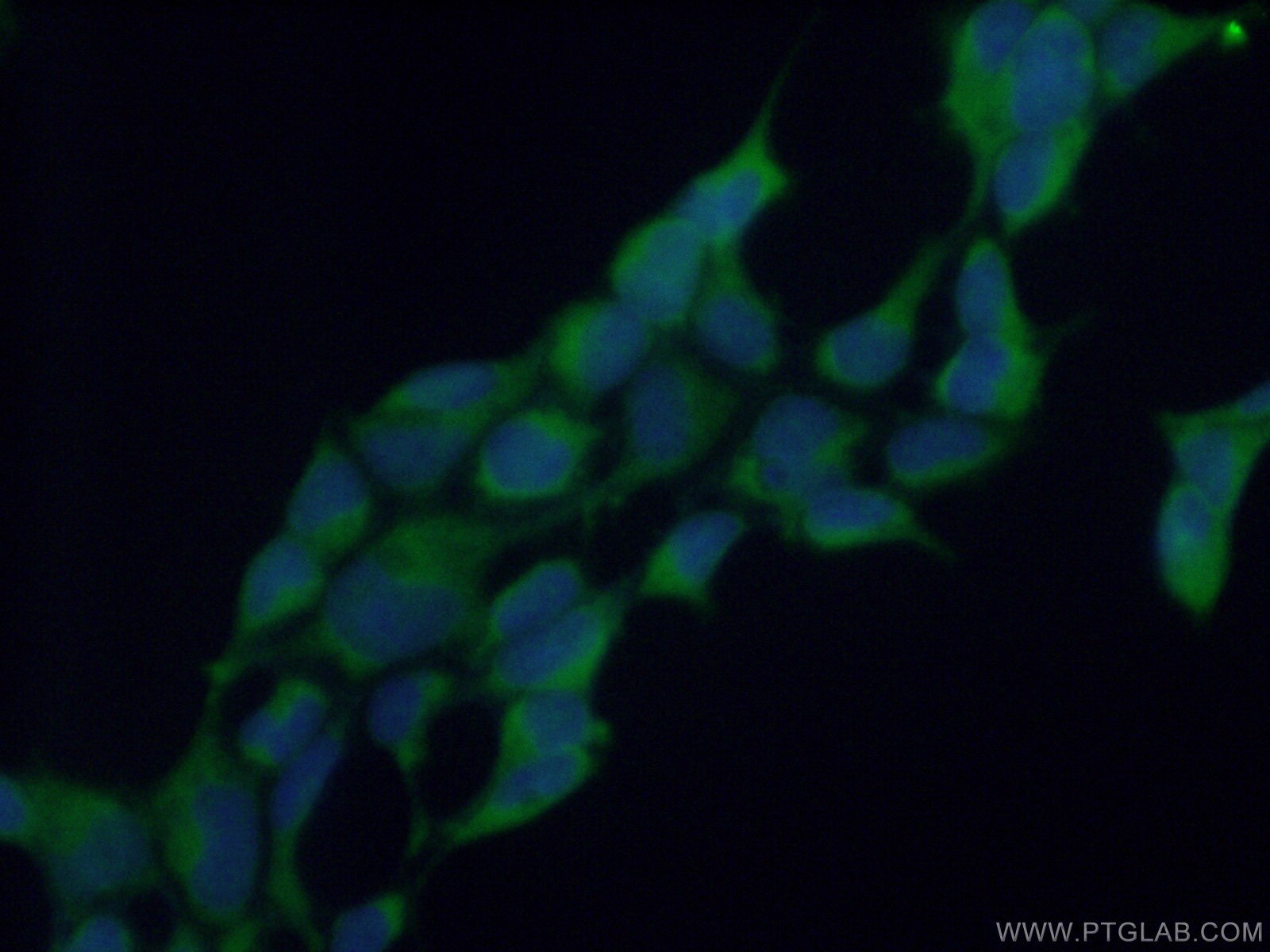
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules HEK-293, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 7 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 3 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
15003-1-AP cible RENALASE dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | RENALASE Protéine recombinante Ag13061 |
| Nom complet | chromosome 10 open reading frame 59 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 38 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 35 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC005364 |
| Symbole du gène | RENALASE |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 55328 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
RNLS, also named as Renalase, C10orf59 and MAO-C, belongs to the renalase family. It is probable FAD-dependent amine oxidase secreted by the kidney, which circulates in blood and modulates cardiac function and systemic blood pressure. RNLS degrades catecholamines such as dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine in vitro. It lowers blood pressure in vivo by decreasing cardiac contractility and heart rate and preventing a compensatory increase in peripheral vascular tone, suggesting a causal link to the increased plasma catecholamine and heightened cardiovascular risk. High concentrations of catecholamines activate plasma renalase and promotes its secretion and synthesis. RNLS has physiologically relevant catecholamine-oxidizing activity. (PMID:15841207 ) This antibody is specific to RNLS.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for RENALASE antibody 15003-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for RENALASE antibody 15003-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for RENALASE antibody 15003-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for RENALASE antibody 15003-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Clin Invest Renalase is a novel, soluble monoamine oxidase that regulates cardiac function and blood pressure. | ||
Front Cardiovasc Med Aerobic Exercise Training Improves Renal Injury in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats by Increasing Renalase Expression in Medulla. | ||
Life Sci Renalase is localized to the small intestine crypt and expressed upon the activation of NF-κB p65 in mice model of fasting-induced oxidative stress. | ||
Exp Biol Med (Maywood) Plasma and urine renalase levels and activity during the recovery of renal function in kidney transplant recipients. |