Anticorps Recombinant de lapin anti-SCAMP5
SCAMP5 Recombinant Antibody for WB, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
243122F5
N° de cat : 85669-2-PBS
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
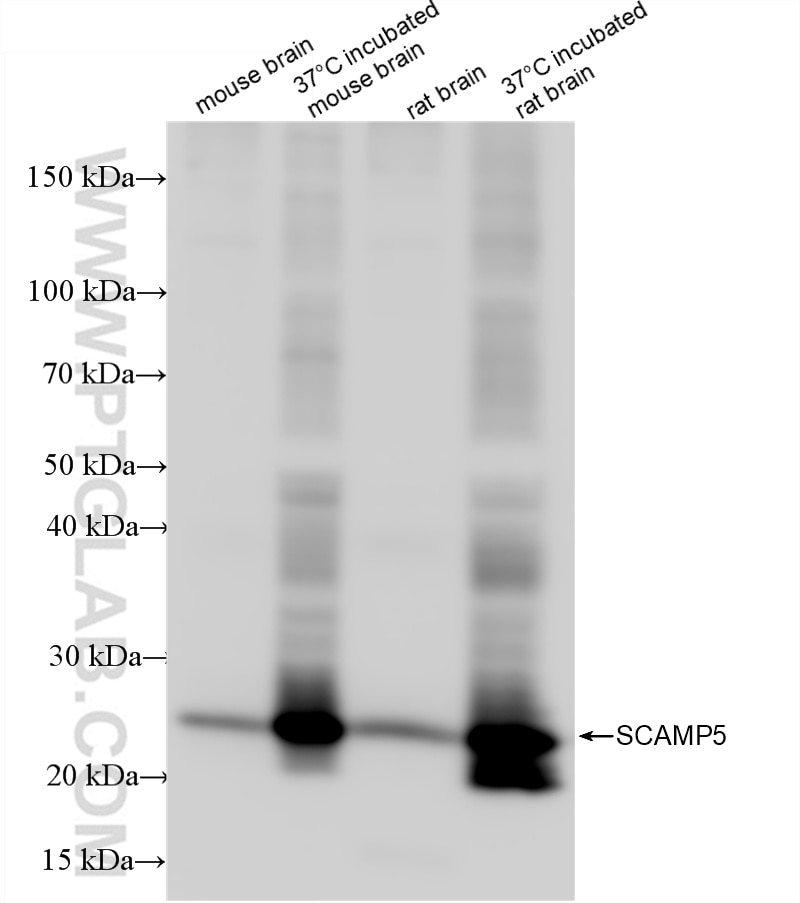
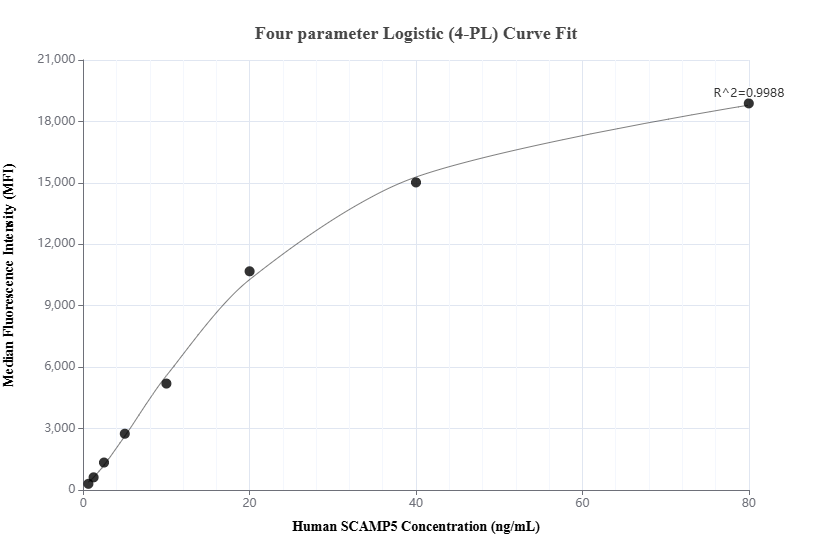
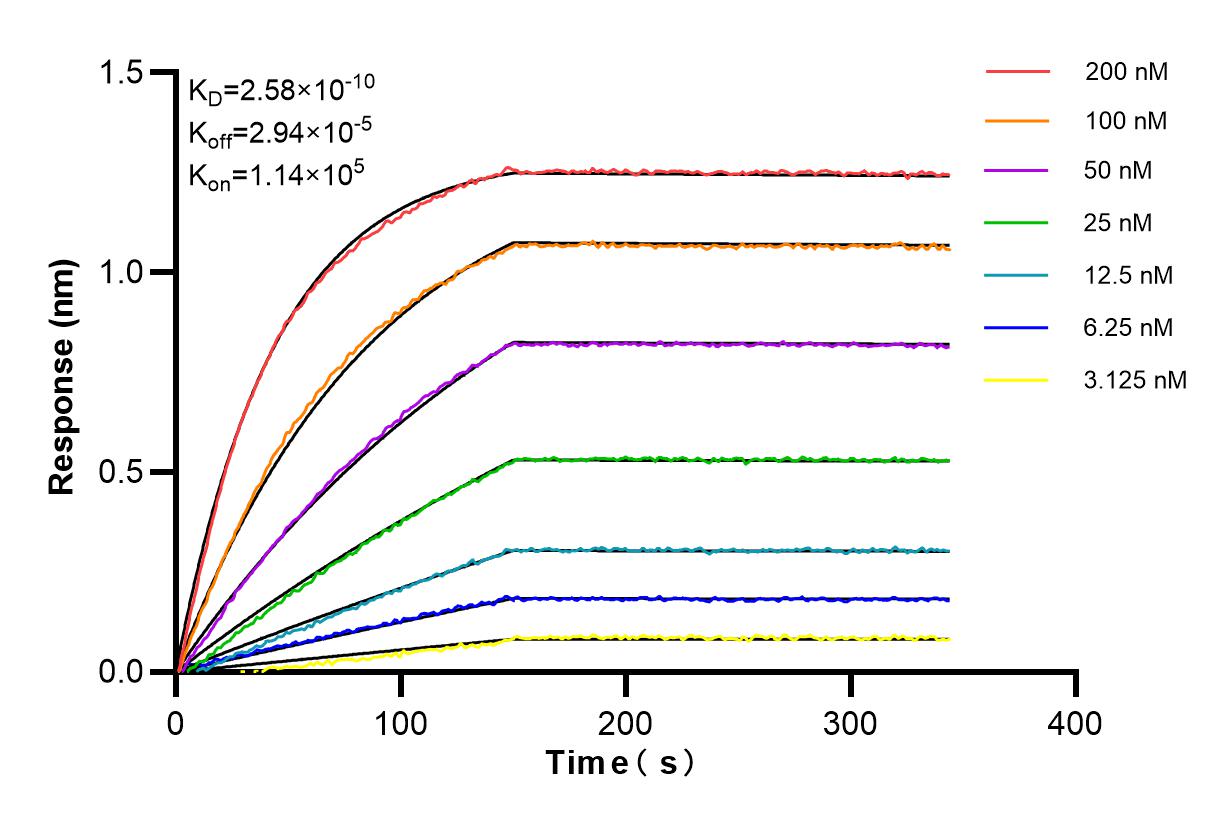
85669-2-PBS cible SCAMP5 dans les applications de WB, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Recombinant |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | SCAMP5 Protéine recombinante Ag31837 |
| Nom complet | secretory carrier membrane protein 5 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 26 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 26 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC024700 |
| Symbole du gène | SCAMP5 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 192683 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Secretory carrier-associated membrane protein 5 (SCAMP5) belongs to the to the SCAMP family. Secretory carrier membrane proteins (SCAMPs) constitute a group of membrane transport proteins in plants, insects and mammals. The mammalian genome contains five types of SCAMP genes, namely, SCAMP1-SCAMP5. (PMID:36217917, PMID:19234194). SCAMPs participate in the vesicle cycling fusion of vesicles and cell membranes and play roles in regulating exocytosis and endocytosis, activating synaptic function and transmitting nerve signals. Among these proteins, SCAMP5 is highly expressed in the brain and has direct or indirect effects on the function of the central nervous system (PMID:36217917). SCAMP5 regulates membrane transport, controls the exocytosis of synaptic vesicles and is related to secretion carrier and membrane function. In addition, SCAMP5 plays a major role in the normal maintenance of the physiological functions of nerve cells (PMID:36217917, PMID:33663553). For optimal WB detection of this membrane protein, we recommend to avoid boiling the sample after lysis.