- Phare
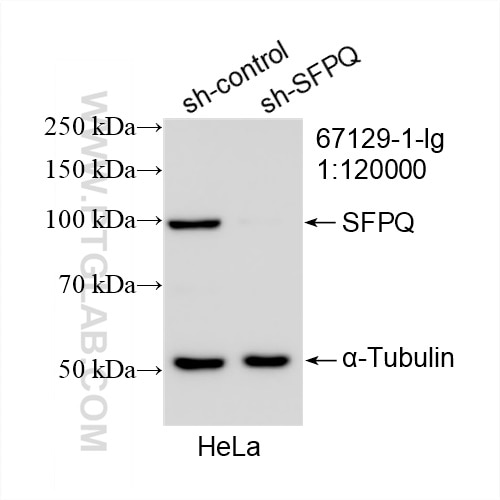
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-SFPQ
SFPQ Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
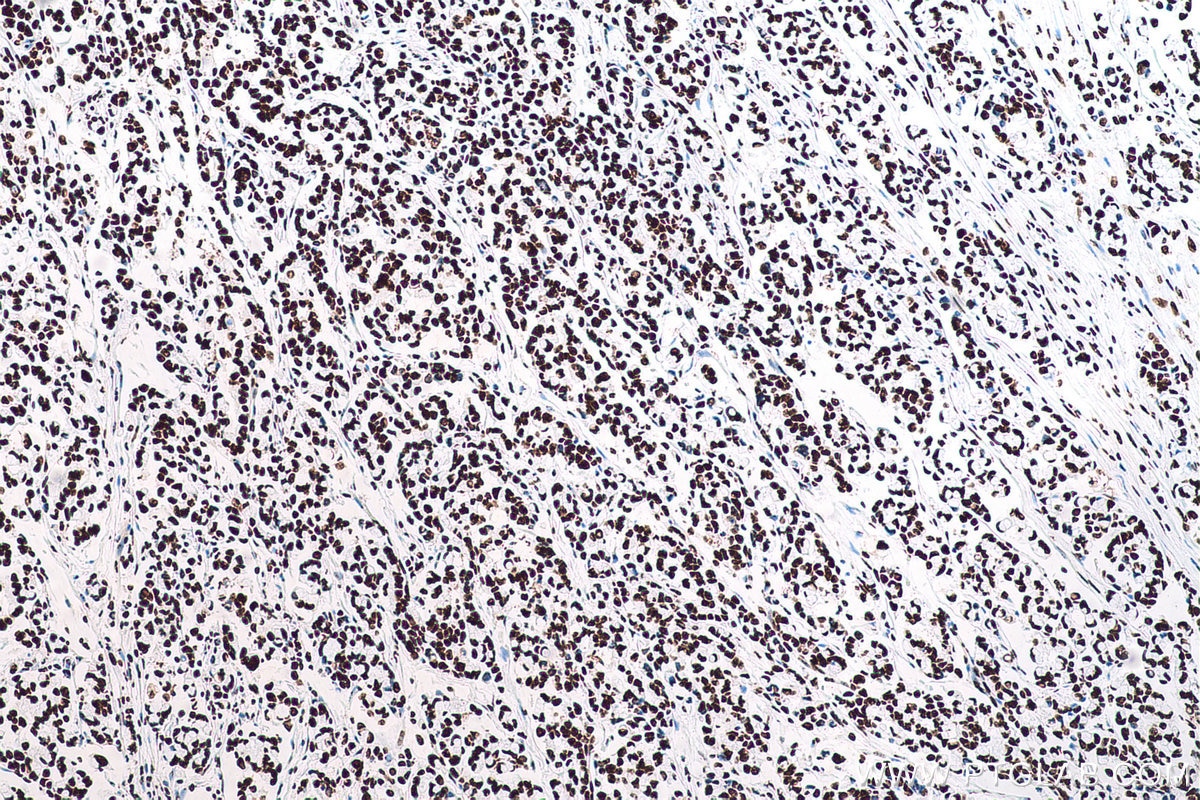
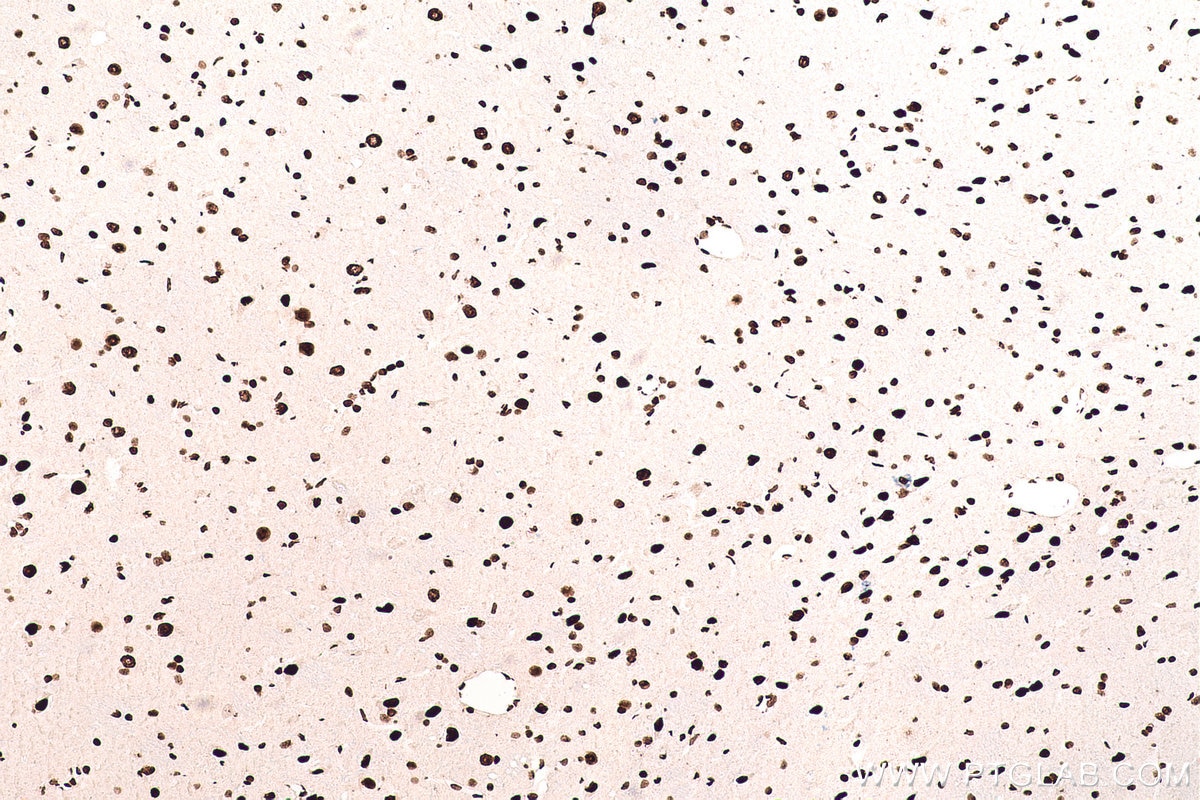
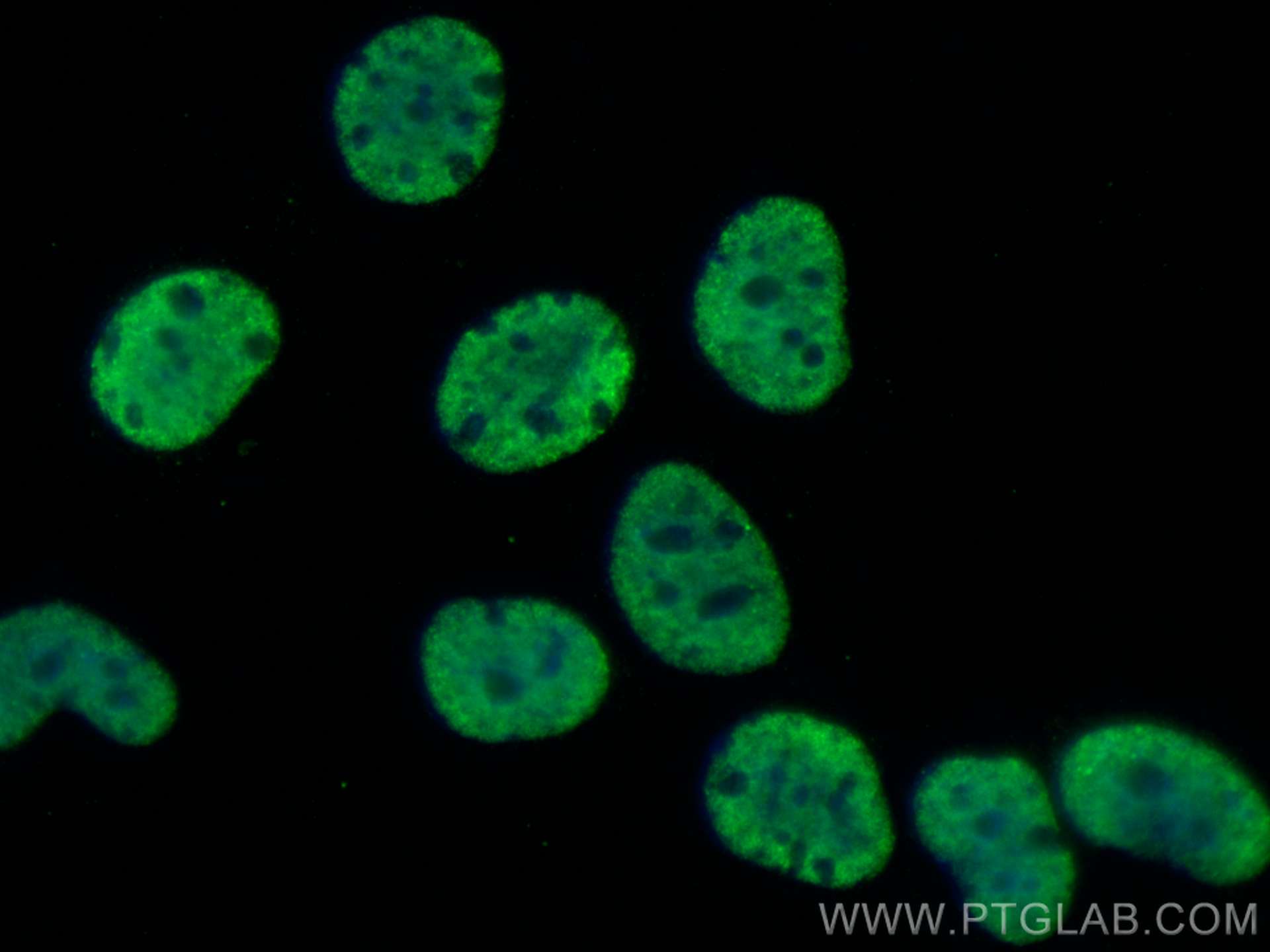
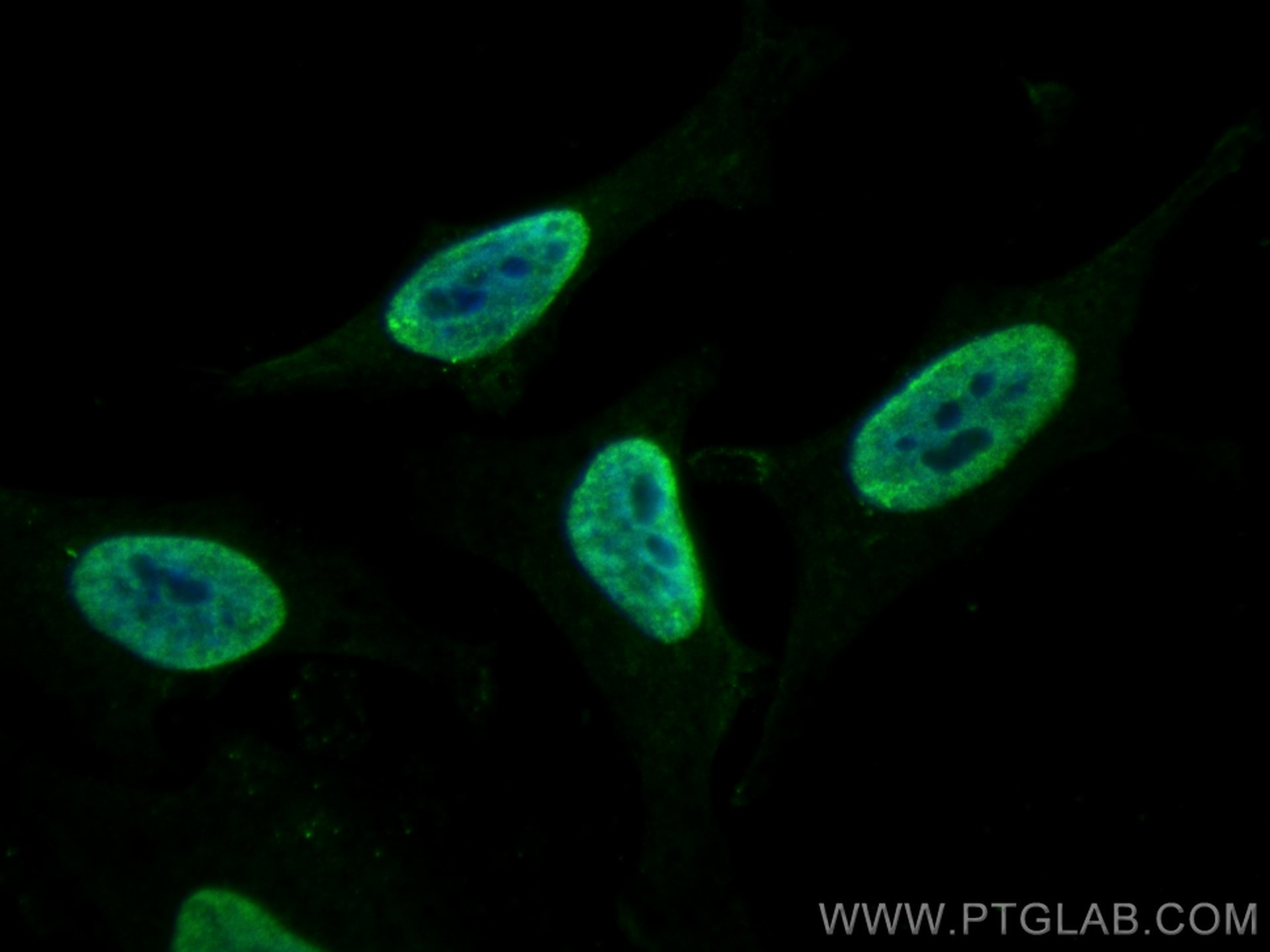
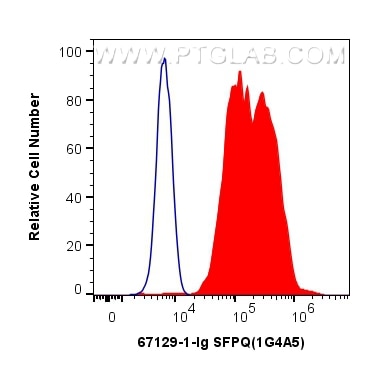
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
1G4A5
N° de cat : 67129-1-PBS
Synonymes
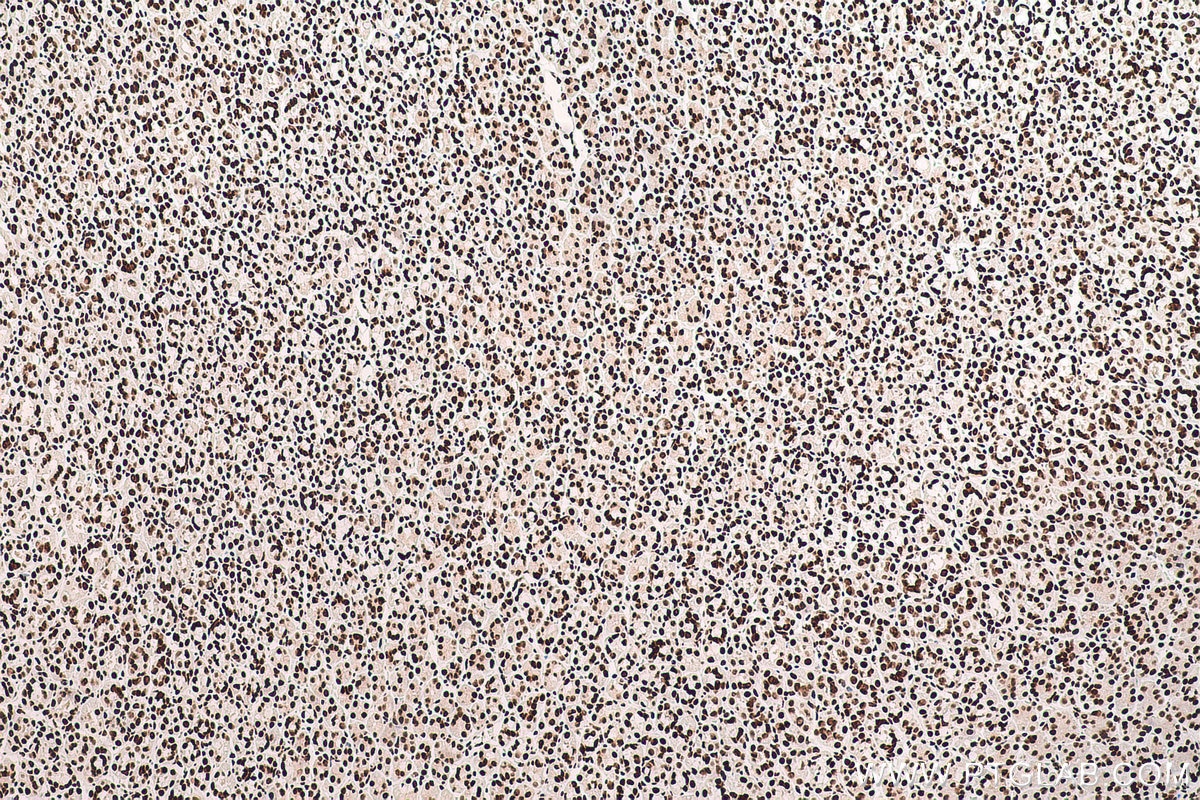
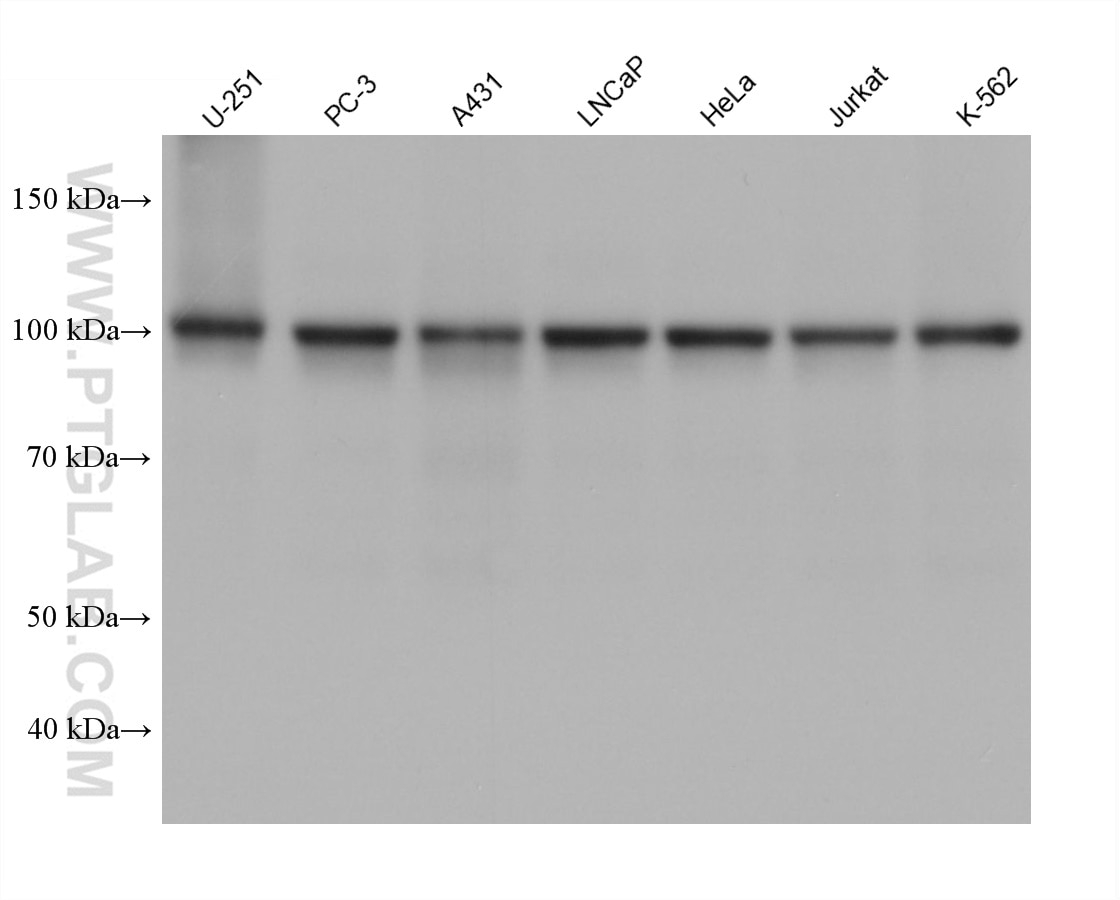
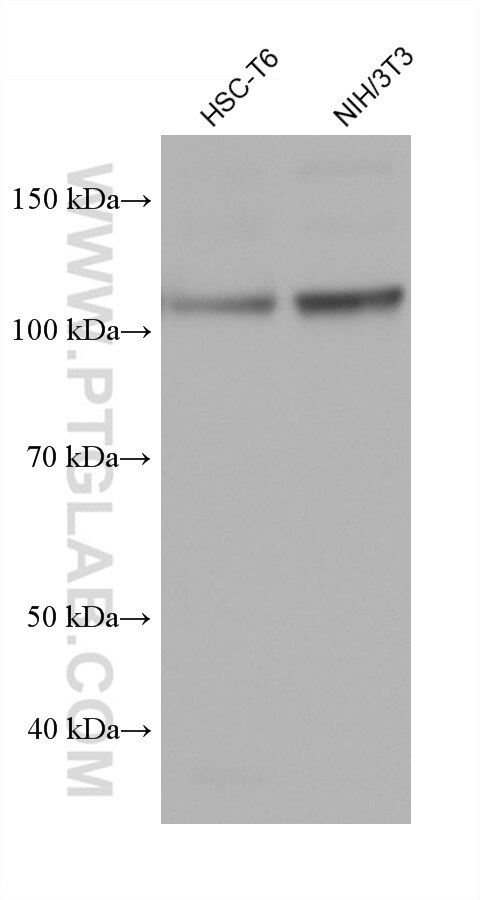
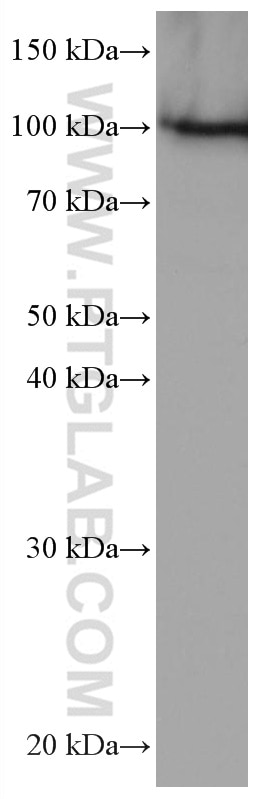
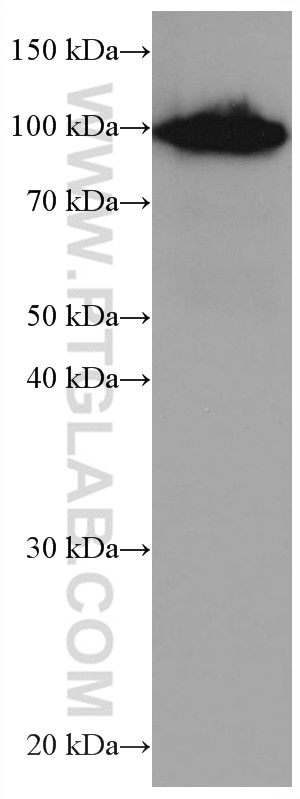
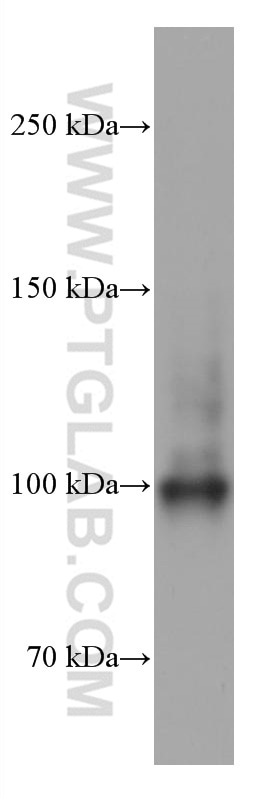
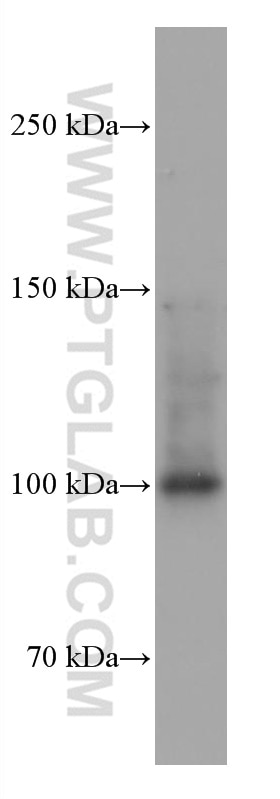
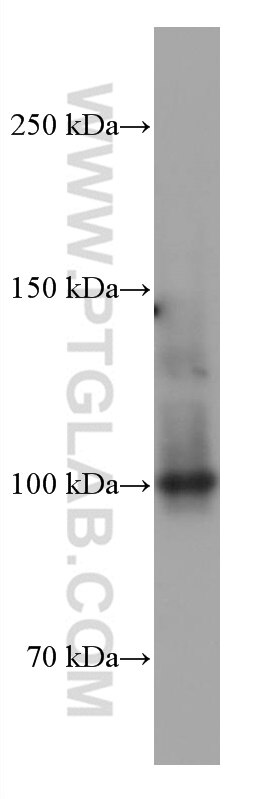
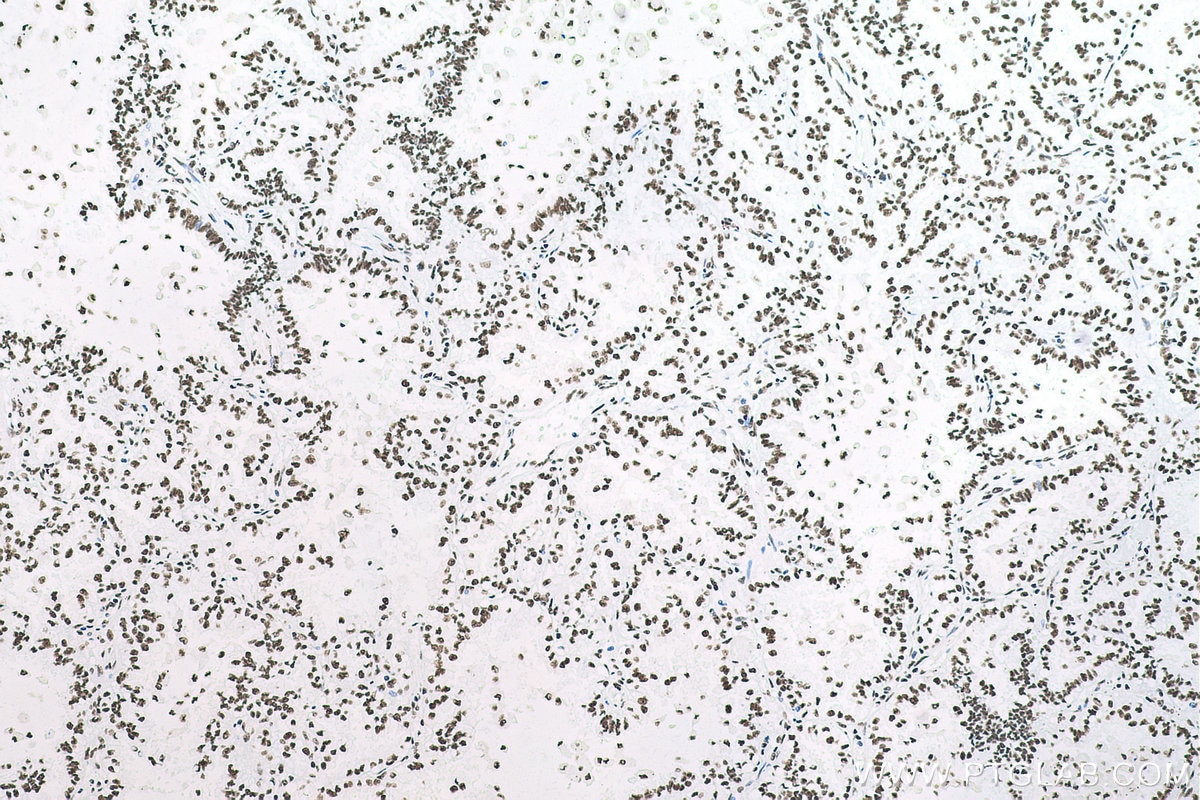
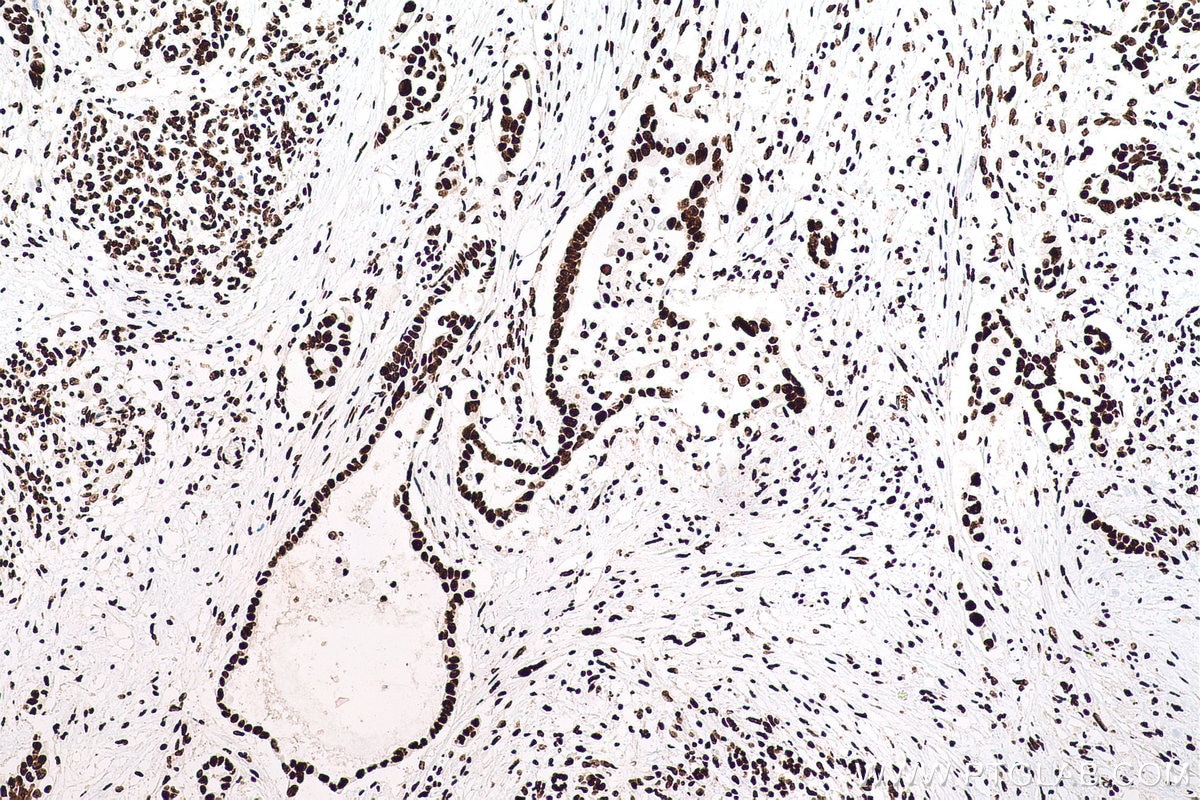
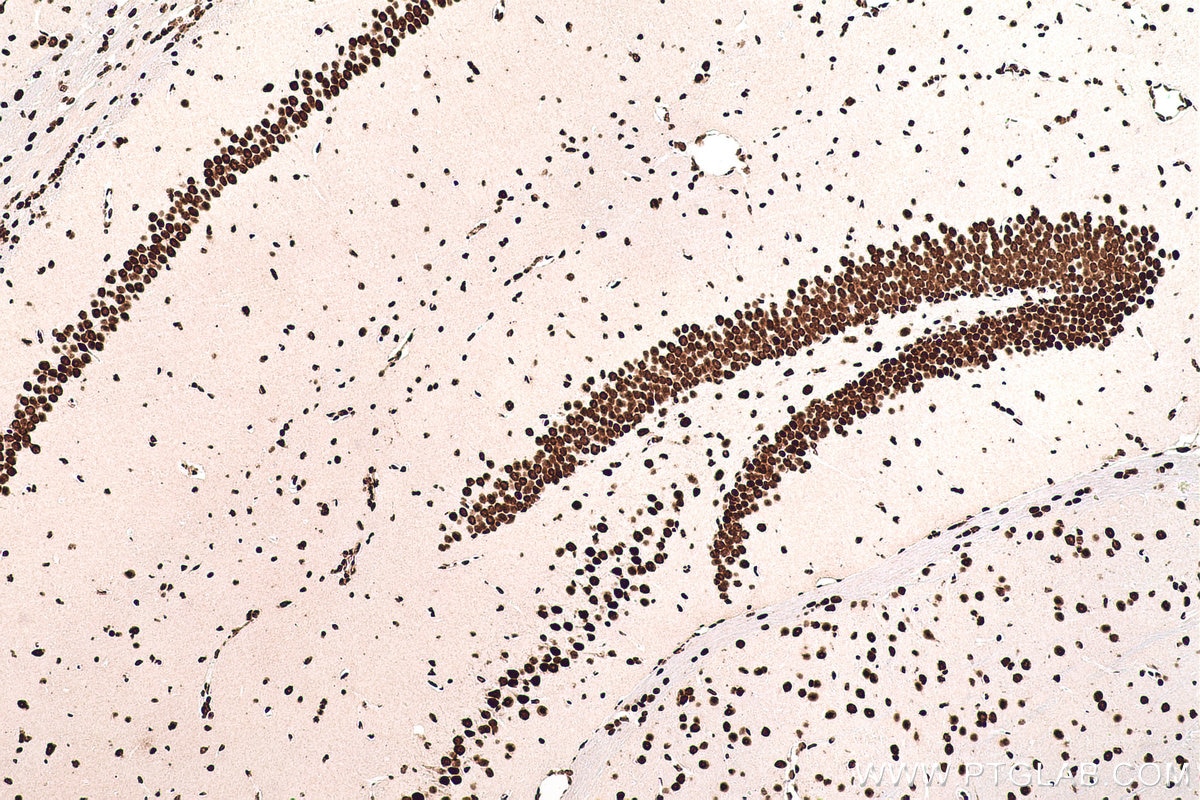
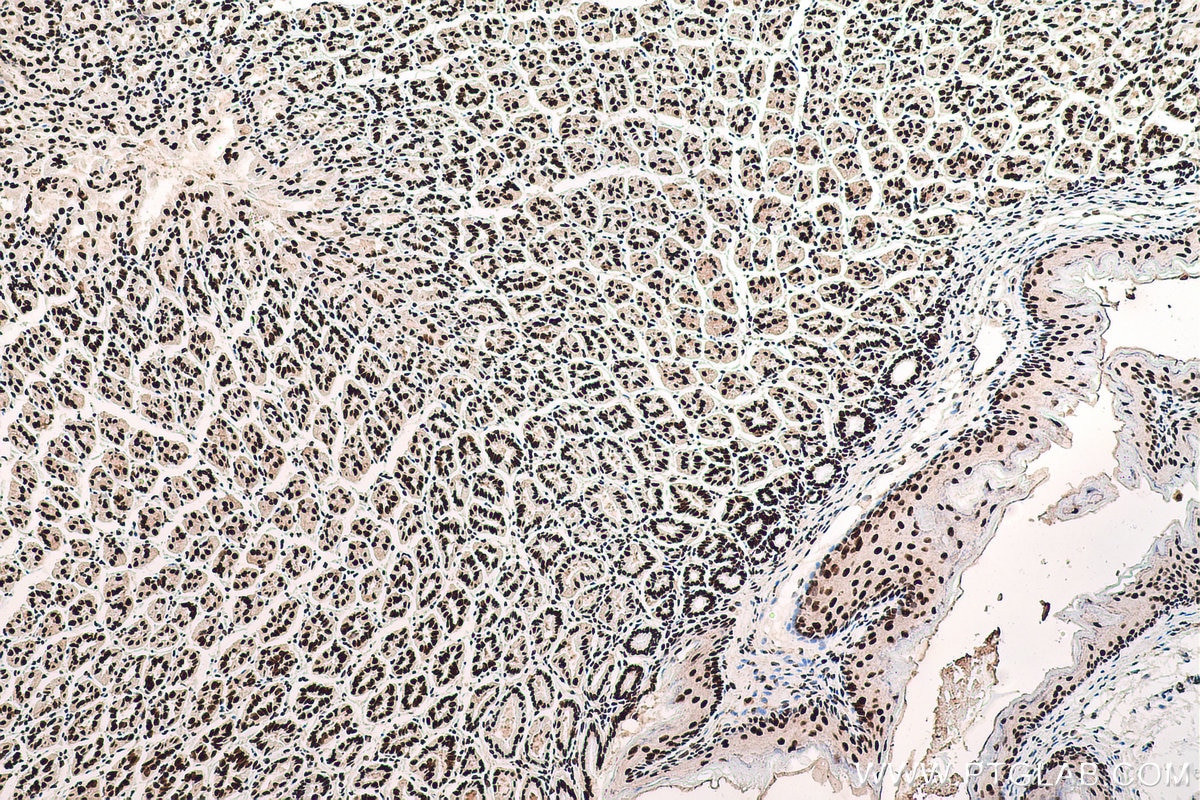
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
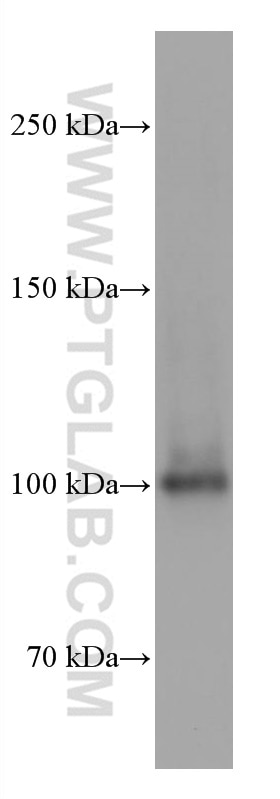
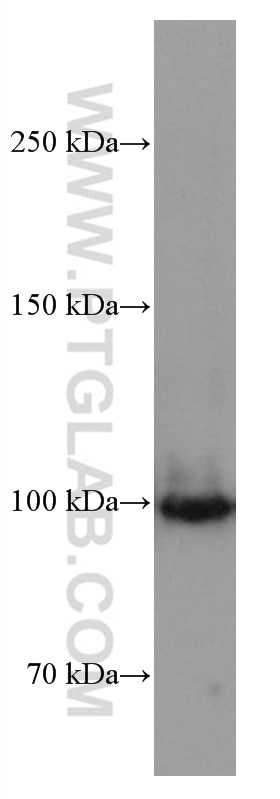
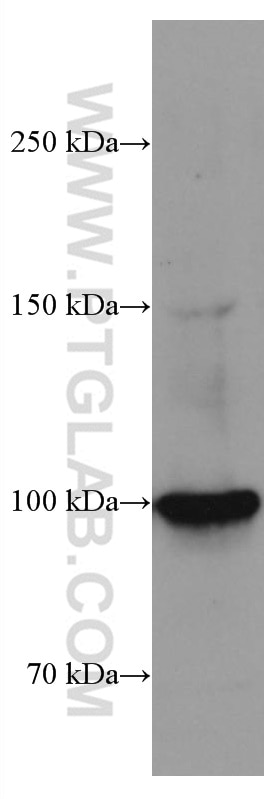
67129-1-PBS cible SFPQ dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | SFPQ Protéine recombinante Ag7181 |
| Nom complet | splicing factor proline/glutamine-rich (polypyrimidine tract binding protein associated) |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 76 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 90-100 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC051192 |
| Symbole du gène | SFPQ |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 6421 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
SFPQ, also named PSF, encodes a nuclear factor implicated in the splicing and regulation of gene expression. SFPQ probably forms a heteromer with NONO and participates in DNA pairing and DNA break repair program. Very recently SFPQ was identified as a downstream target of tau, complete nuclear depletion and cytoplasmic accumulation of SFPQ were shown in the neurons and astrocytes of brains with Alzheimer's disease (AD), more strikingly, reduced SFPQ levels may progress together with tau pathology, these observation strongly suggests the important role of SFPQ pathology in neurodegenerative diseases including AD. SFPQ encompasses 707 amino acids and has a molecular weight of 76 kDa, although it typically migrates on a sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) gel at an apparent molecular weight of ∼100 kDa. Proteolytic cleavage products of apparent molecular weights of 47 and 68 kDa, and an alternatively spliced form of 669 amino acids, have also been described in various cell types. (PMID: 25832716). Splicing Factor Proline and Glutamine rich (SFPQ) as the most significant intron-retaining transcript across diverse ALS-causing mutations (VCP, SOD1 and FUS). SFPQ protein binds extensively to its retained intron, which exhibits high cytoplasmic abundance in VCP mutation compared with controls. Crucially, the protein is less abundant in the nuclei of VCP mutation cultures and is ultimately lost from nuclei of MNs in mouse models (SOD1mu and VCP mutation transgenic mouse models) and human sporadic ALS post-mortem samples. In summary, our study implicates SFPQ IR and nuclear loss as general molecular hallmarks of familial and sporadic ALS.