- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-SUMO2/3
SUMO2/3 Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2b
Réactivité testée
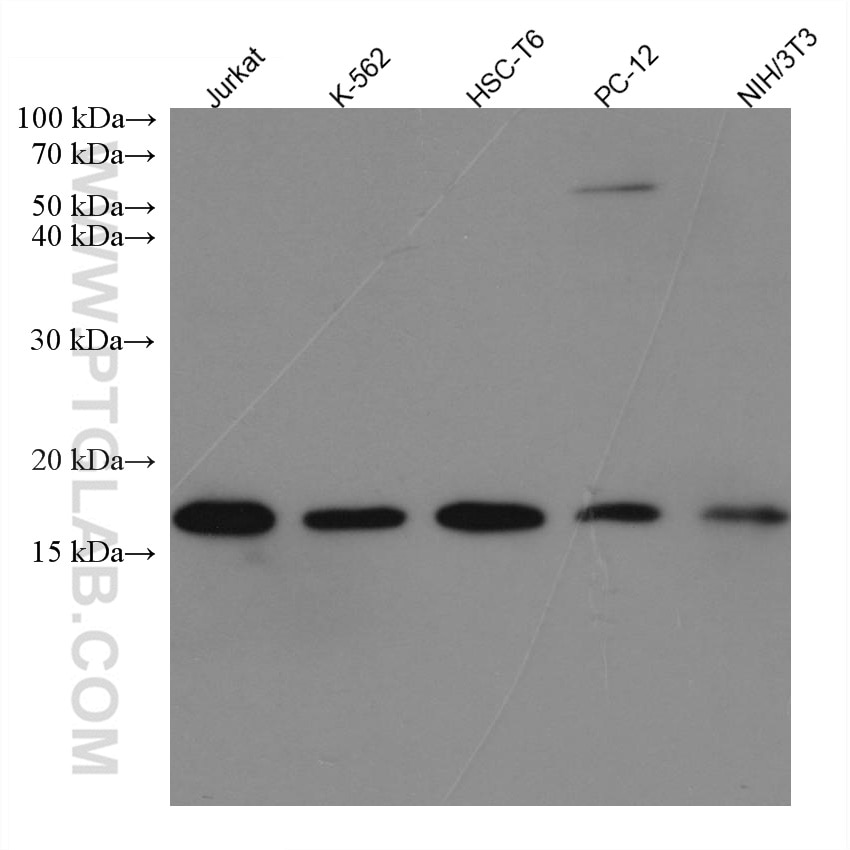
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
1A1B3
N° de cat : 67154-1-PBS
Synonymes
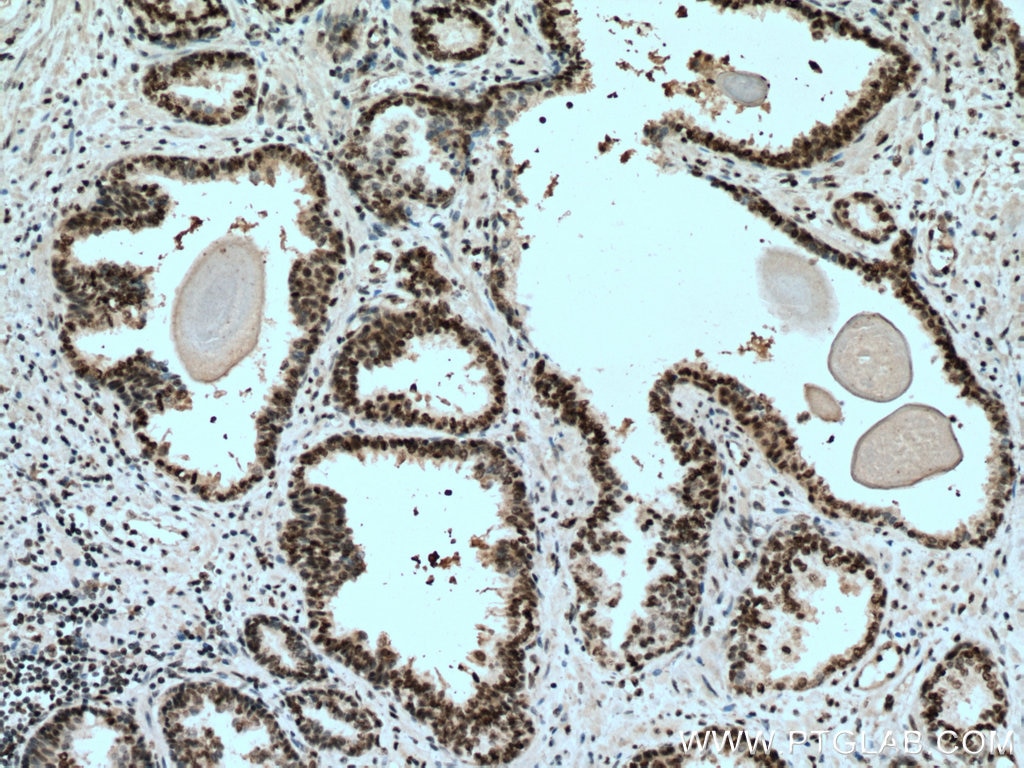
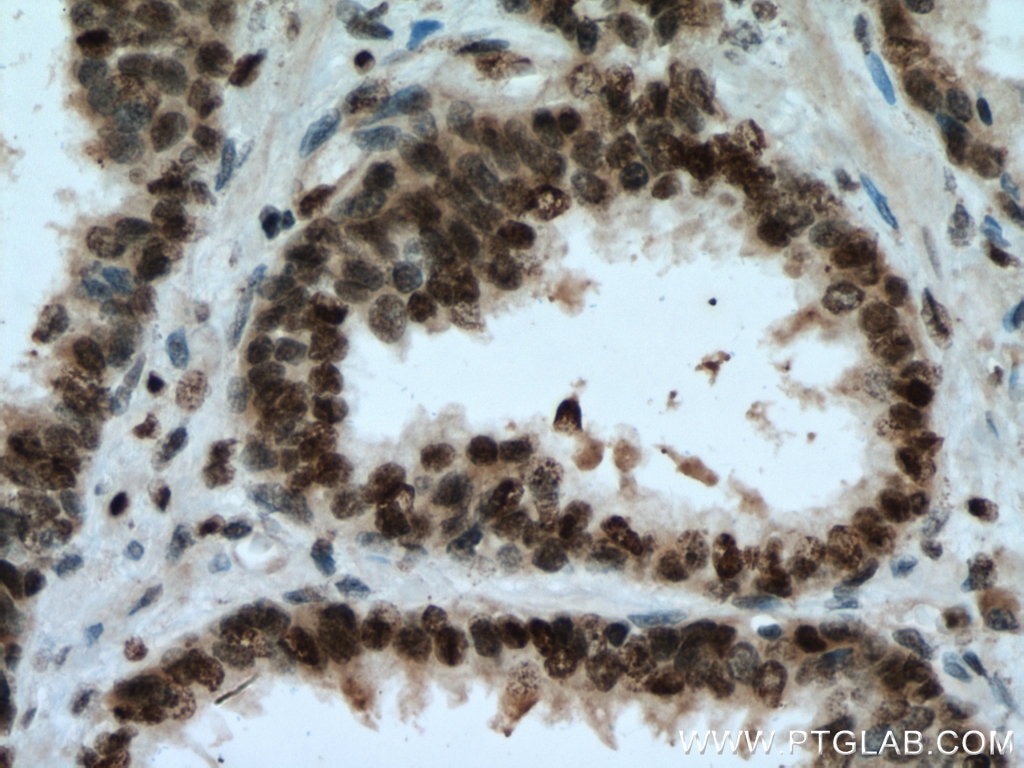
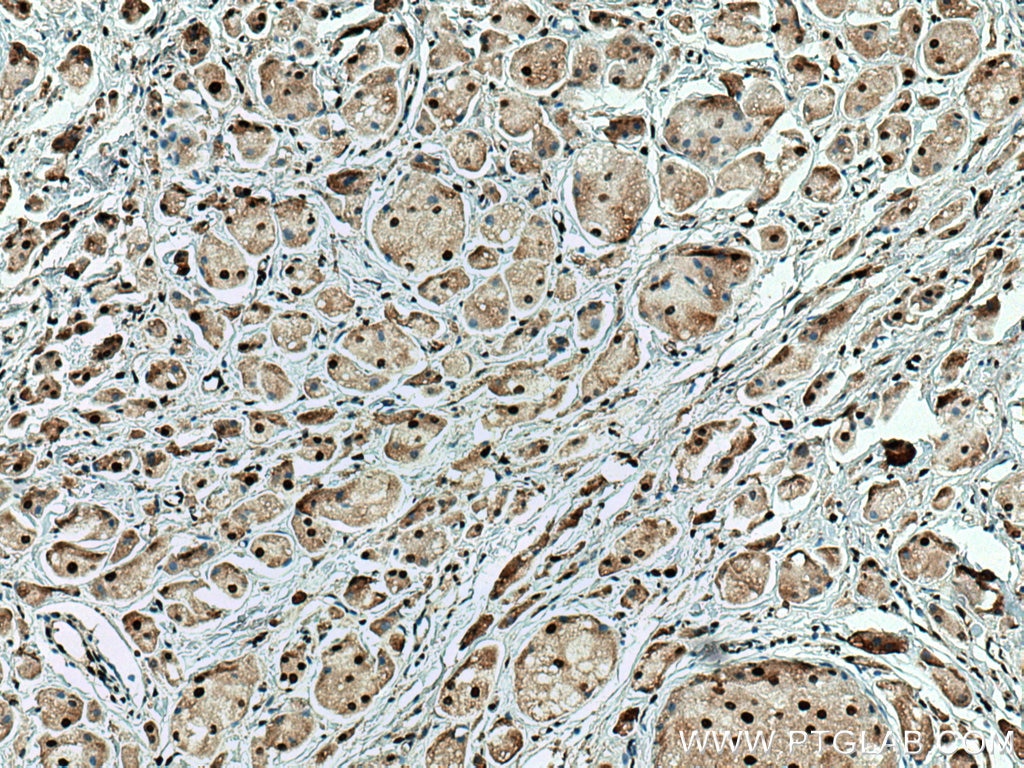
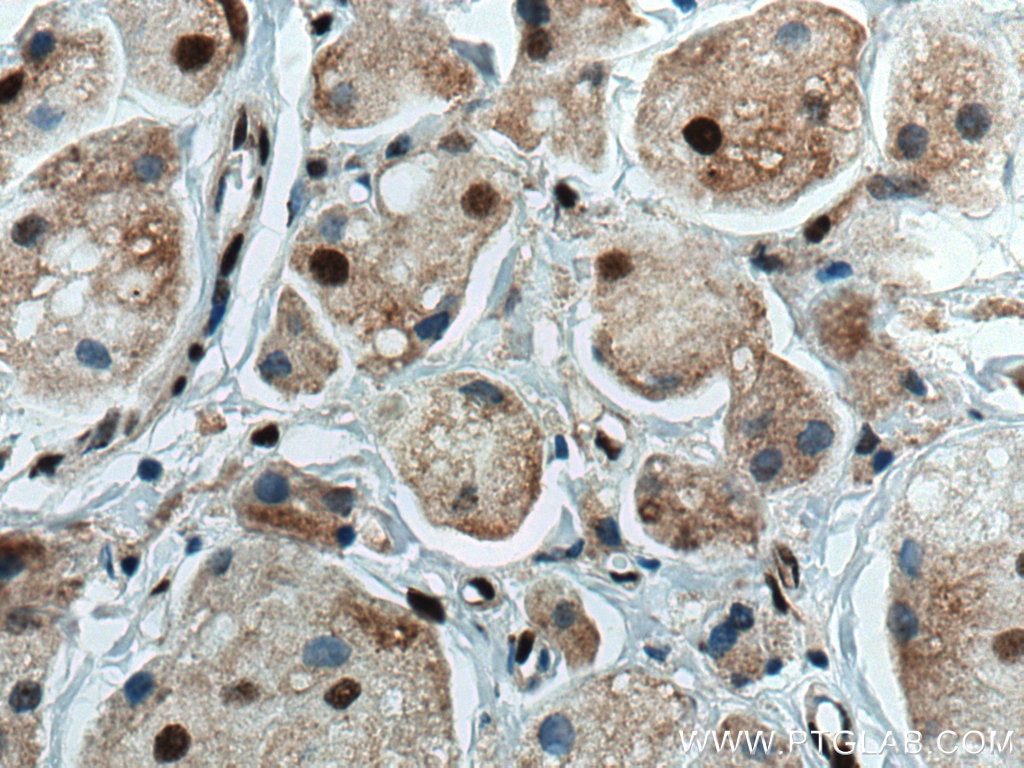
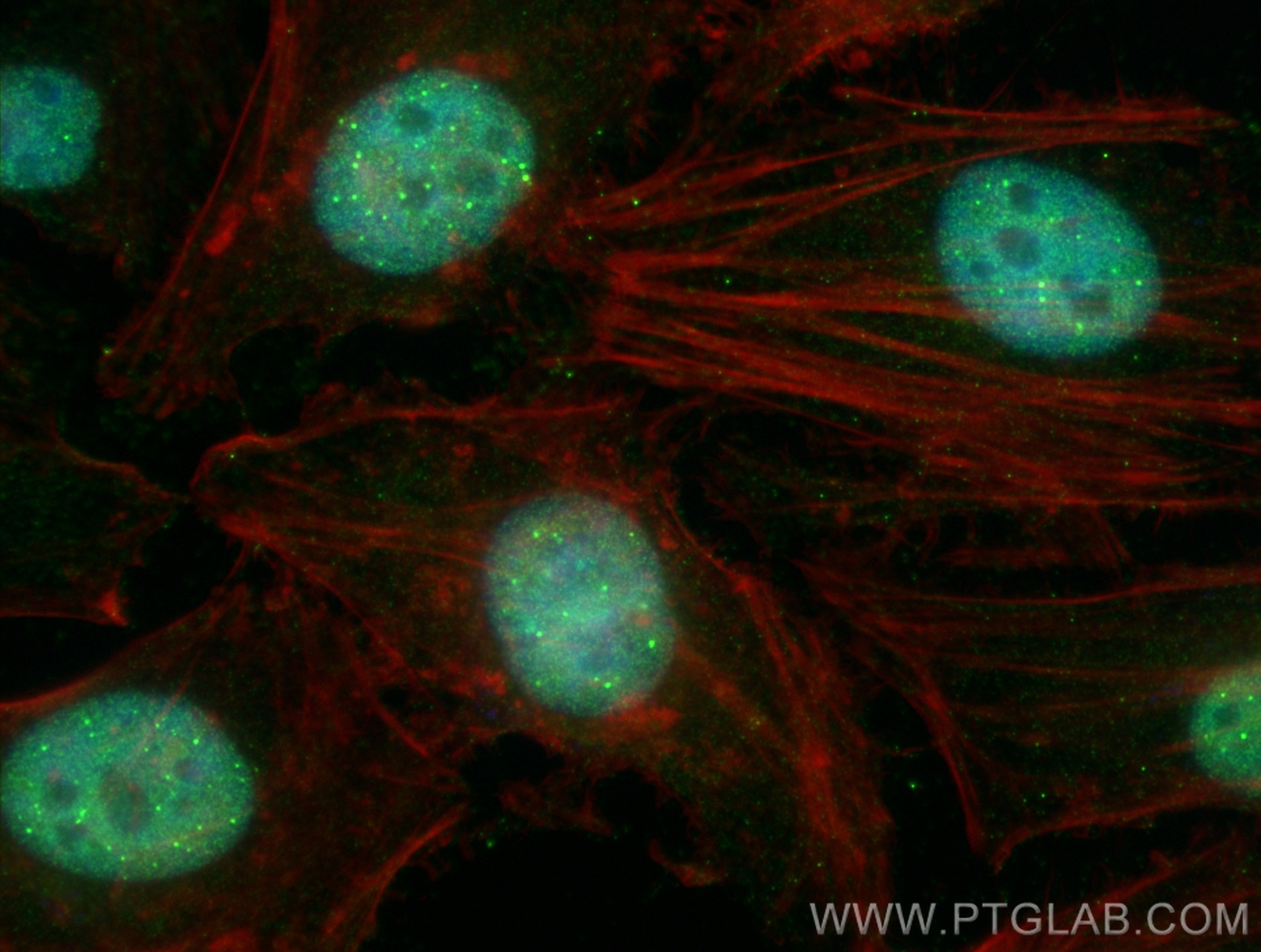
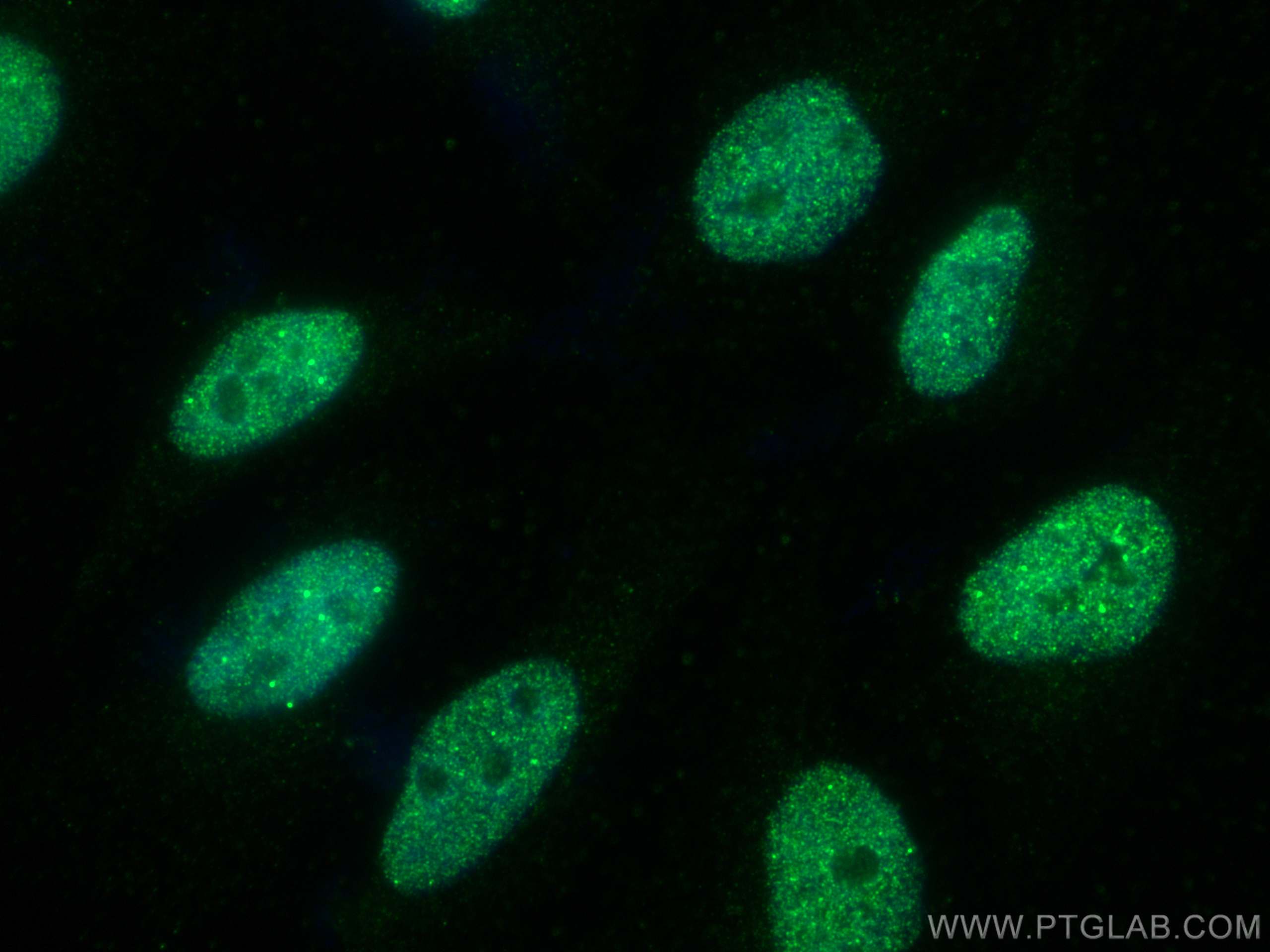
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
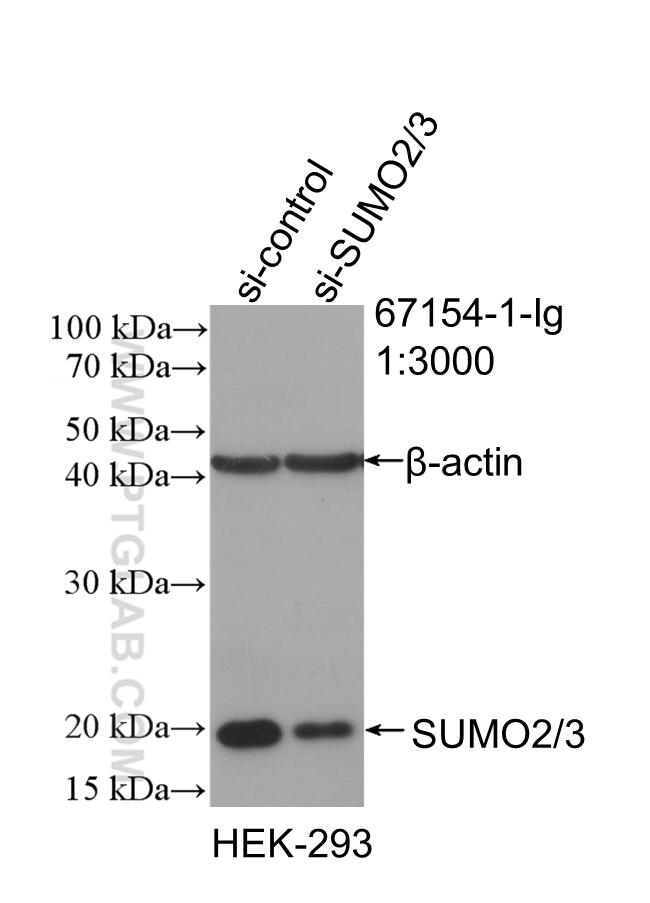
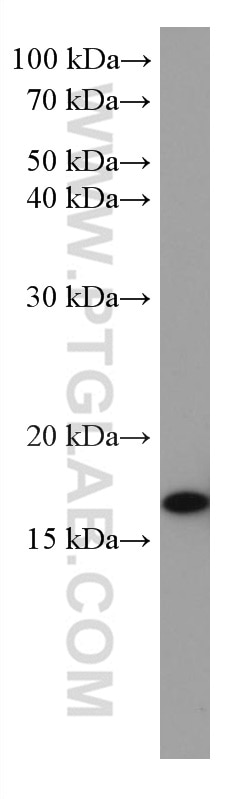
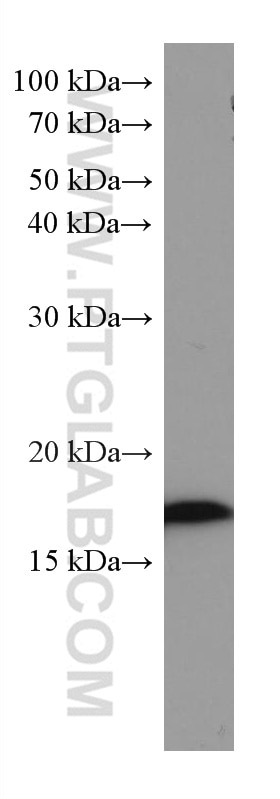
67154-1-PBS cible SUMO2/3 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | SUMO2/3 Protéine recombinante Ag28672 |
| Nom complet | SMT3 suppressor of mif two 3 homolog 2 (S. cerevisiae) |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 11 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 18 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC008450 |
| Symbole du gène | SUMO2 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 6613 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Ubiquitin is most famous for its function in targeting proteins for degradation by the 26S proteasome, ubiquitin needs to be attached to a substrate in chains (polyubiquitylation) before being recognized by proteasome. Similarly, SUMO (small ubiquitin-related modifier) can be linked to substrates in chains (polysumoylation), SUMO modification has been implicated in many important cellular processes including the control of genome stability, signal transduction, targeting to and formation of nuclear compartments, cell cycle and meiosis. There are 4 confirmed SUMO isoforms in human, SUMO-1, SUMO-2, SUMO-3 and SUMO-4. SUMO-2 and SUMO-3 are nearly identical but are distinct from SUMO-1. SUMO2/3 conjugation was recently widely involved in neuroprotective activities. A substitution (M55V) of SUMO4 was strongly associated with the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes (T1D) involving NF kappa B related mechanisms.