Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-TRAPPC9/NIBP
TRAPPC9/NIBP Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 19549-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
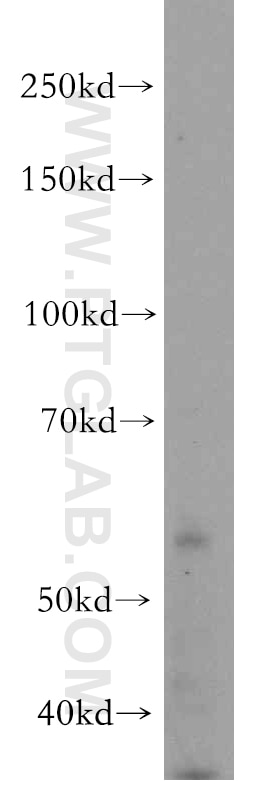
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules SH-SY5Y, tissu cérébral humain, tissu rénal de souris |
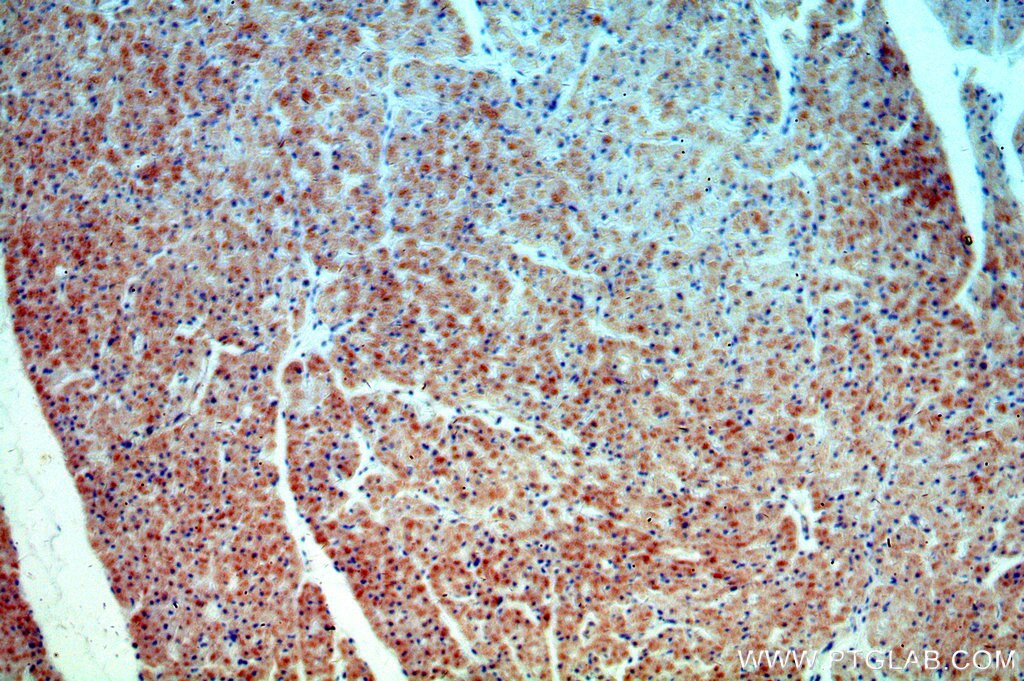
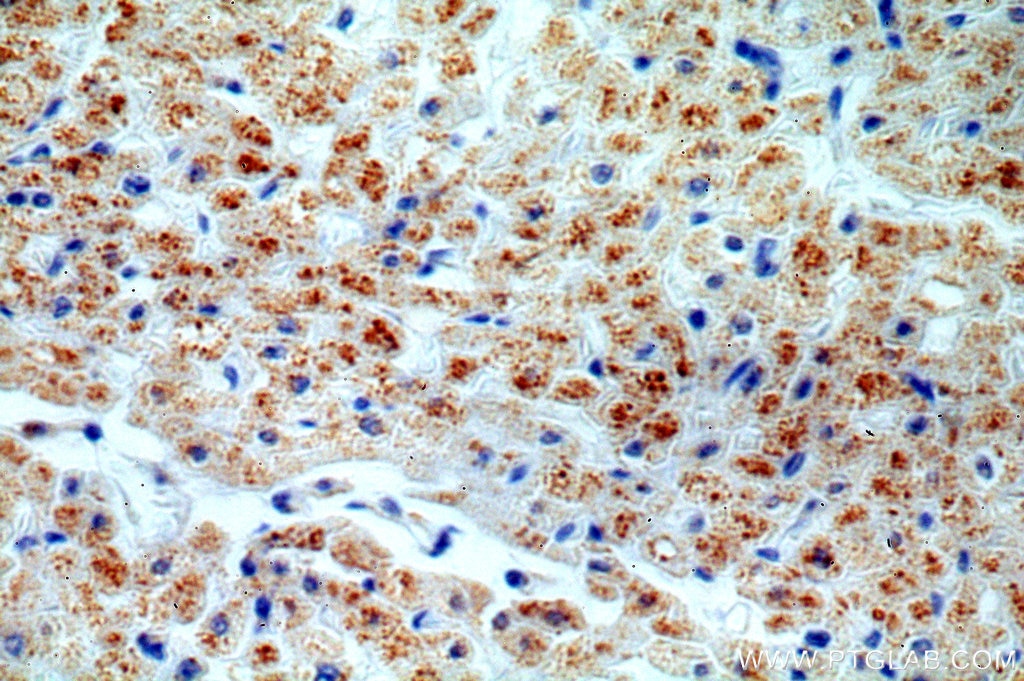
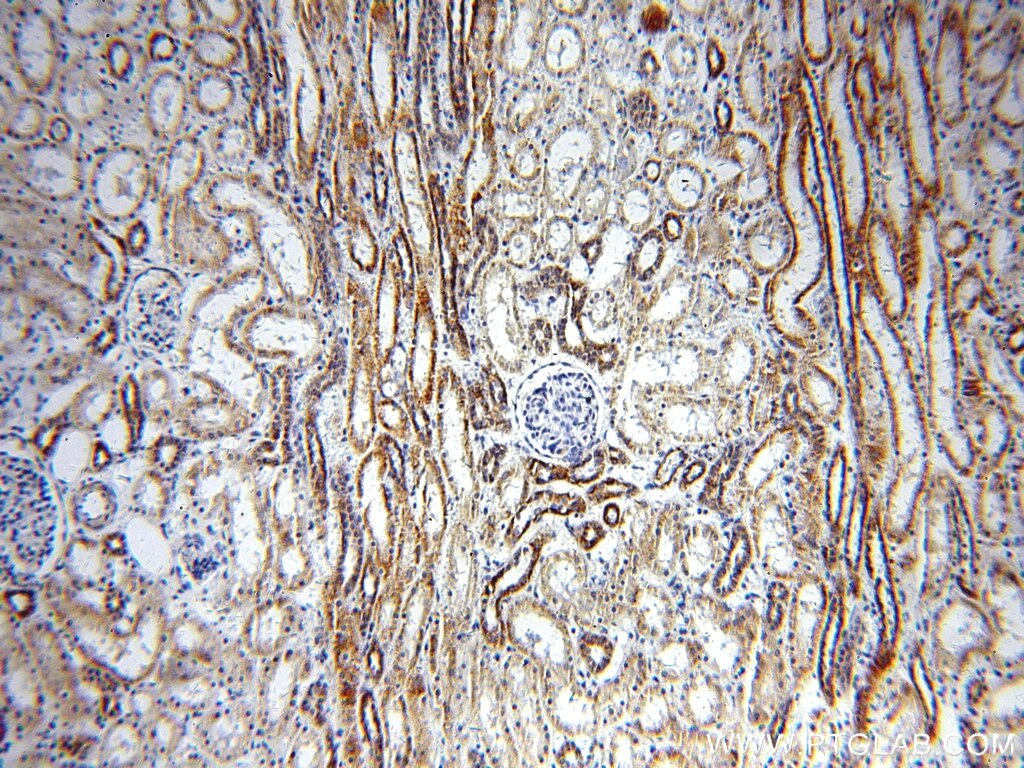
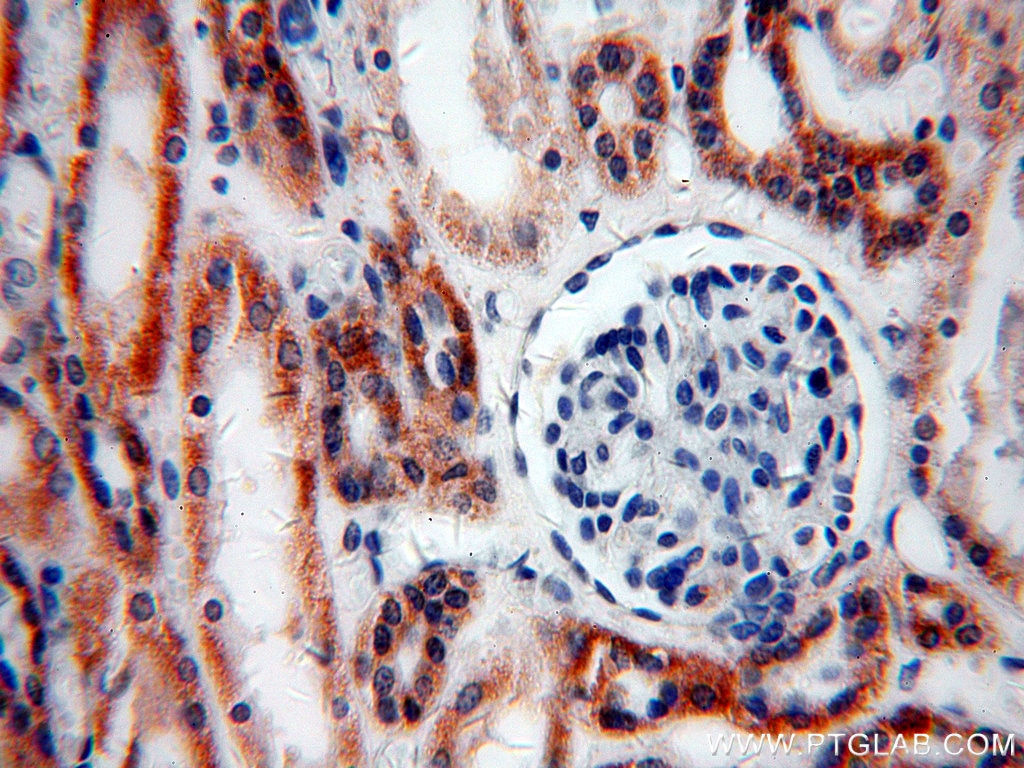
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu cardiaque humain, tissu rénal humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:3000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Informations sur le produit
19549-1-AP cible TRAPPC9/NIBP dans les applications de WB, IHC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Peptide |
| Nom complet | trafficking protein particle complex 9 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 139 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 56 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | NM_031466 |
| Symbole du gène | NIBP/Trappc9 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 83696 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
TRAPPC9, also named NIK- and IKBKB-binding protein (NIBP), is involved in the NF-kappaB signaling pathway and directly interacts with IKK-beta and MAP3K14. TRAPPC9 functions as an activator of NF-kappa-B via increased phosphorylation of the IKK complex. TARPPC9 may also function in neuronal cells differentiation and defects in TRAPPC9 are the cause of mental retardation autosomal recessive type 13 (MRT13), which is characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptative behavior. TARPPC9 is a component of the multisubunit TRAPP (transport protein particle) complex and it may play a role in vesicular transport from endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi.