Anticorps Recombinant de lapin anti-TNF-alpha
TNF-alpha Recombinant Antibody for WB, IF/ICC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
souris
Applications
WB, IF/ICC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
240702B7
N° de cat : 80258-6-PBS
Synonymes
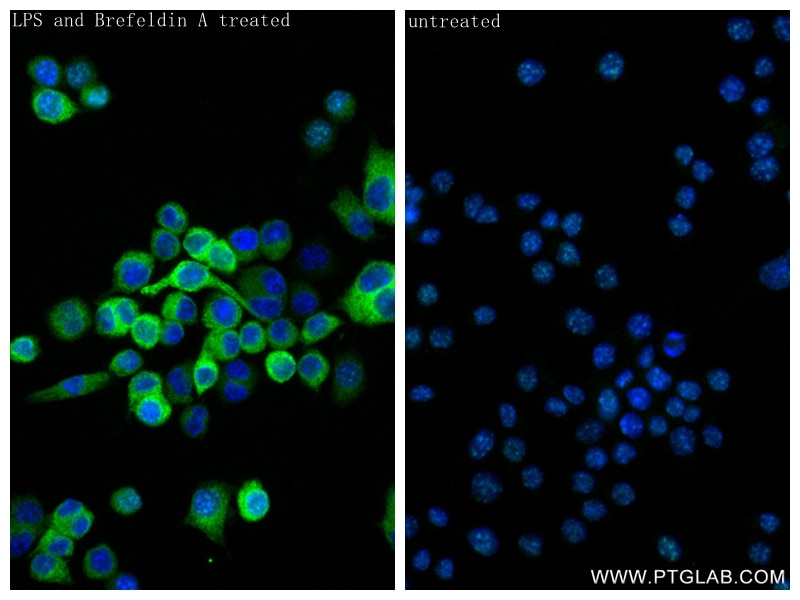
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
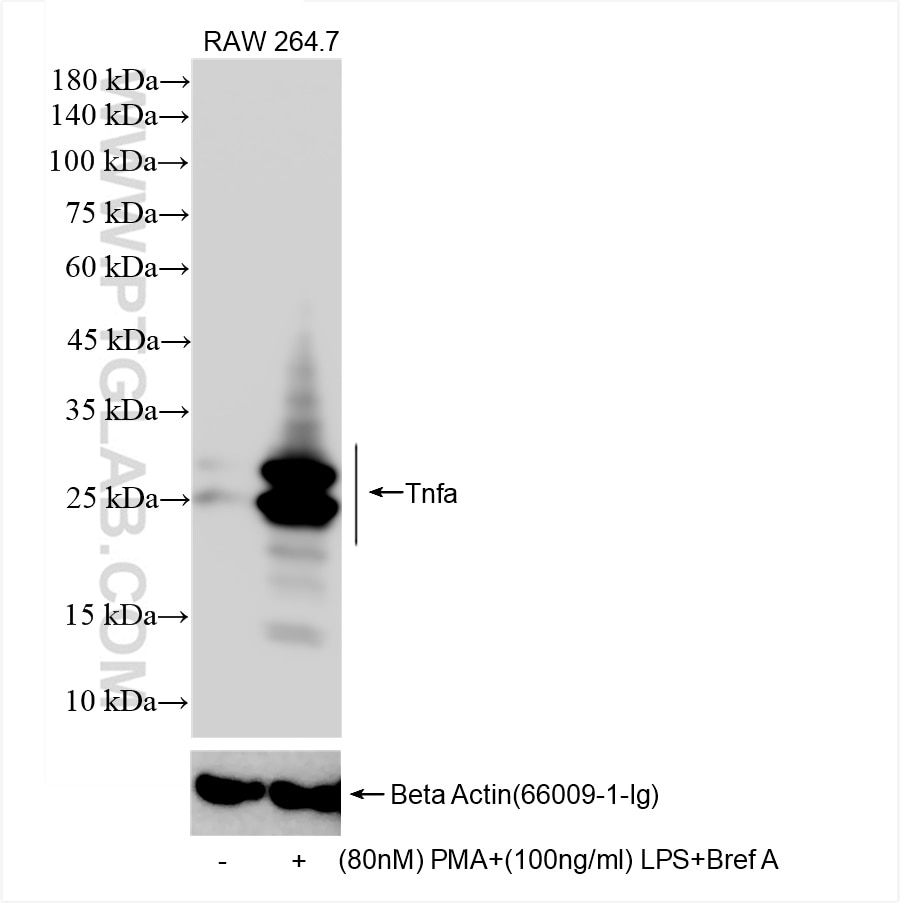
80258-6-PBS cible TNF-alpha dans les applications de WB, IF/ICC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons souris
| Réactivité | souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Recombinant |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Protéine recombinante |
| Nom complet | tumor necrosis factor |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 25-26 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | NM-013693 |
| Symbole du gène | TNF-alpha |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 21926 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Protein A purfication |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
TNF, as also known as TNF-alpha, or cachectin, is a multifunctional proinflammatory cytokine that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily. It is expressed as a 26 kDa membrane bound protein and is then cleaved by TNF-alpha converting enzyme (TACE) to release the soluble 17 kDa monomer, which forms homotrimers in circulation. It is produced chiefly by activated macrophages, although it can be produced by many other cell types such as CD4+ lymphocytes, NK cells, neutrophils, mast cells, eosinophils, and neurons. It can bind to, and thus functions through its receptors TNFRSF1A/TNFR1 and TNFRSF1B/TNFBR. This cytokine is involved in the regulation of a wide spectrum of biological processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, lipid metabolism, and coagulation. Mouse and human TNF-alpha share 79% amino acid sequence identity. Unlike human TNF-alpha, the mouse form is glycosylated. In mouse deficiency of this gene is associated with defects in response to bacterial infection, with defects in forming organized follicular dendritic cell networks and germinal centers, and with a lack of primary B cell follicles.