- Phare
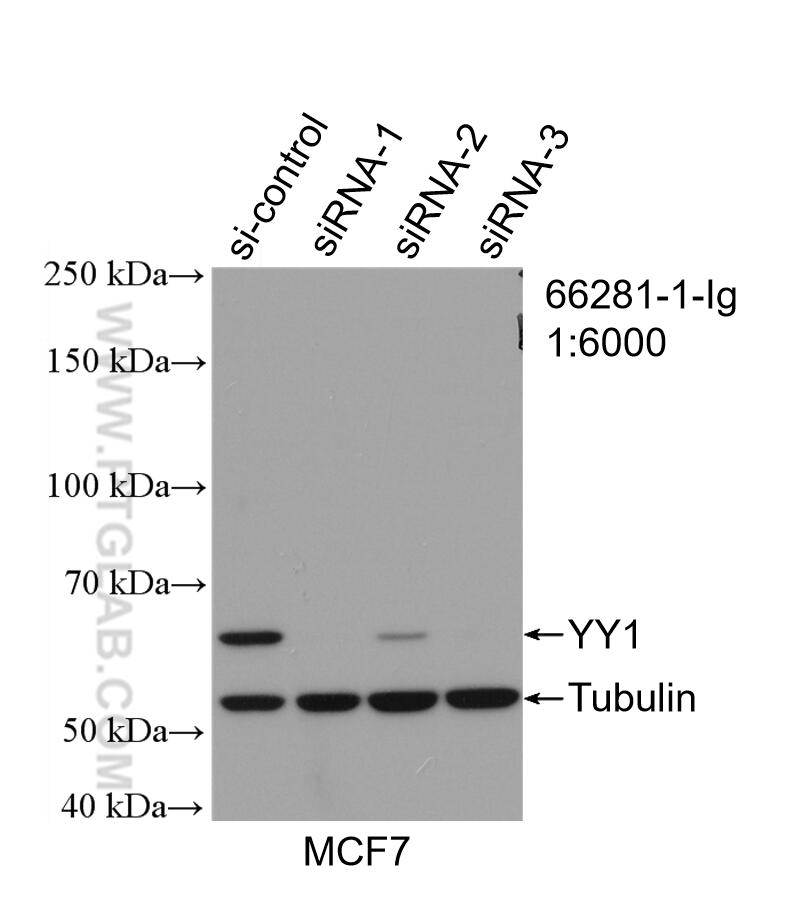
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-YY1
YY1 Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2a
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, singe, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
2E11C5
N° de cat : 66281-1-PBS
Synonymes
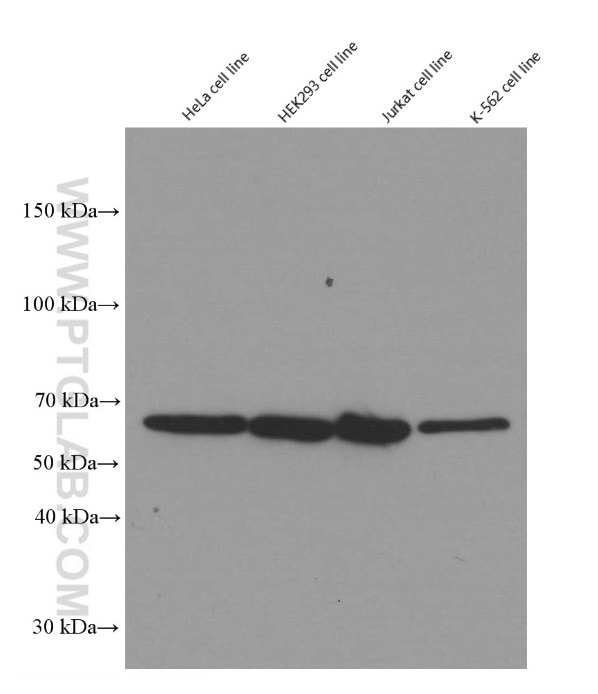
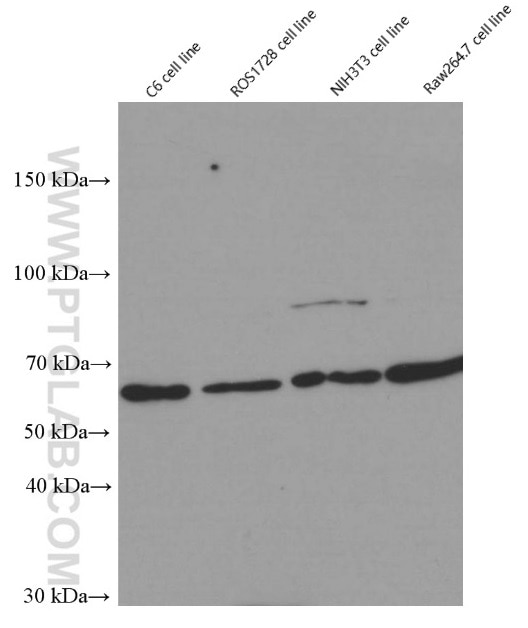
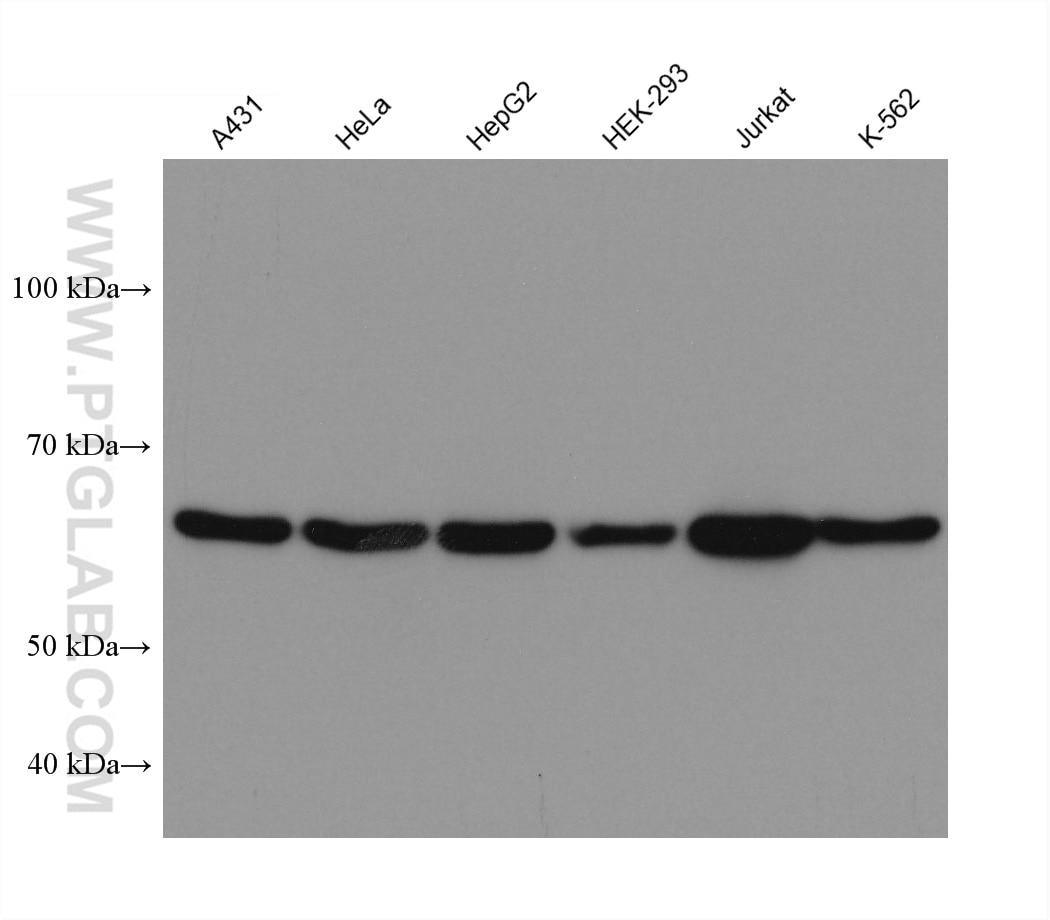
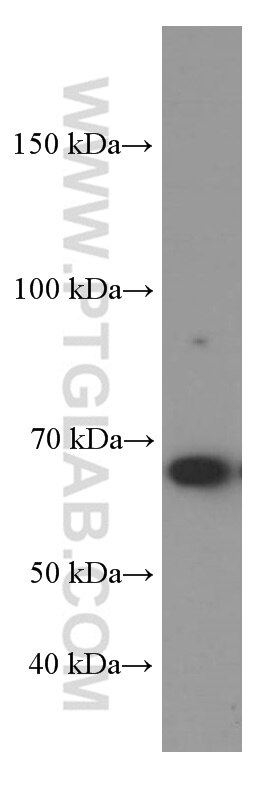
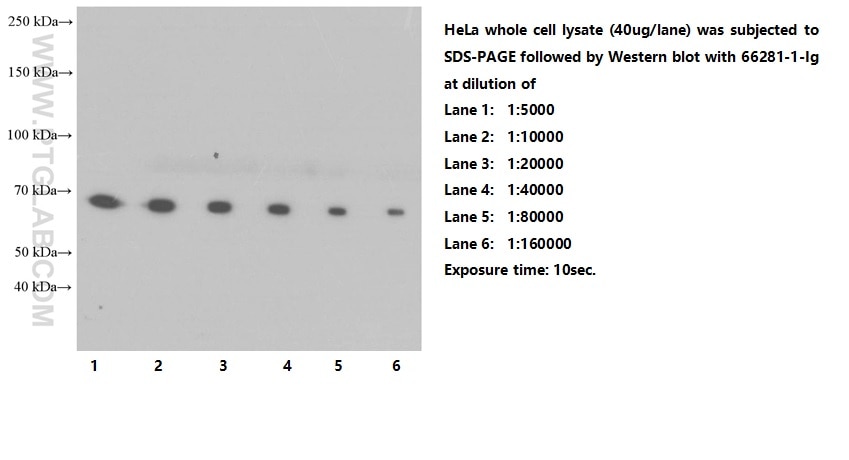
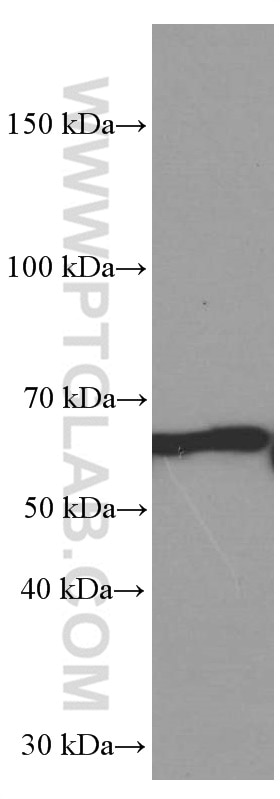
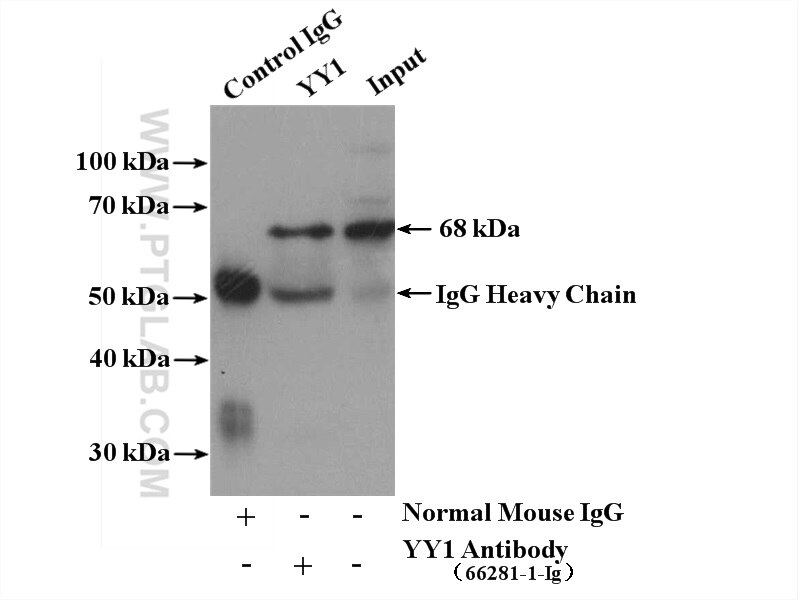
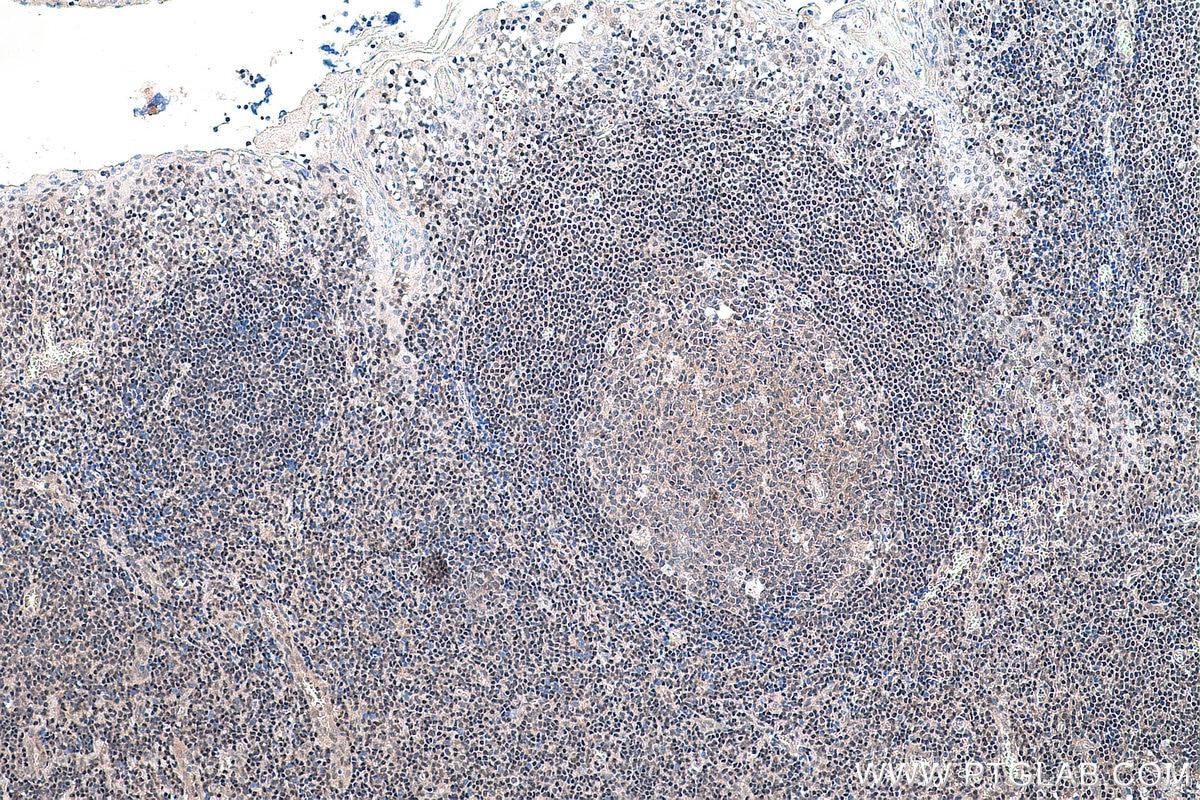
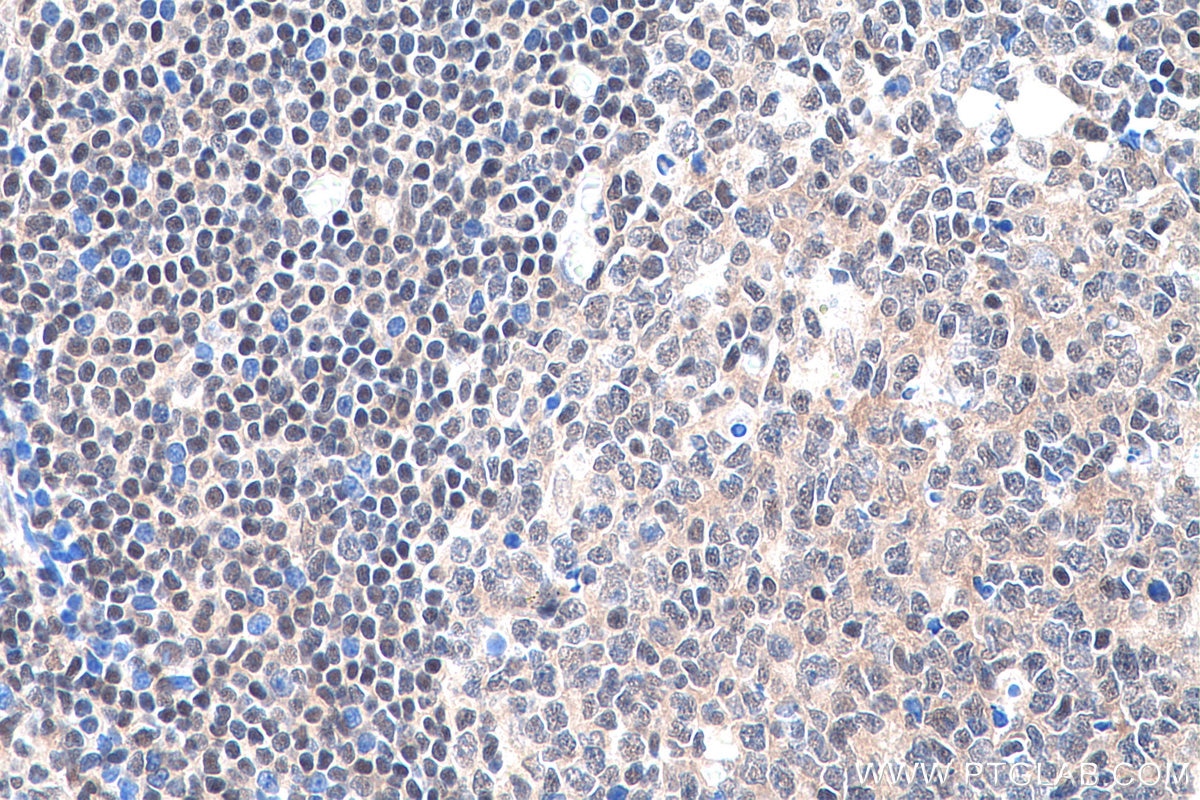
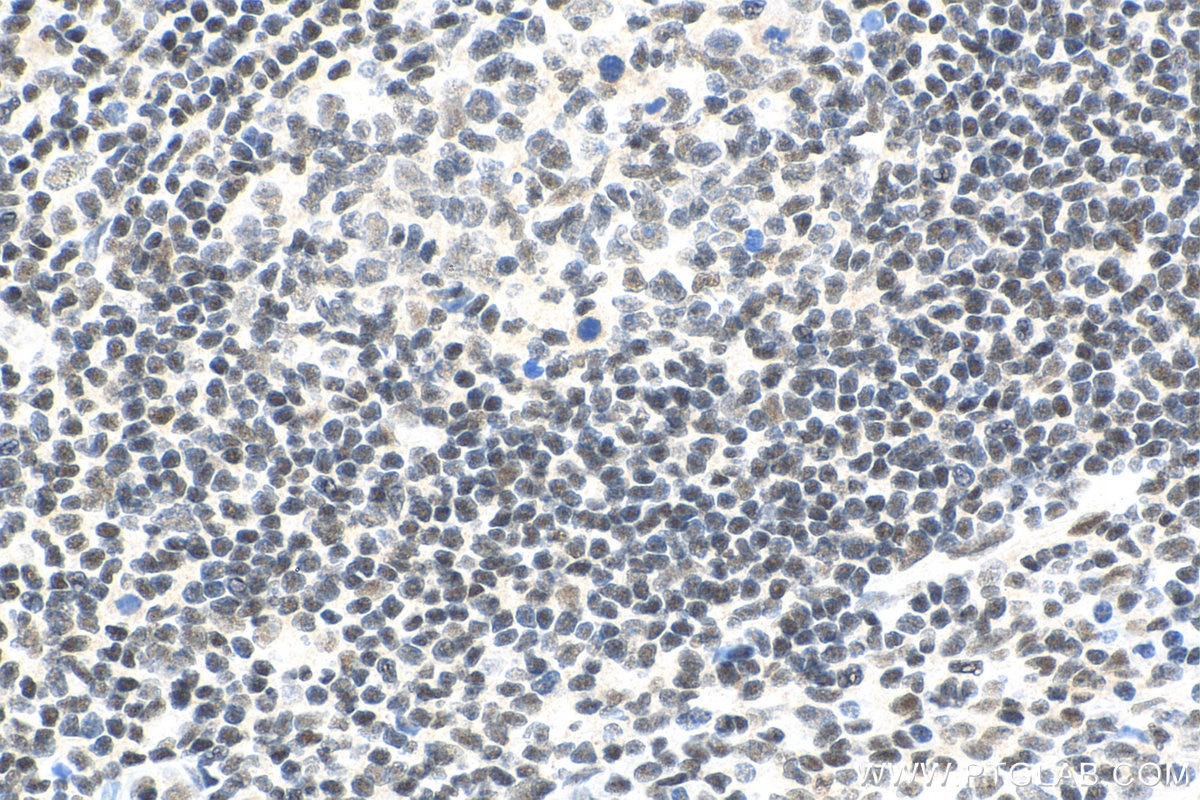
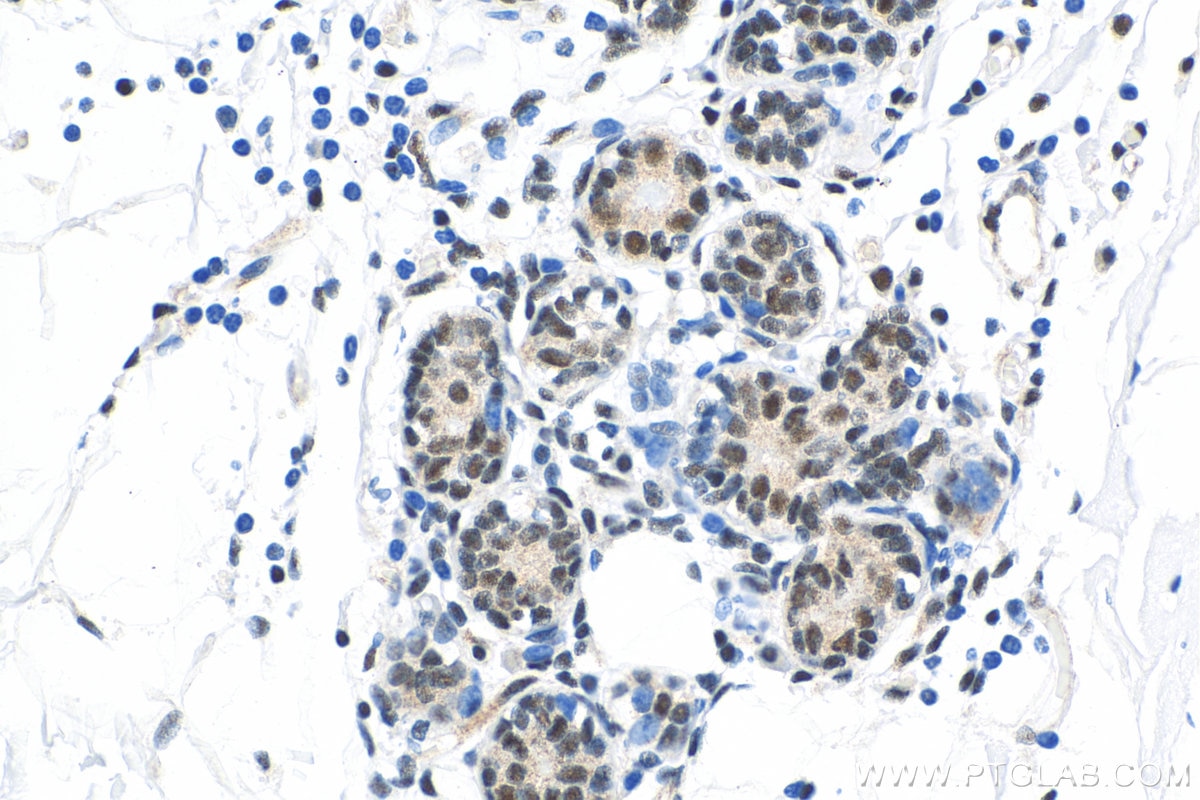
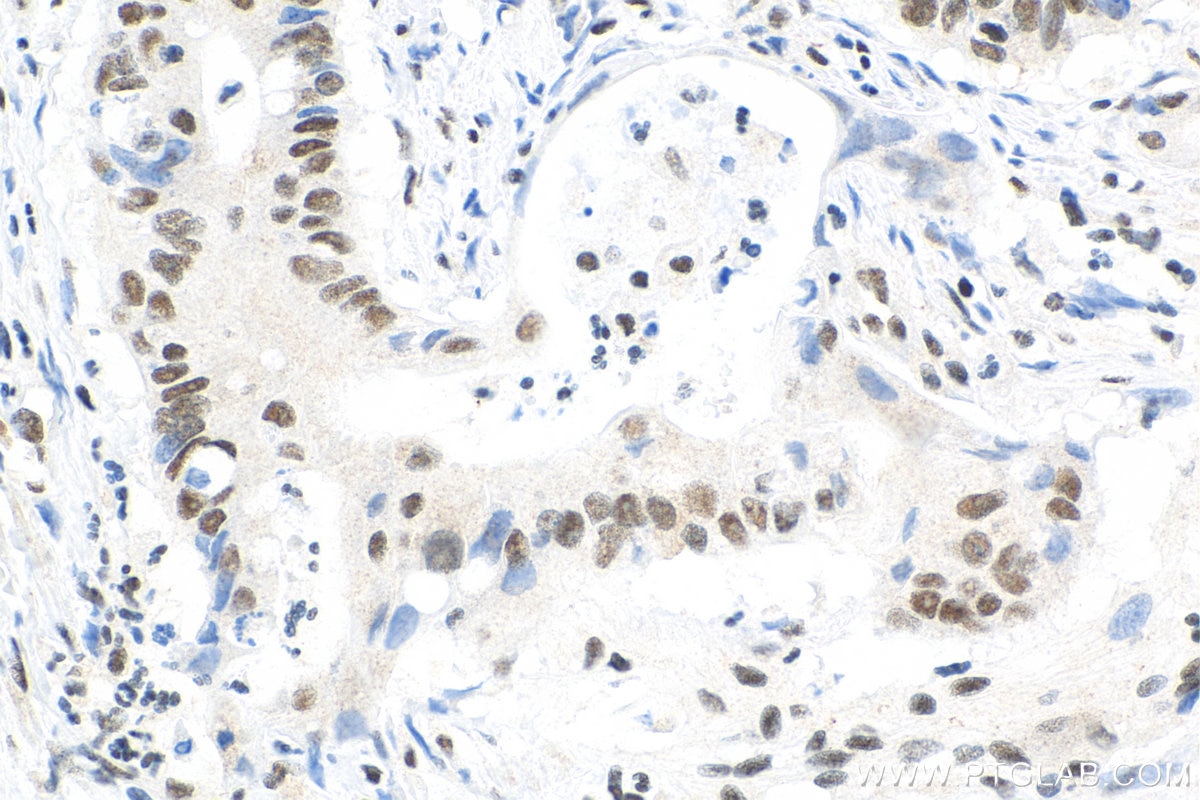
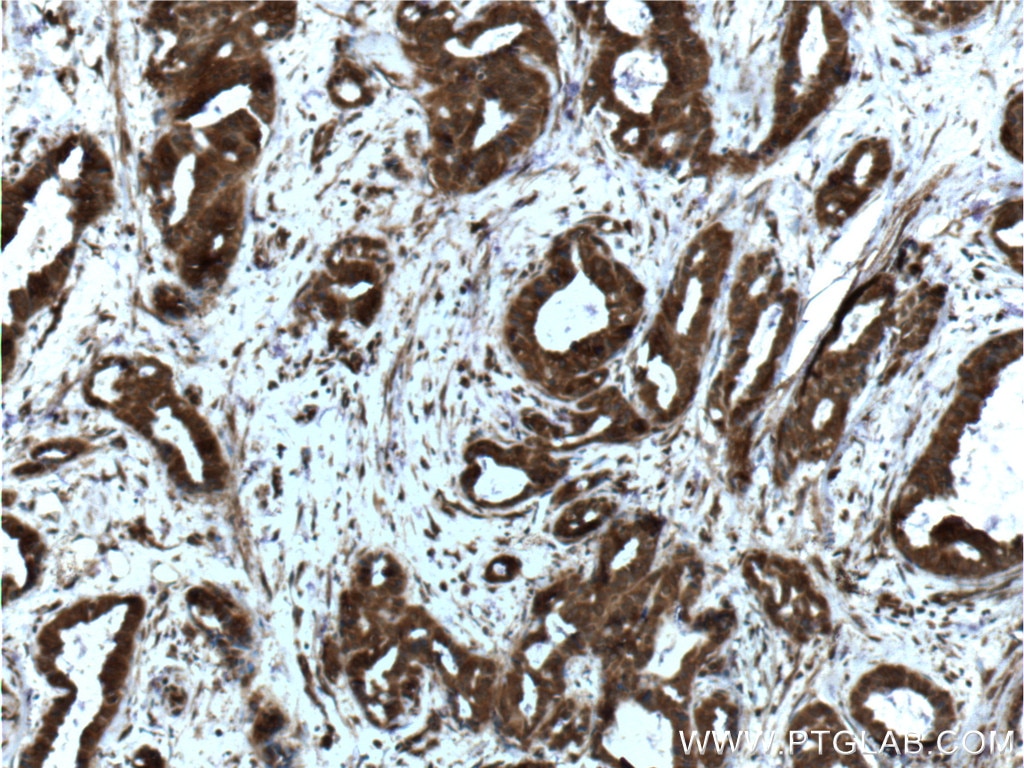
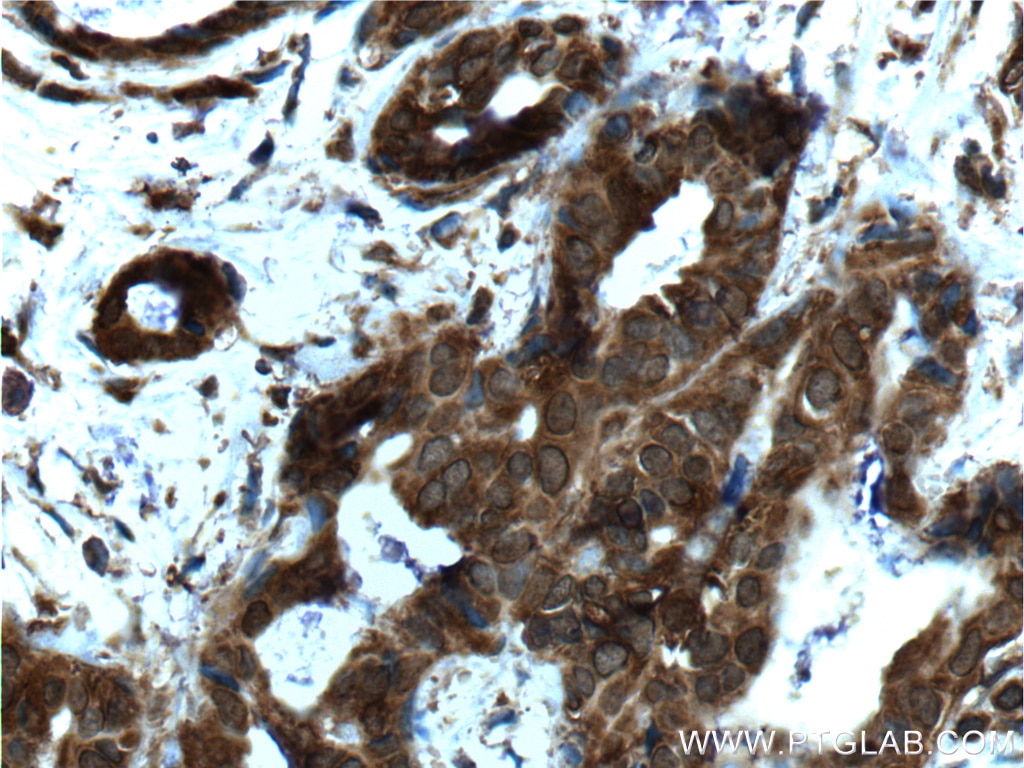
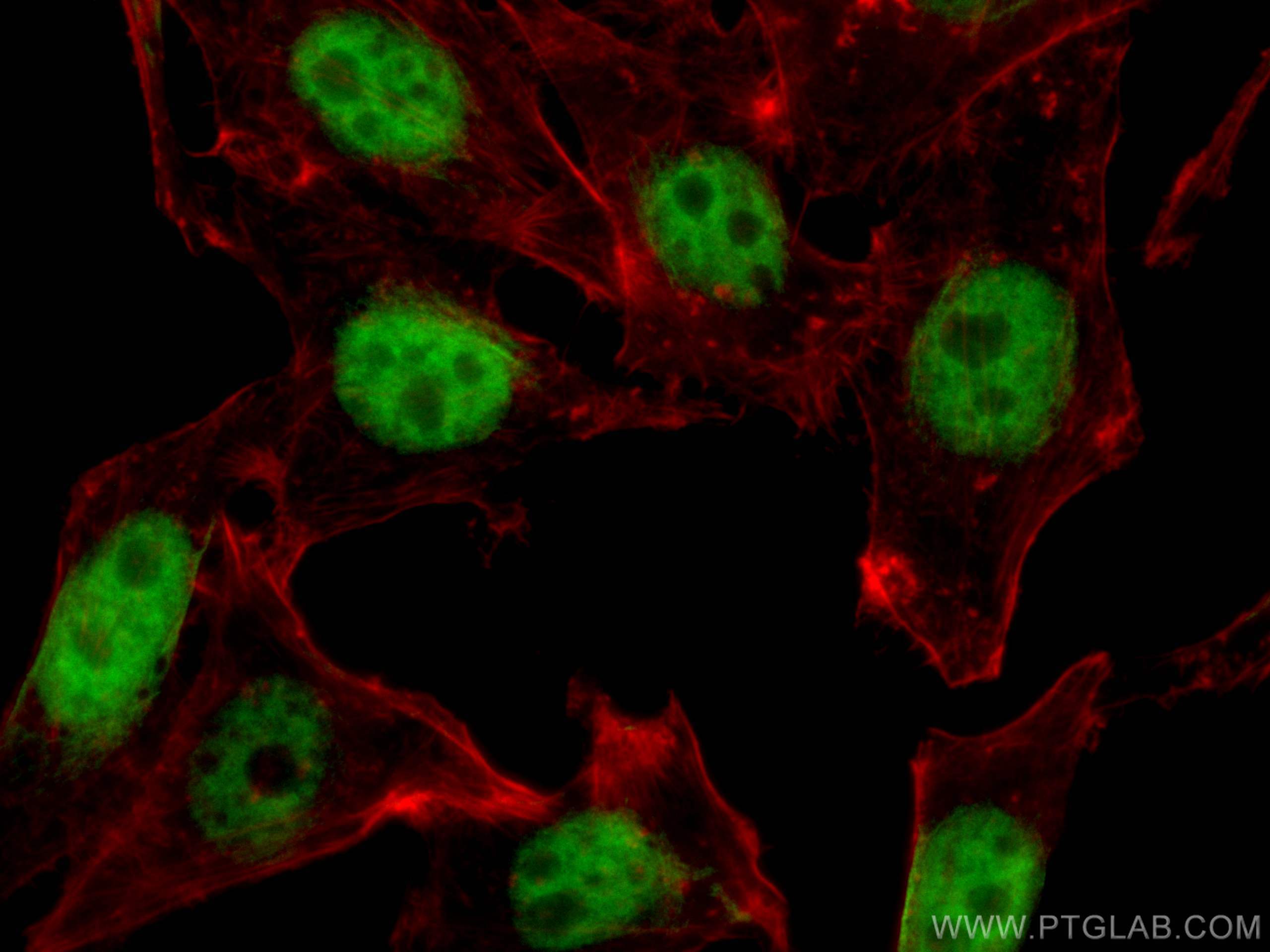
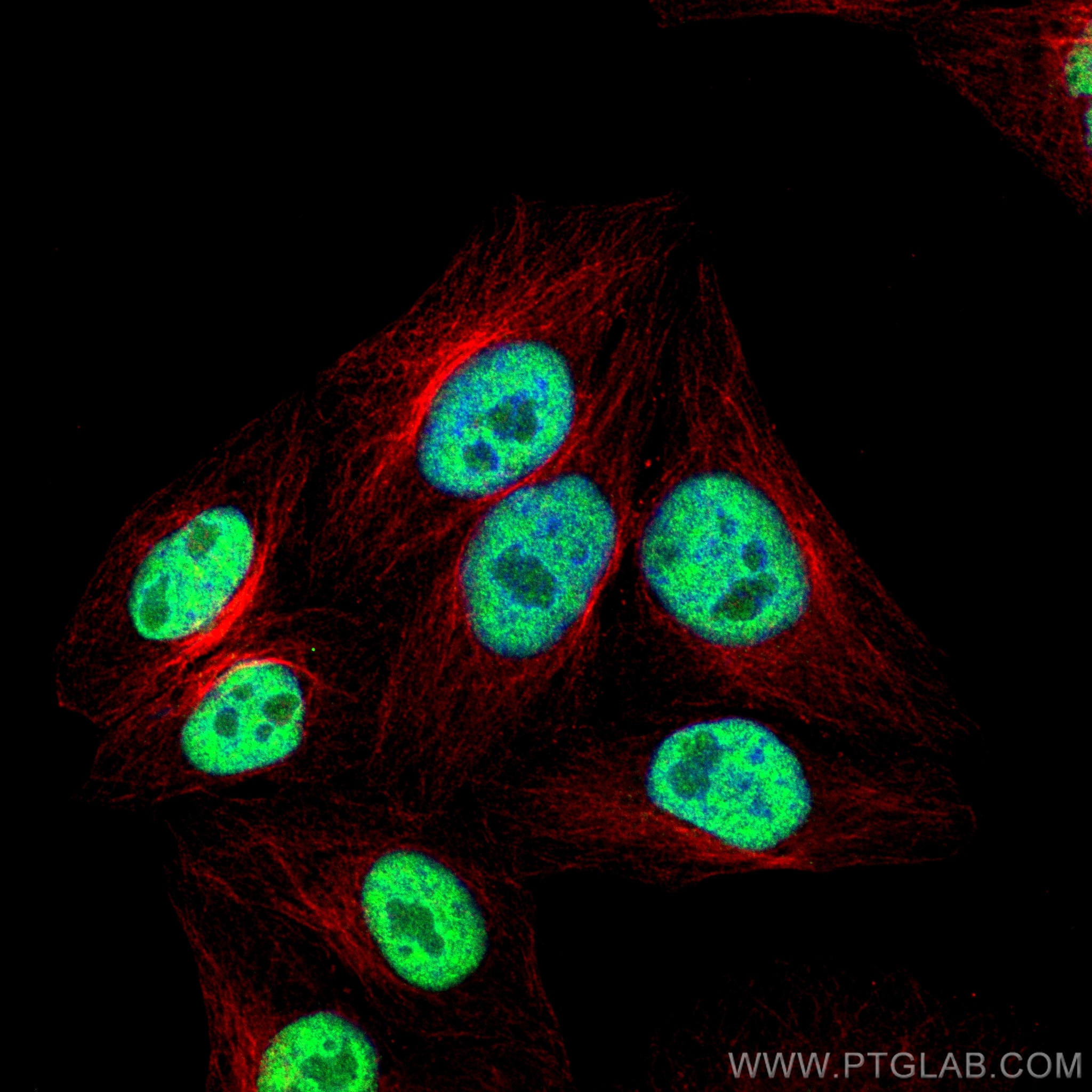
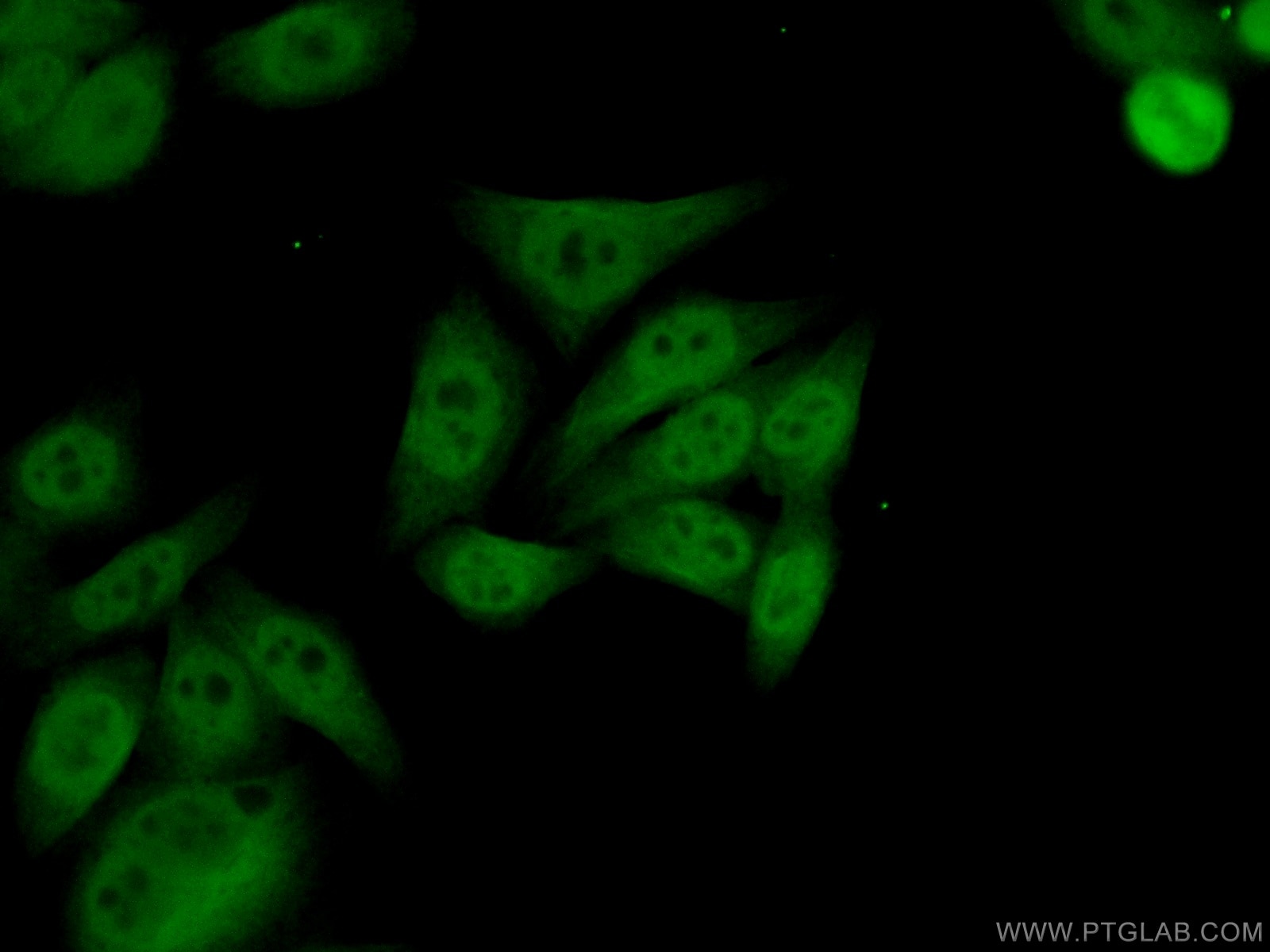
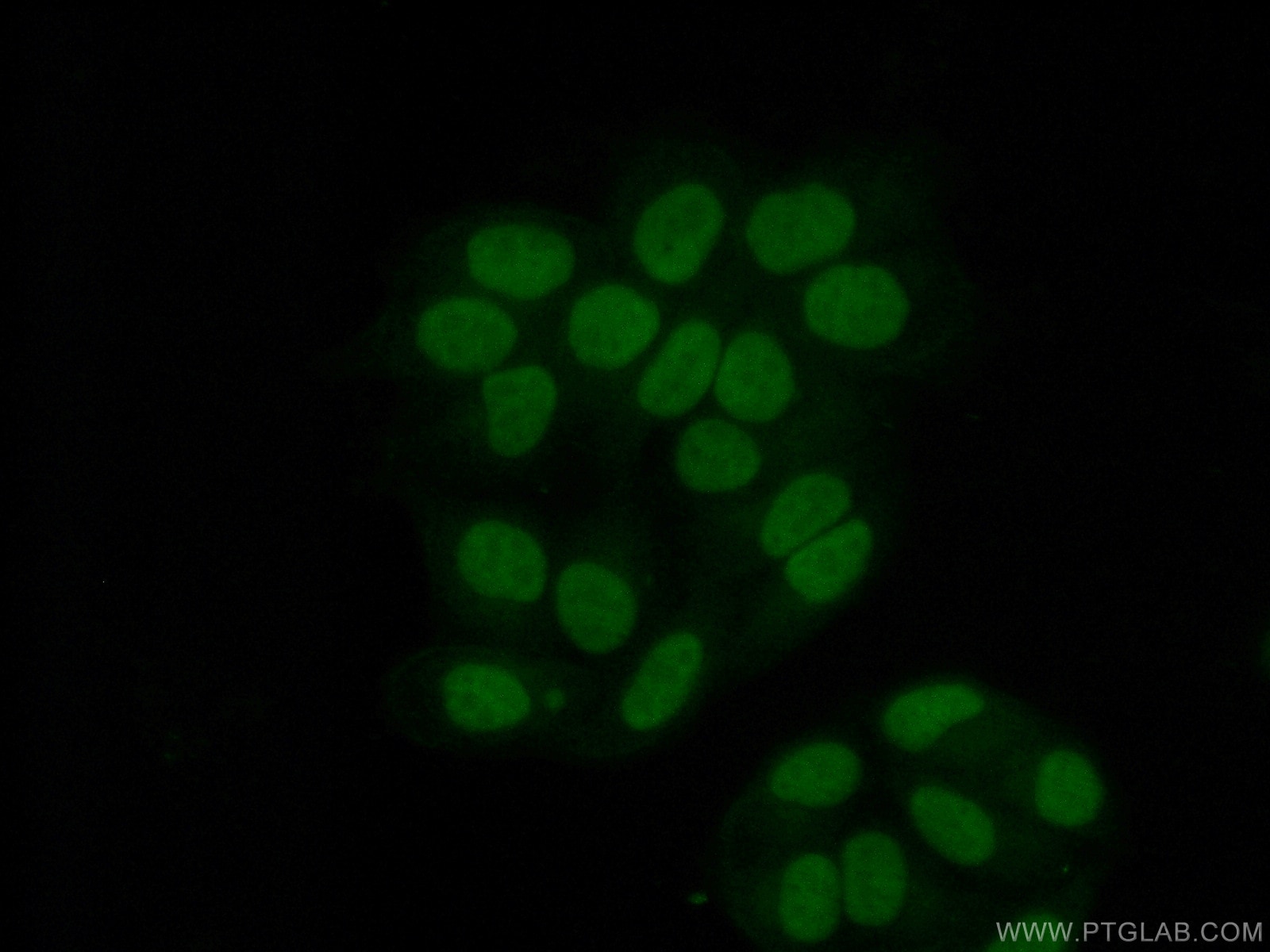
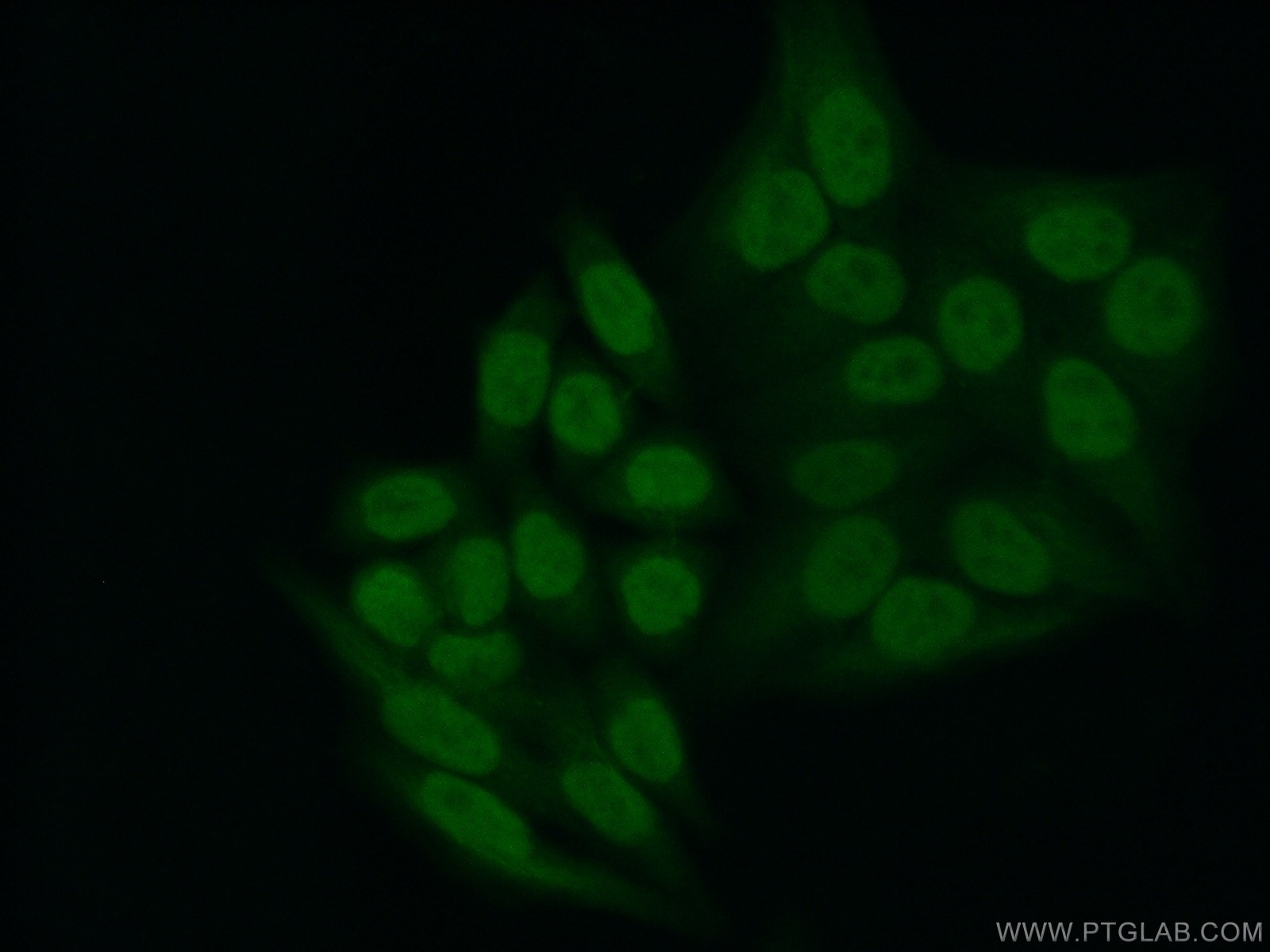
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
66281-1-PBS cible YY1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, singe, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, singe, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | YY1 Protéine recombinante Ag17732 |
| Nom complet | YY1 transcription factor |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 414 aa, 45 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 65-70 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC037308 |
| Symbole du gène | YY1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 7528 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
YY1, also named as DELTA, INO80S and NF-E1, contains four C2H2-type zinc fingers and belongs to the YY transcription factor family. YY1 is a multifunctional transcription factor that exhibits positive and negative control on a large number of cellular and viral genes by binding to sites overlapping the transcription start site. YY1 may direct histone deacetylases and histone acetyltransferases to a promoter in order to activate or repress the promoter, thus implicating histone modification in the YY1. The open reading frame of the human YY1 cDNA encodes a protein of 414 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of 44 kDa. However, YY1 migrates on SDS gels as a 65-68 kDa protein, probably due to the structure of the protein. It is a ubiquitously expressed transcription factor with fundamental roles in embryogenesis, differentiation, replication and proliferation.