Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-ZO-1
ZO-1 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris et plus (1)
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 30487-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
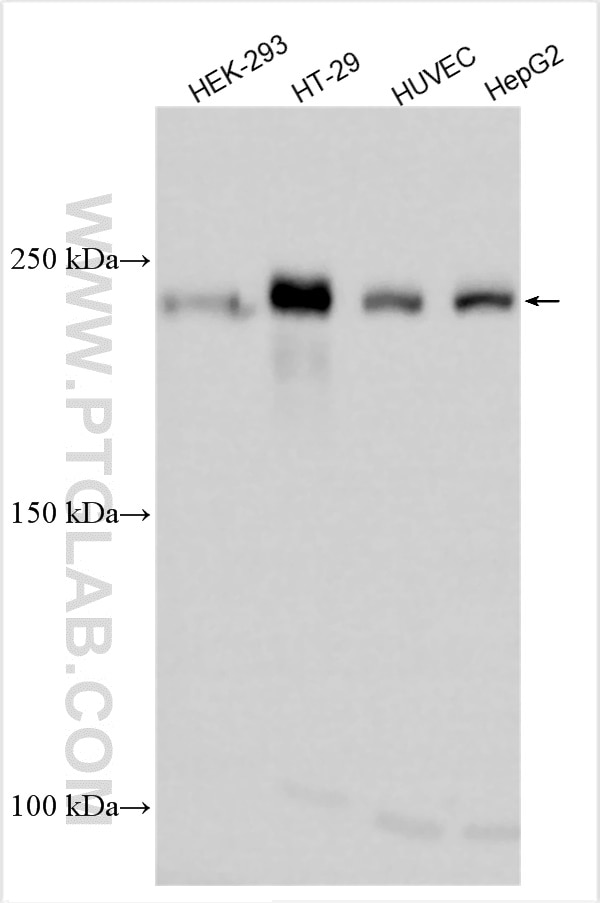
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HEK-293, cellules HepG2, cellules HT-29, cellules HUVEC |
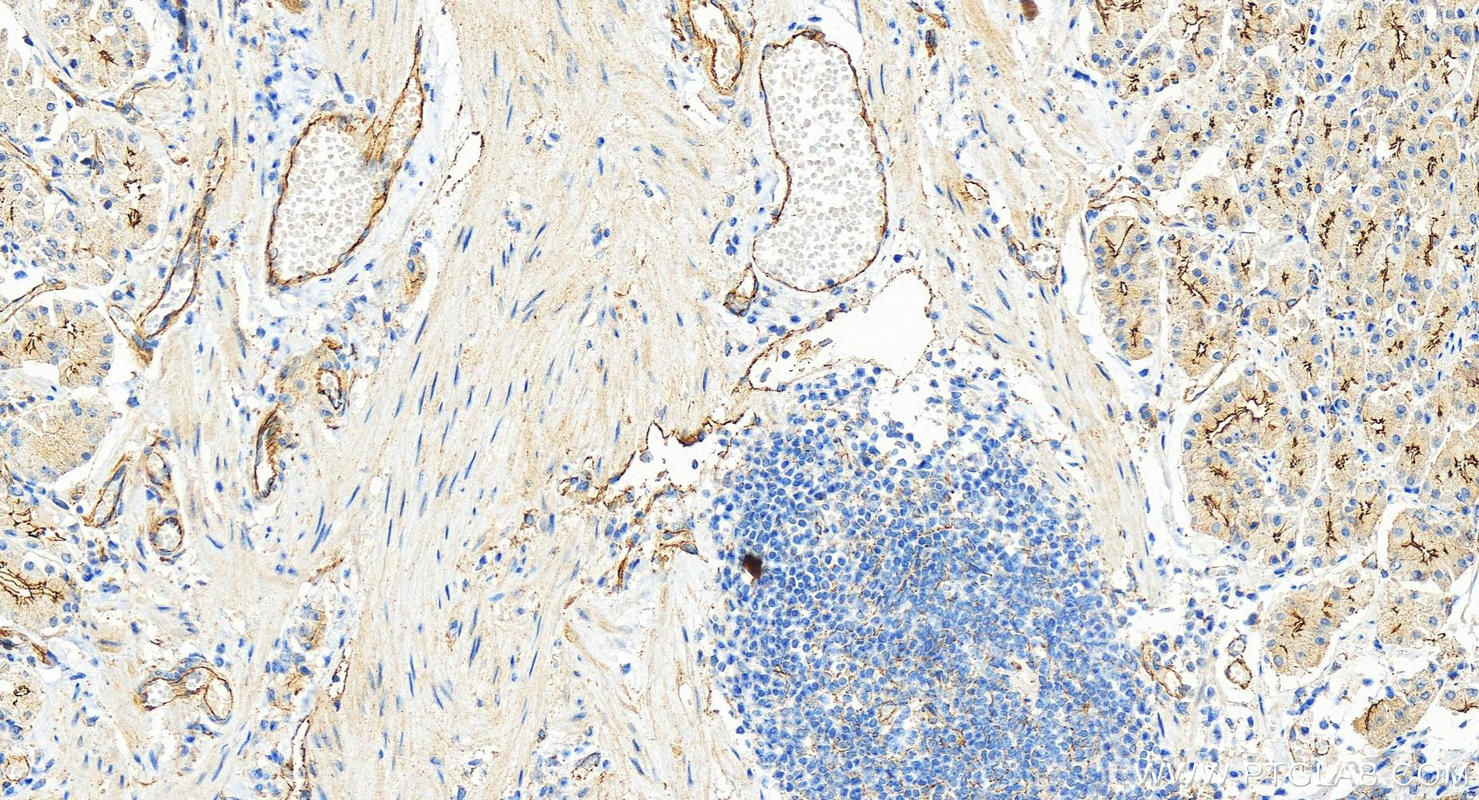
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu d'estomac humain, il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
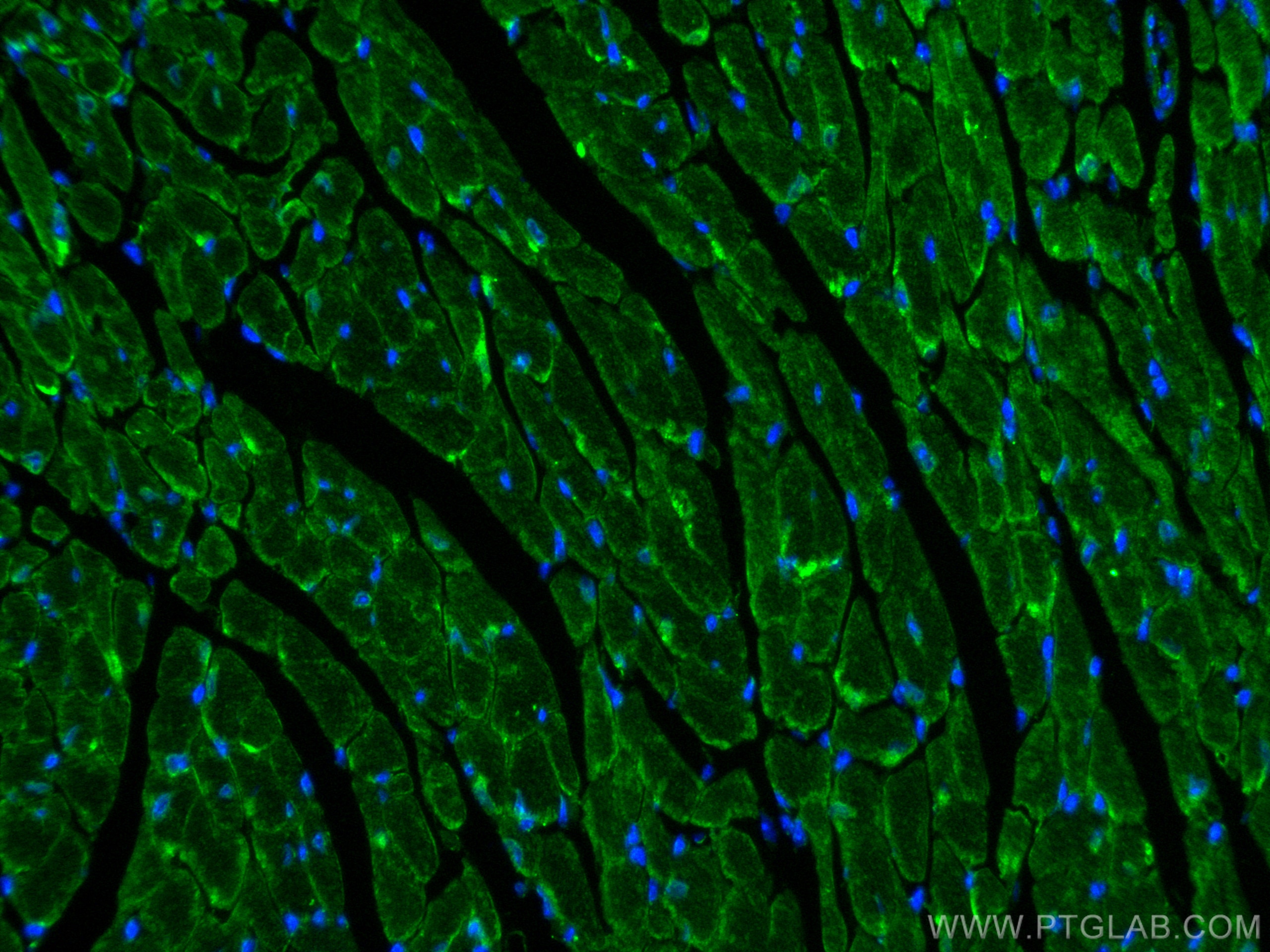
| Résultats positifs en IF-P | tissu cardiaque de souris, |
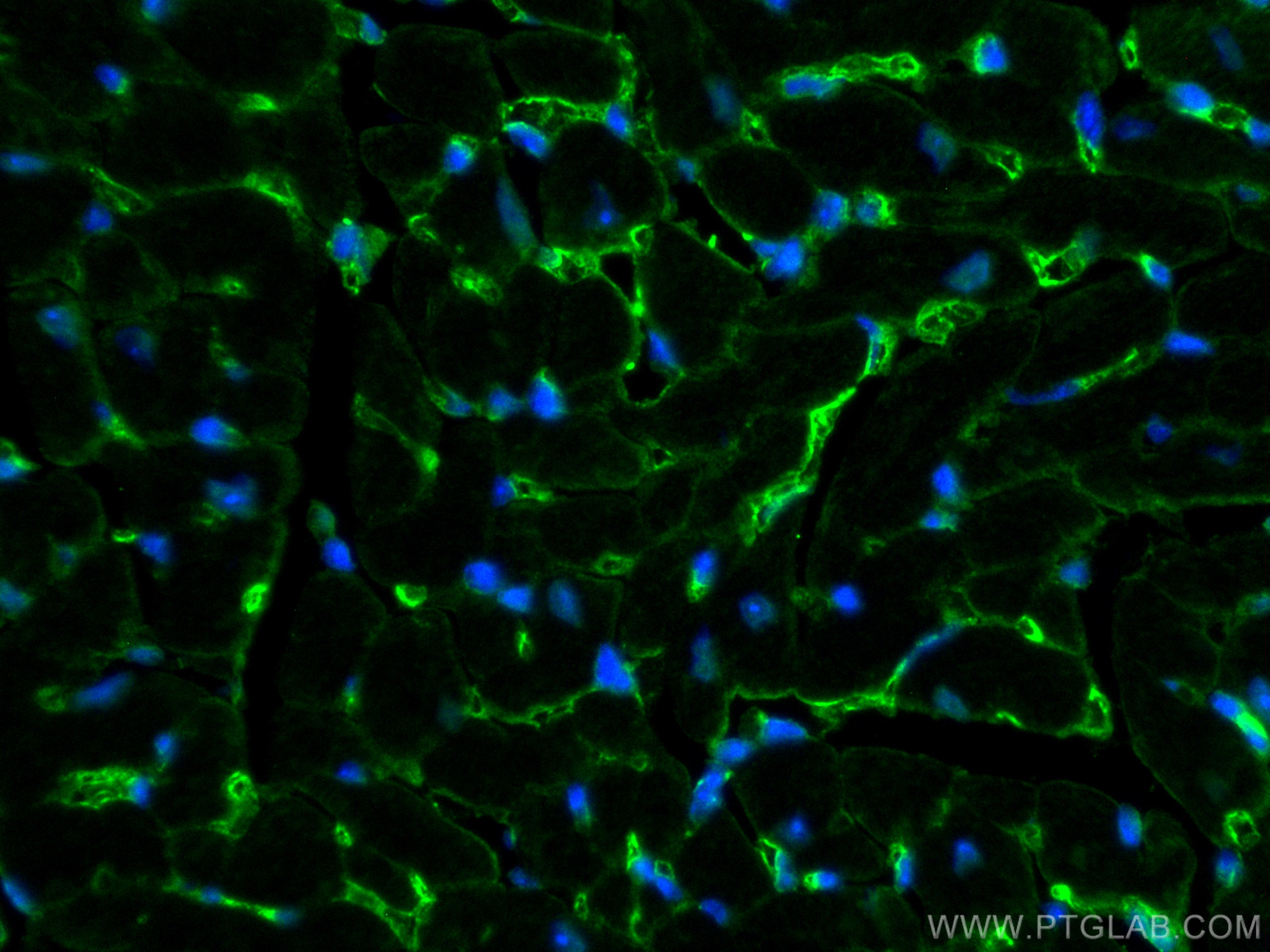
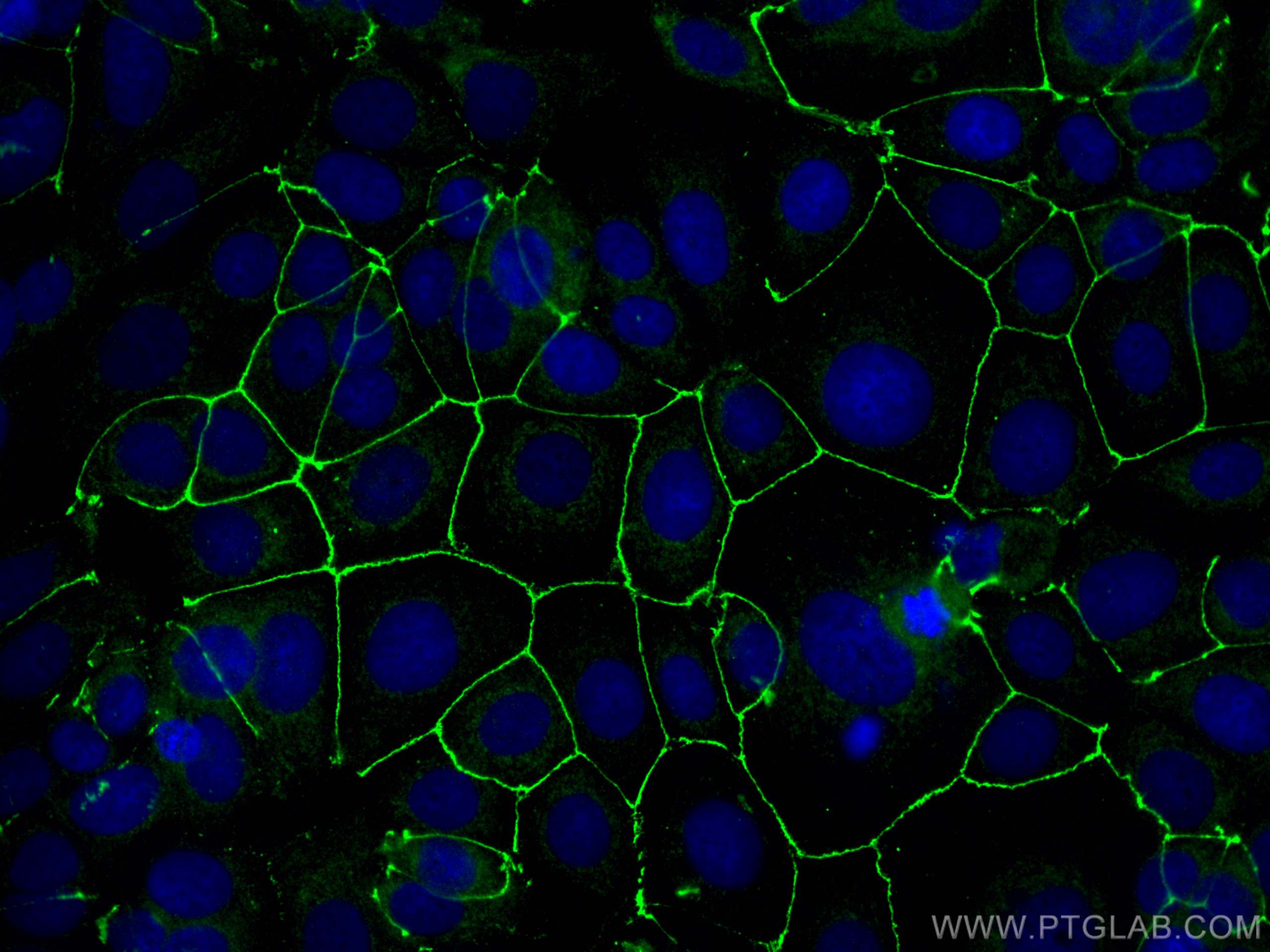
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules MCF-7, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:400-1:1600 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 4 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
30487-1-AP cible ZO-1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | ZO-1 Protéine recombinante Ag33182 |
| Nom complet | tight junction protein 1 (zona occludens 1) |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 1748 aa, 195 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 230 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC111712 |
| Symbole du gène | ZO-1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 7082 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Tight junction (or zonula occludens) forms the continuous intercellular barrier between epithelial and endothelial cells, which is required to separate tissue spaces and regulate selective movement of solutes across the epithelium and endothelium (PMID: 20066090). ZO-1 (also known as TJP1) is a peripheral membrane phosphoprotein located on the cytoplasmic face and is expressed in tight junctions of both epithelial and endothelial cells (PMID: 3528172). It binds the transmembrane proteins occludin and the claudins linking them to cytoskeletal actin (PMID: 17418867). ZO-1 belongs to a family of multidomain proteins known as the membrane-associated guanylate kinase homologs (MAGUKs). It is a pivotal tight junction protein and may be involved in signaling mechanisms regulating cell proliferation and differentiation (PMID: 22782886).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for ZO-1 antibody 30487-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for ZO-1 antibody 30487-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for ZO-1 antibody 30487-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Mol Med 5α-Hydroxycostic acid inhibits choroidal neovascularization in rats through a dual signalling pathway mediated by VEGF and angiopoietin 2 | ||
Cells The Natural Product Secoemestrin C Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells via p38-S100A8 Feed-Forward Regulatory Loop | ||
Biomed Pharmacother Disruption of blood-brain barrier and endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition are attenuated by Astragalus polysaccharides mediated through upregulation of ETS1 expression in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis | ||
Int J Colorectal Dis AQP3 mediates autophagy through SIRT1/p62 signal to alleviate intestinal epithelial cell damage caused by sepsis |