Anti-IgG VHH Beads for Immunoprecipitation
A Smarter Alternative to Protein A/G
While Protein A and G remain the most common choices for antibody capture, their broad and unspecific Fc binding and potential for leaching from beads can compromise specificity and lead to interfering background in sensitive assays. Our VHH (Nanobody) Beads are optimized for targeted precision, clean results, and redefine specificity and purity in immunoprecipitation.
-
No protein A/G contamination
-
Species-specific IgG binding
-
Consistent and clean results
Available IgG IP Beads
Anti-Rabbit / Anti-Mouse VHH Beads
Our anti-rabbit / anti-mouse VHH beads are conjugated with a mix of three high-affinity VHHs (Nanobodies) targeting rabbit IgG, mouse IgG1, and mouse kappa light chains. This combination ensures broad compatibility with the most commonly used rabbit and mouse antibodies.
Whether you're performing routine IPs across various antibody subtypes or working with antibodies of unknown isotype, these beads offer a powerful, reliable alternative to protein A or protein G, delivering clean, efficient pulldowns with consistent performance.
| Target | Formats | Available Sizes | Specificity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rabbit / Mouse | Agarose | Magnetic agarose | 1ml, 2ml, 5ml | Rabbit IgG, Mouse IgG1, 2a*, 2b*, 3* *kappa light chain |
Co-IP of whole MCM-Complex via specific anti-MCM6 antibody
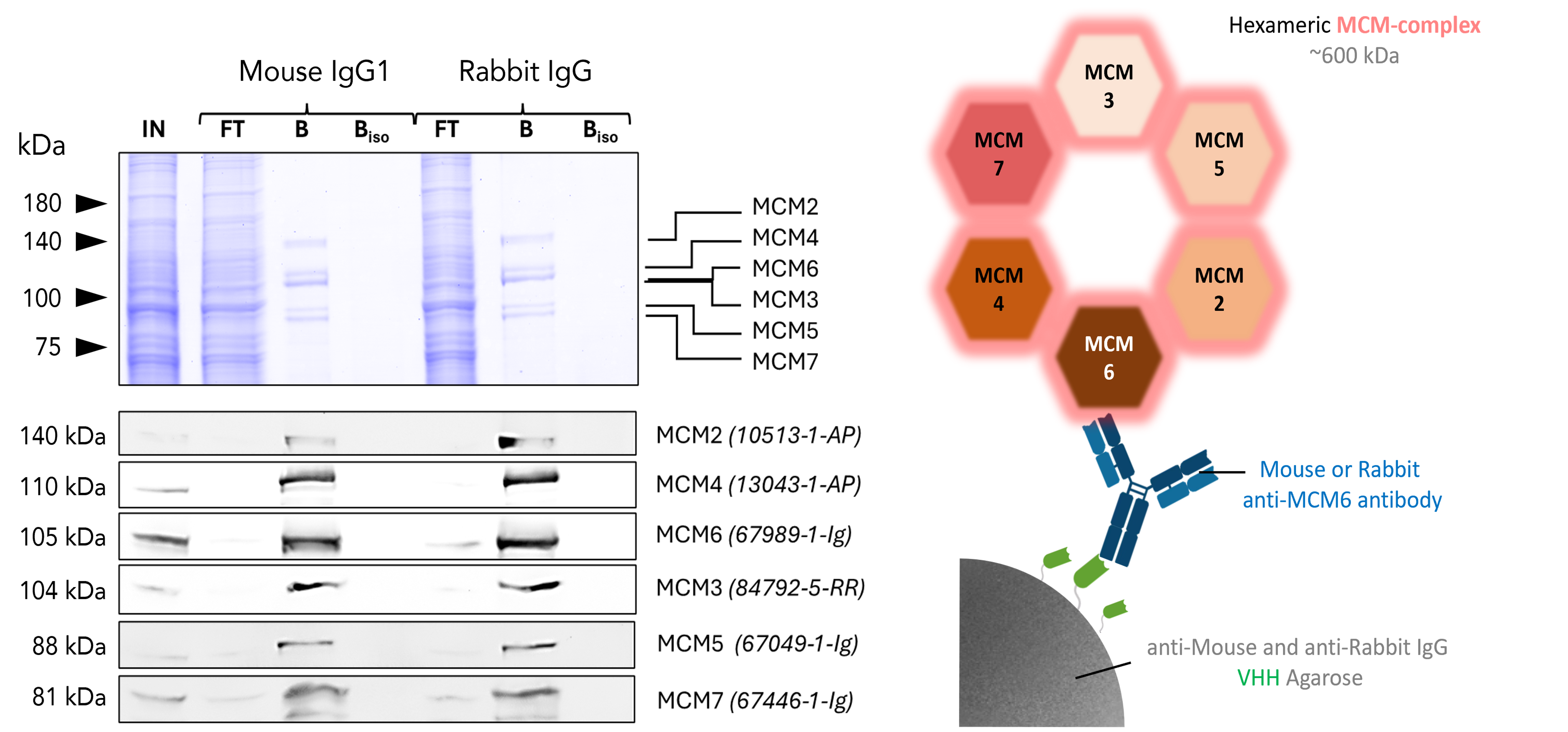
Co-IP of MCM complex via pulldown of MCM6 using 5 µg of anti-MCM6 antibodies and anti-rabbit IgG / anti-mouse IgG VHH agarose. All subunits of the 600 kDa hetero-hexameric complex are successfully precipitated using both a mouse IgG1 (67989-1-Ig) and a rabbit (13347-2-AP) MCM6 antibody, as shown by western blot analysis using subunit specific antibodies. Apparent molecular weights are provided. For input (IN) and flowthrough (FT) fractions, 1% was loaded. For bound (B) fraction and bound fraction of isotype control antibody (BISO), 20% was loaded. Product codes for PTG-antibodies are provided in parentheses. BISO is an isotype control used as negative control (ms1: 66260-1-Ig; rb: 30000-0-AP). Results were reproducible for anti-rabbit IgG/ anti-mouse IgG Magnetic VHH Agarose.
Species specificity of anti-rabbit IgG / anti-mouse IgG VHH agarose
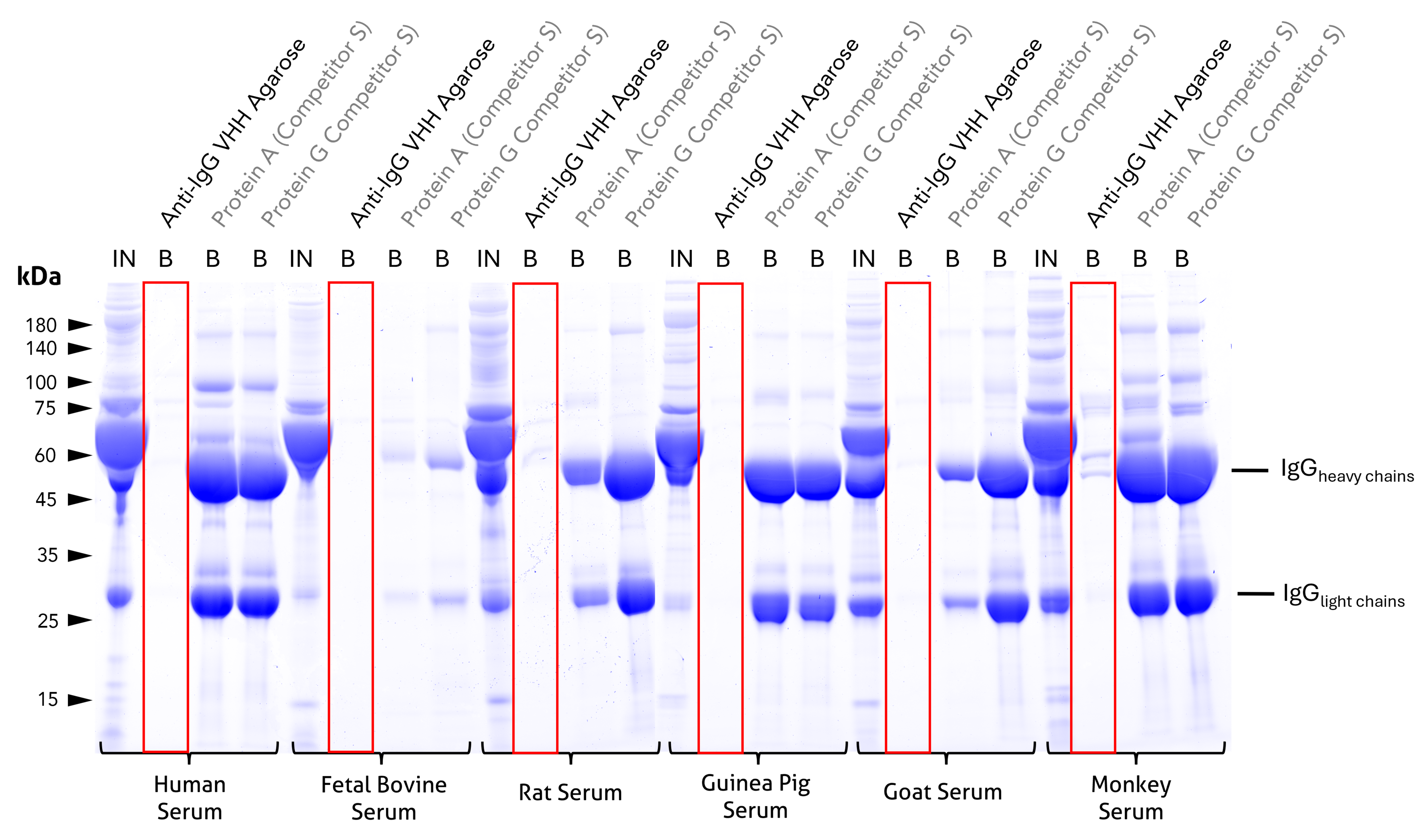
Cross-reactivity test and comparison to competitor Protein A and Protein G beads. Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel showing input (IN) and bound (B) fractions for different beads incubated with 1:10 diluted sera of relevant model species. Unlike the tested protein A or G beads, bound fractions of Proteintech anti-rabbit IgG / anti-mouse IgG VHH agarose reveal no cross-reactivity to human, bovine, rat, guinea pig, or goat IgGs and only minor cross-reactivity to cyno monkey IgGs. For IN and B fractions 1% and 25% were loaded, respectively. Lanes of anti-IgG VHH beads are highlighted red. Results were reproducible for anti-rabbit IgG/ anti-mouse IgG Magnetic VHH Agarose.
Clean precipitation and detection of PCNA with anti-rabbit IgG / anti-mouse IgG VHH beads using anti-PCNA antibody
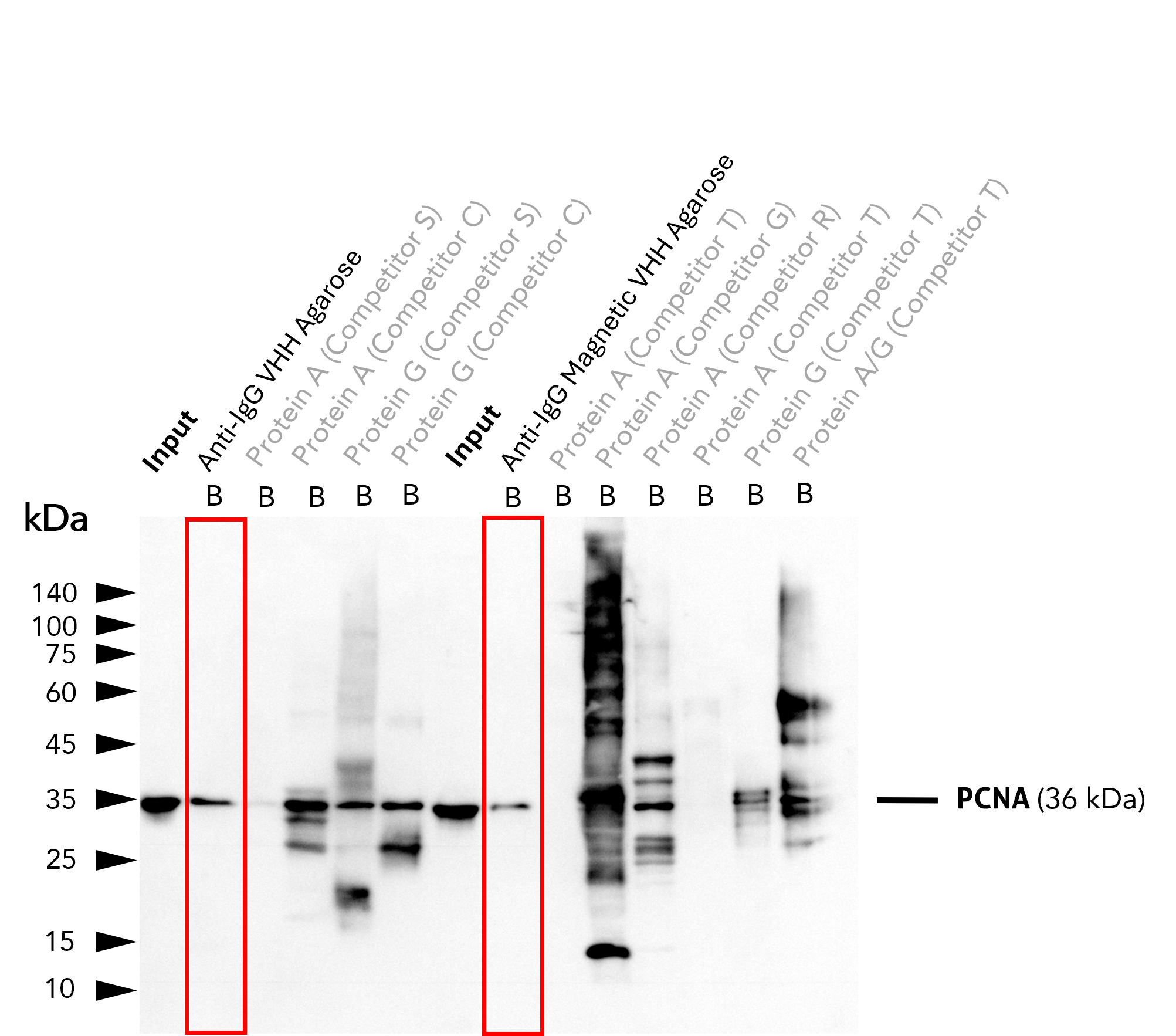
IP of PCNA using 5 µg of anti-PCNA antibody (IgG1, 60097-1-Ig) by anti-rabbit IgG / anti-mouse IgG VHH beads. For Western blot analysis, the PCNA polyclonal antibody (10205-2-AP, 1:2000) was labeled using a conformation-specific HRP-conjugated secondary to avoid staining of heavy and light chain of the IP-antibody. In contrast to many competitors' protein A and G beads, clean pull-down of PCNA by Proteintech anti-rabbit IgG/ anti-mouse IgG VHH Beads (Ag. = Agarose; M.Ag. = Magnetic Agarose) facilitates unambiguous identification of the target protein. Other beads show leaching of protein A or protein G fragments into the final IP fractions, which can lead to binding of the detection antibody and unspecific signals, as reported previously (Grant et al., 2019, Biol Proced Online, doi: 10.1186/s12575-019-0095-z). For input (IN) and bound (B) fractions, 1% and 30% were loaded, respectively. Lanes of anti-IgG VHH beads are highlighted in red.
VHH Agarose
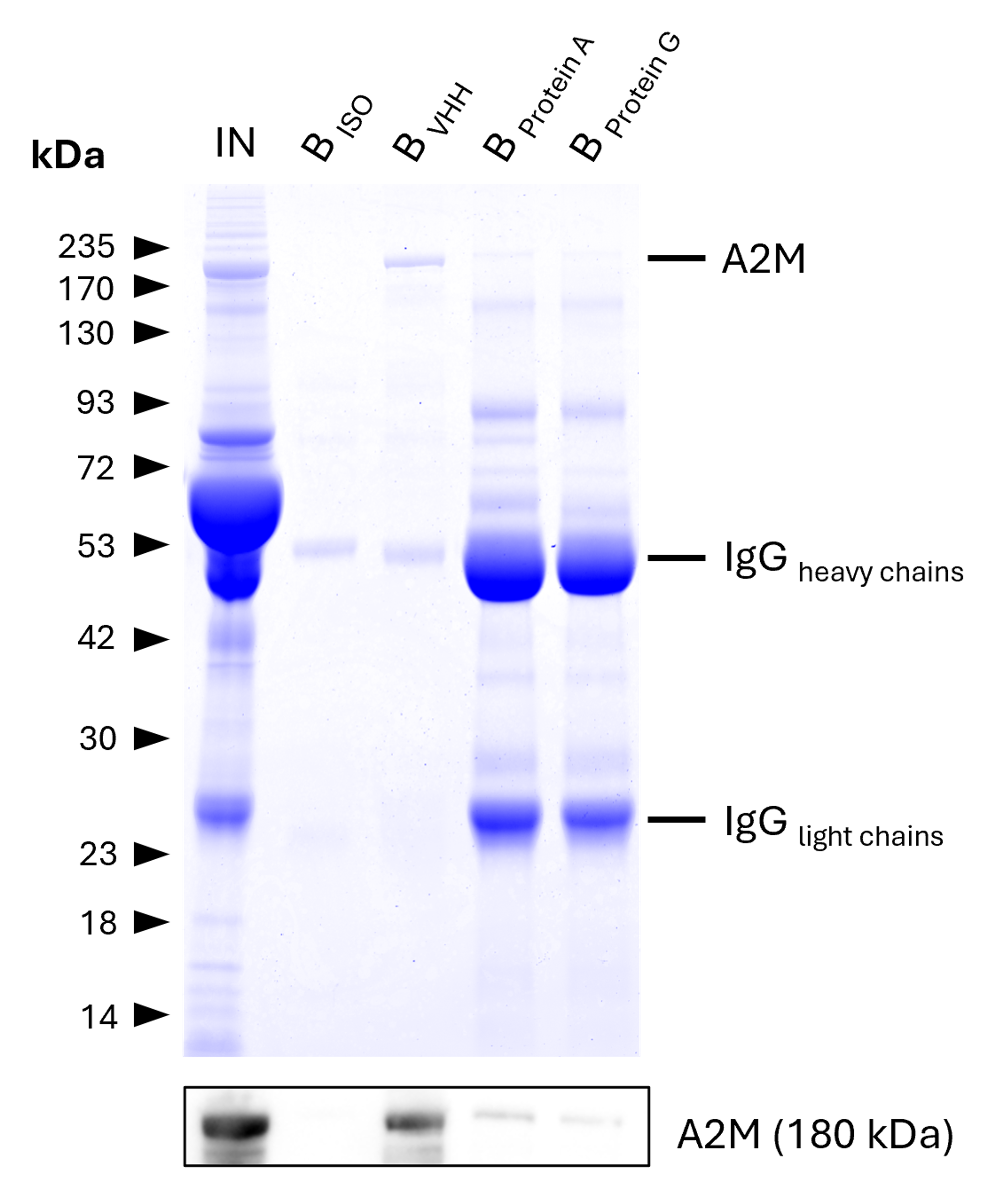
IP of Alpha-2-Macroglobulin (A2M) from human serum using anti-rabbit IgG / anti-mouse IgG VHH Agarose and comparison to Protein A and G beads. IP was performed using 5 μg of rabbit anti-A2M IgG (13545-1-AP) in 1:10 diluted human serum. 0.5% and 6.25% of input (IN) and bound (B) fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, respectively. 5 μg of rabbit isotype control antibody (BISO, 98136-1-RR) was used as negative control. The Coomassie-stained gel shows precipitation of A2M by anti-rabbit IgG / anti-mouse IgG VHH agarose and reveals its absence for ´protein A and G beads. This is likely due to human IgGs competing with the spiked IP-antibody for the latter beads. Results were verified using Western blot analysis, which detected A2M at approximately 180 kDa using an anti-A2M primary IgG (13545-1-AP, 1:5000). Data was reproducible for anti-rabbit IgG / anti-mouse IgG magnetic VHH agarose.
Binding efficiency – Agarose
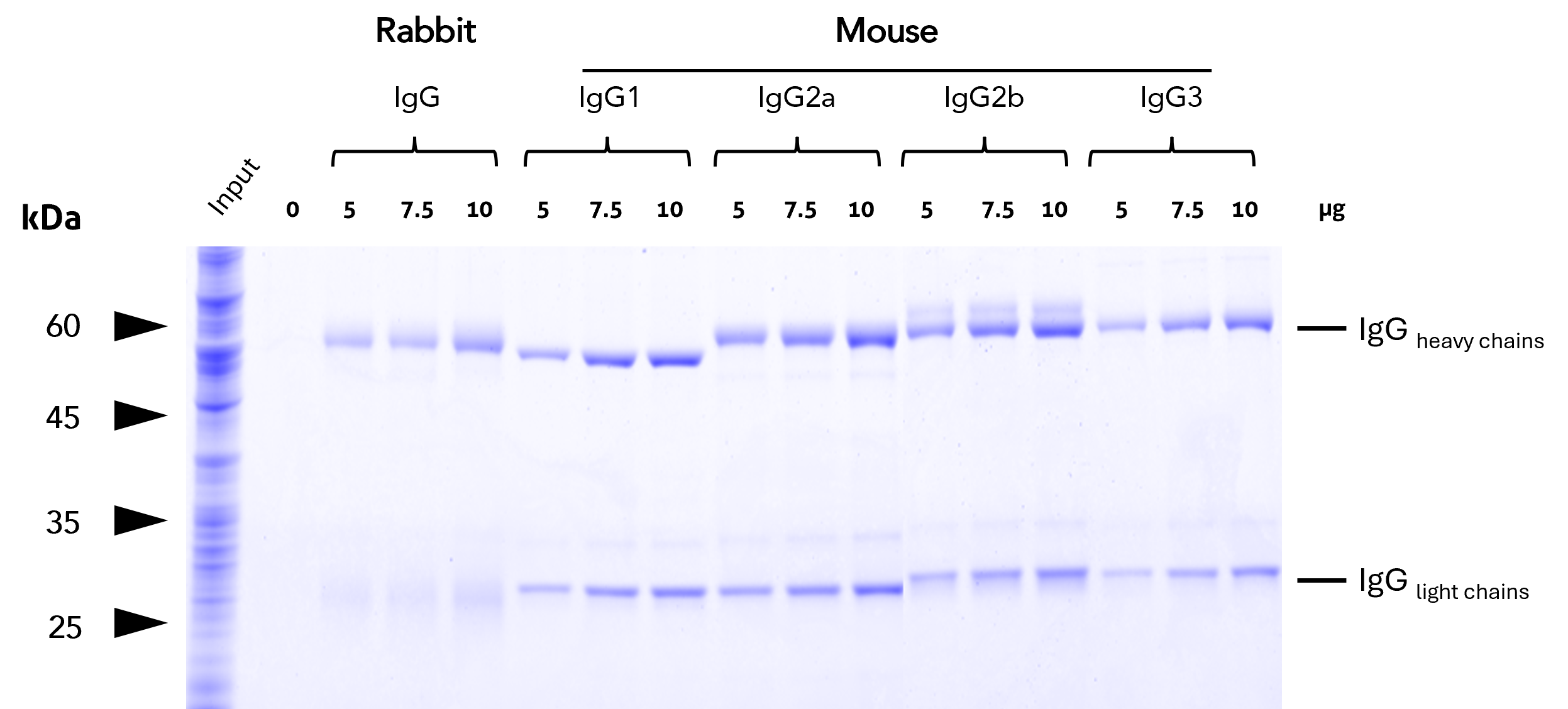
Binding efficiency and specificity of anti-rabbit IgG / anti-mouse IgG VHH agarose for rabbit and mouse IgG subclasses. Binding of antibodies of different subtypes was tested at increasing concentrations from HEK293T cell lysate. The high capacity of the anti-IgG VHH beads allows for efficient binding of all IgGs tested.
Binding efficiency – Magnetic agarose
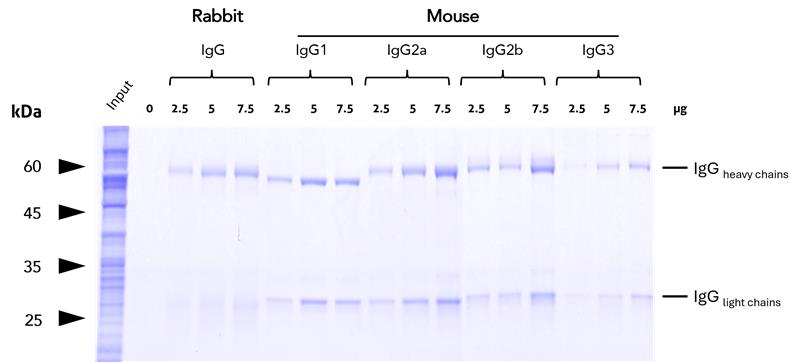
Binding efficiency and specificity of anti-rabbit IgG / anti-mouse IgG magnetic VHH agarose for rabbit and mouse IgG subclasses. Binding of antibodies of different subtypes was tested at increasing concentrations from HEK293T cell lysate. The high capacity of the anti-IgG VHH beads allows for efficient binding of all IgGs tested.
Magnetic VHH agarose
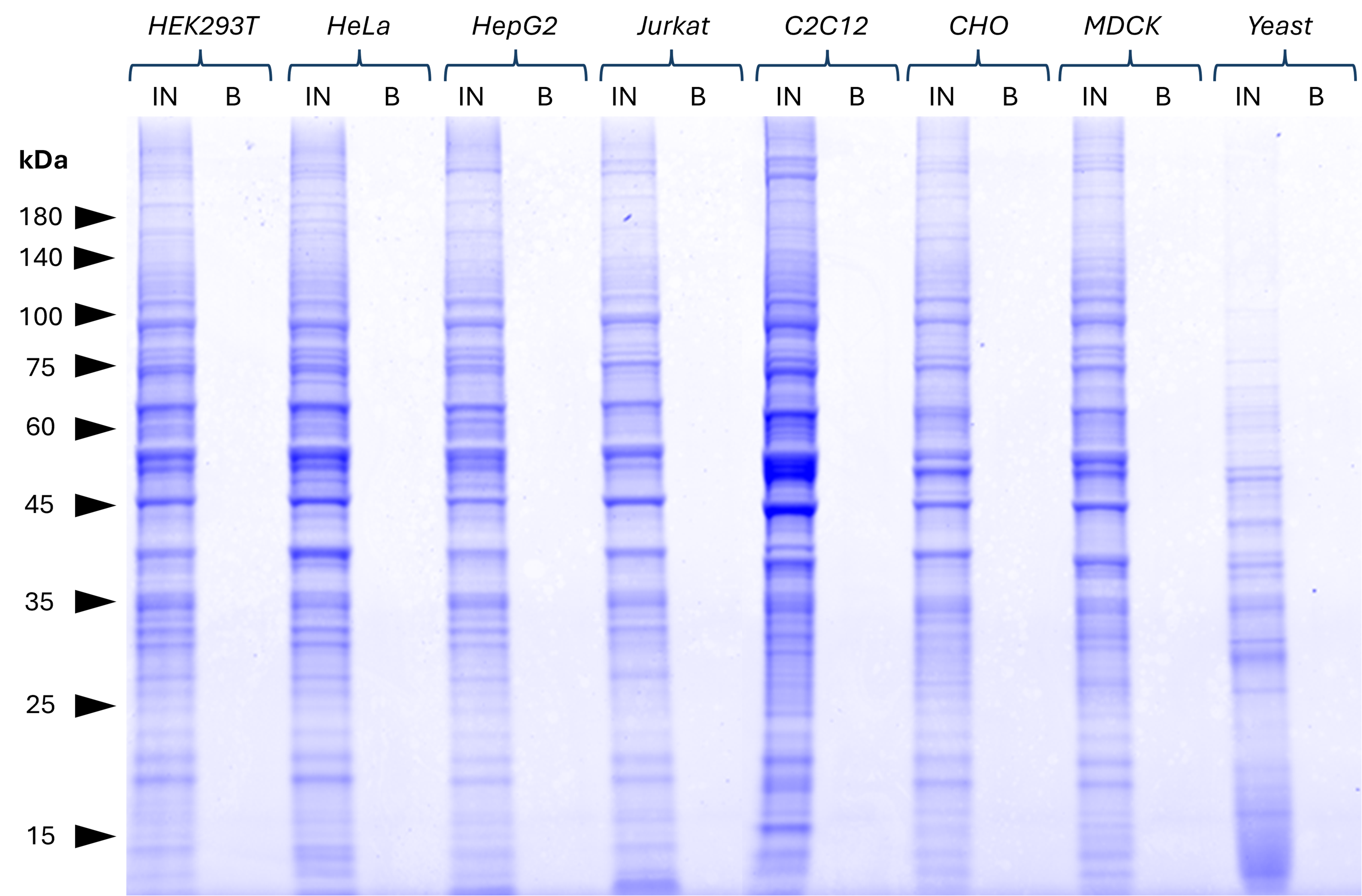
No background binding of anti-rabbit IgG/ anti-mouse IgG magnetic VHH agarose in commonly used cell lines. Various cell lysates (derived from 1x107 cells) were tested for non-specific binding to the beads. Clean backgrounds were observed in bound (B) fractions of the Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel for all lysates. This indicates that no significant non-specific binding occurs. 25% of B fraction and 1% of Input (IN) fractions were loaded. HEK293T, HeLa, HepG2, Jurkat: Human; C2C12: Mouse; CHO: Hamster; MDCK: Canine; Yeast: Fungi. Results were reproducible for anti-rabbit IgG / anti-mouse IgG VHH agarose.
Magnetic VHH agarose
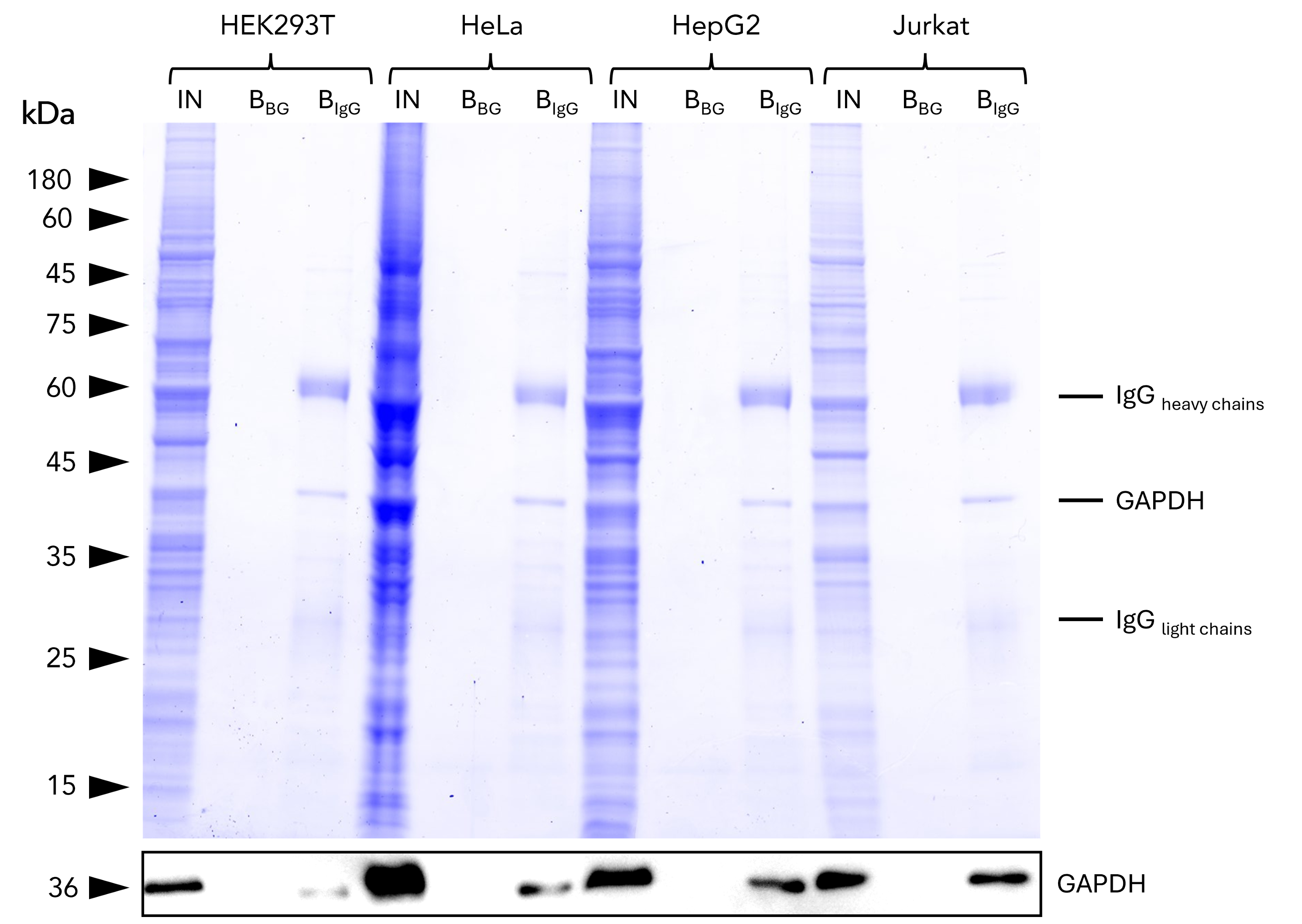
IP of GAPDH from common human cell lines using anti-rabbit IgG/ anti-mouse IgG magnetic VHH agarose. IP was performed using 5 μg of rabbit anti-GAPDH IgG (10494-1-AP) with 1x107 cells used per IP reaction. 1% and 25% of input (IN) and bound (B) fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, respectively. Bound fractions without antibody spiked (BBG) are shown as background control. The Coomassie-stained gel shows precipitation of GAPDH by anti-rabbit IgG / anti-mouse IgG magnetic VHH agarose, what was verified using Western blot analysis using the anti-GAPDH mouse monoclonal antibody (60004-1-Ig). Results are reproducible for anti-rabbit IgG / anti-mouse IgG VHH agarose.