- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
CEBPB Polyklonaler Antikörper
CEBPB Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus und mehr (1)
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, CoIP, ChIP, RIP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 23431-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
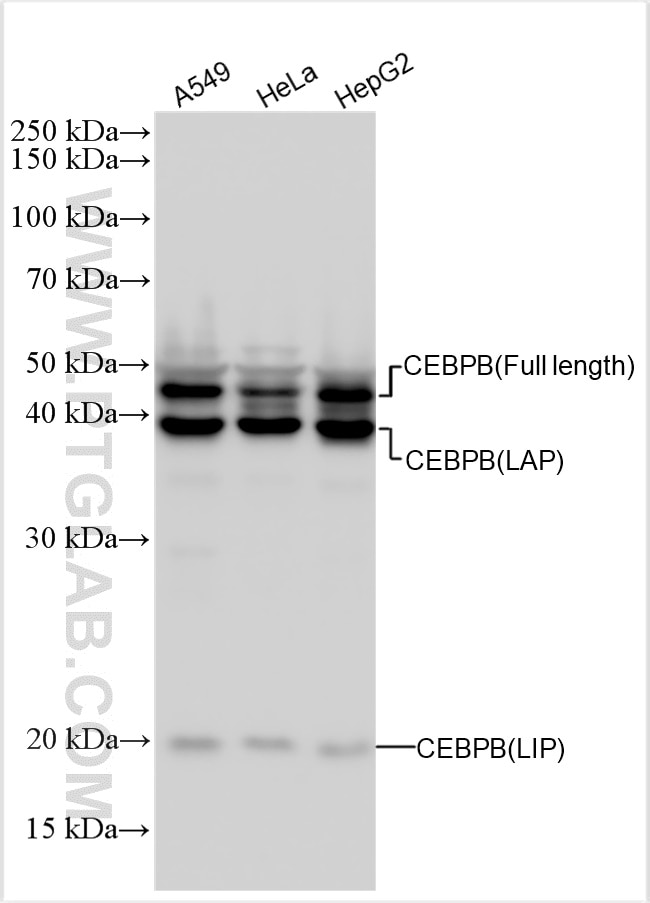
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | A549-Zellen, HeLa-Zellen, HepG2-Zellen |
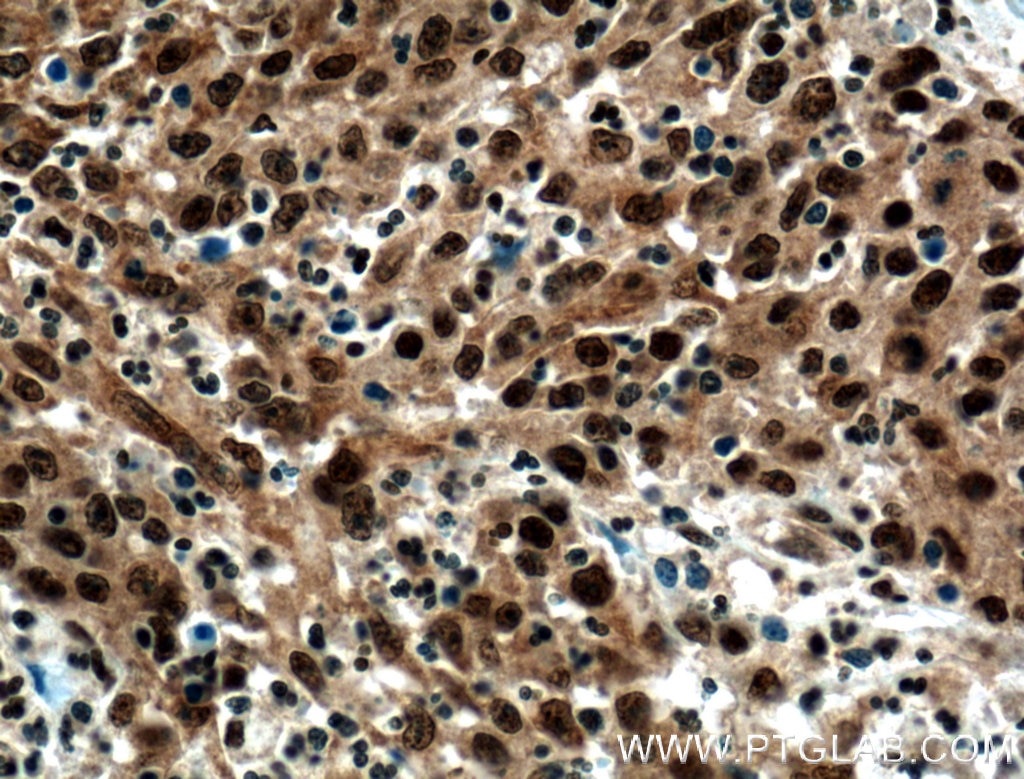
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Kolonkarzinomgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
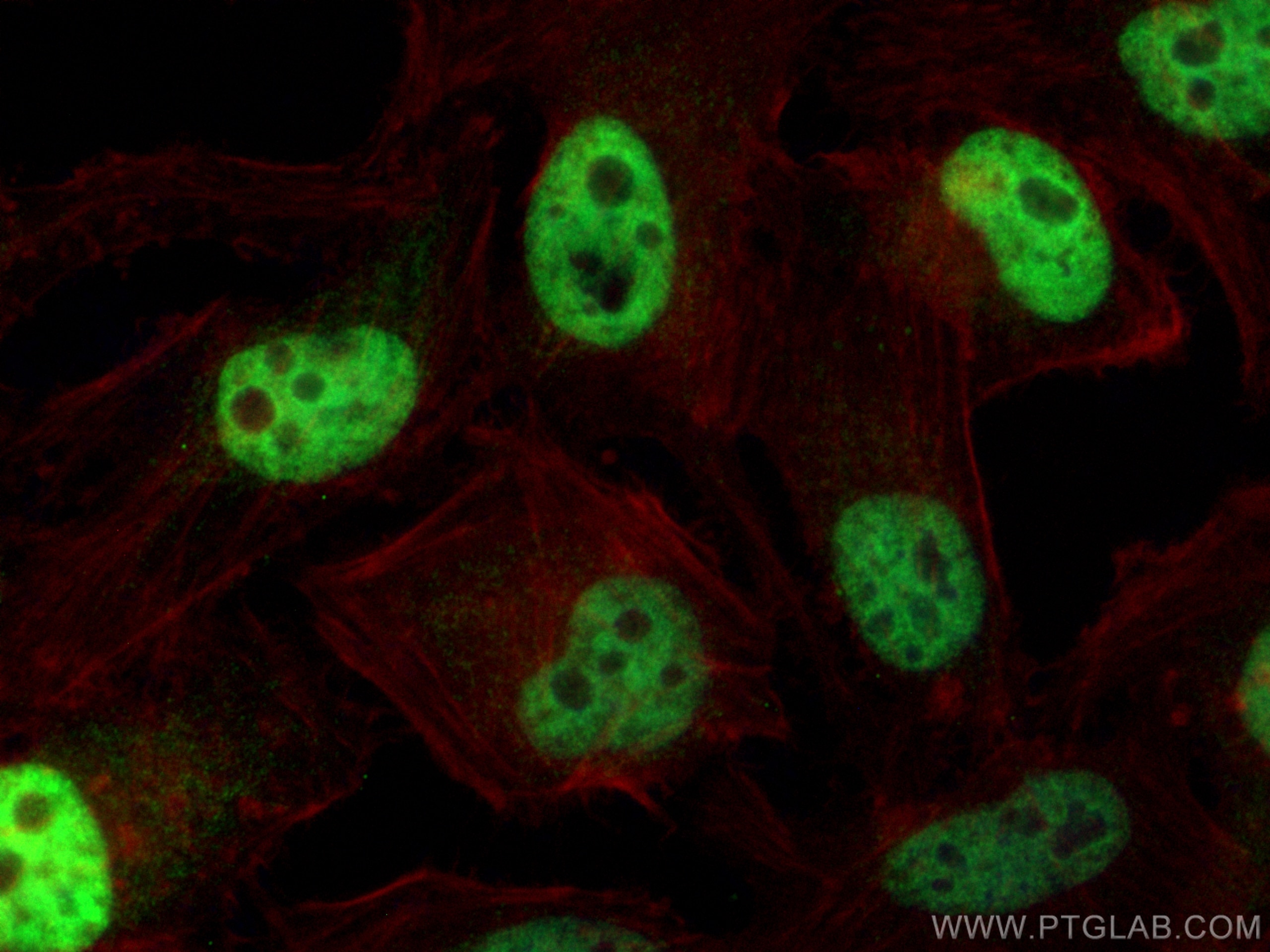
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | HeLa-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 4 publications below |
| WB | See 37 publications below |
| IHC | See 5 publications below |
| IF | See 6 publications below |
| CoIP | See 3 publications below |
| ChIP | See 10 publications below |
| RIP | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
23431-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, CoIP, ChIP, RIP, ELISA CEBPB und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | CEBPB fusion protein Ag20073 |
| Vollständiger Name | CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), beta |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 345 aa, 36 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 42 kDa,46 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC007538 |
| Gene symbol | CEBPB |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1051 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (CEBPB), also known as LAP, is a important transcriptional activator in the regulation of genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses. It specifically binds to an IL-1 response element in the IL-6 gene. CEBPb mRNAs possess alternative translation-initiation codons, which result in the formation of truncated forms of the protein.Three variants of CEBPBs have been detected: a 46 kDa full-length liver-enriched transcription-activating protein (LAP1), a 42 kDa LAP2 and a 20 kDa liver-enriched transcription-inhibitory protein (LIP). (PMID:18820298). This antibody is specific to CEBPB.
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for CEBPB antibody 23431-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for CEBPB antibody 23431-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IF protocol for CEBPB antibody 23431-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Adv Sci (Weinh) HIPK1 Inhibition Protects against Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy by Inhibiting the CREB-C/EBPβ Axis | ||
J Immunother Cancer YY1 complex in M2 macrophage promotes prostate cancer progression by upregulating IL-6 | ||
Cardiovasc Diabetol NLRP3 inflammasome-modulated angiogenic function of EPC via PI3K/ Akt/mTOR pathway in diabetic myocardial infarction | ||
Aging (Albany NY) Functional rare variant in a C/EBP beta binding site in NINJ2 gene increases the risk of coronary artery disease.
| ||
Int J Mol Sci ERK1/2-CEBPB Axis-Regulated hBD1 Enhances Anti-Tuberculosis Capacity in Alveolar Type II Epithelial Cells | ||
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol The paracrine isthmin1 transcriptionally regulated by C/EBPβ exacerbates pulmonary vascular leakage in murine sepsis |