- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
Cytokeratin 13 Polyklonaler Antikörper
Cytokeratin 13 Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus und mehr (1)
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 10164-2-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | A431-Zellen, Maushautgewebe |
| Erfolgreiche IP | A431-Zellen |
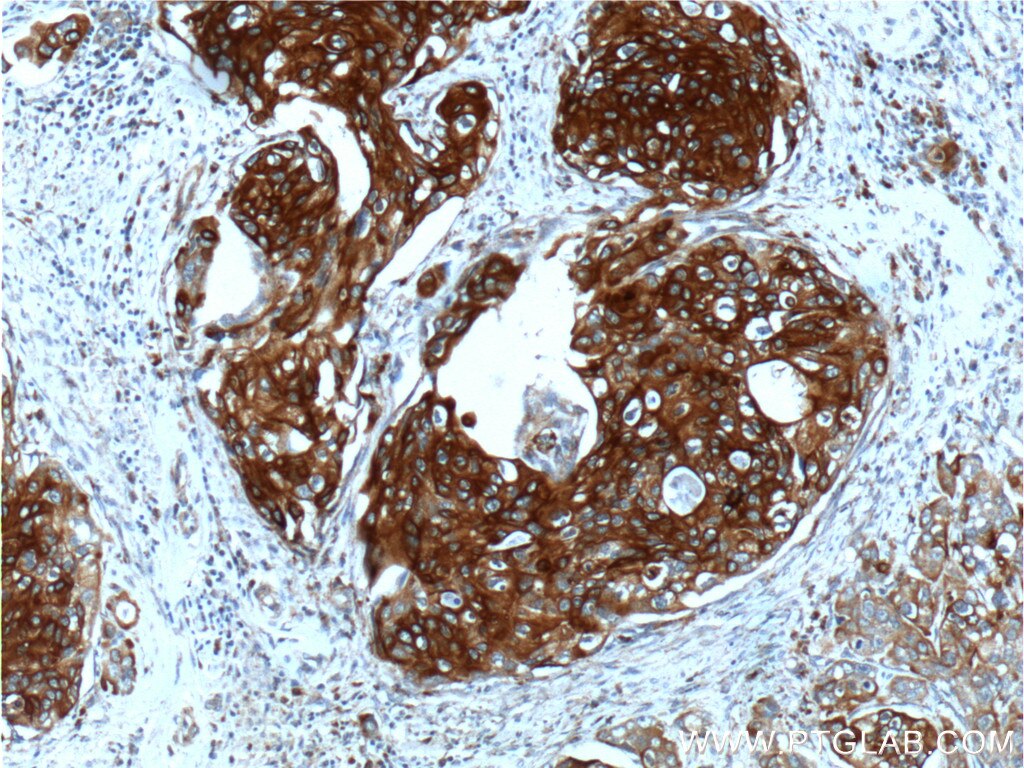
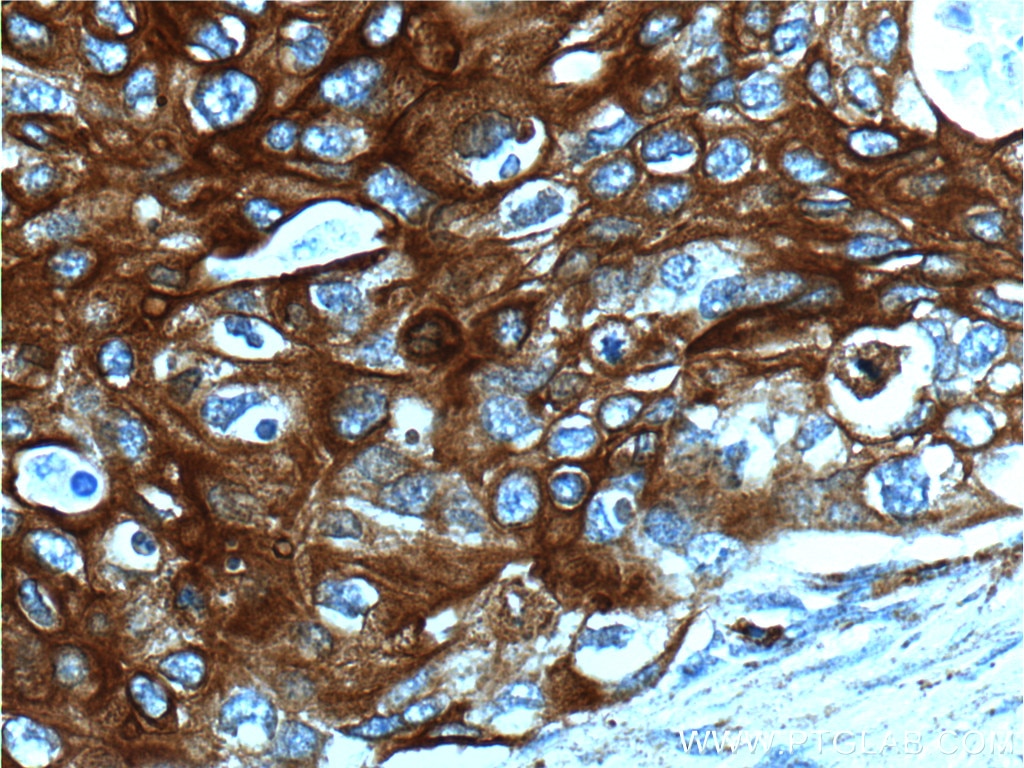
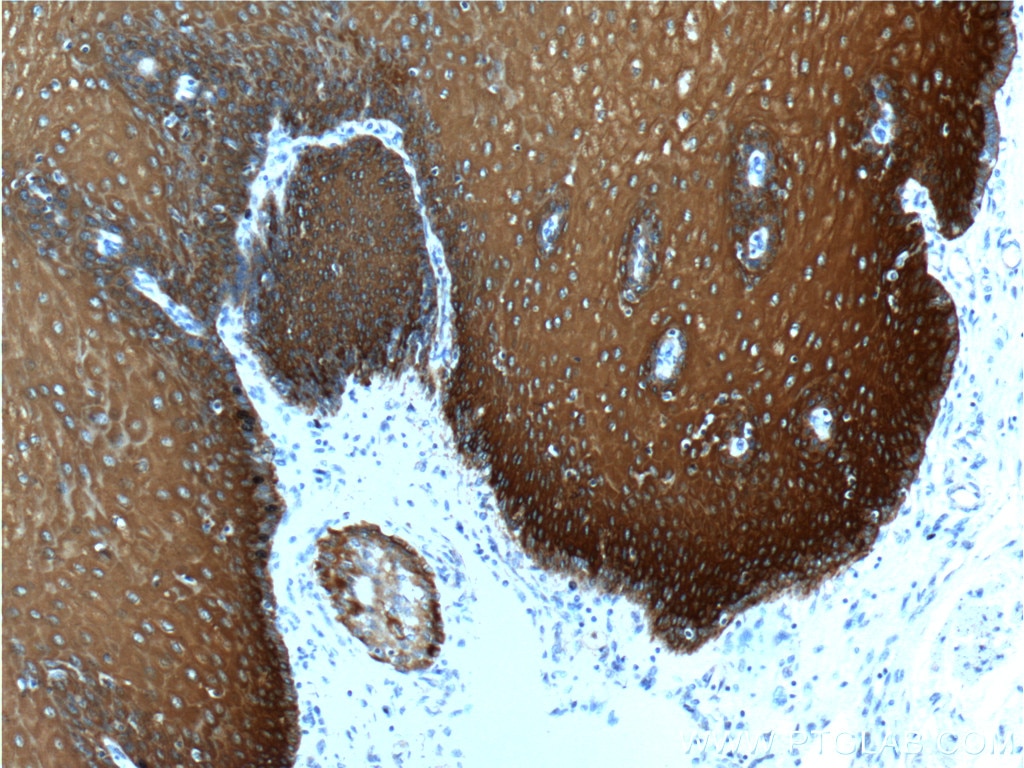
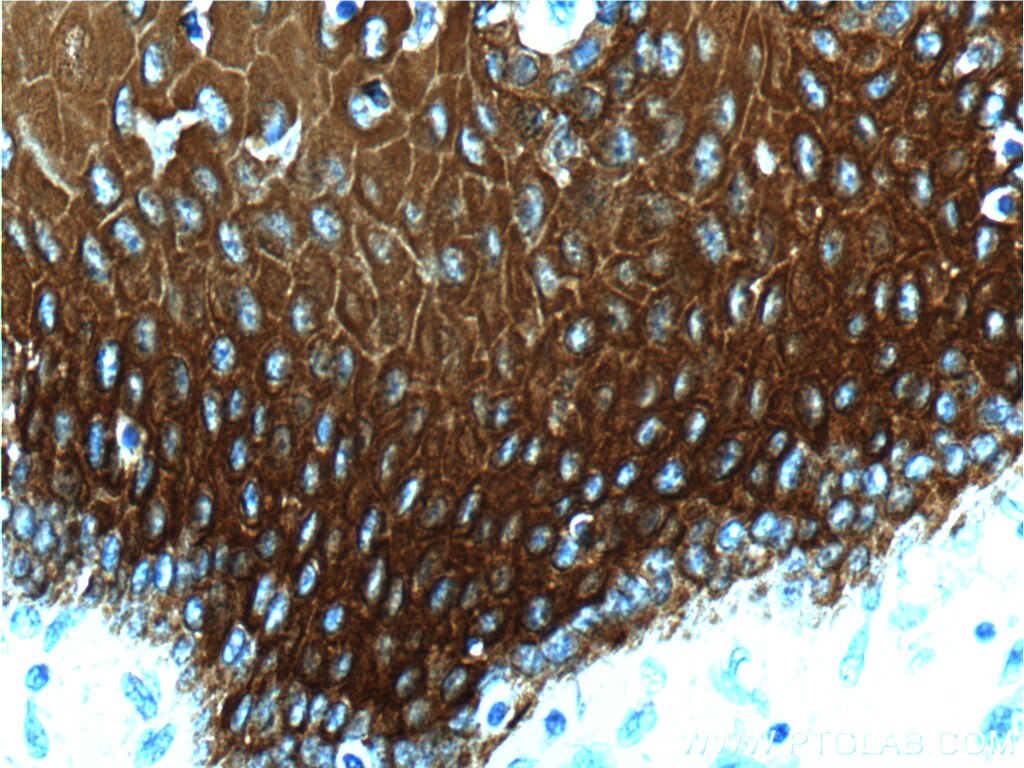
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Zervixkarzinomgewebe, humanes Ösophagusgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
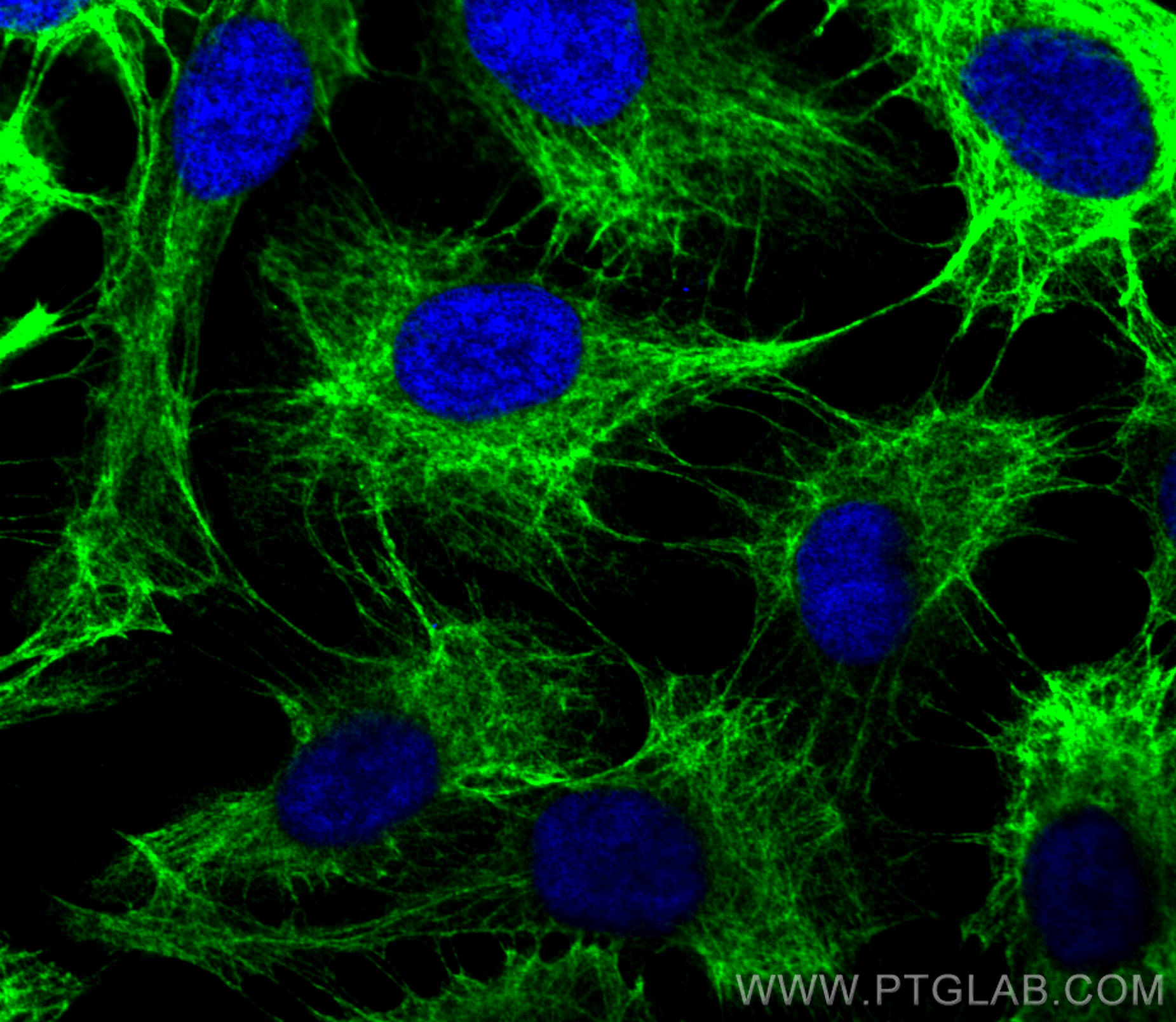
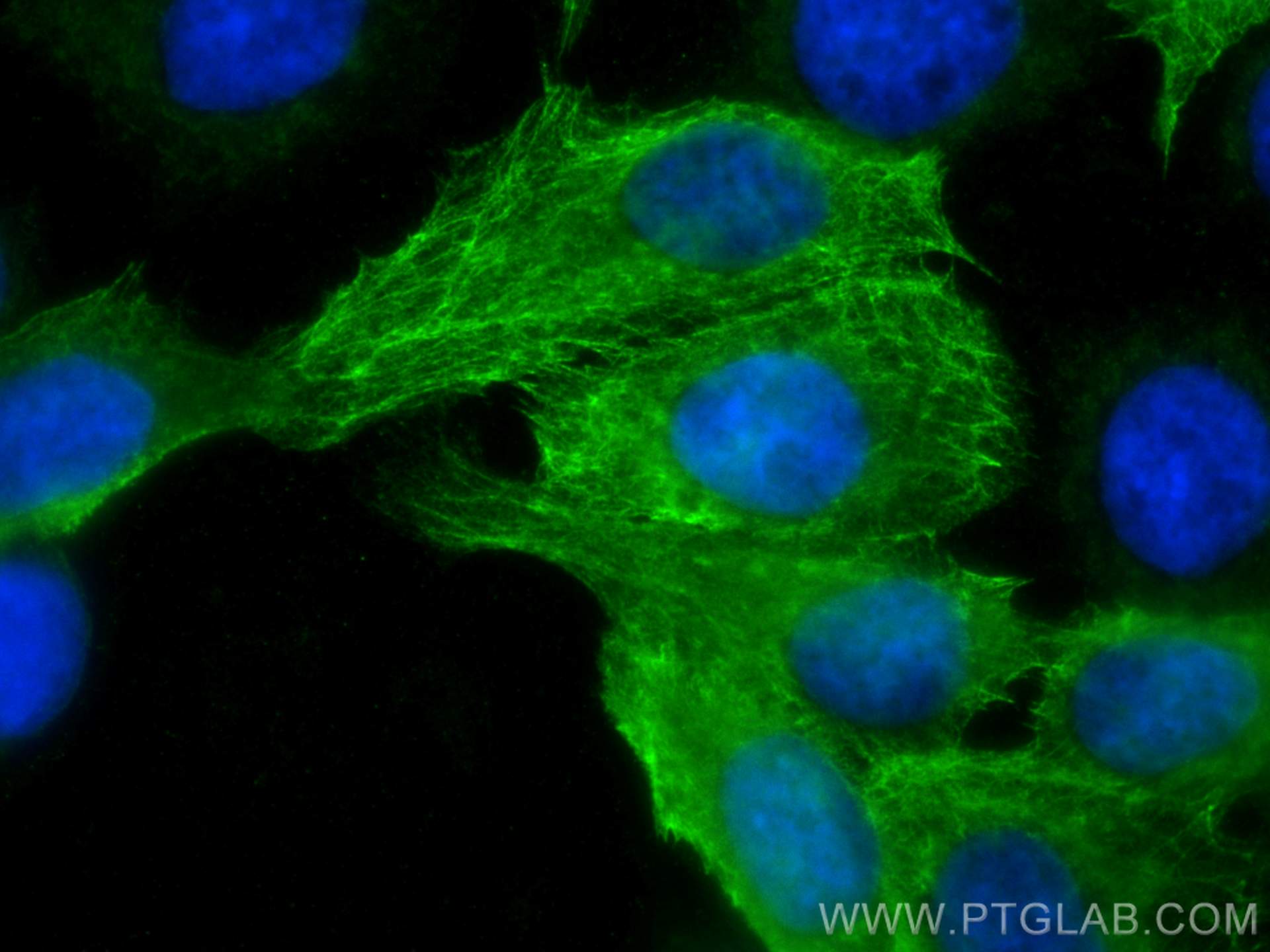
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | HaCaT-Zellen, A431-Zellen |
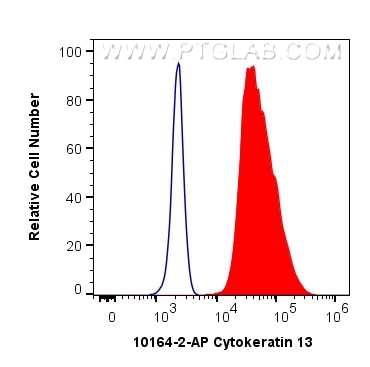
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in FC (Intra) | A431-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:10000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Durchflusszytometrie (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 6 publications below |
| IHC | See 5 publications below |
| IF | See 14 publications below |
Produktinformation
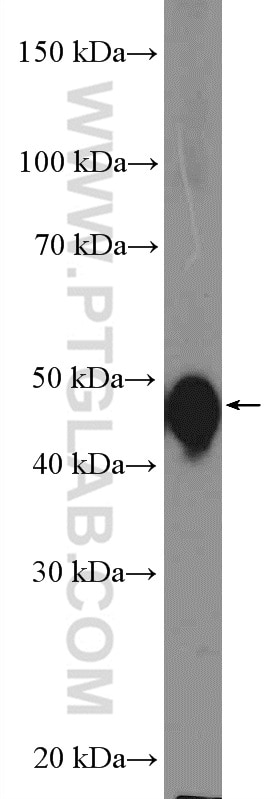
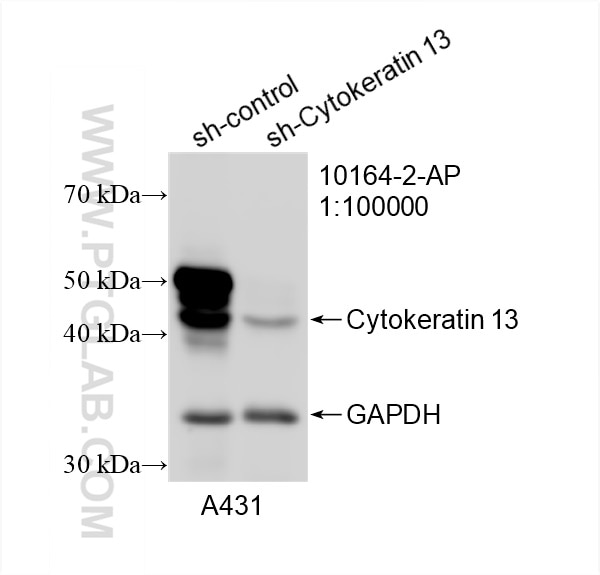
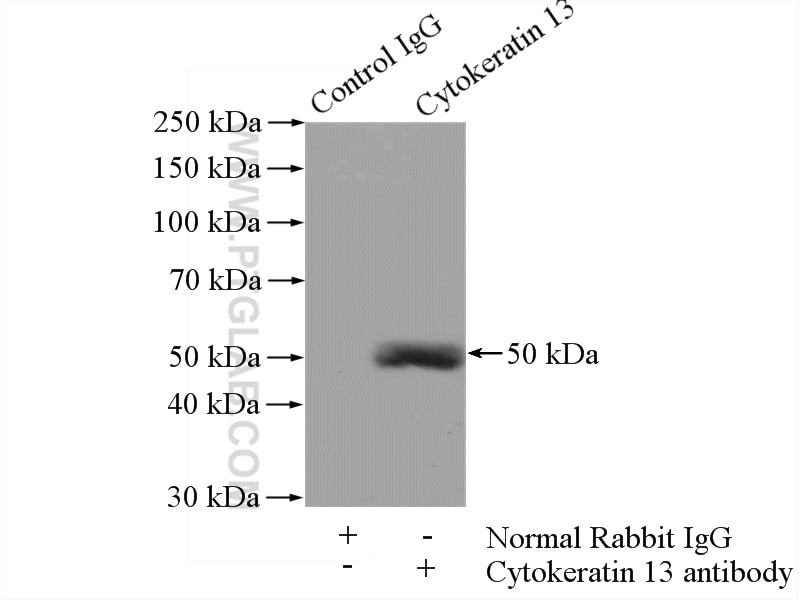
10164-2-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA Cytokeratin 13 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Affe, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Cytokeratin 13 fusion protein Ag0217 |
| Vollständiger Name | keratin 13 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 50 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 50 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC002661 |
| Gene symbol | Cytokeratin 13 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3860 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Keratin 13 is a member of the keratin family. The keratins are intermediate filament proteins responsible for the structural integrity of epithelial cells and are subdivided into cytokeratins and hair keratins. Most of the type I cytokeratins consist of acidic proteins which are arranged in pairs of heterotypic keratin chains. This type I cytokeratin is paired with keratin 4 and expressed in the suprabasal layers of non-cornified stratified epithelia. Mutations in keratin 13 gene and keratin 4 have been associated with the autosomal dominant disorder White Sponge Nevus. The type I cytokeratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 17q21.2.
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Cytokeratin 13 antibody 10164-2-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for Cytokeratin 13 antibody 10164-2-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IF protocol for Cytokeratin 13 antibody 10164-2-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IP protocol for Cytokeratin 13 antibody 10164-2-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Theranostics Differential effect of cancer-associated fibroblast-derived extracellular vesicles on cisplatin resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-876-3p | ||
Elife Chloride channels regulate differentiation and barrier functions of the mammalian airway. | ||
Cell Commun Signal Liprin-α1 modulates cancer cell signaling by transmembrane protein CD82 in adhesive membrane domains linked to cytoskeleton. | ||
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol Do airway epithelium air-liquid cultures represent the in vivo airway epithelium transcriptome? | ||
Stem Cells Int Pyridoxal-5'-Phosphate Promotes Immunomodulatory Function of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase-1 and TLR4/NF-κB Pathway. |