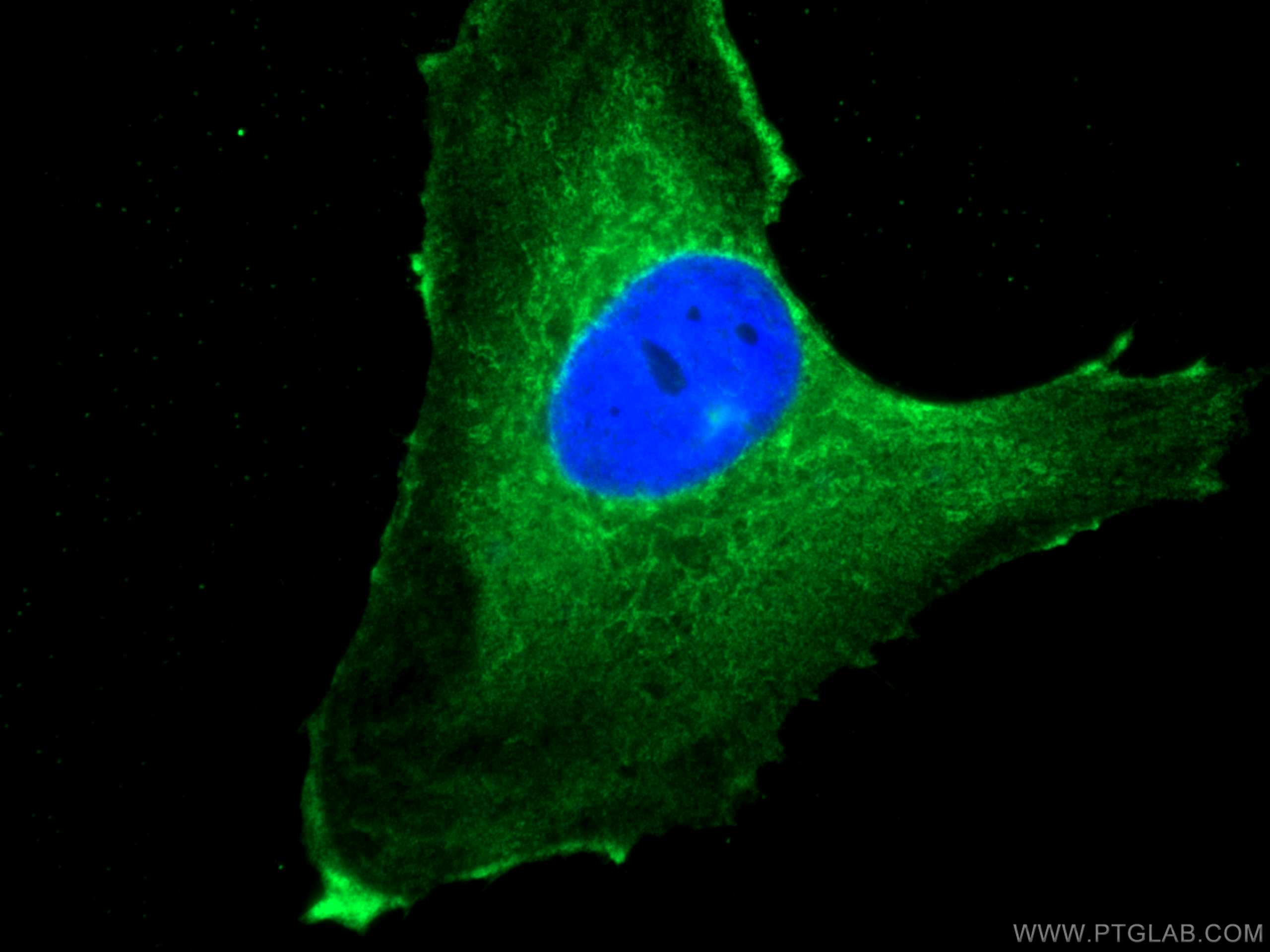
NEU1 Monoklonaler Antikörper
NEU1 Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG1
Getestete Reaktivität
Hausschwein, human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
1F6D1
Kat-Nr. : 67032-1-Ig
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
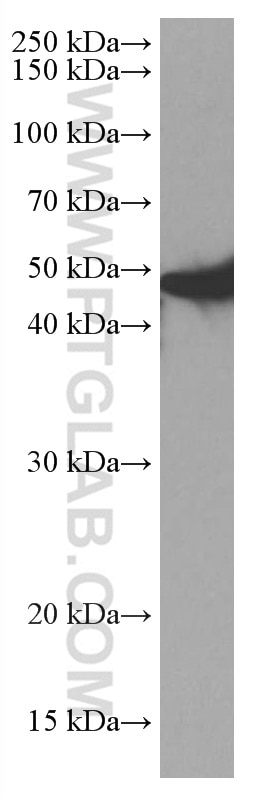
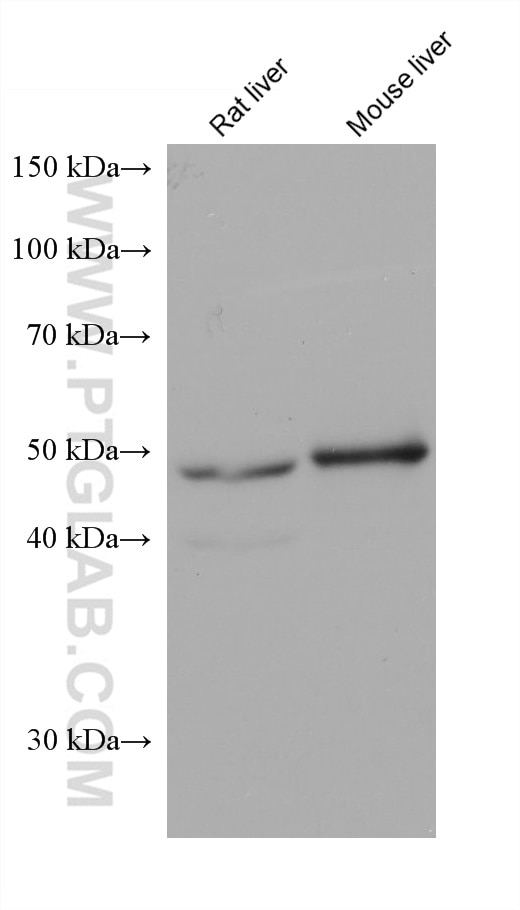
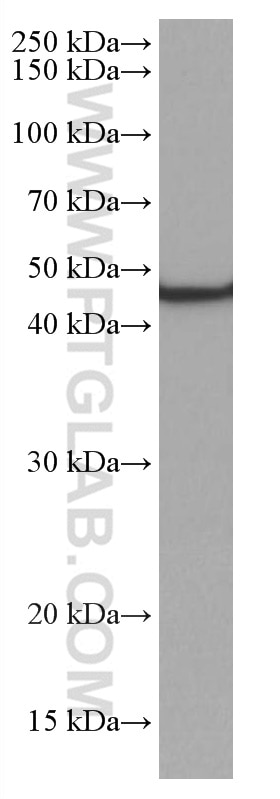
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | PC-12-Zellen, Mauslebergewebe, Hausschwein-Lebergewebe, Rattenlebergewebe, Ratten-Pankreasgewebe |
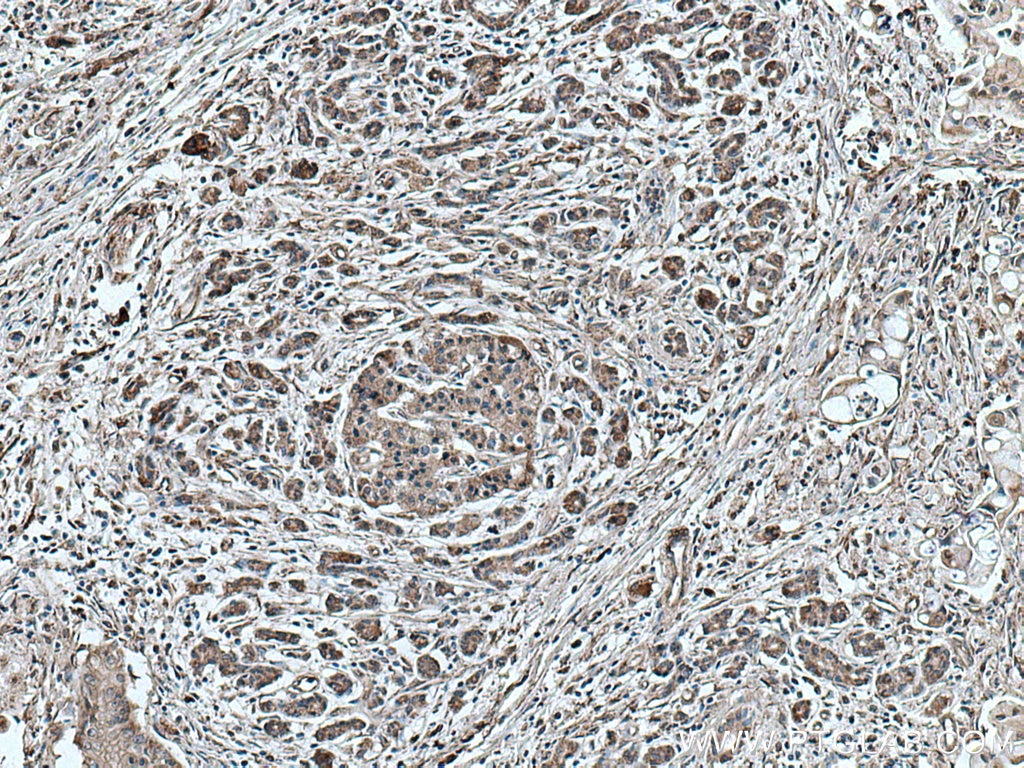
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Pankreaskarzinomgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | U-251-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:150-1:600 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 5 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 3 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
67032-1-Ig bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA NEU1 und zeigt Reaktivität mit Hausschwein, human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | Hausschwein, human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG1 |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | NEU1 fusion protein Ag27945 |
| Vollständiger Name | sialidase 1 (lysosomal sialidase) |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 45 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 45-48 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC011900 |
| Gene symbol | NEU1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4758 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-G-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
NEU1 (lysosomal sialidase) encodes a kind of lysosomal enzyme that could cleave terminal silic acids from glycoproteins or glycolipids to regulate various biological processes by conformational change (PMID:28130415). In the lysosome, NEU1 is one member of a heterotrimeric complex, the others are beta-galactosidase and cathepsin A. The NEU1 is widely expressed in mammalian tissues and involved in lysosomal storage disorder sialidosis, autoimmune diseases and the malignancy and metastasis of cancer cells (PMID:19075514). NUE1 also expresses on the plasma membrane where it modulates several signalling molecules about inflamation, exocytosis, phagocytosis, cell adhesion and proliferation (PMID:21928149). Addition, it is reported that mutation in NEU1 of human could lead to sialidosis (PMID:14517945).
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for NEU1 antibody 67032-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for NEU1 antibody 67032-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IF protocol for NEU1 antibody 67032-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci Long non-coding RNA TOB1-AS1 modulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion through miR-23a/NEU1 axis via Wnt/b-catenin pathway in gastric cancer. | ||
Br J Pharmacol Neuraminidase is a host-directed approach to regulate neutrophil responses in sepsis and COVID-19 | ||
Biomed Pharmacother Oseltamivir enhances 5-FU sensitivity in esophageal squamous carcinoma with high SPNS1 | ||
Virology H1N1 swine influenza viruses upregulate NEU1 expression through histone H3 acetylation regulated by HDAC2 | ||
Research (Wash D C) Proteogenomic Characterization of High-Grade Lung Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Deciphers Molecular Diversity and Potential Biomarkers of Different Histological Subtypes in Chinese Population |