UBE3A Monoklonaler Antikörper
UBE3A Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG1
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus
Anwendung
WB, IHC, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
3D6H9
Kat-Nr. : 60038-1-Ig
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
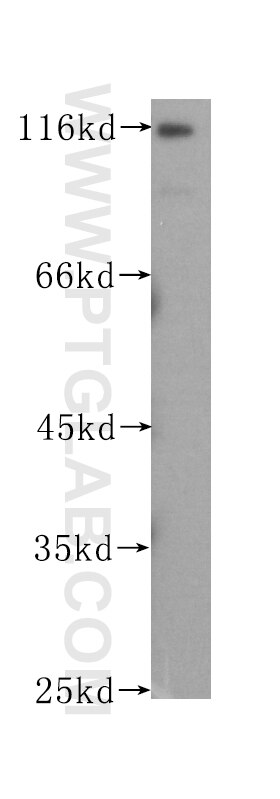
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HeLa-Zellen |
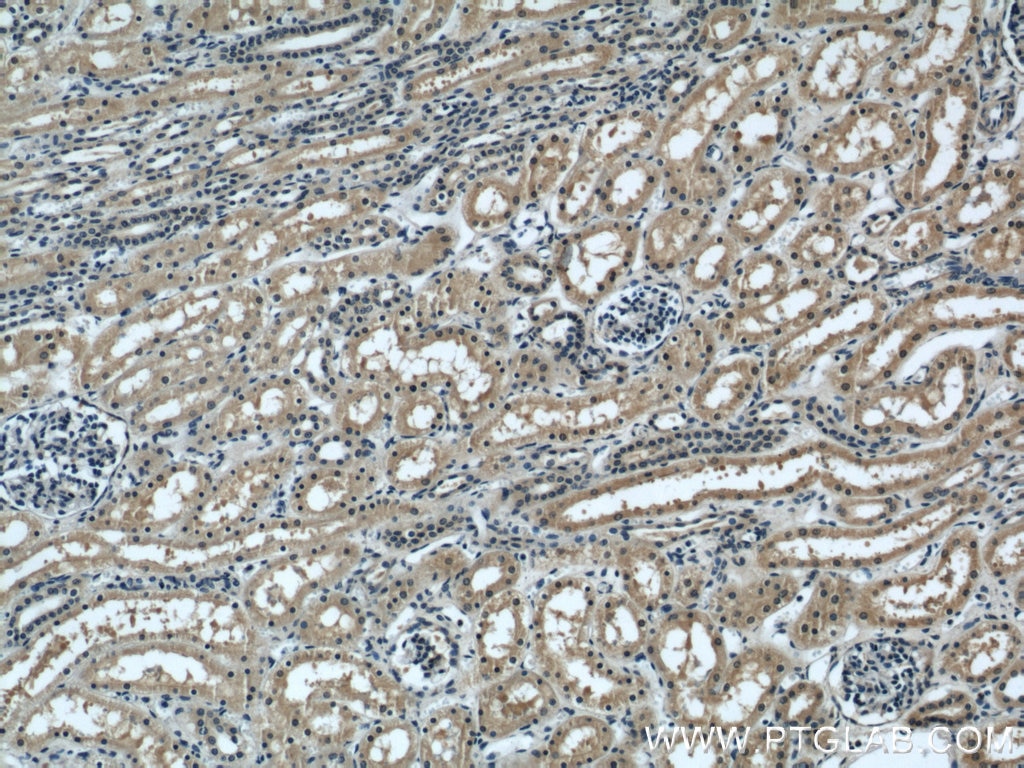
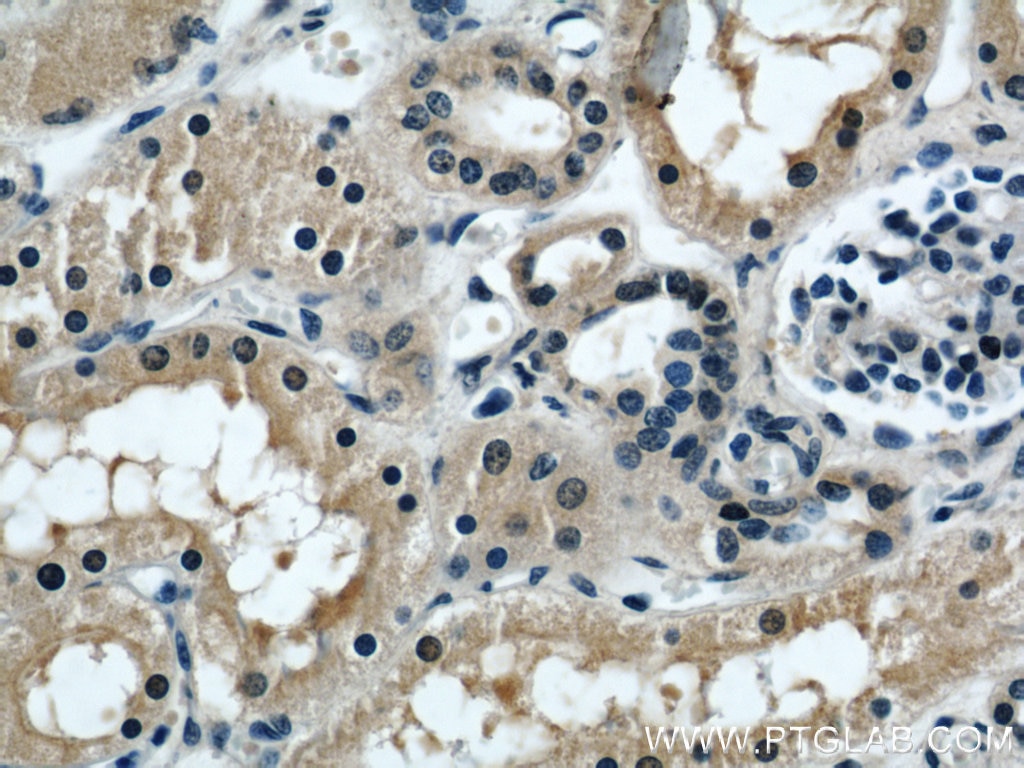
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Nierengewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:200-1:1000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:400 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Produktinformation
60038-1-Ig bindet in WB, IHC, ELISA UBE3A und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG1 |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | UBE3A fusion protein Ag0346 |
| Vollständiger Name | ubiquitin protein ligase E3A |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 852 aa, 98 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 100 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC002582 |
| Gene symbol | UBE3A |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7337 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-G-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
UBE3A(Ubiquitin-protein ligase E3A) is also named as E6AP, EPVE6AP, HPVE6A and belongs to the E3 ubiquitin protein ligase family. It functions as both an E3 ligase in the ubiquitin proteasome pathway and as a transcriptional coactivator. It is also initially identified as a cellular protein that mediates in vitro association of the human papillomavirus E6 protein with p53, leading to the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of p53(PMID:1661671). Defects in UBE3A are a cause of Angelman syndrome (AS)(PMID:10508479 ). It has 3 isoforms produced by alternative splicing.