VAMP8 Polyklonaler Antikörper
VAMP8 Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF, IP, CoIP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 15546-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
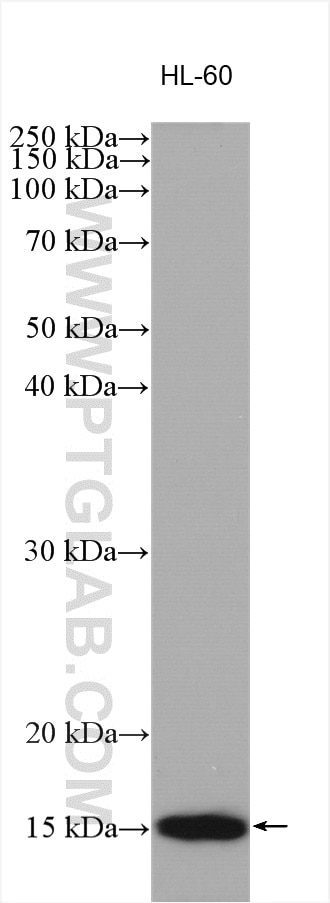
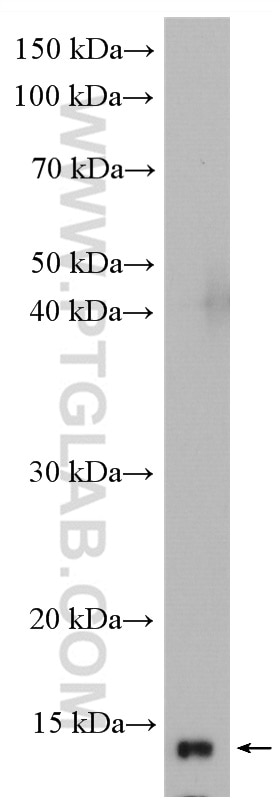
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HL-60-Zellen, PC-12-Zellen, THP-1-Zellen |
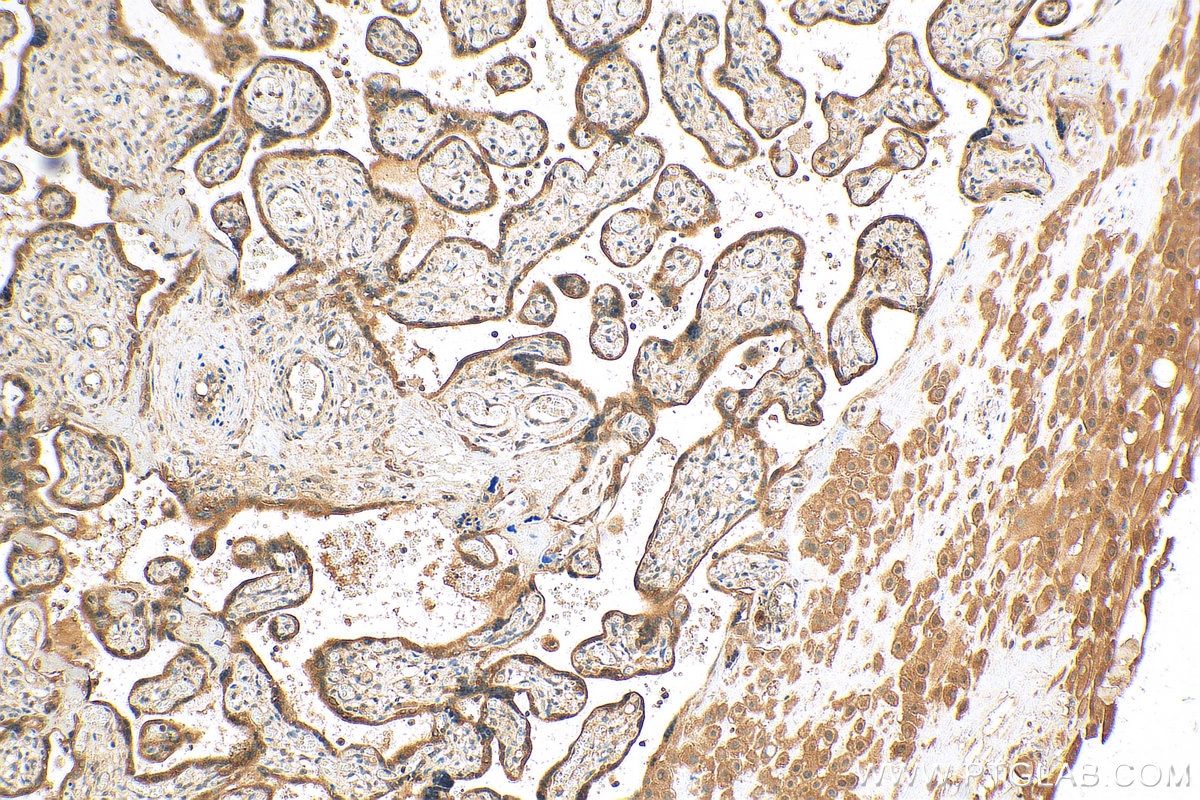
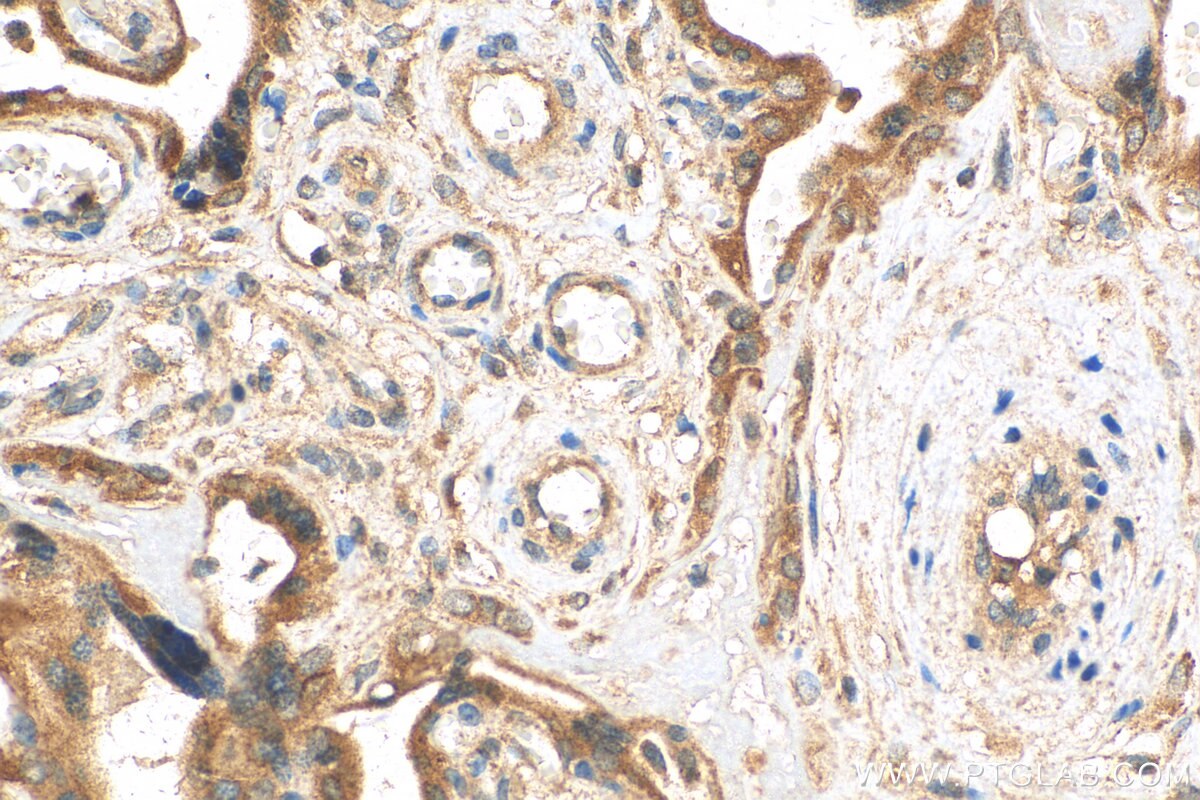
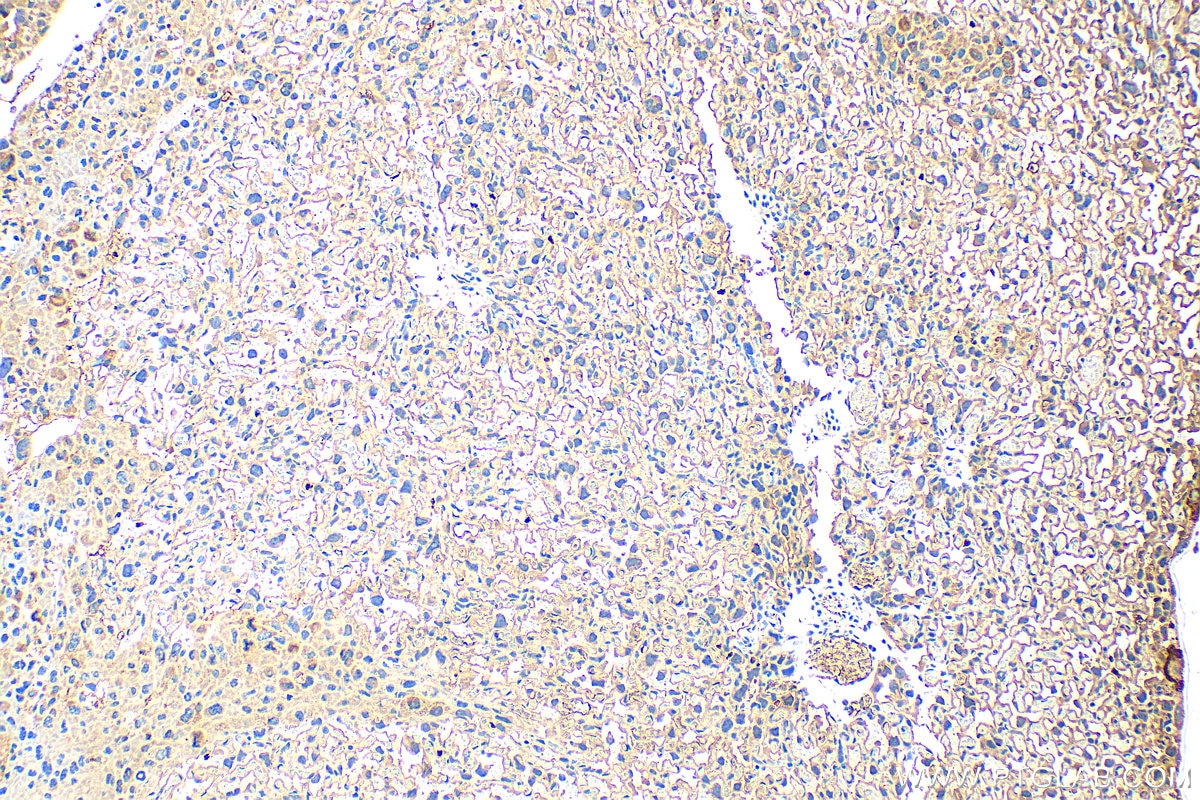
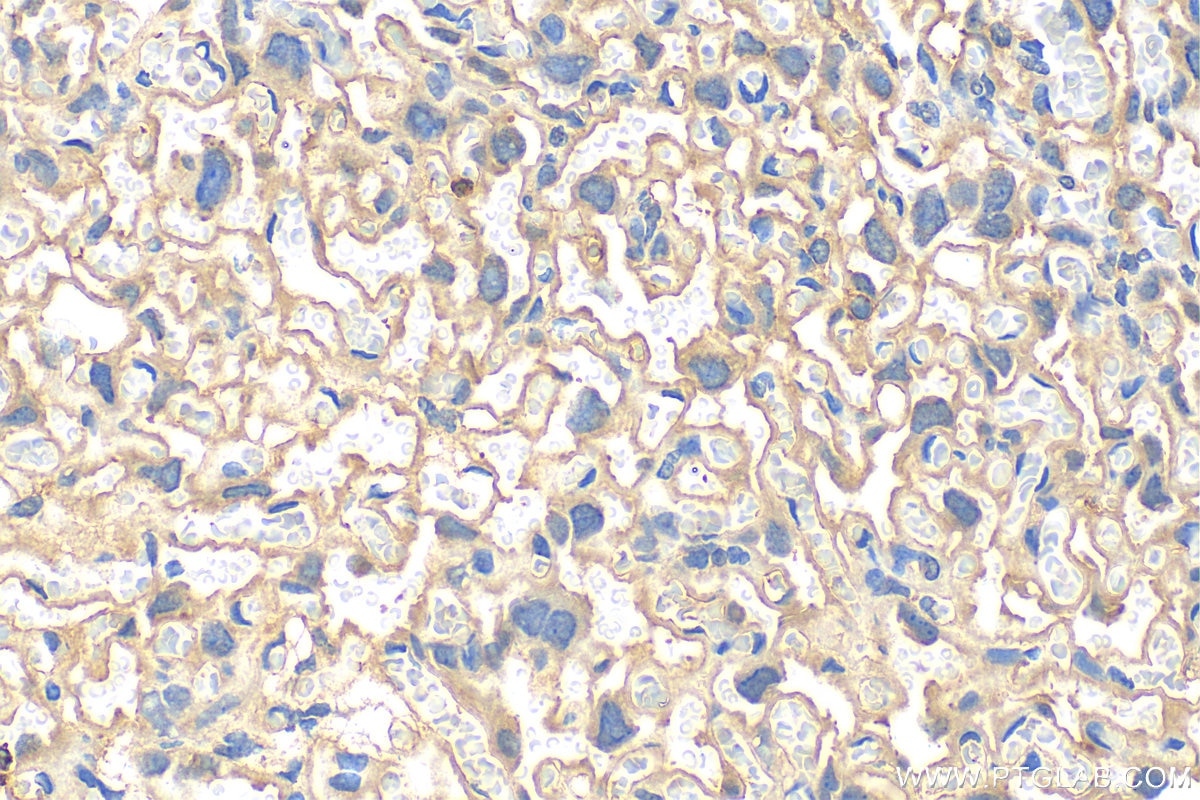
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Plazenta-Gewebe, Maus-Plazenta-Gewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 18 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
| IP | See 2 publications below |
| CoIP | See 2 publications below |
Produktinformation
15546-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF, IP, CoIP, ELISA VAMP8 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | VAMP8 fusion protein Ag7903 |
| Vollständiger Name | vesicle-associated membrane protein 8 (endobrevin) |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 11 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 15 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC001634 |
| Gene symbol | VAMP8 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8673 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
VAMP8, also named as endobrevin, is a member of the vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP)/synaptobrevin family and the SNARE (soluble NSF-attachment protein receptor) superfamily. Characterized by a common sequence called the SNARE motif, SNARE proteins are involved in membrane fusion and vesicular transport (PMID: 11252968). VAMP8 is involved in autophagy through the direct control of autophagosome membrane fusion with the lysososome membrane. It is required for dense-granule secretion in platelets and plays a role in regulated enzyme secretion in pancreatic acinar cells. VAMP8 is also involved in the abscission of the midbody during cell division, which leads to completely separate daughter cells.
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for VAMP8 antibody 15546-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for VAMP8 antibody 15546-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Extracell Vesicles Identification of the SNARE complex that mediates the fusion of multivesicular bodies with the plasma membrane in exosome secretion | ||
Autophagy SDC1-dependent TGM2 determines radiosensitivity in glioblastoma by coordinating EPG5-mediated fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes | ||
Cell Mol Life Sci IGF2BP1-HAX-1 positive feedback loop-mediated HAX-1 overexpression blocks autophagic flux and promotes chemoresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma | ||
Arch Toxicol Mystery of methamphetamine-induced autophagosome accumulation in hippocampal neurons: loss of syntaxin 17 in defects of dynein-dynactin driving and autophagosome-late endosome/lysosome fusion. | ||
Ecotoxicol Environ Saf Weakened interaction of ATG14 and the SNARE complex blocks autophagosome-lysosome fusion contributes to fluoride-induced developmental neurotoxicity. | ||
Stem Cell Res Ther Microtubule destabilization caused by silicate via HDAC6 activation contributes to autophagic dysfunction in bone mesenchymal stem cells. |