IHC Figures
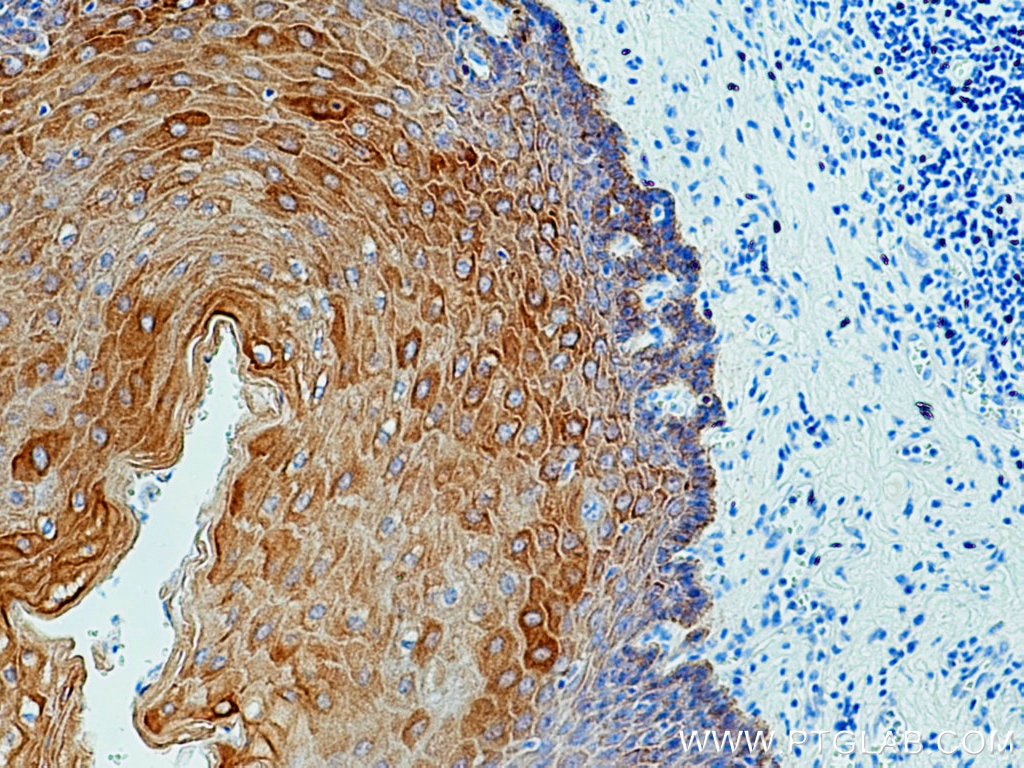
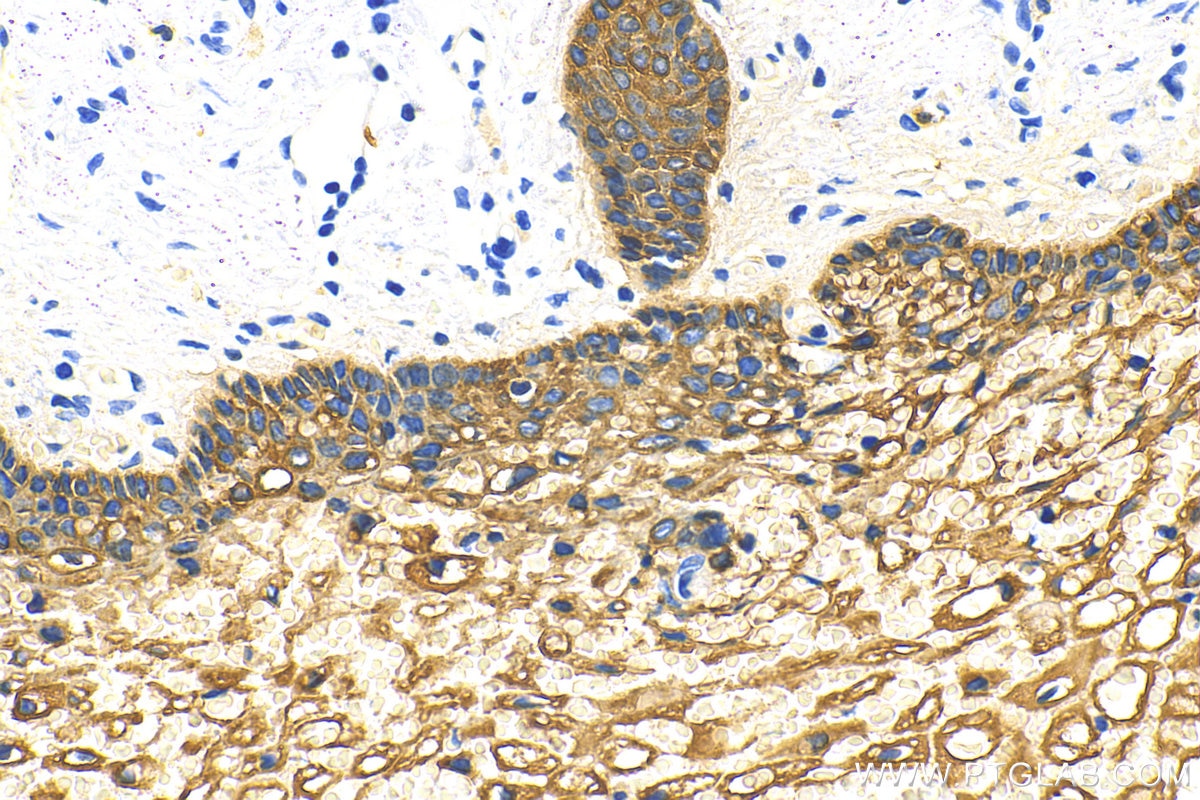
IHC staining of human oesophagus using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human oesophagus tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 10x lens)..
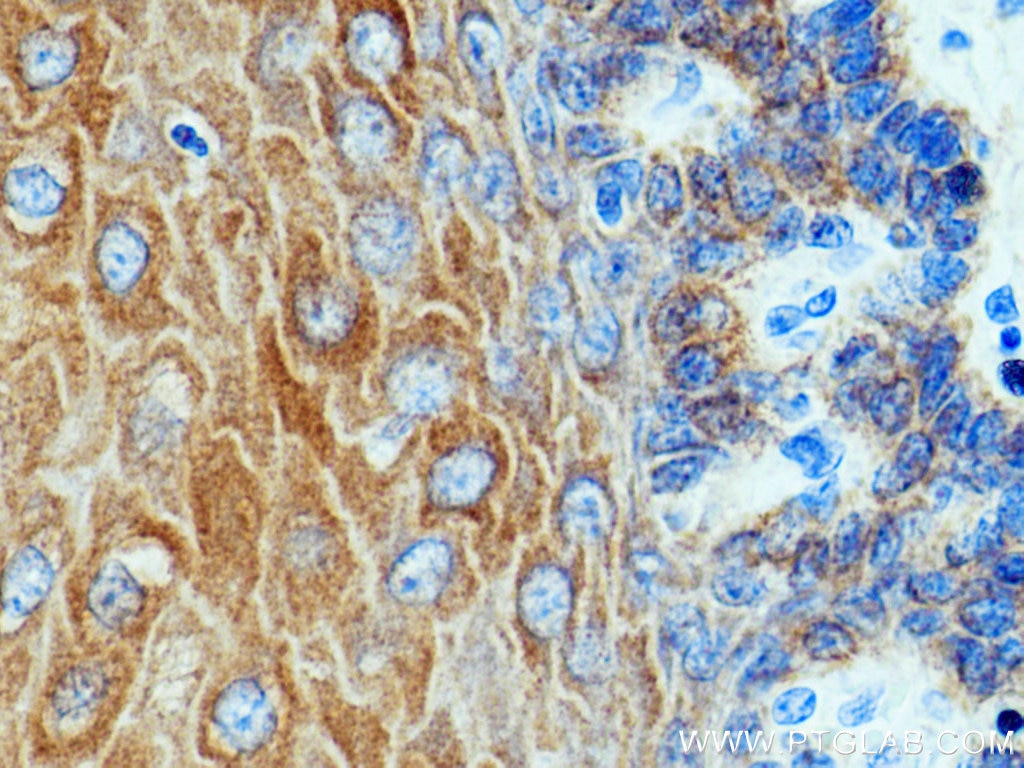
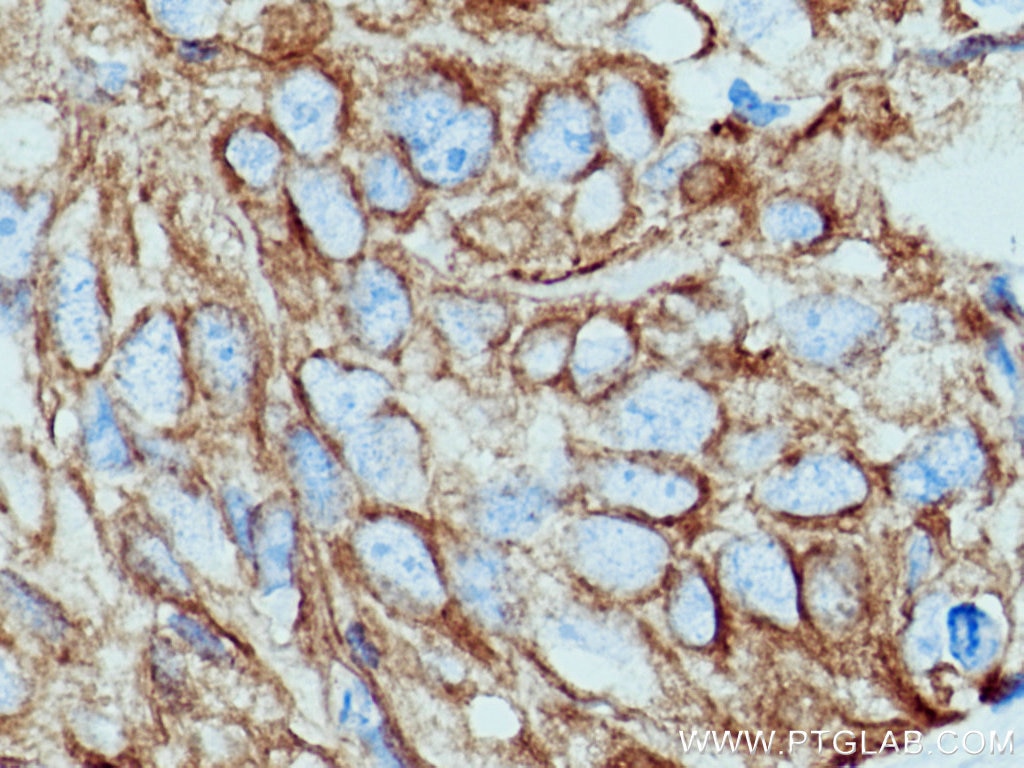
IHC staining of human oesophagus using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human oesophagus tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 40x lens)..
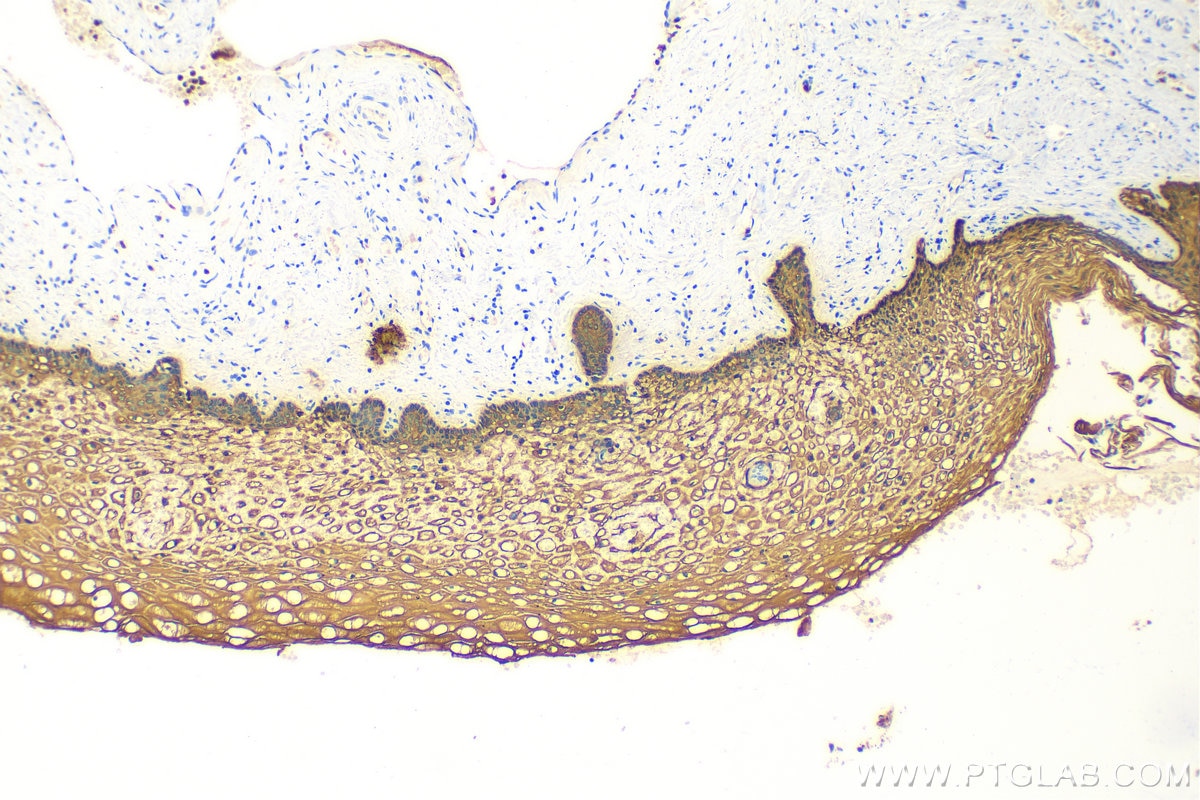
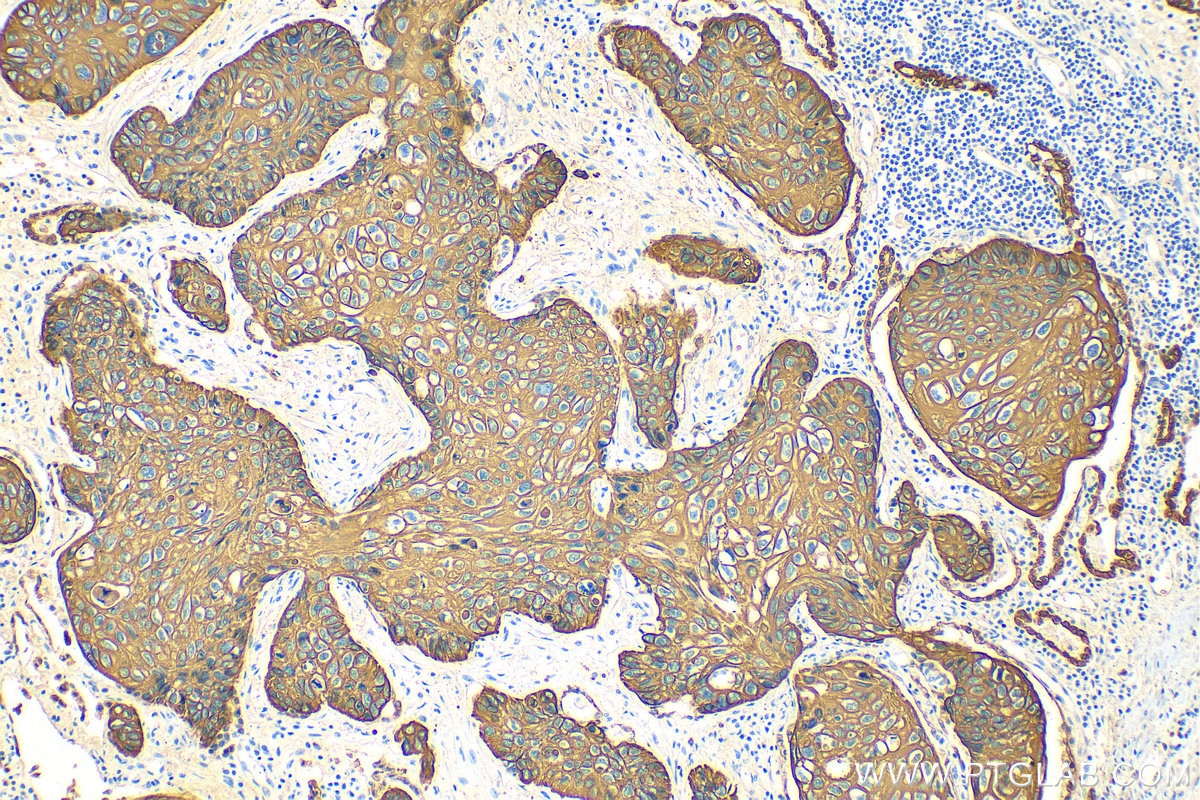
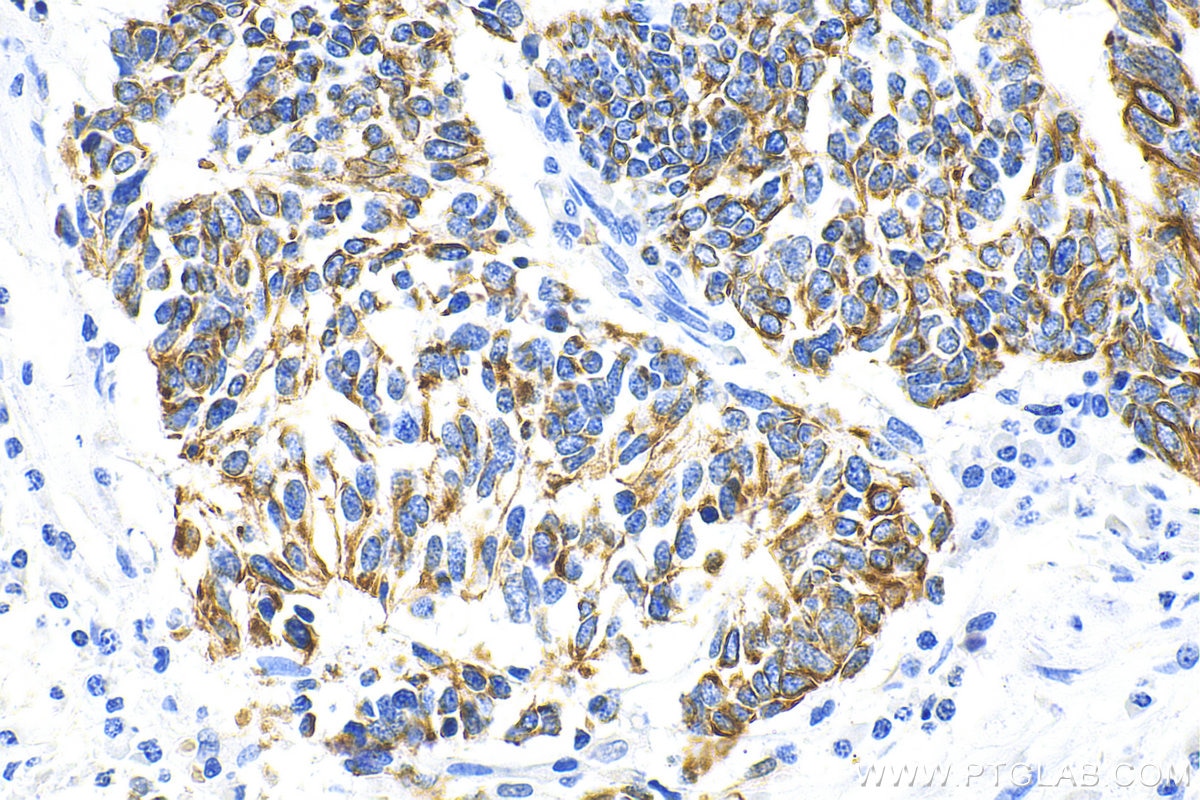
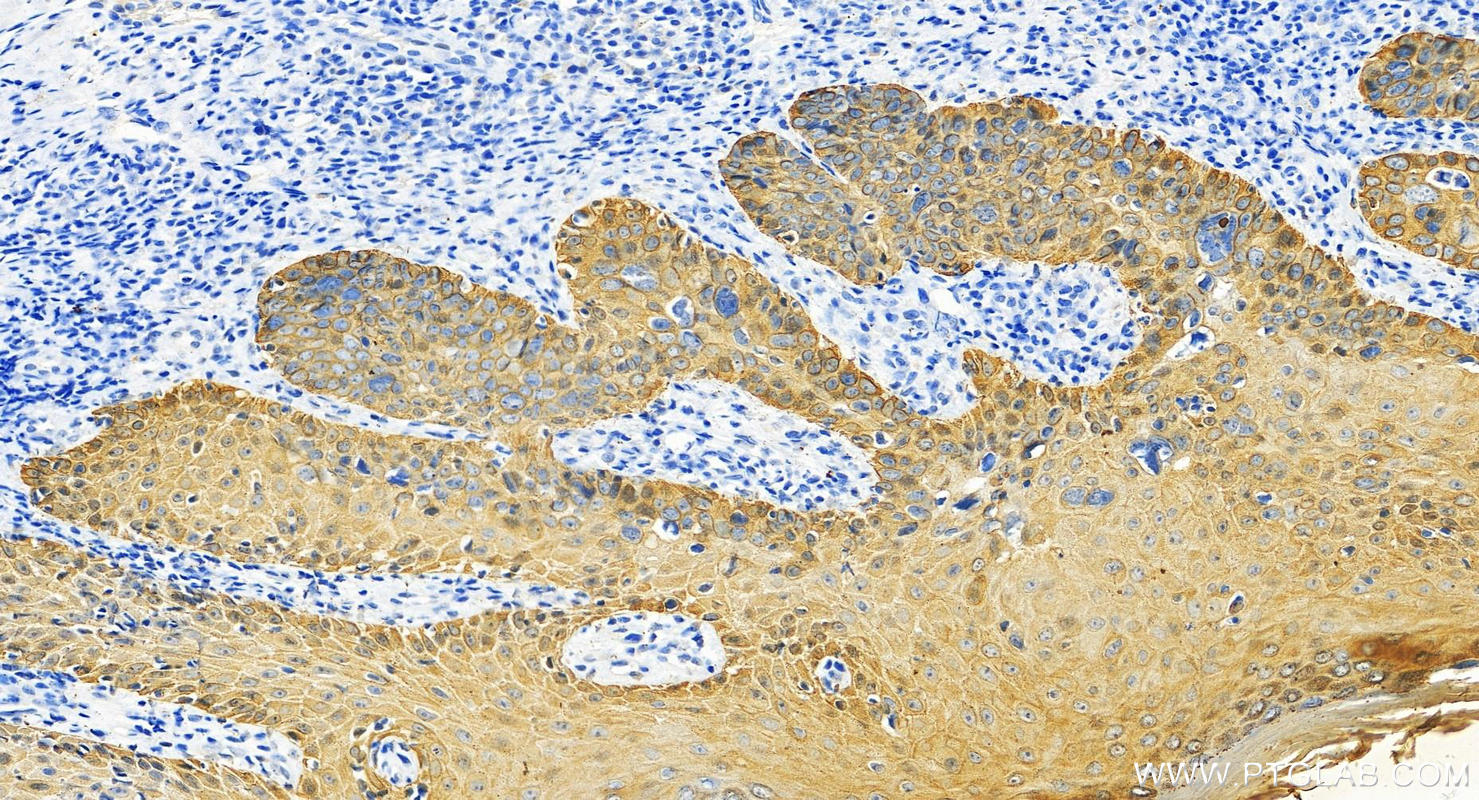
IHC staining of human cervical cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human cervical cancer tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 10x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
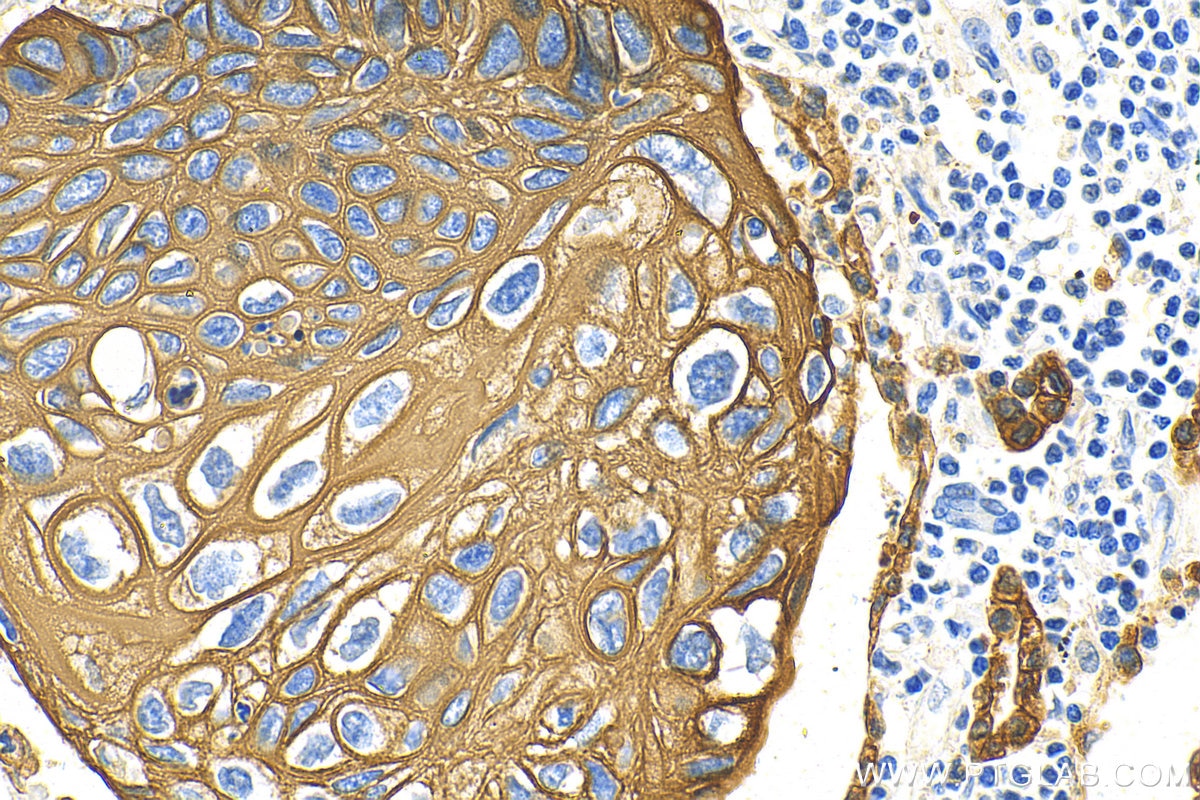
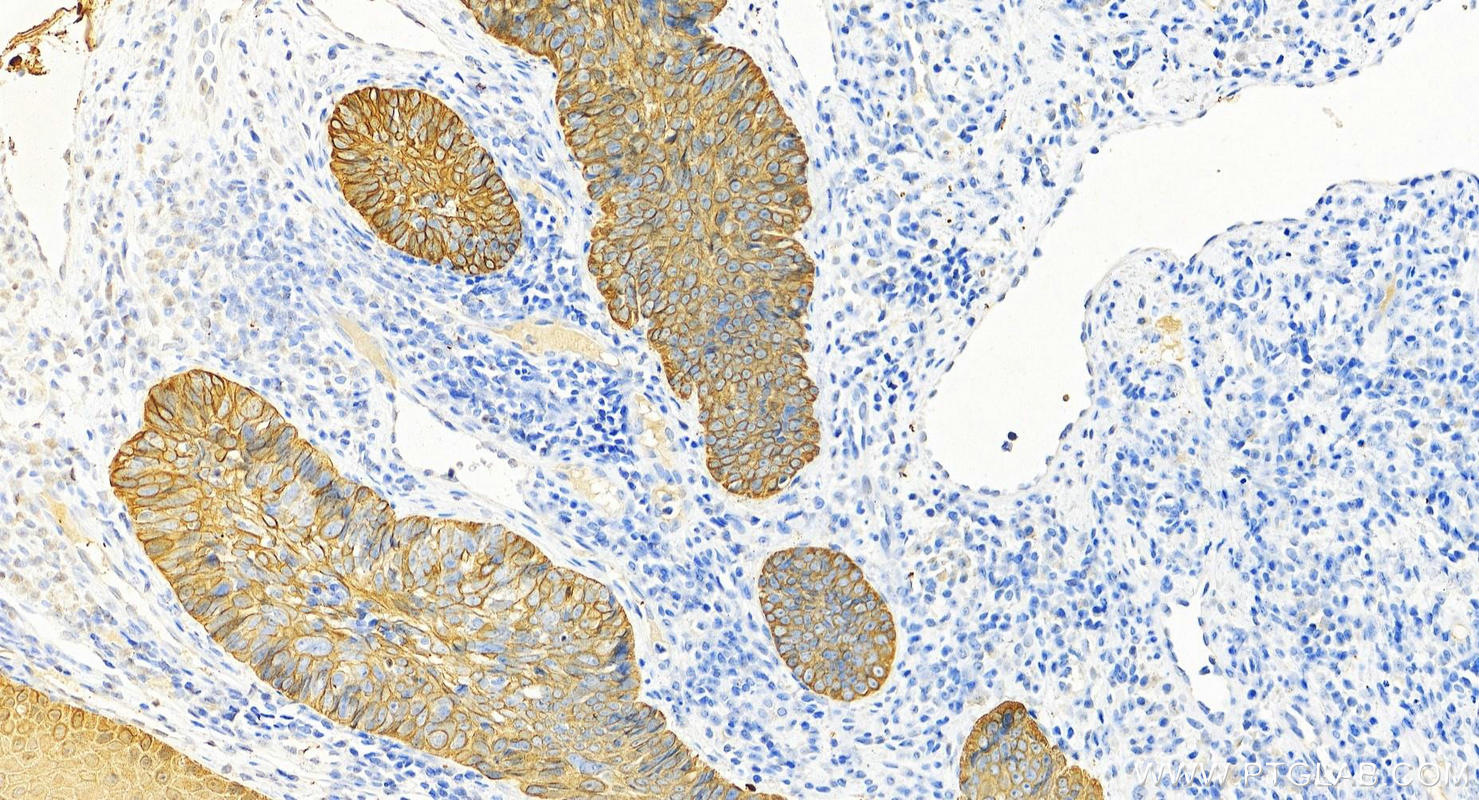
IHC staining of human cervical cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human cervical cancer tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 40x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
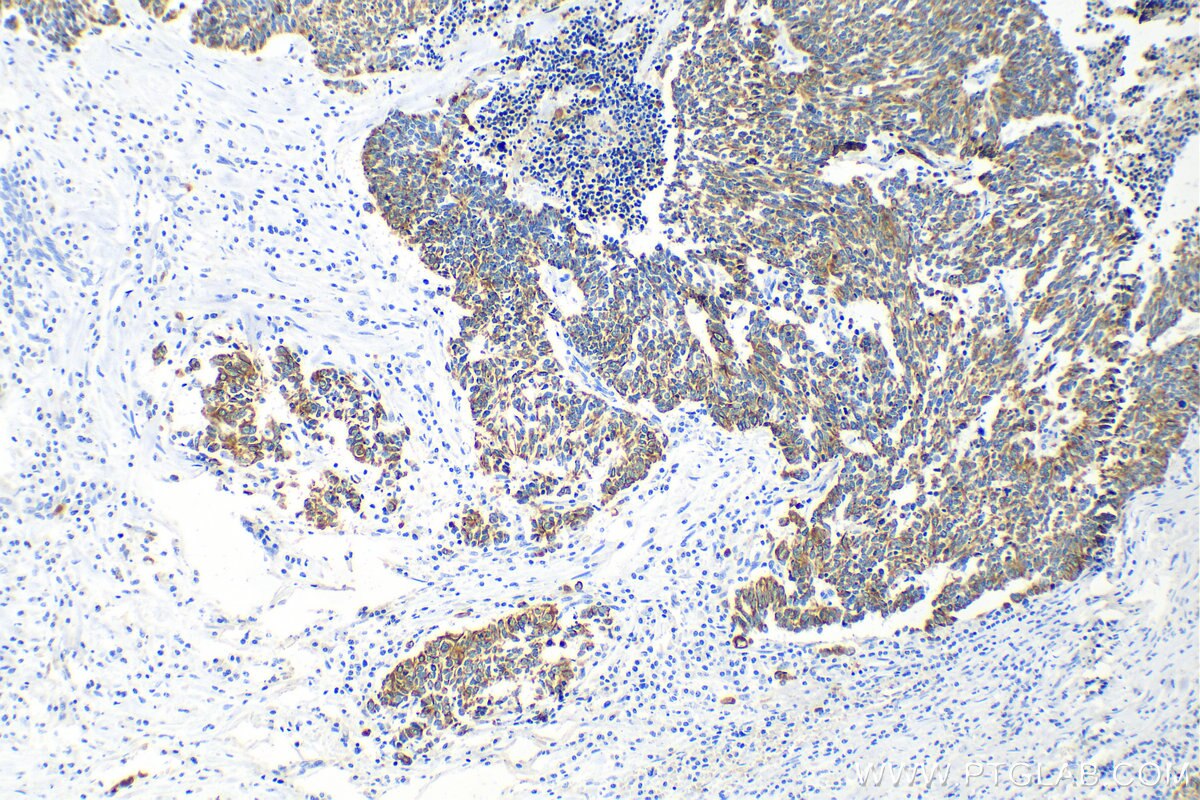
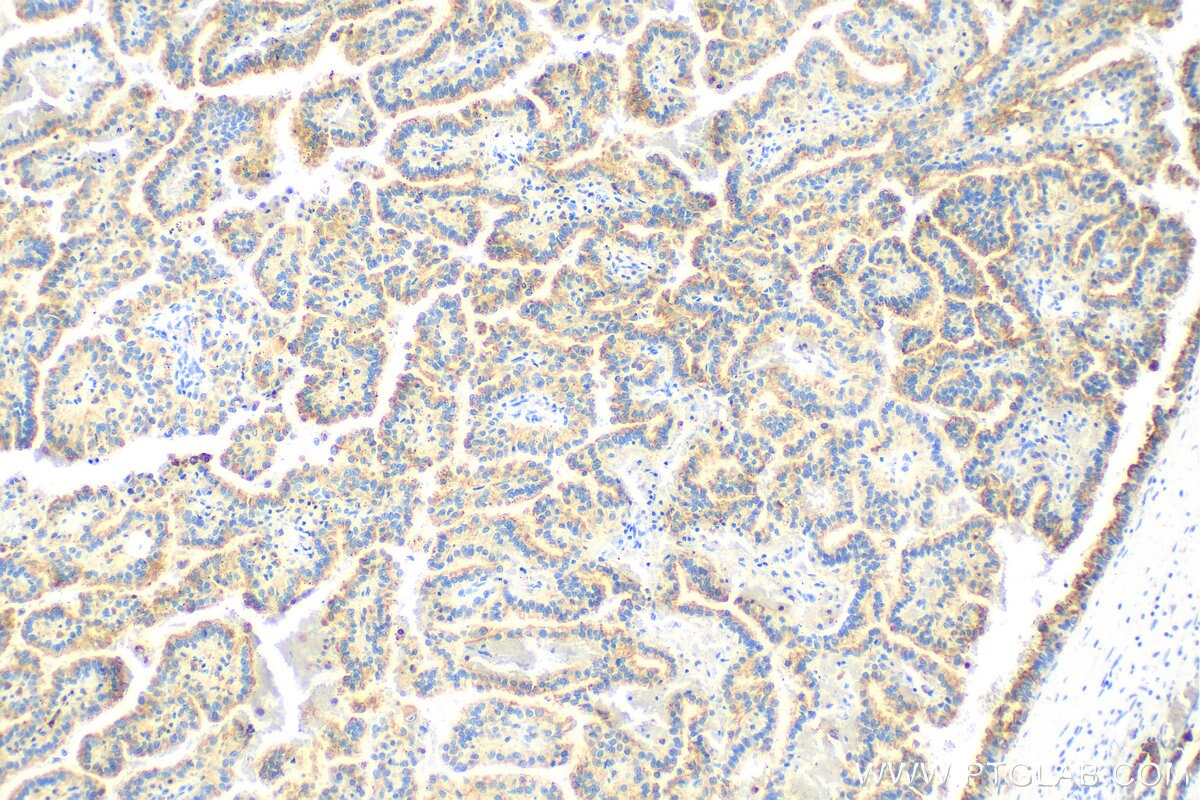
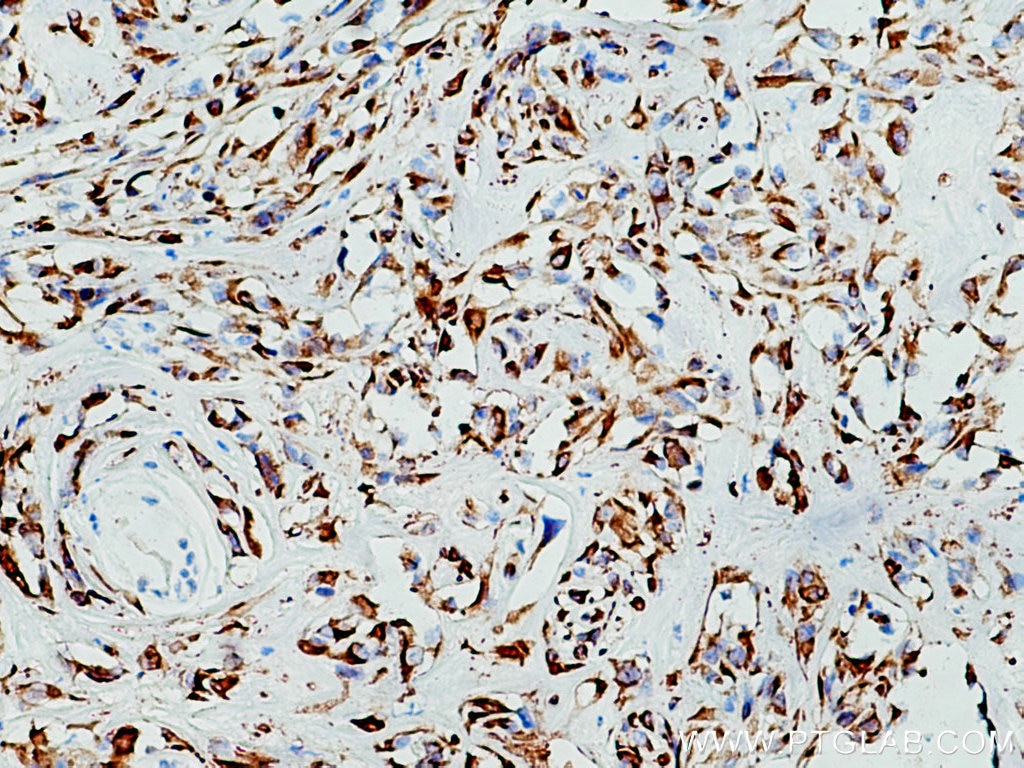
IHC staining of human lung cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 10x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
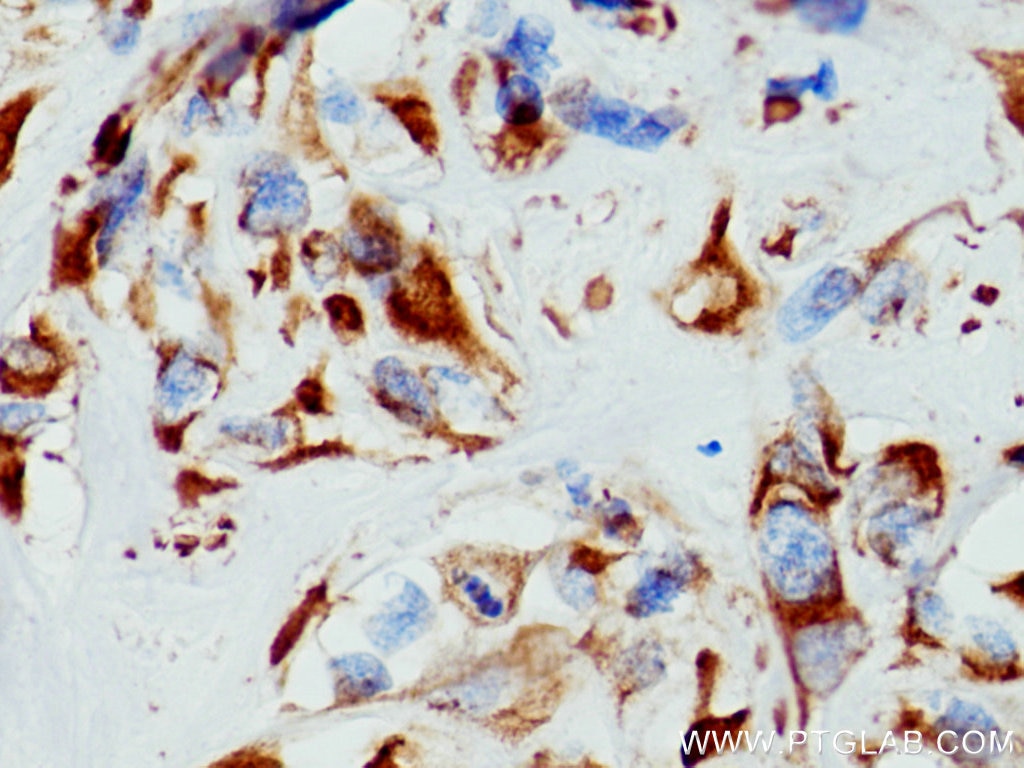
IHC staining of human lung cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 40x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IHC staining of human lung cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 10x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IHC staining of human lung cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 40x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
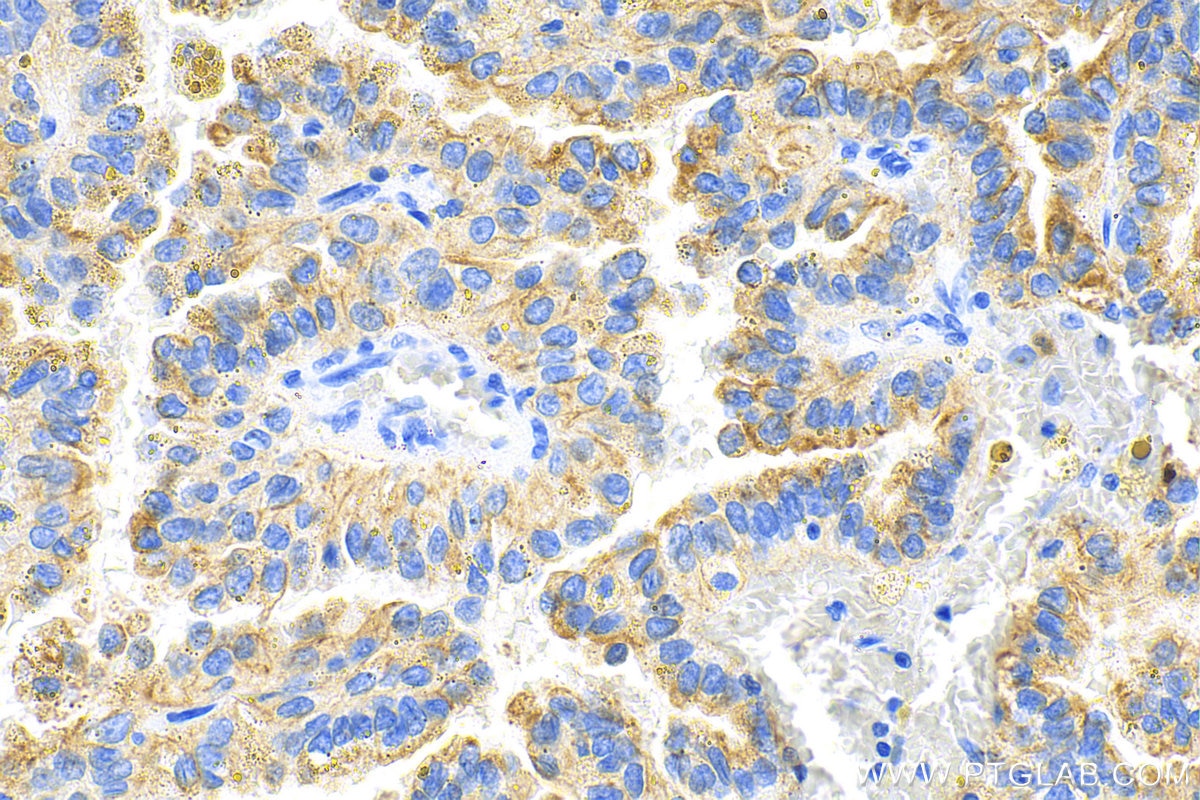
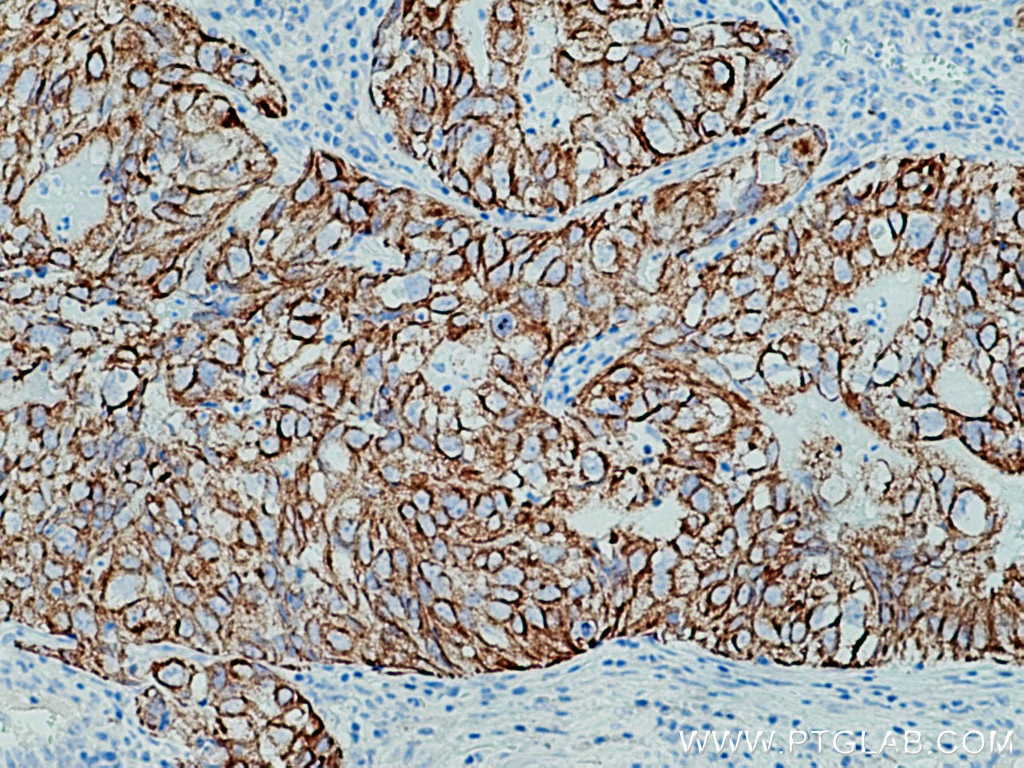
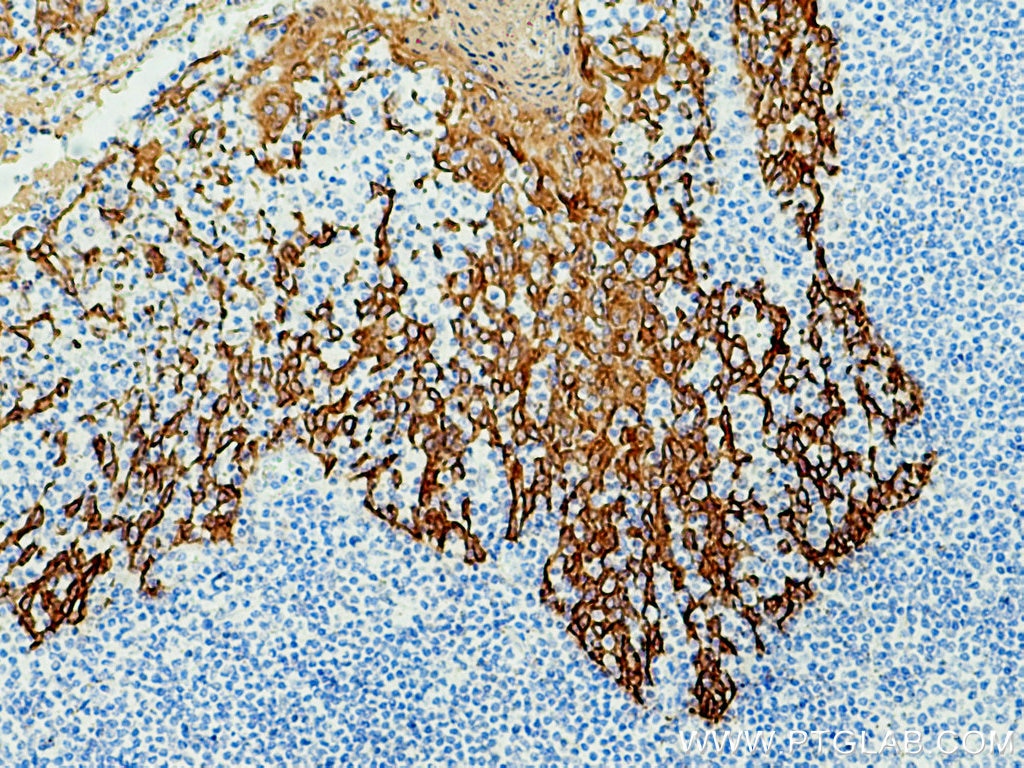
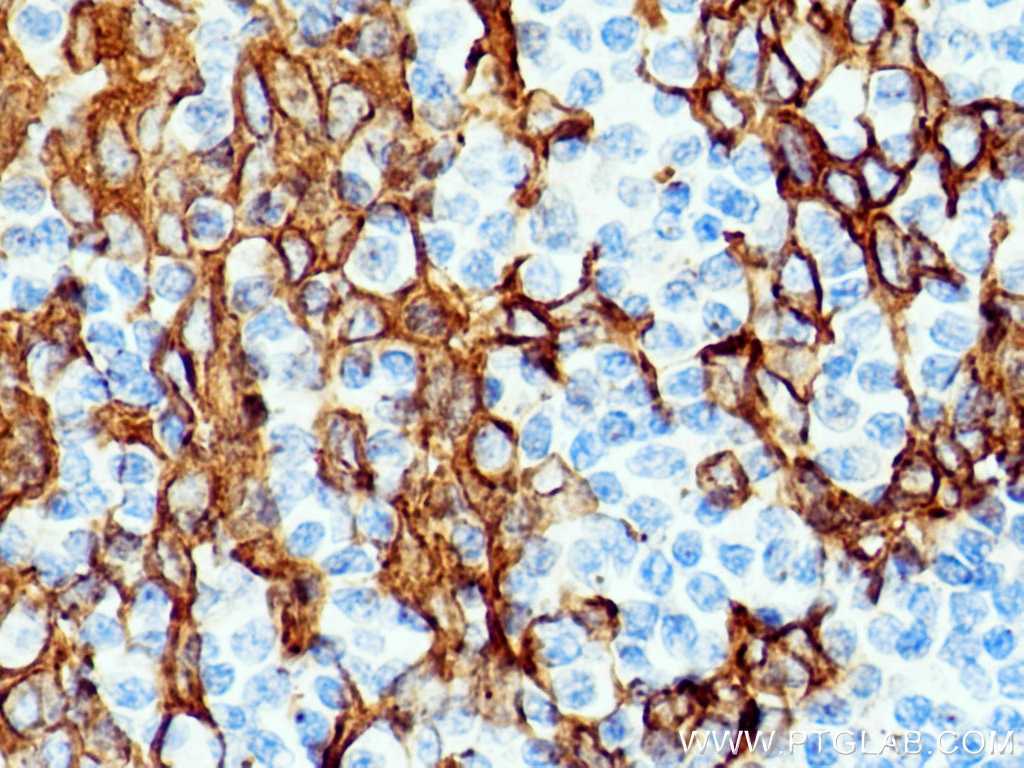
IHC staining of human renal cell carcinoma using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human renal cell carcinoma tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 10x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IHC staining of human renal cell carcinoma using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human renal cell carcinoma tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 40x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
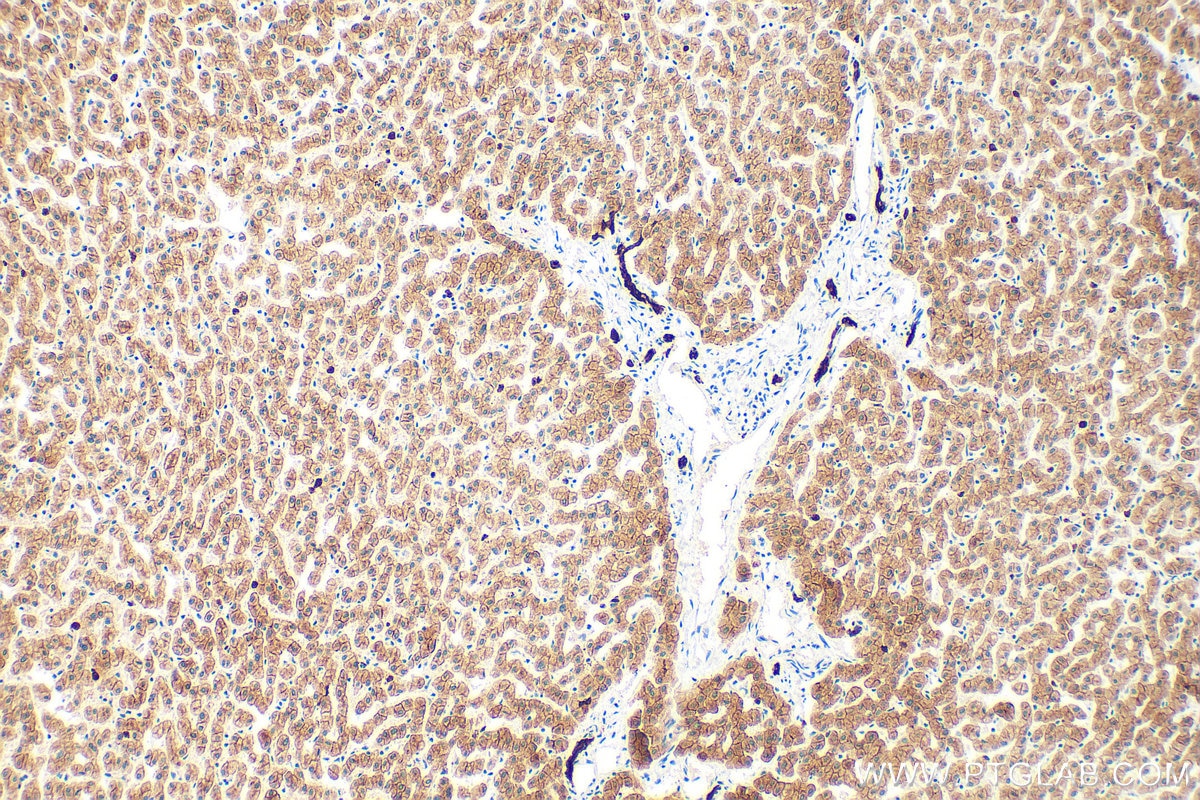
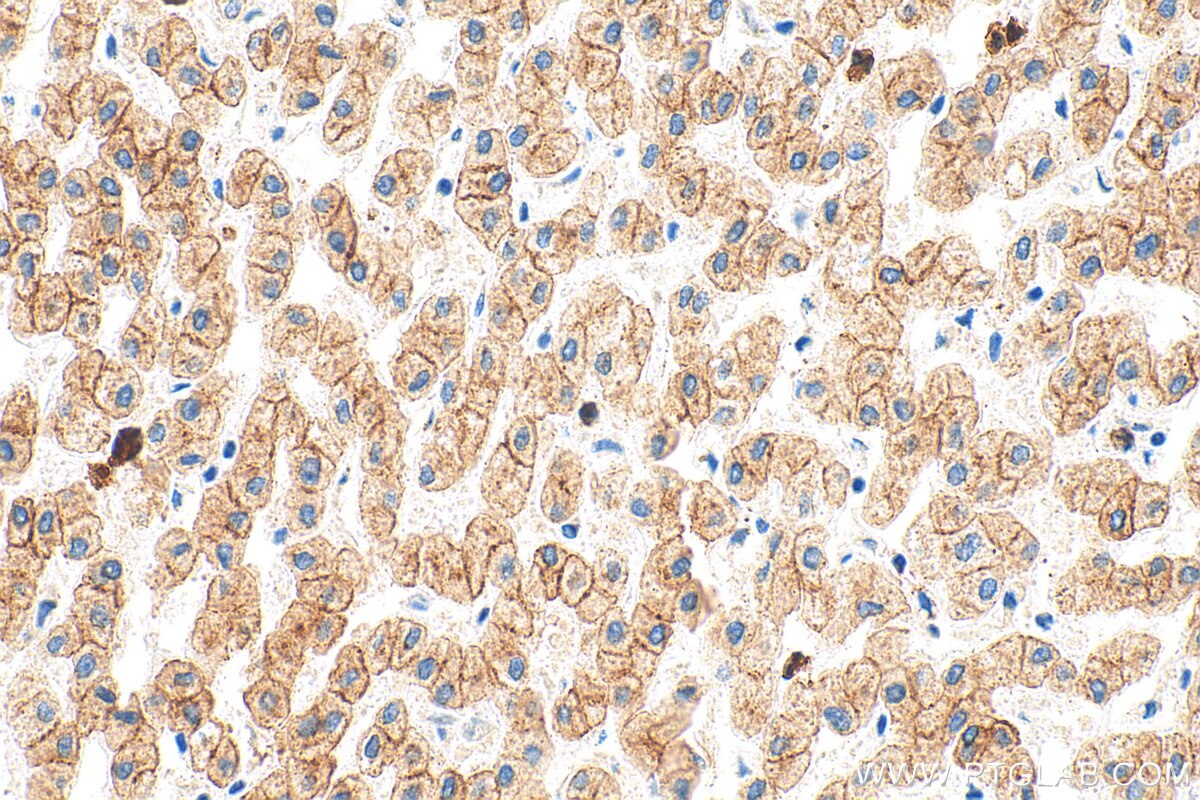
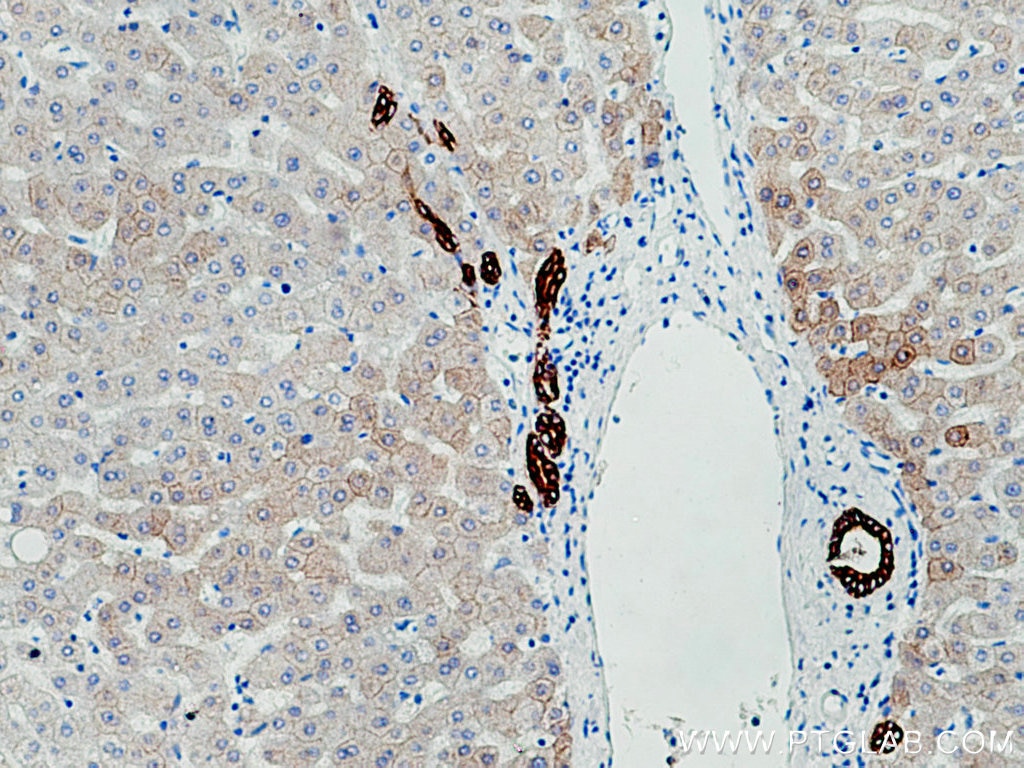
IHC staining of human liver using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human liver tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (Pan-Keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 10x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
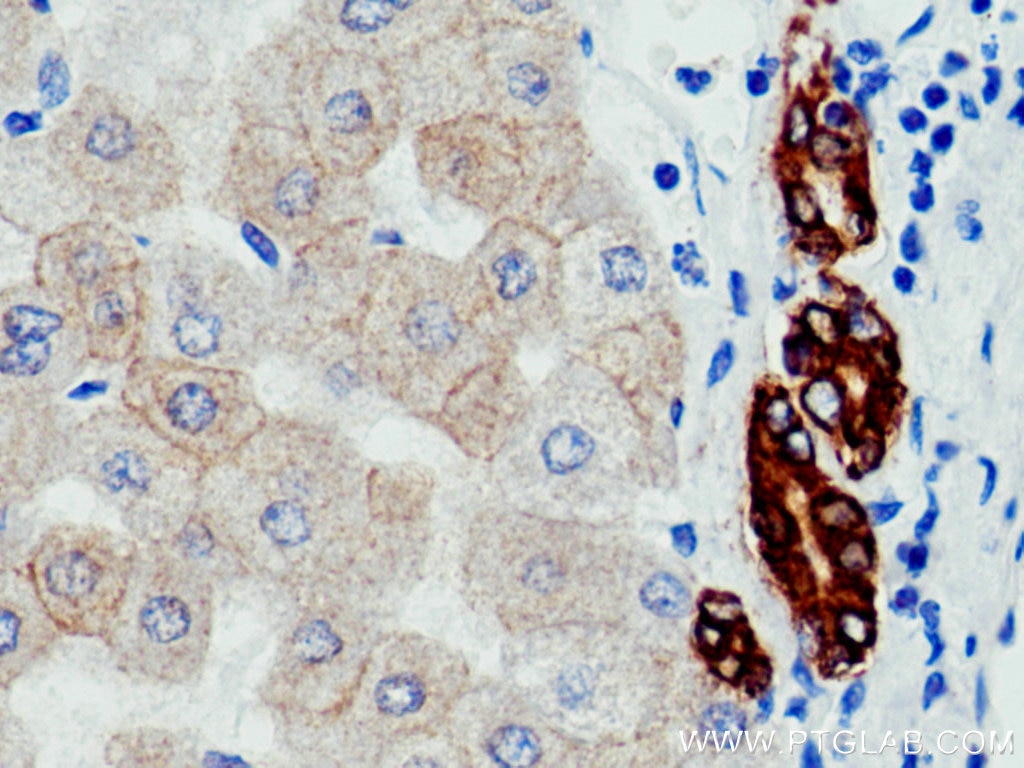
IHC staining of human liver using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human liver tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (Pan-Keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 40x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IHC staining of human brown disease using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human brown disease slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:20000 (under 20x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IHC staining of human brown disease using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human brown disease slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:20000 (under 20x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
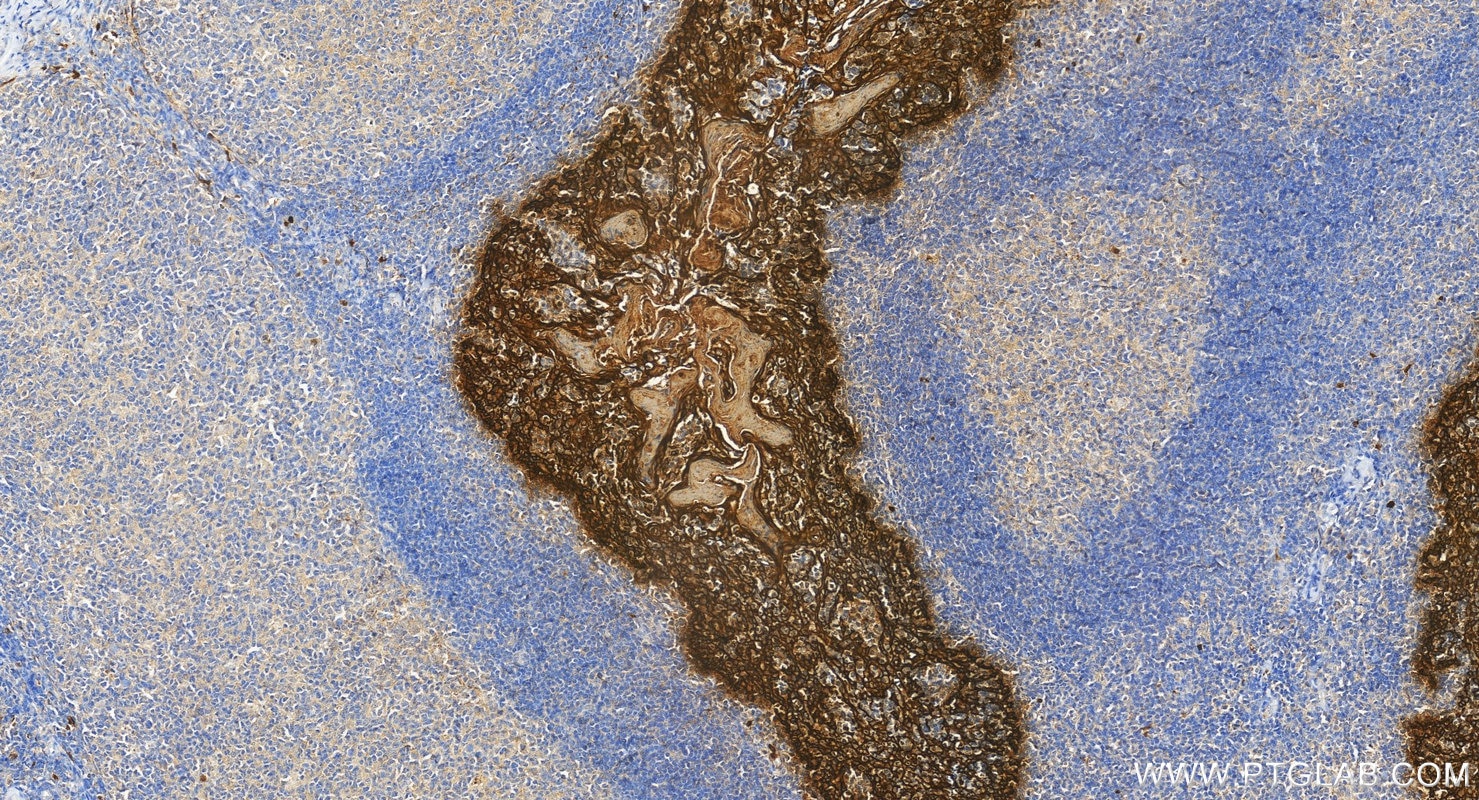
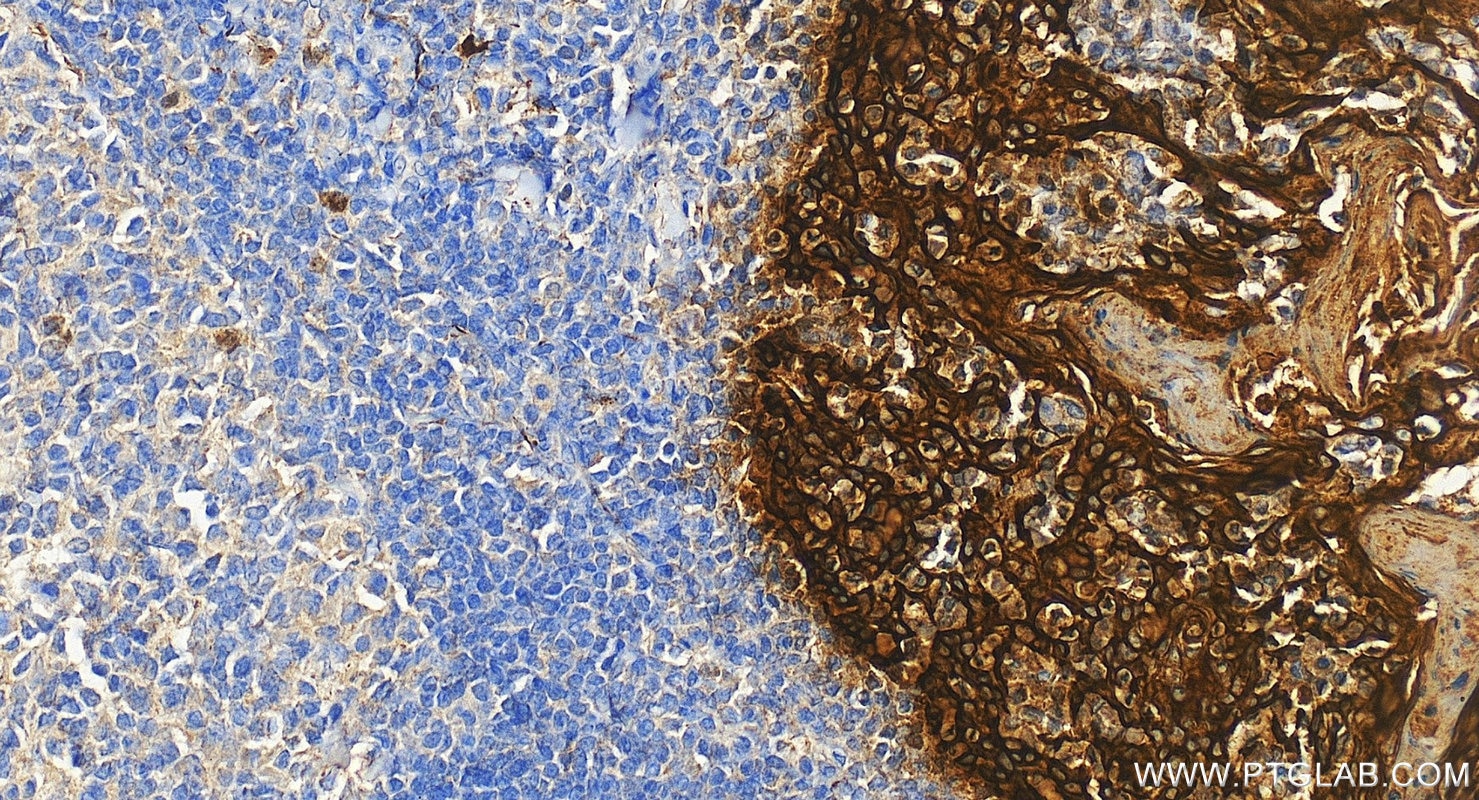
IHC staining of human tonsillitis using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsillitis tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (Pan-Keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 20x lens).
IHC staining of human tonsillitis using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsillitis tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (Pan-Keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 20x lens).
IHC staining of human liver using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human liver tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 10x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IHC staining of human liver using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human liver tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 40x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IHC staining of human lung cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung adenocarcinoma tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 10x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IHC staining of human lung cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung adenocarcinoma tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 40x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IHC staining of human renal cell carcinoma using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human renal cell carcinoma tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 10x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IHC staining of human renal cell carcinoma using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human renal cell carcinoma tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 40x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IHC staining of human tonsillitis using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsillitis tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 10x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IHC staining of human tonsillitis using 26411-1-AP
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsillitis tissue slide using 26411-1-AP (pan-keratin antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 (under 40x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IF-P Figures
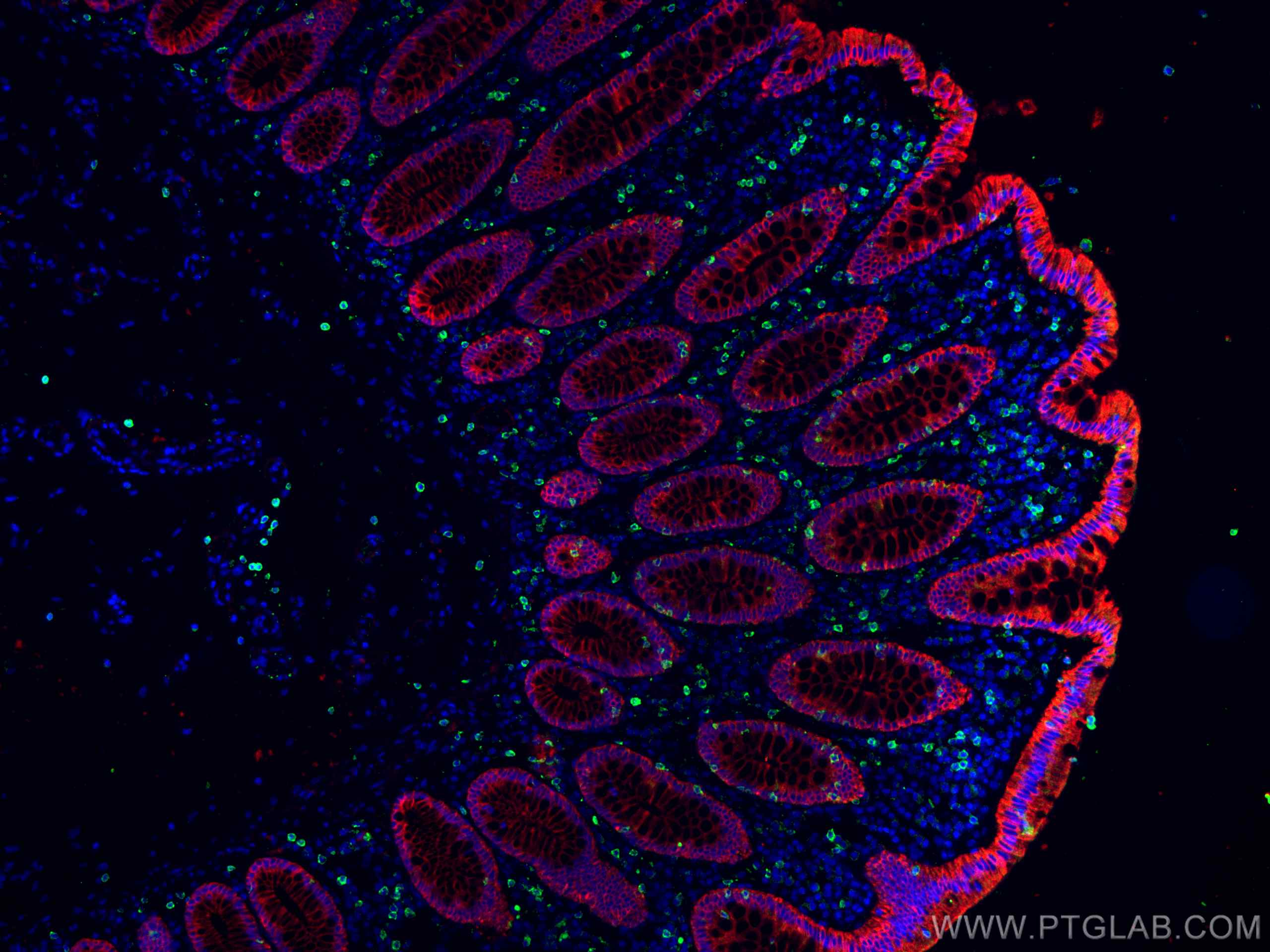
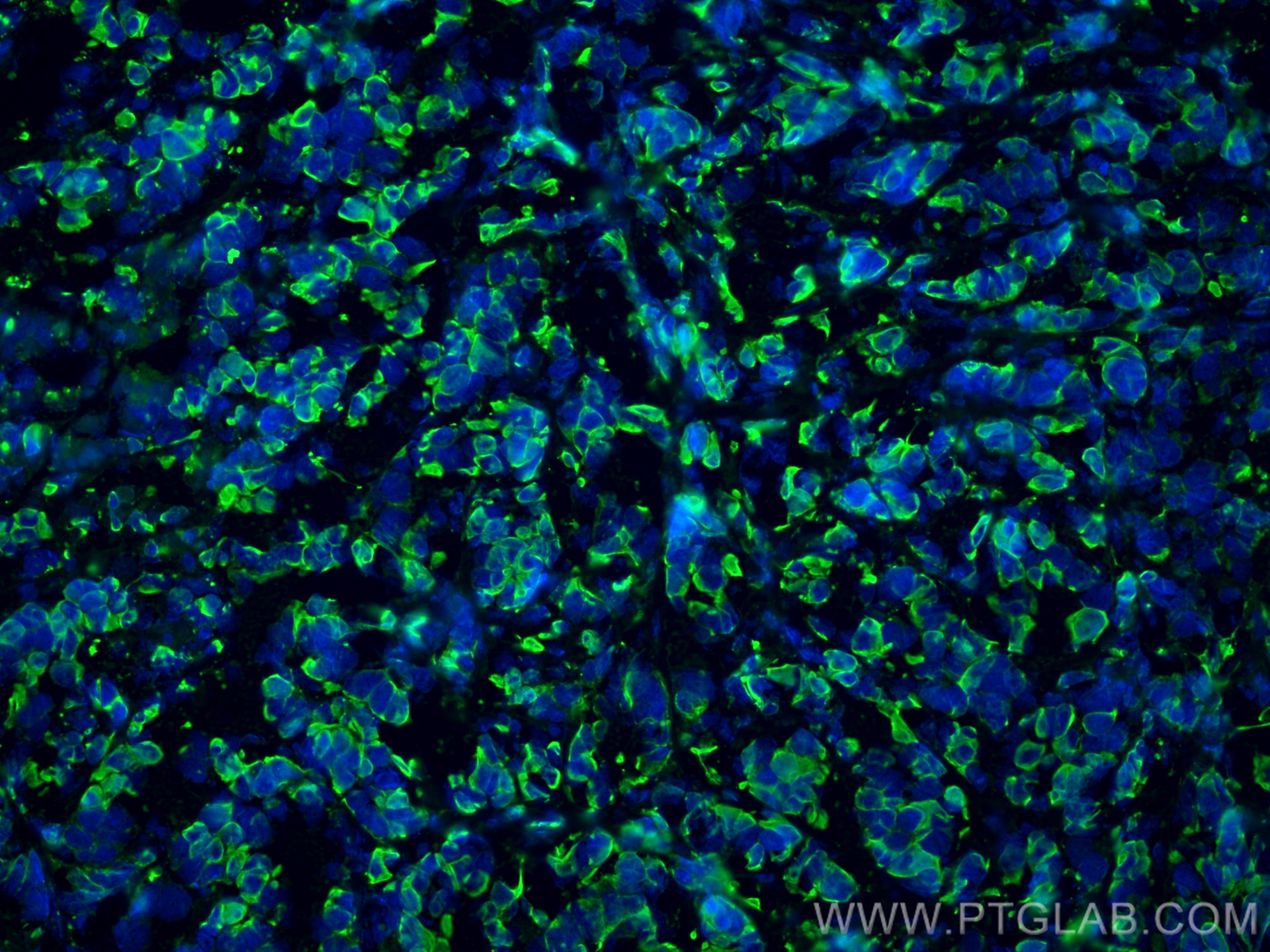
IF Staining of human colon cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed human colon cancer tissue using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:400 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L), CD8 antibody (66868-1-Ig, Clone: 1G2B10, green).
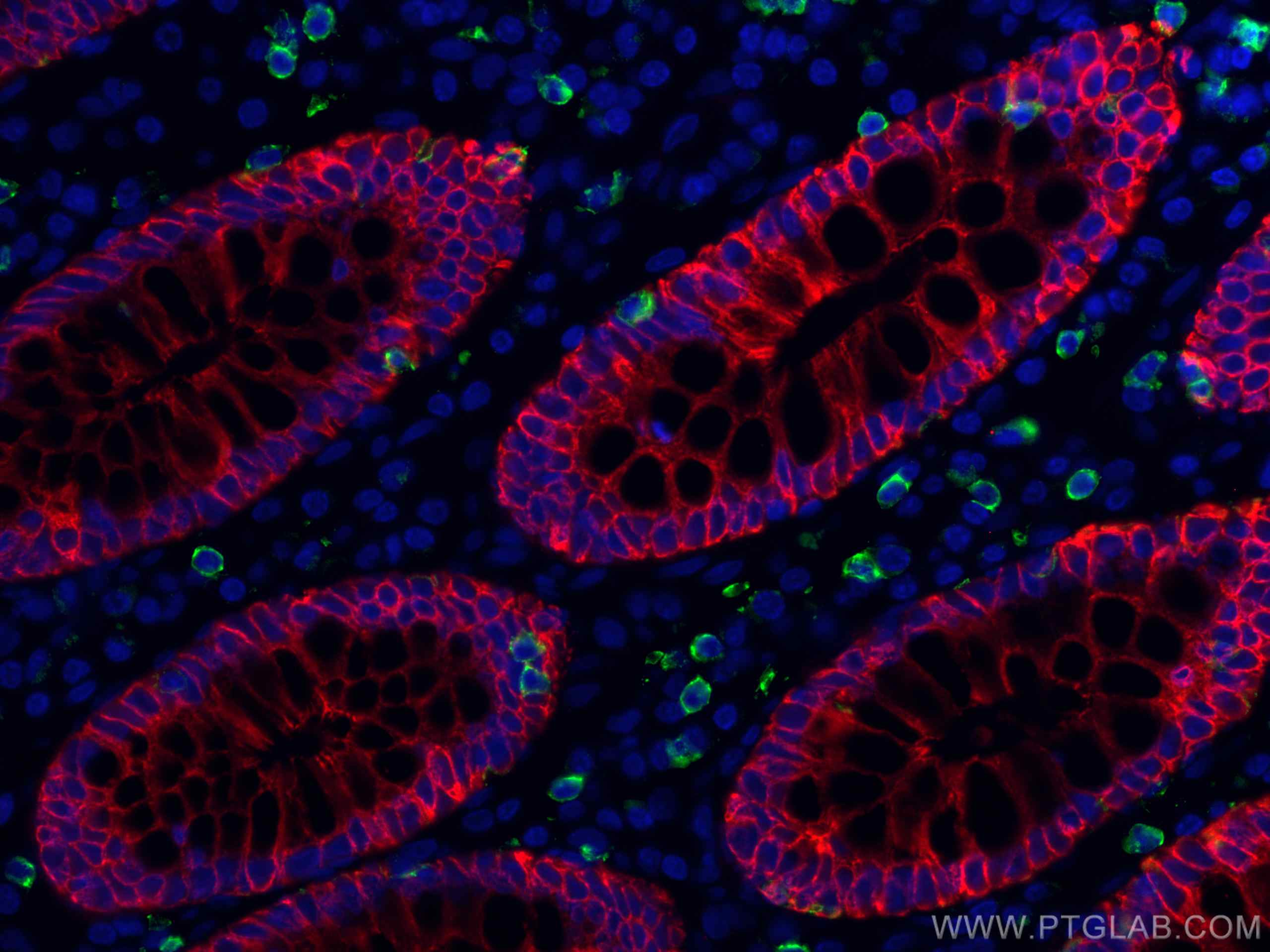
IF Staining of human colon cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed human colon cancer tissue using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:400 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L), CD8 antibody (66868-1-Ig, Clone: 1G2B10, green).
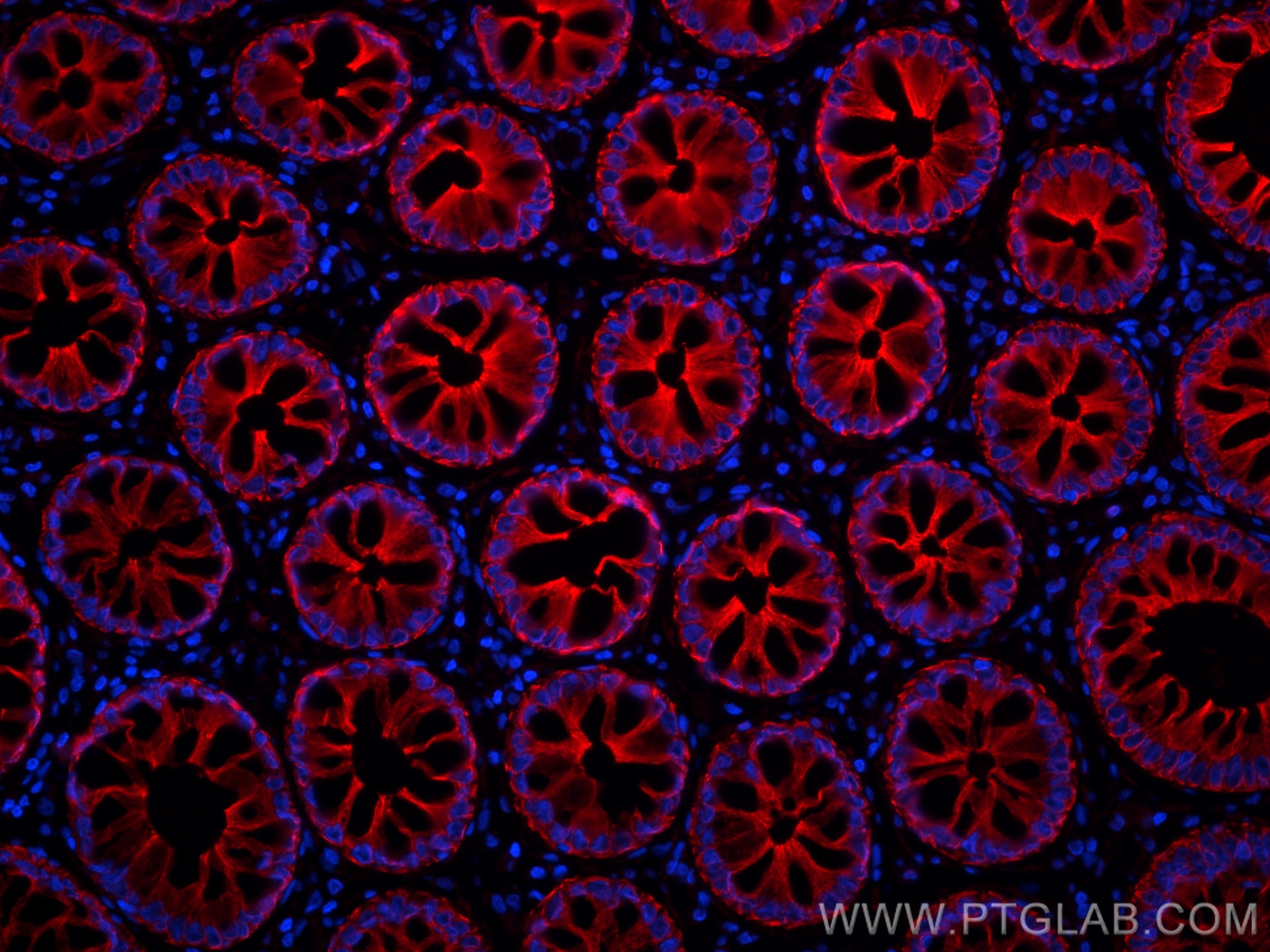
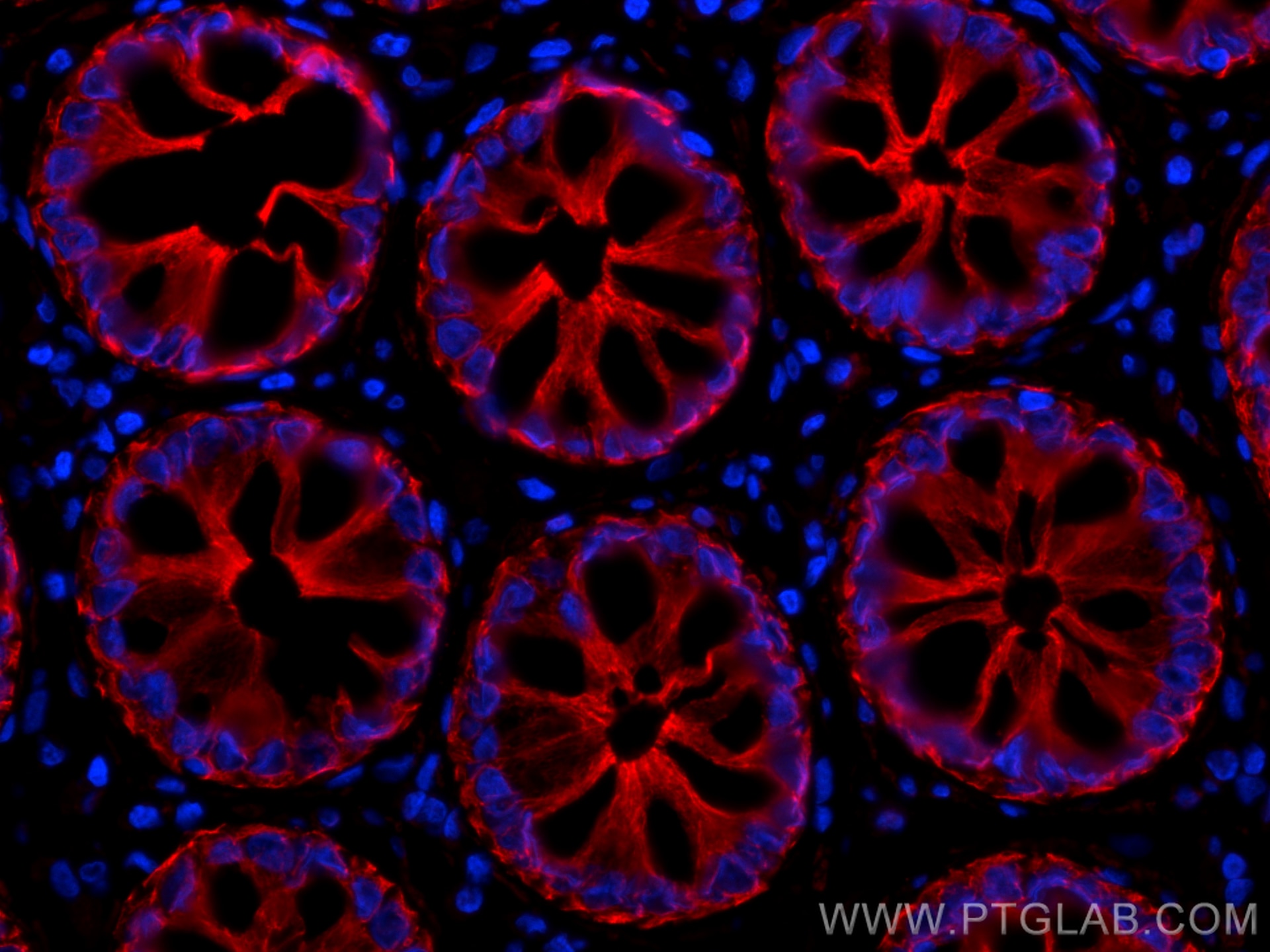
IF Staining of human rectal cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed paraffin-embedded human rectal cancer tissue using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:200 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-4). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IF Staining of human rectal cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed paraffin-embedded human rectal cancer tissue using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:200 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-4). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IF-P Figures
IF Staining of human colon cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed human colon cancer tissue using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:400 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L), CD8 antibody (66868-1-Ig, Clone: 1G2B10, green).
IF Staining of human colon cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed human colon cancer tissue using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:400 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L), CD8 antibody (66868-1-Ig, Clone: 1G2B10, green).
IF Staining of human rectal cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed paraffin-embedded human rectal cancer tissue using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:200 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-4). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IF Staining of human rectal cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed paraffin-embedded human rectal cancer tissue using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:200 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-4). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0).
IF/ICC Figures
IF Staining of A431 using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (-20°C Methanol) fixed A431 cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:200 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-2).
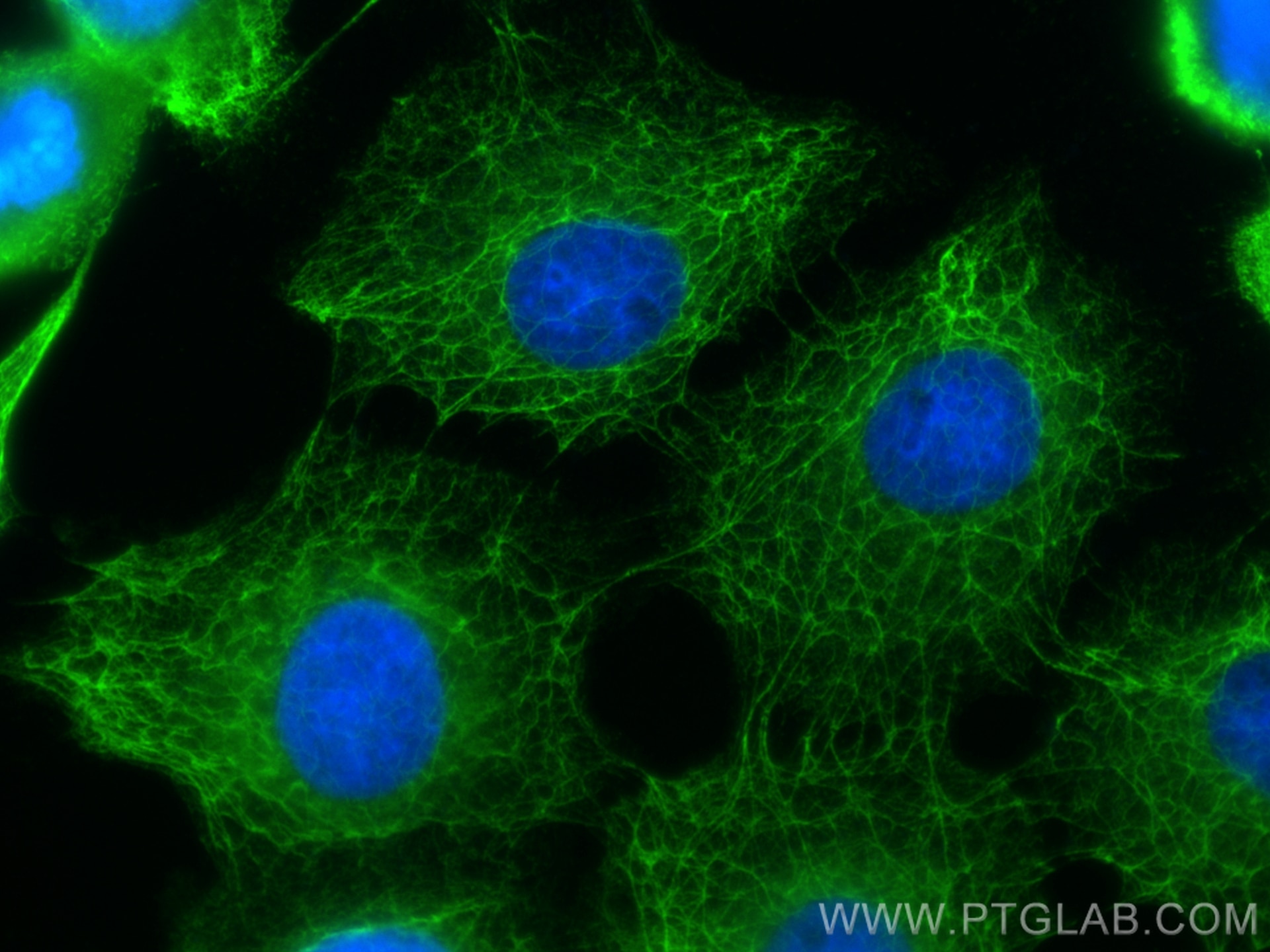
IF Staining of HeLa using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed HeLa cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:200 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L).
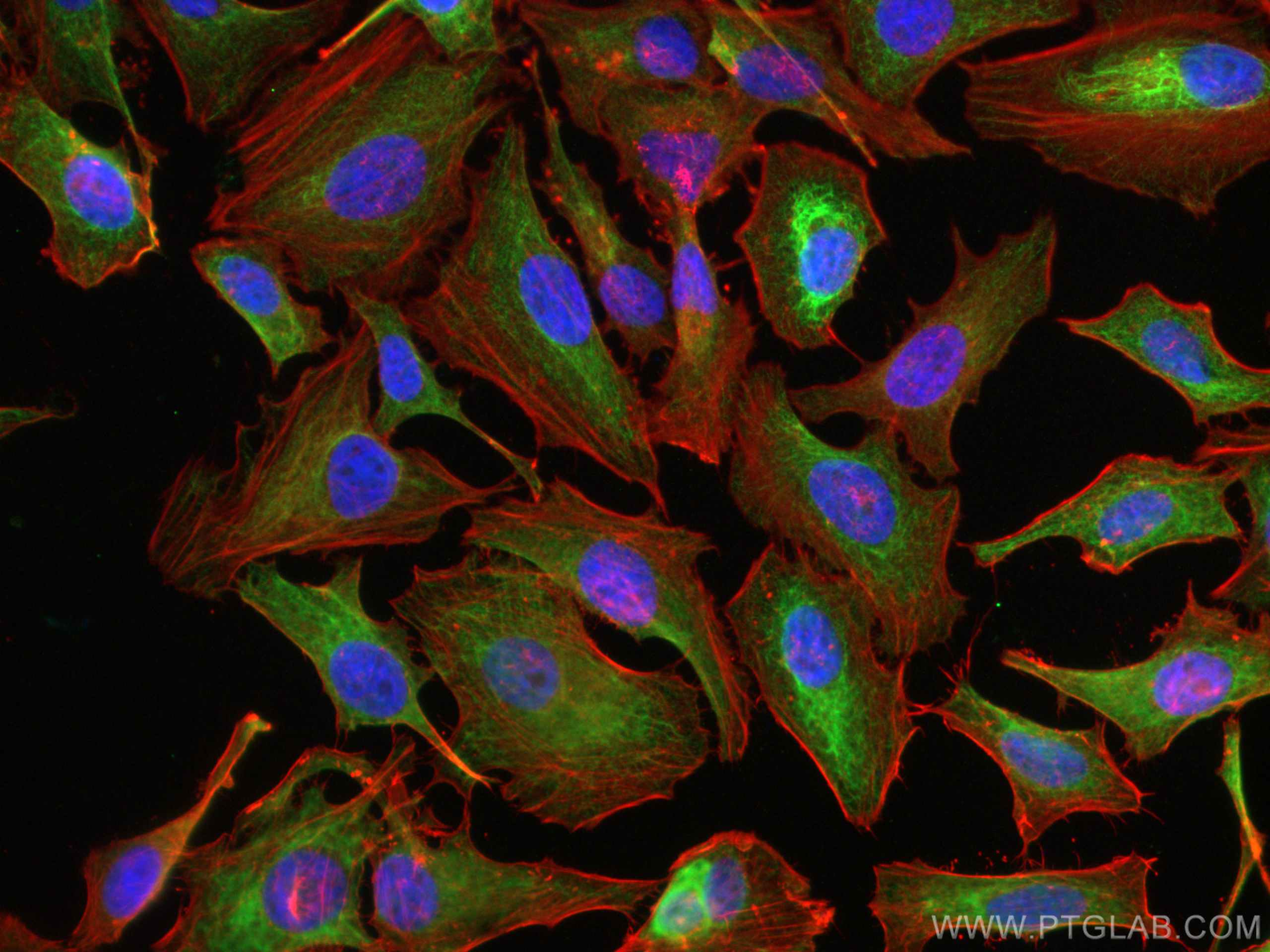
IF Staining of mouse breast cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed mouse breast cancer using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:400 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-2).
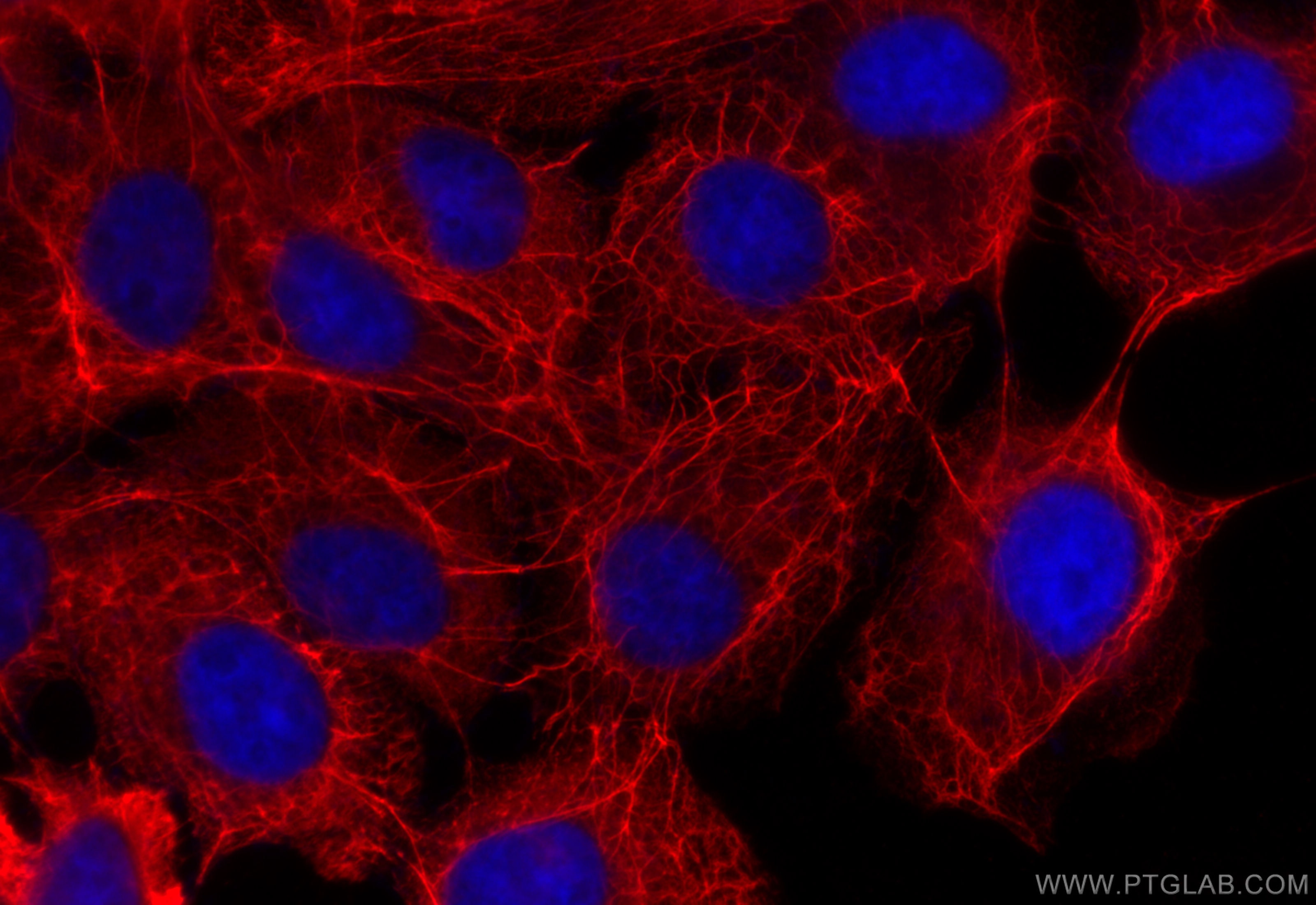
IF Staining of HeLa using 26411-1-AP
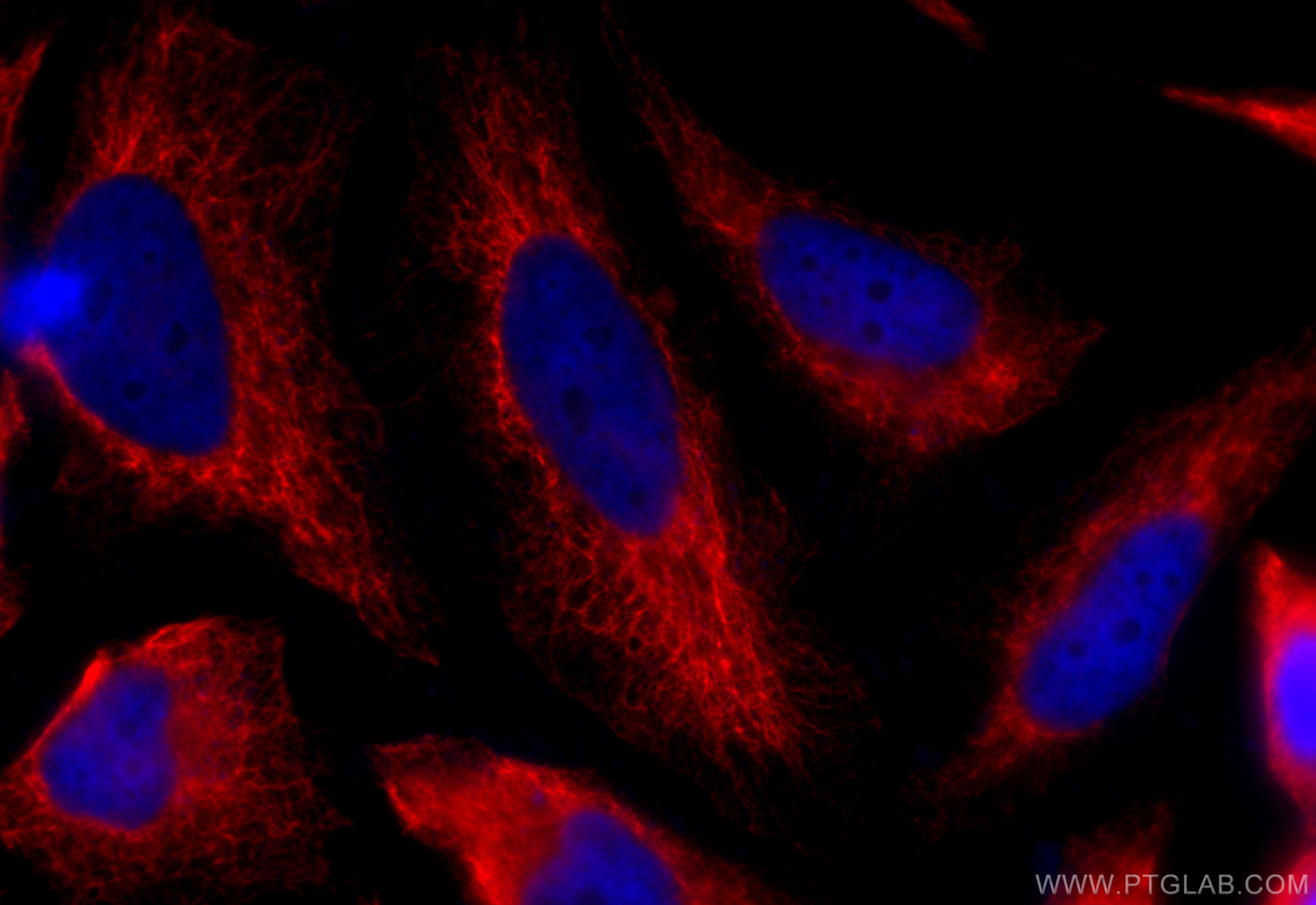
Immunofluorescent analysis of (-20°C Ethanol) fixed HeLa cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:200 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-4).
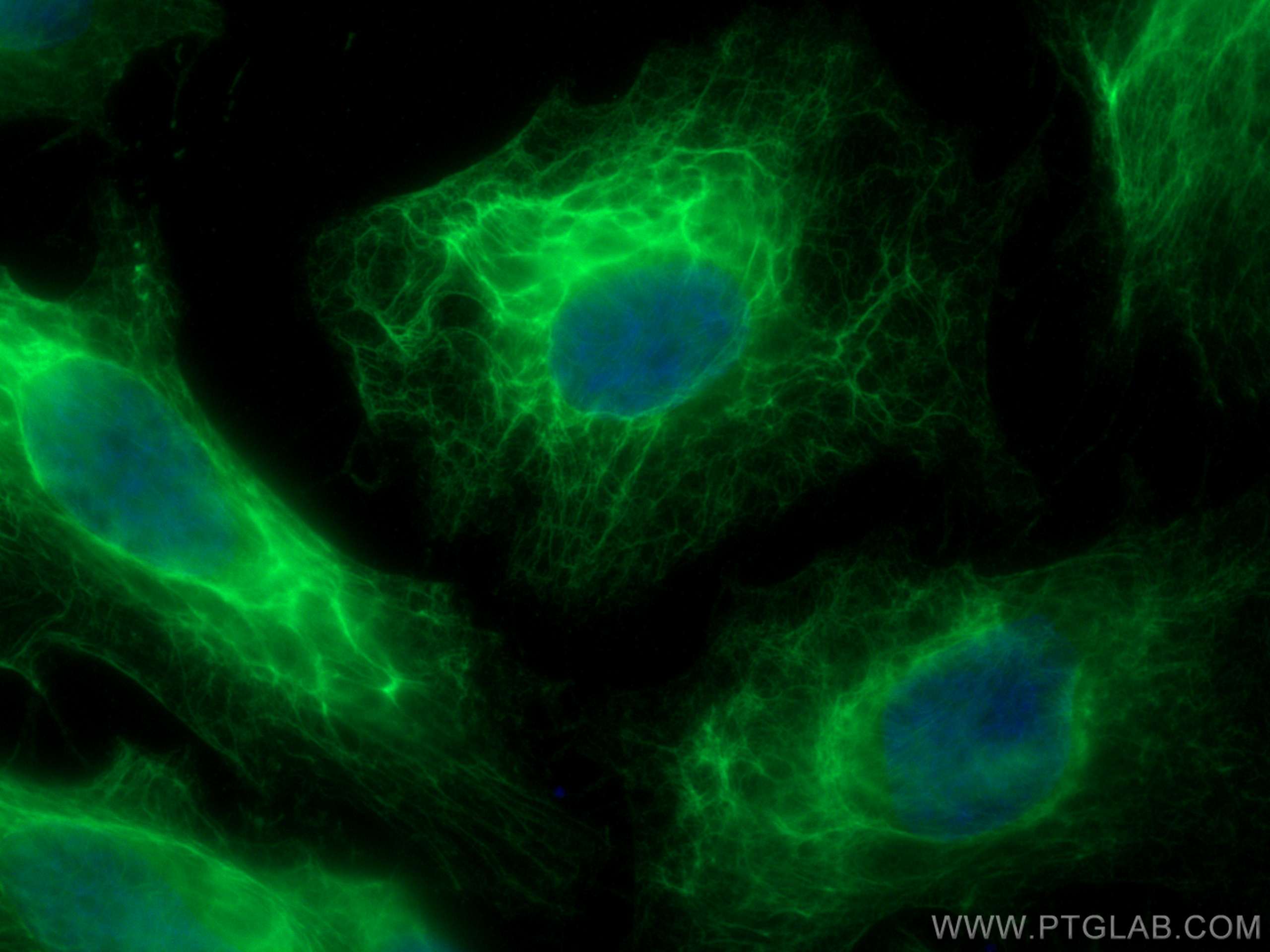
IF Staining of HeLa using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (-20°C Ethanol) fixed HeLa cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:400 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L).
IF Staining of A431 using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (-20°C Methanol) fixed A431 cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:250 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-4).
IF/ICC Figures
IF Staining of A431 using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (-20°C Methanol) fixed A431 cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:200 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-2).
IF Staining of HeLa using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed HeLa cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:200 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L).
IF Staining of mouse breast cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed mouse breast cancer using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:400 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-2).
IF Staining of HeLa using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (-20°C Ethanol) fixed HeLa cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:200 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-4).
IF Staining of HeLa using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (-20°C Ethanol) fixed HeLa cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:400 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L).
IF Staining of A431 using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (-20°C Methanol) fixed A431 cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:250 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-4).
IF/ICC Figures
IF Staining of A431 using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (-20°C Methanol) fixed A431 cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:200 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-2).
IF Staining of HeLa using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed HeLa cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:200 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L).
IF Staining of mouse breast cancer using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed mouse breast cancer using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:400 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-2).
IF Staining of HeLa using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (-20°C Ethanol) fixed HeLa cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:200 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-4).
IF Staining of HeLa using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (-20°C Ethanol) fixed HeLa cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:400 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L).
IF Staining of A431 using 26411-1-AP
Immunofluorescent analysis of (-20°C Methanol) fixed A431 cells using pan-keratin antibody (26411-1-AP) at dilution of 1:250 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) (SA00013-4).