- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-BHLHE40
BHLHE40 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF, IP, ChIP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 17895-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
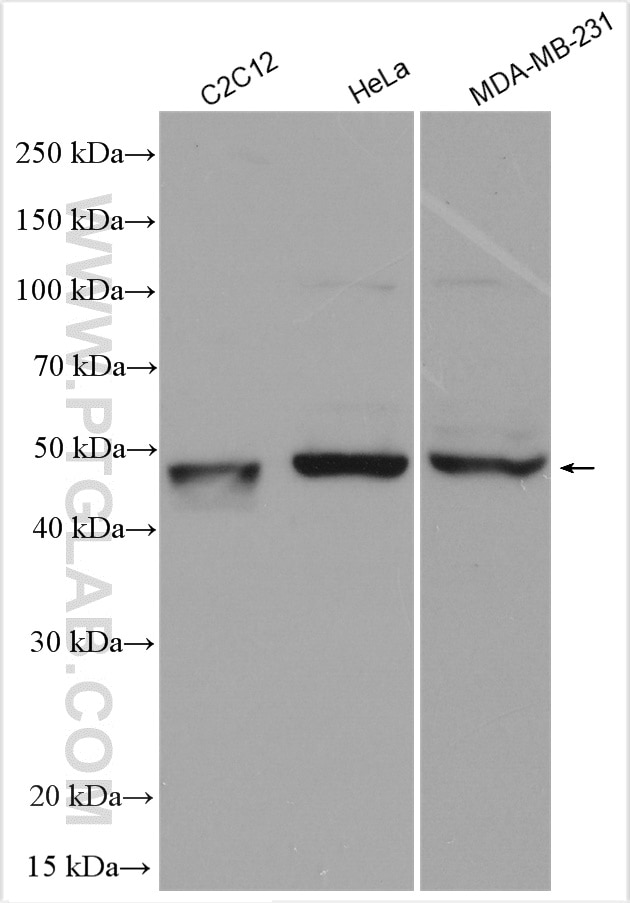
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules C2C12, cellules HeLa, cellules MDA-MB-231 |
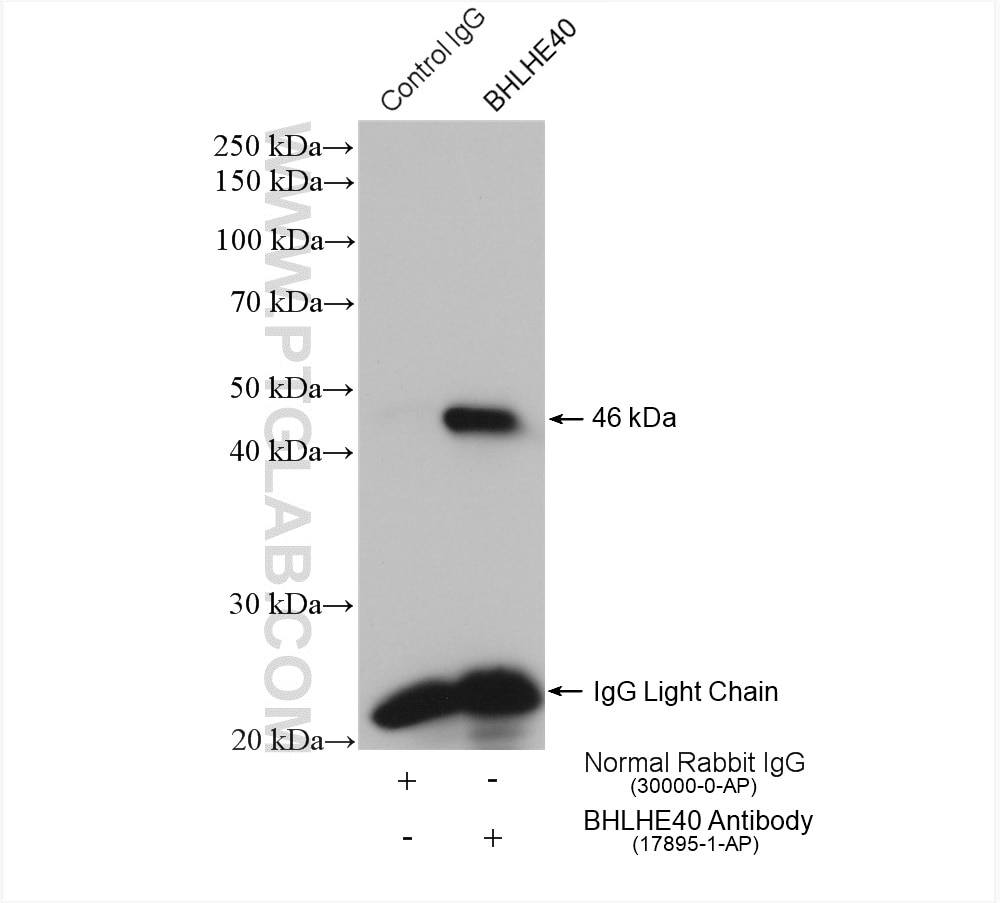
| Résultats positifs en IP | cellules HeLa, |
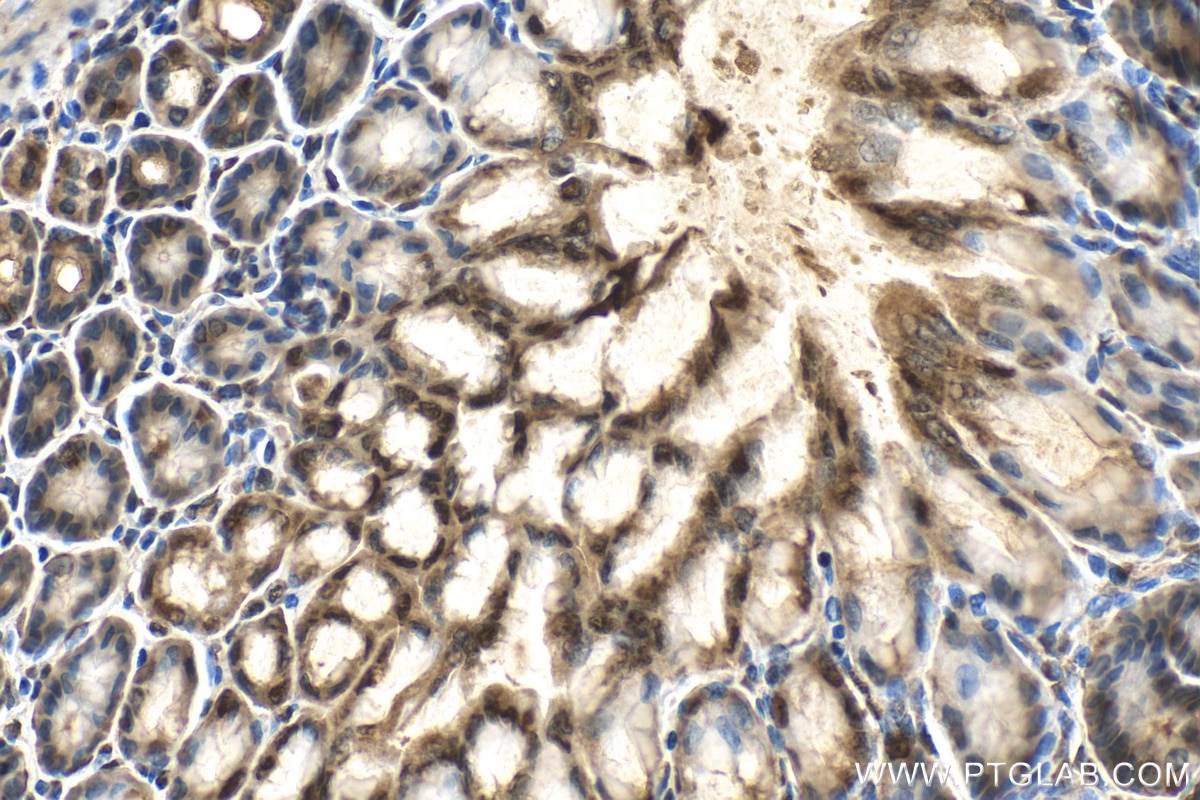
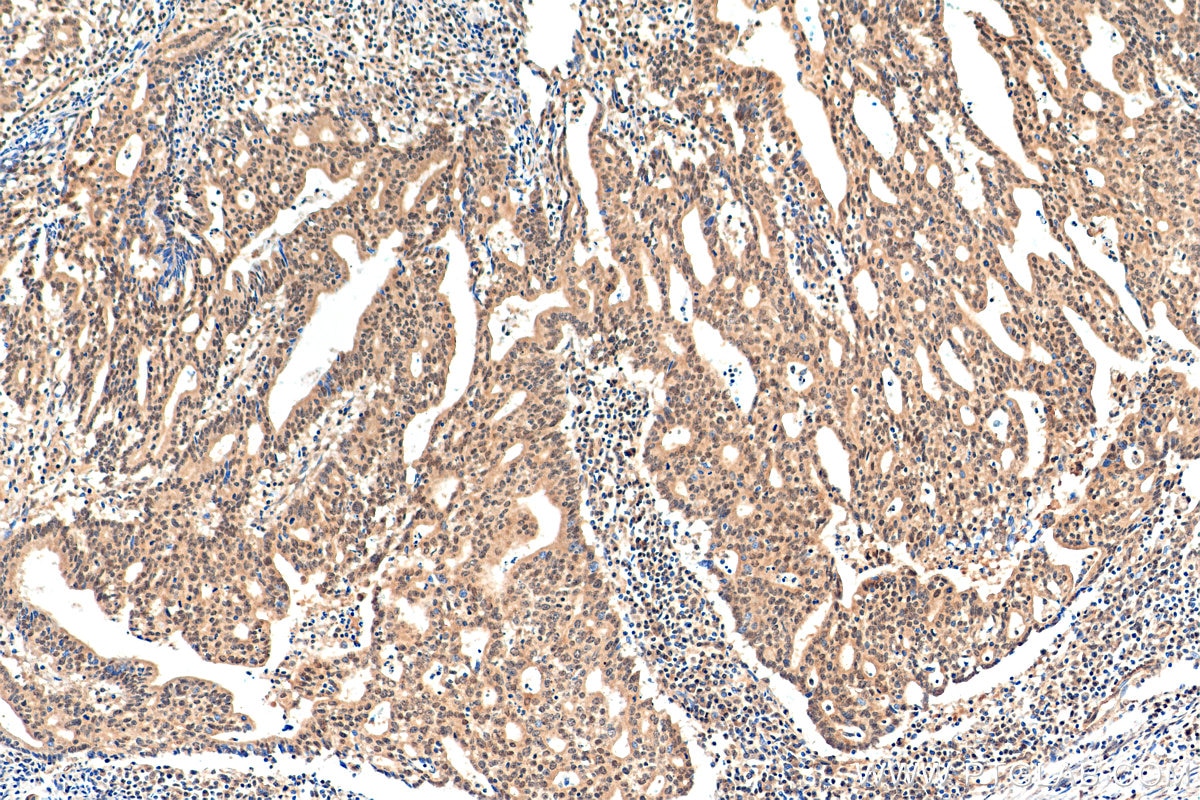
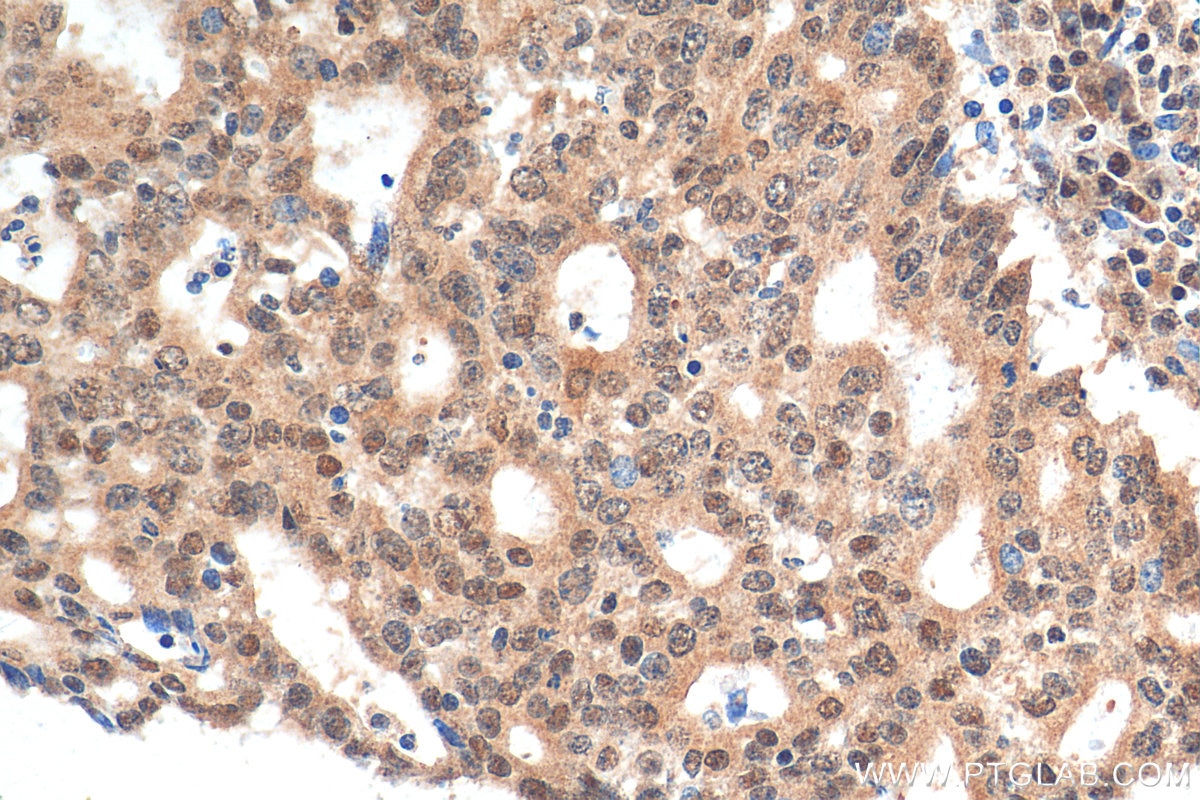
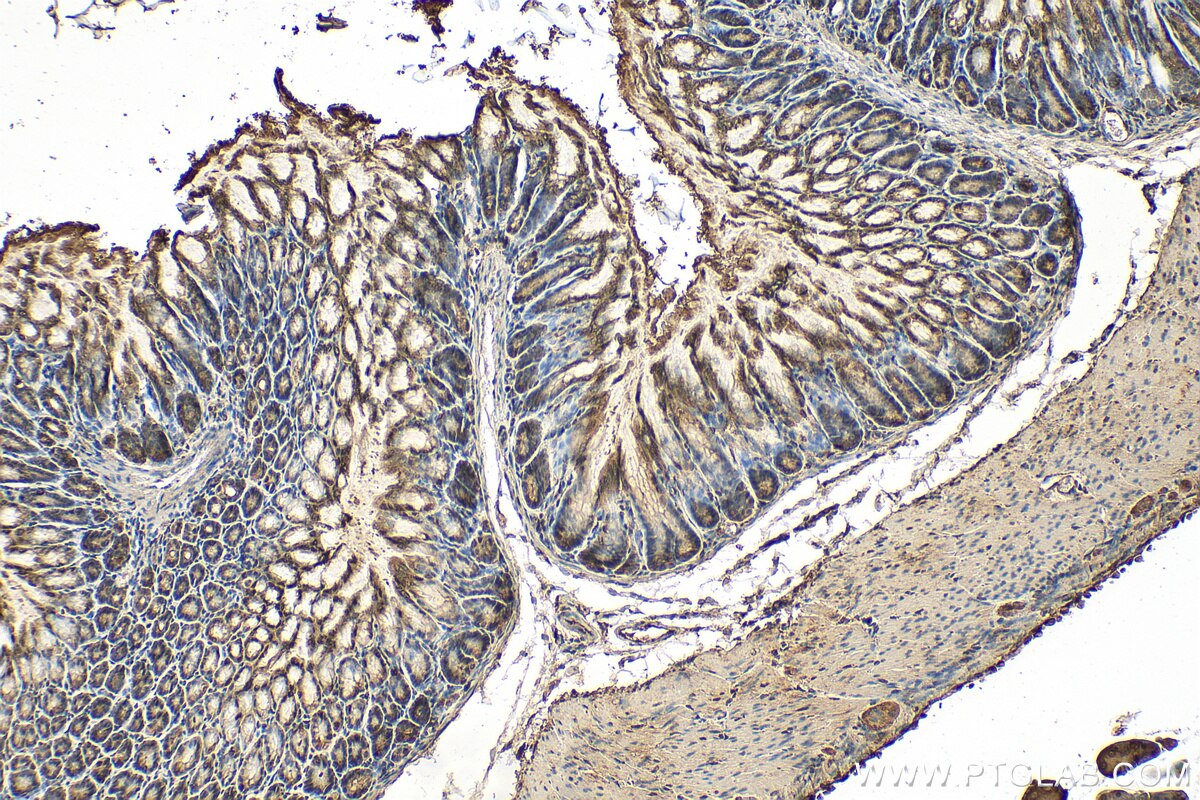
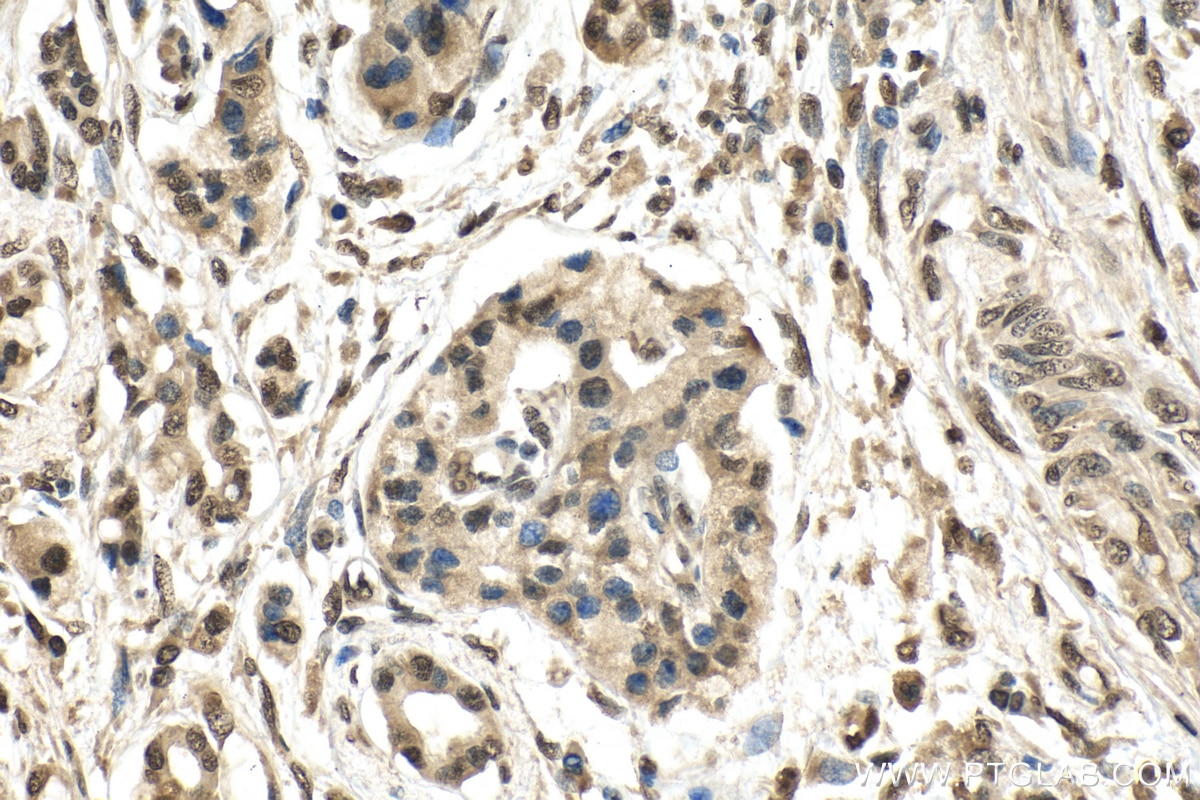
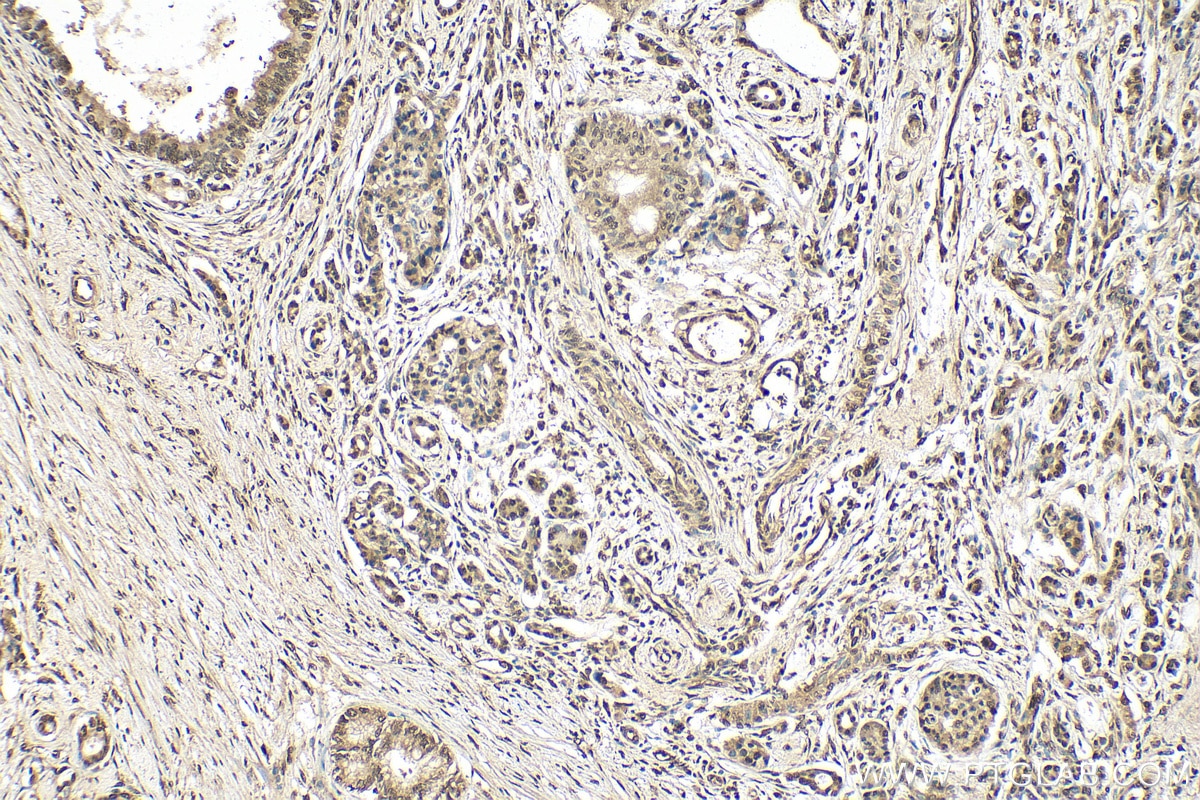
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer de l'endomètre humain, tissu de cancer du pancréas humain, tissu d'estomac de souris il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 5 publications below |
| WB | See 14 publications below |
| IHC | See 5 publications below |
| IF | See 3 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
| ChIP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
17895-1-AP cible BHLHE40 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF, IP, ChIP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | BHLHE40 Protéine recombinante Ag12236 |
| Nom complet | basic helix-loop-helix family, member e40 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 412 aa, 46 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 46-50 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC082238 |
| Symbole du gène | BHLHE40 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 8553 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
BHLHE40 (Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Family Member E40), also known as BHLHB2, STRA13, DEC1, or SHARP2, is a member of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) protein family, a large superfamily of transcriptional regulators expressed in many organisms. BHLHE40 is known to regulate a wide variety of essential cellular processes, including cell cycle, cellular proliferation, programmed cell death, cellular development and differentiation, as well as circadian rhythms (PMID: 34551158). It is reported that BHLHE40 is overexpressed in gastric, breast, and brain tumors; and downregulated in colorectal, esophageal, pancreatic and lung cancer (PMID: 32577154).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for BHLHE40 antibody 17895-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for BHLHE40 antibody 17895-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for BHLHE40 antibody 17895-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Front Cell Dev Biol Bhlhe40/Sirt1 Axis-Regulated Mitophagy Is Implicated in All-Trans Retinoic Acid-Induced Spina Bifida Aperta.
| ||
Ann N Y Acad Sci LncRNA-ES3 inhibition by Bhlhe40 is involved in high glucose-induced calcification/senescence of vascular smooth muscle cells. | ||
Front Cardiovasc Med 17β-Estradiol Inhibits Proliferation and Oxidative Stress in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells by Upregulating BHLHE40 Expression.
| ||
Biochem Biophys Res Commun Loss of circadian protein TIMELESS accelerates the progression of cellular senescence. | ||
J Physiol Biochem Long noncoding RNA SNHG1 alleviates high glucose-induced vascular smooth muscle cells calcification/senescence by post-transcriptionally regulating Bhlhe40 and autophagy via Atg10 | ||
Front Cardiovasc Med Cardiac-specific knockdown of Bhlhe40 attenuates angiotensin II (Ang II)-Induced atrial fibrillation in mice |