- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-GFAP
GFAP Polyclonal Antibody for IF-P
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
IF-P
Conjugaison
CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye
N° de cat : CL488-16825
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
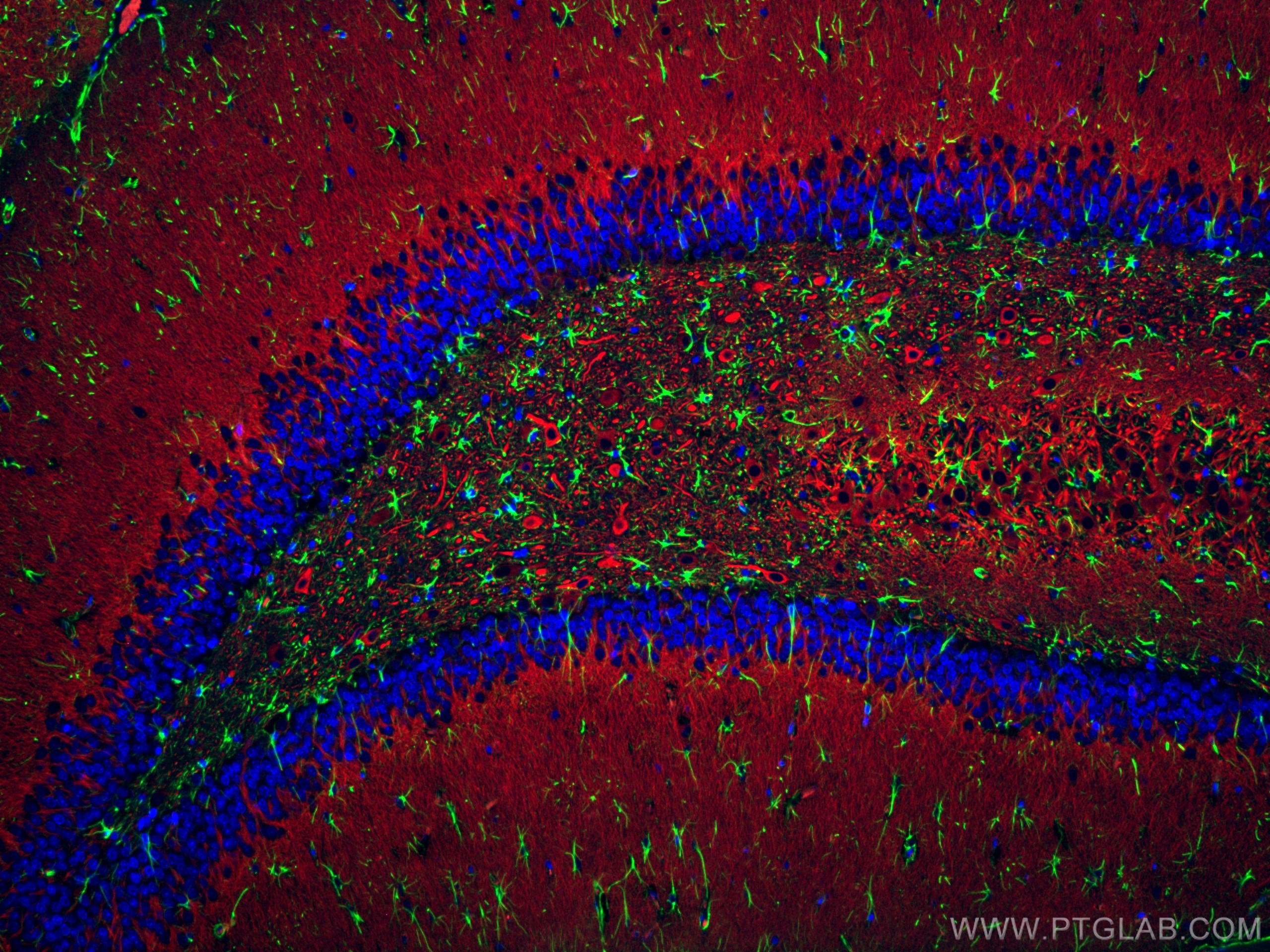
| Résultats positifs en IF-P | tissu cérébral de rat, tissu cérébral de souris |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| IF | See 6 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
CL488-16825 cible GFAP dans les applications de IF-P et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | GFAP Protéine recombinante Ag10423 |
| Nom complet | glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 432 aa, 50 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 45-50 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC013596 |
| Symbole du gène | GFAP |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 2670 |
| Conjugaison | CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 493 nm / 522 nm |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20 °C. Éviter toute exposition à la lumière. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Function
GFAP (Glial fibrillary acidic protein) is a type III intermediate filament (IF) protein specific to the central nervous system (CNS). GFAP is one of the main components of the intermediate filament network in astrocytes and has been proposed as playing a role in cell migration, cell motility, maintaining mechanical strength, and in mitosis.Tissue specificity
GFAP is expressed in central nervous system cells, predominantly in astrocytes. GFAP is commonly used as an astrocyte marker. However, GFAP is also present in peripheral glia and in non-CNS cells, including fibroblasts, chondrocytes, lymphocytes, and liver stellate cells (PMID: 21219963).Involvement in disease
- Mutations in GFAP lead to Alexander disease (OMIM: 203450), an autosomal dominant CNS disorder. The mutations present in affected individuals are thought to be gain-of-function.
- Upregulation of GFAP is a hallmark of reactive astrocytes, in which GFAP is present in hypertrophic cellular processes. Reactive astrogliosis is present in many neurological disorders, such as stroke, various neurodegenerative diseases (including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease), and neurotrauma.
Isoforms
Astrocytes express 10 different isoforms of GFAP that differ in the rod and tail domains (PMID: 25726916), which means that they differ in molecular size. Isoform expression varies during the development and across different subtypes of astrocytes. Not all isoforms are upregulated in reactive astrocytes.Post-translational modifications
Intermediate filament proteins are regulated by phosphorylation. Six phosphorylation sites have been identified in GFAP protein, at least some of which are reported to control filament assembly (PMID: 21219963).Cellular localization
GFAP localizes to intermediate filaments and stains well in astrocyte cellular processes.Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL Plus 488 GFAP antibody CL488-16825 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Glia Mechanosensitive channel Piezo1 is an essential regulator in cell cycle progression of optic nerve head astrocytes | ||
Biomolecules Interplay between Energy Supply and Glutamate Toxicity in the Primary Cortical Culture | ||
Neuropharmacology Neuromolecular and behavioral effects of Cannabidiol on depressive-associated behaviors and neuropathic pain conditions in mice | ||
Biol Trace Elem Res The Role of the cGAS/STING Pathway in Arsenic-Induced Neurotoxicity: Insights from the Crosstalk Between Astrocytes and Neurons | ||
J Nanobiotechnology Tungsten-based polyoxometalate nanoclusters as ferroptosis inhibitors modulating S100A8/A9-mediated iron metabolism pathway for managing intracerebral haemorrhage | ||
J Integr Neurosci FKBP51 is Involved in Epileptic Seizure by Regulating PSD95 in a PTZ-Induced Epileptic Mouse Model |