Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-Glucagon
Glucagon Polyclonal Antibody for IF-P
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
IF-P
Conjugaison
CoraLite® Plus 647 Fluorescent Dye
N° de cat : CL647-15954
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
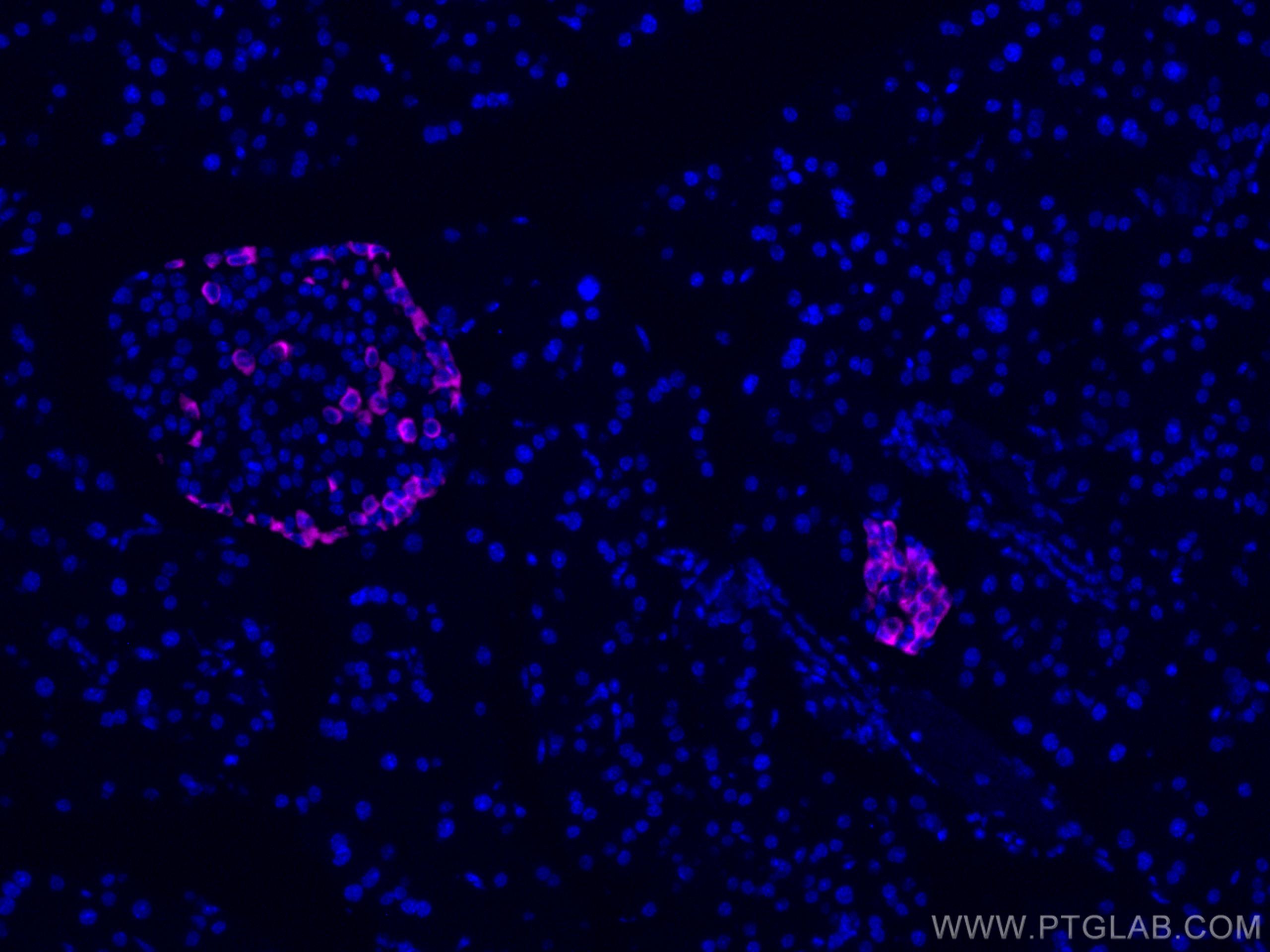
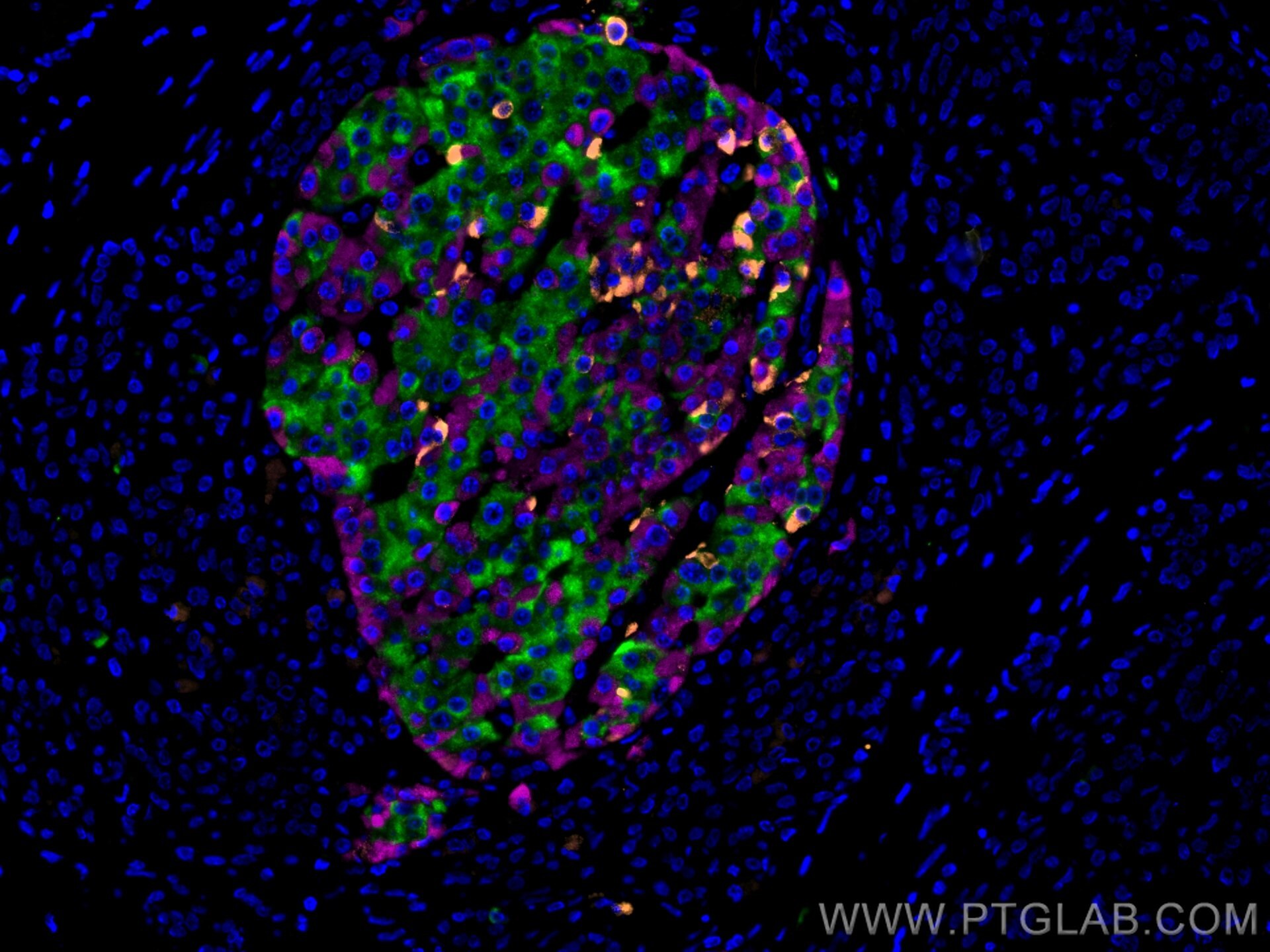
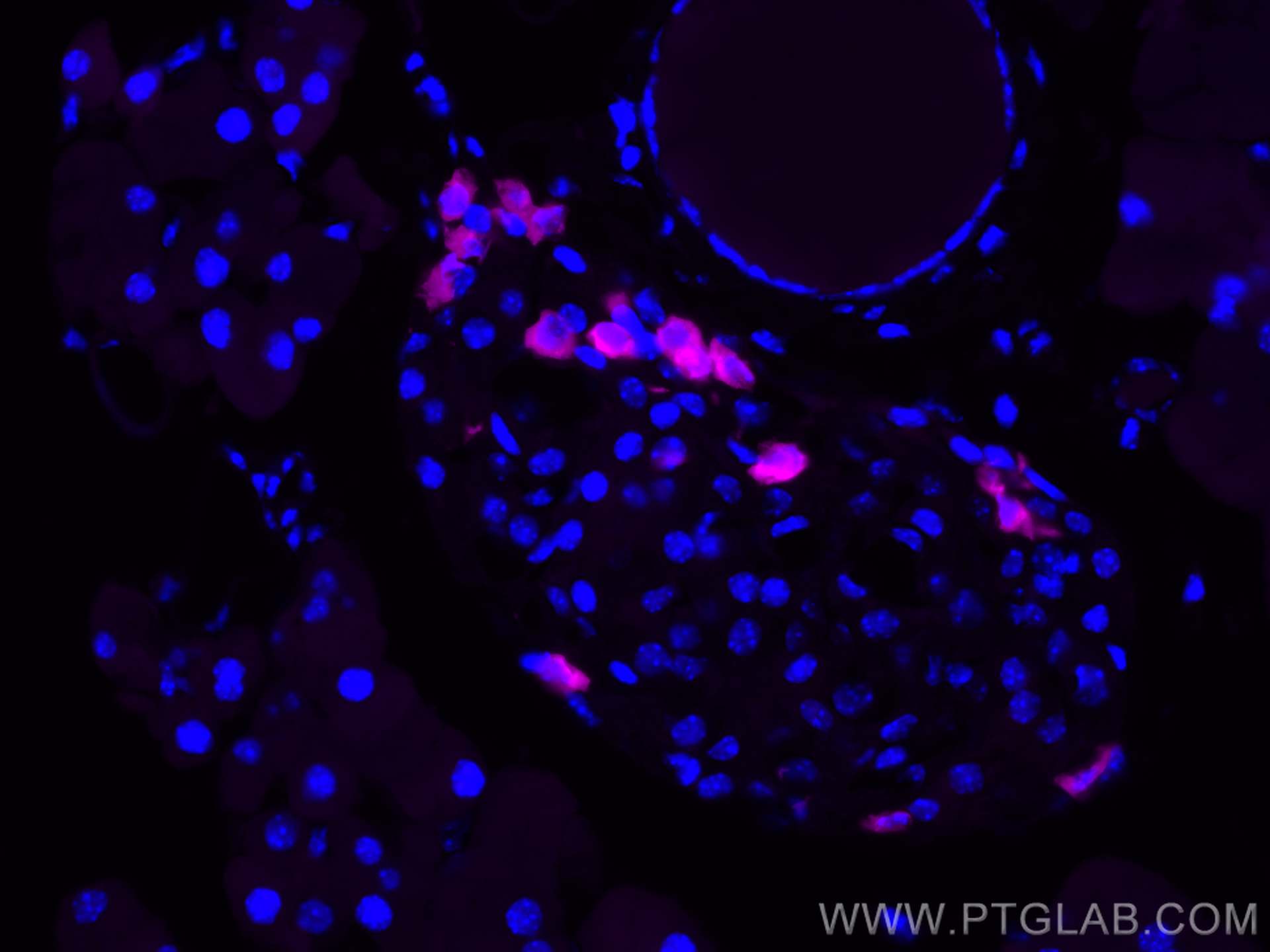
| Résultats positifs en IF-P | tissu pancréatique de souris, tissu de cancer du pancréas humain |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
CL647-15954 cible Glucagon dans les applications de IF-P et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Glucagon Protéine recombinante Ag8677 |
| Nom complet | glucagon |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 180 aa, 21 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC005278 |
| Symbole du gène | Glucagon |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 2641 |
| Conjugaison | CoraLite® Plus 647 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 654 nm / 674 nm |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20 °C. Éviter toute exposition à la lumière. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Background
Glucagon is a protein cleaved from a precursor protein encoded by the GCG gene. The distinct peptides formed from this precursor include Glucagon, Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 (GLP-1), Glucagon-Like Peptide 2 (GLP-2), and oxyntomodulin. Glucagon is essential in maintaining blood glucose homeostasis and therefore has a key role in Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
What is the molecular weight of Glucagon?
21 kDa. Glucagon is composed of 180 amino acids and is a ligand for a specific G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR).
Where is it expressed?
Glucagon is a hormone secreted by the pancreas, in the α cells of the islets of Langerhans (PMID: 18880761). GLP-1, GLP-2, and oxyntomodulin are secreted by gut endocrine cells of the GI tract and also by selected neurons in the brain. These secreted proteins are transported to the target organ in plasma.
What is the function of glucagon?
The regulation of blood glucose levels is controlled by a balance of the hormones INS and glucagon in a negative feedback loop. A drop in blood glucose, or hypoglycemia, stimulates the release of glucagon. This initiates a cascade of signals, ultimately causing the conversion of stored glycogen into free glucose in a process called glycogenolysis, which takes place in liver and muscle cells. Glucagon can also stimulate gluconeogenesis in the liver, the process of forming glucose from non-carbohydrate sources such as amino acids (PMID: 13477815).
What diseases are associated with glucagon?
Glucagon is key in homeostasis of blood glucose and maintaining the balance between hyperglycaemia and hypoglycemia. It is therefore important in the study of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes mellitus, where dysfunction of the pancreatic cells leads to a deregulation of blood glucose levels (PMID: 19326096). In both forms of the disease, glucagon secretion is impaired, from too much being secreted during hyperglycaemia, to too little being released to normalize hypoglycemia (PMID: 18197838).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL Plus 647 Glucagon antibody CL647-15954 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |