- Phare
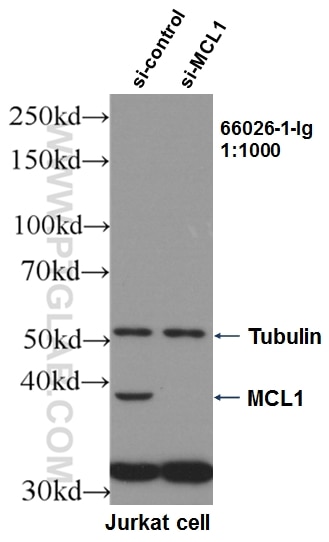
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-MCL1
MCL1 Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2b
Réactivité testée
Humain et plus (3)
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, CoIP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
1E3C2
N° de cat : 66026-1-Ig
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
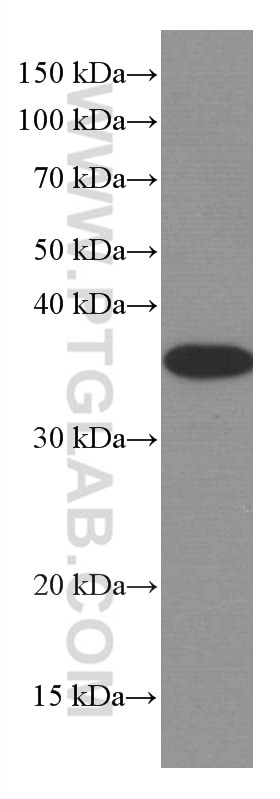
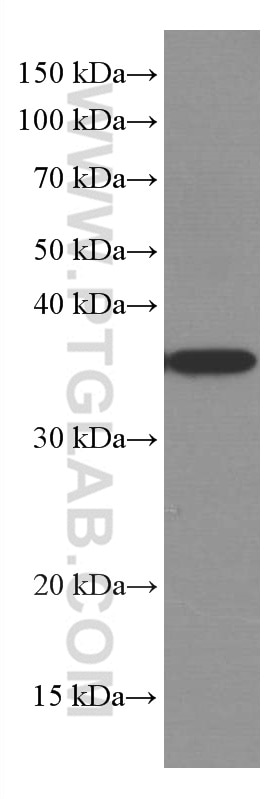
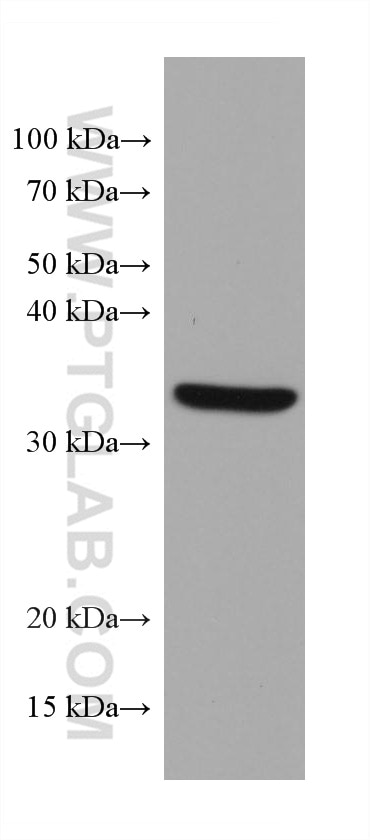
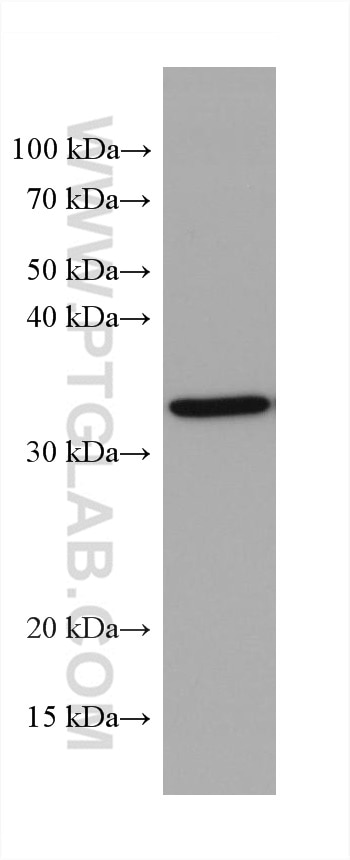
Applications testées
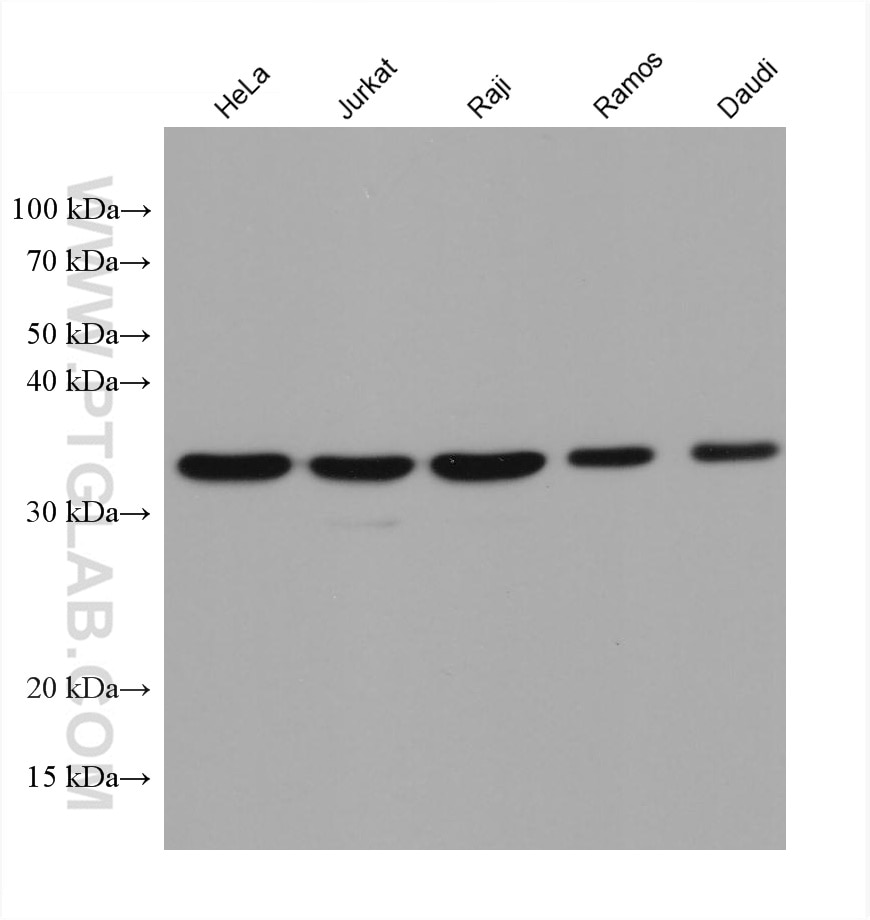
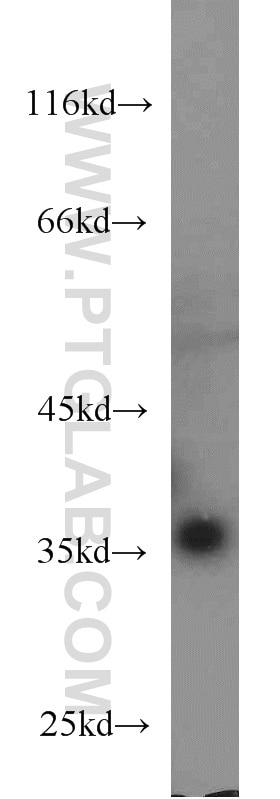
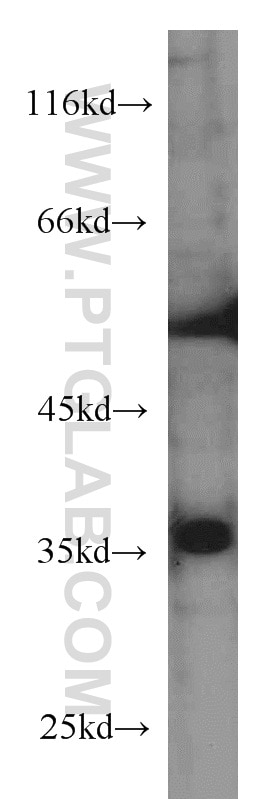
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HeLa, cellules A431, cellules A549, cellules Daudi, cellules Jurkat, cellules Raji, cellules Ramos |
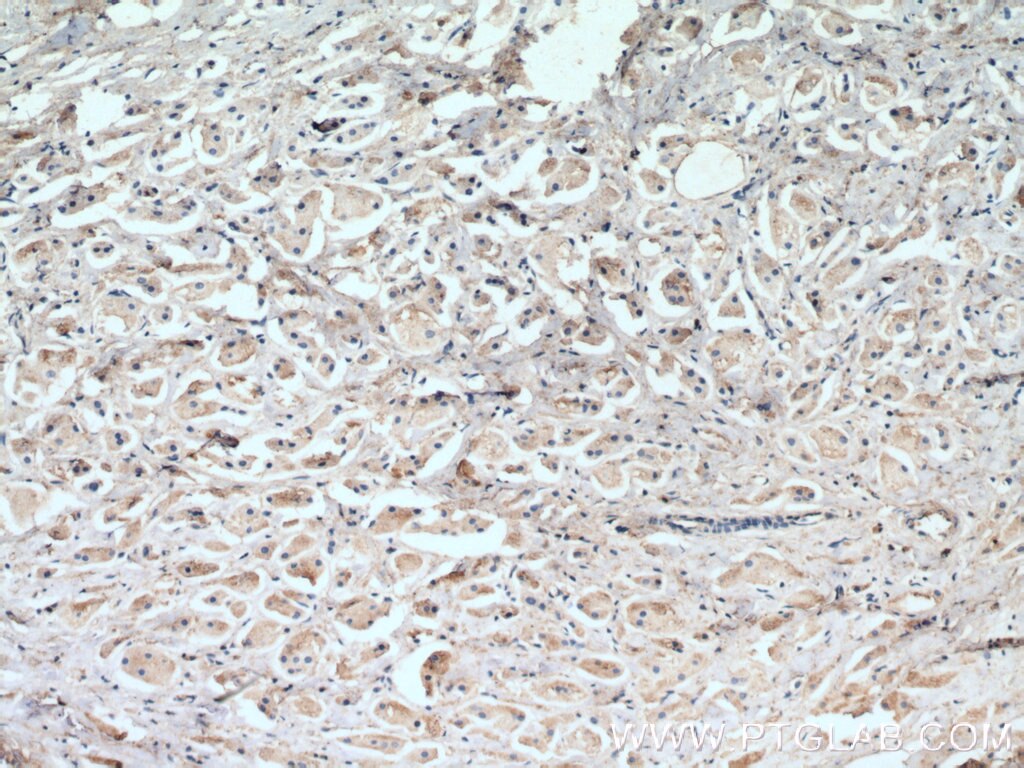
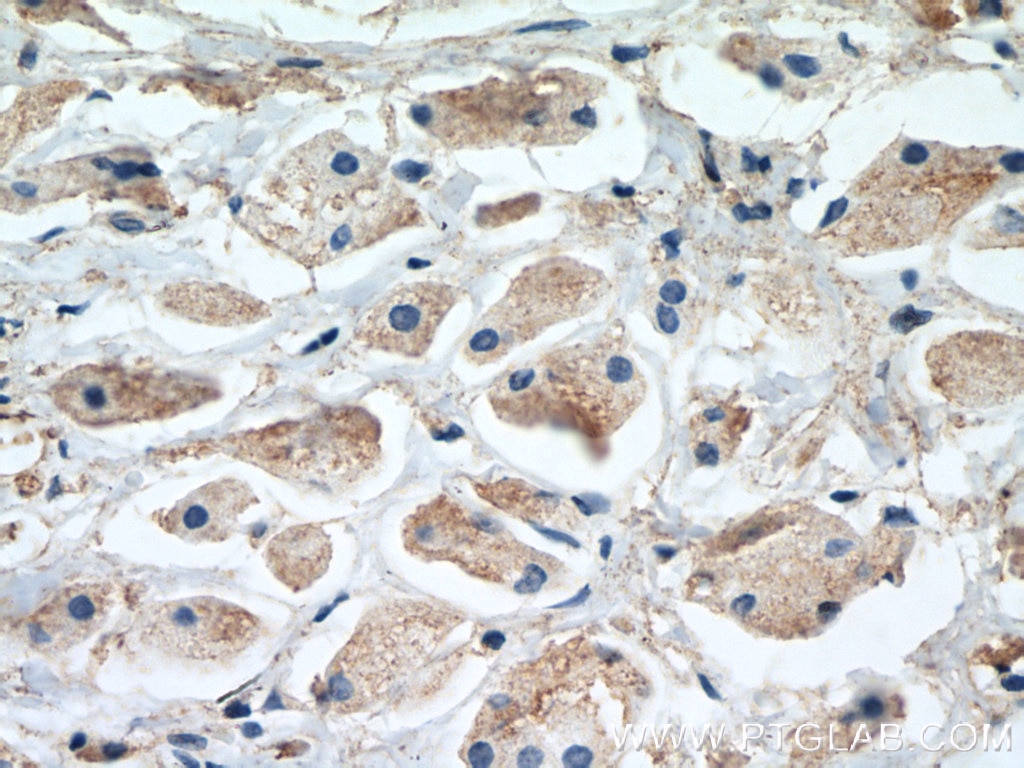
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer du sein humain, il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
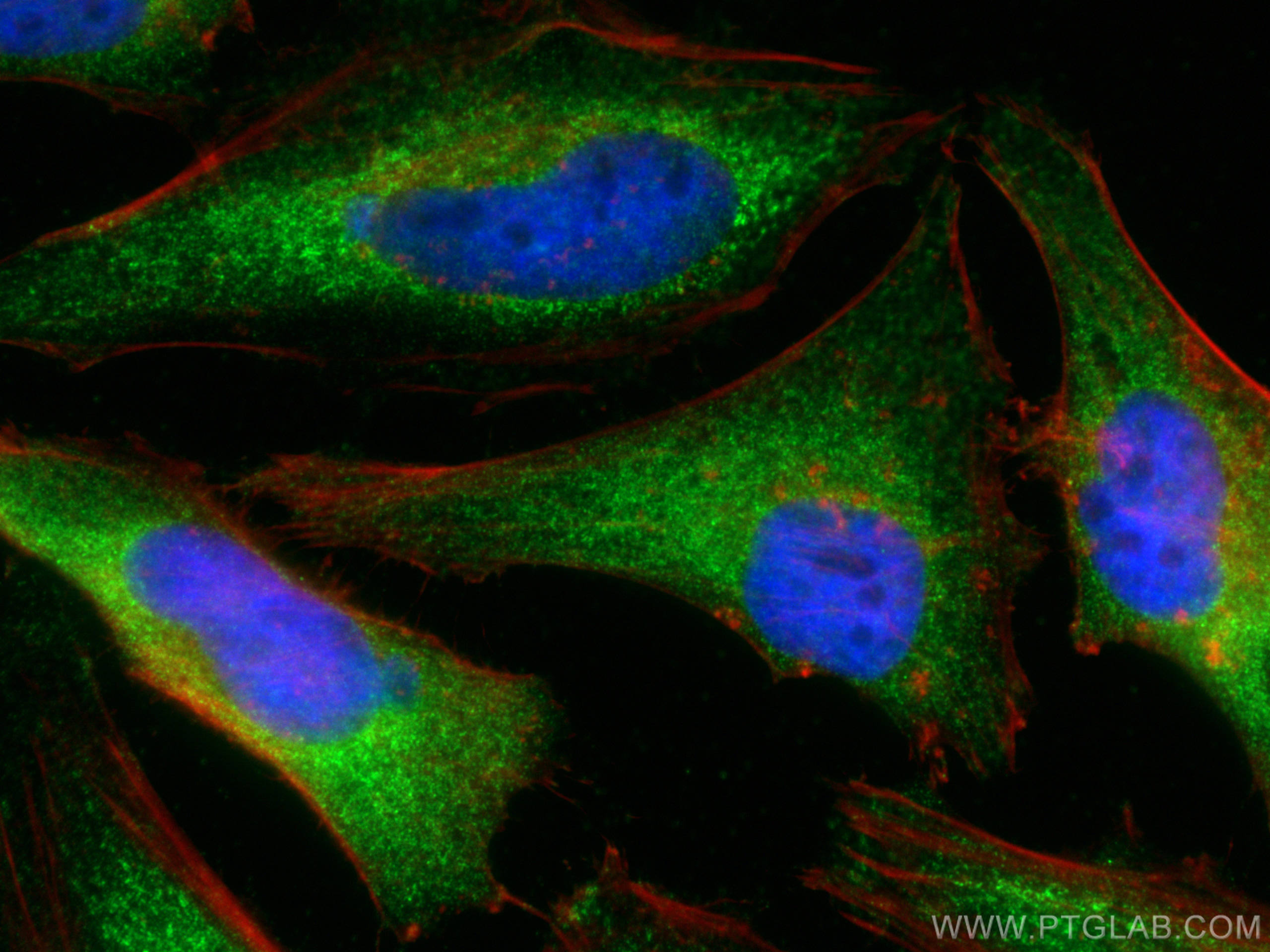
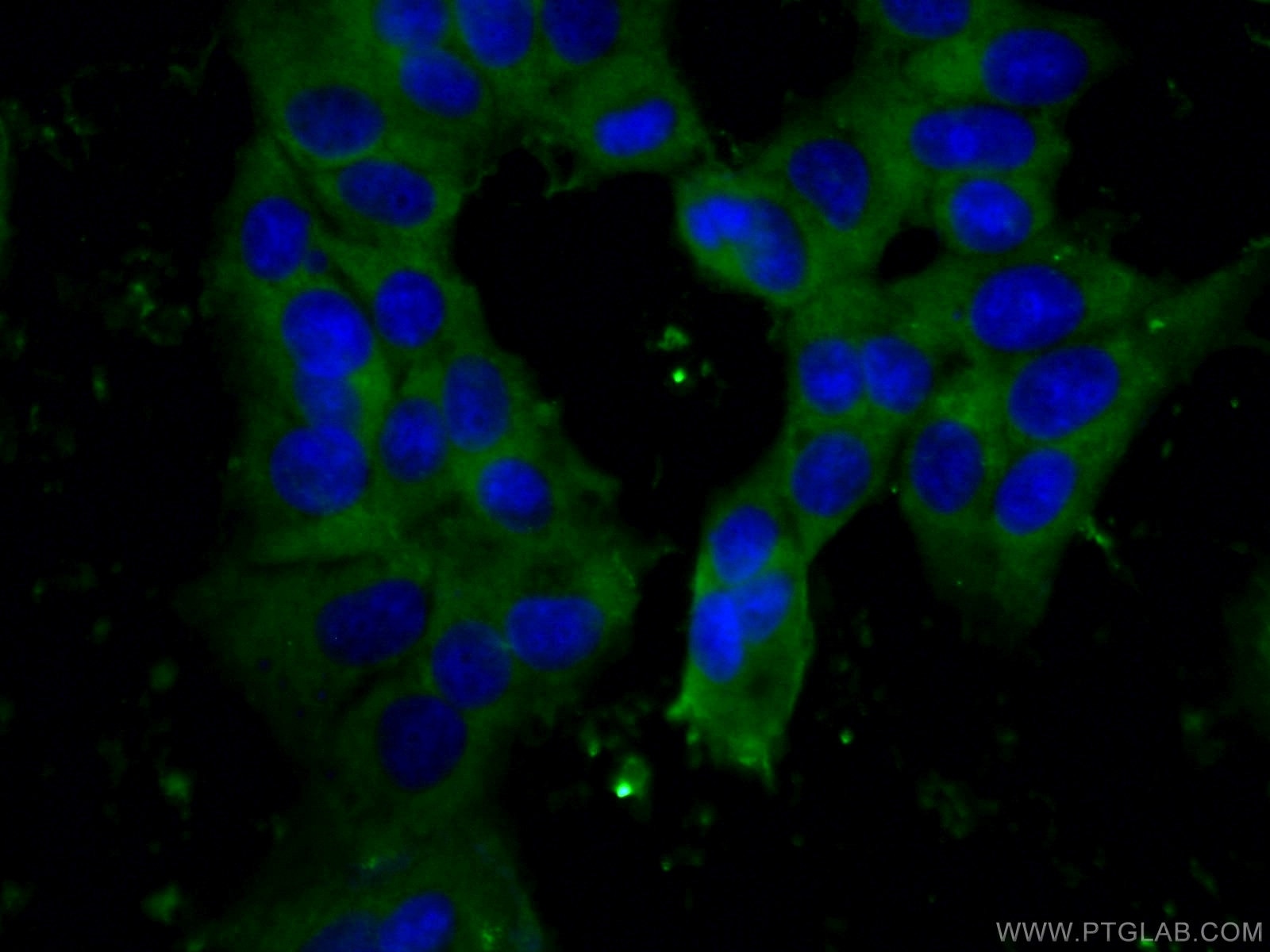
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules HeLa, cellules MCF-7 |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:10000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:250-1:1000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 19 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
66026-1-Ig cible MCL1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, CoIP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain
| Réactivité | Humain |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris, Hamster |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | MCL1 Protéine recombinante Ag10609 |
| Nom complet | myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1 (BCL2-related) |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 350 aa, 37 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC107735 |
| Symbole du gène | MCL1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 4170 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
MCL-1 is an anti-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family originally isolated from the ML-1 human myeloid leukemia cell line. Similar to BCL2 and BCL2L1, MCL1 can interact with BAX and/or BAK1 to inhibit mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. Mcl-1 is critical for the proliferation and survival of myeloma cells in vitro, and overexpression of Mcl-1 protein in myeloma cells is associated with relapse and short event-free survival in multiple myeloma patients. Recent studies show that MCL-1 is upregulated in numerous haematological and solid tumour malignancies. Therefore, MCL-1 has been suggested as a potential new therapeutic target.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for MCL1 antibody 66026-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for MCL1 antibody 66026-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for MCL1 antibody 66026-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Int J Mol Sci Intermittent Fasting Aggravates Lupus Nephritis through Increasing Survival and Autophagy of Antibody Secreting Cells in MRL/lpr Mice. | ||
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis Extracellular ATP (eATP) inhibits the progression of endometriosis and enhances the immune function of macrophages | ||
Epigenetics Decreased DHRS2 expression is associated with HDACi resistance and poor prognosis in ovarian cancer. | ||
J Nat Prod Hernandezine Regulates Proliferation and Autophagy-Induced Apoptosis in Melanoma Cells. | ||
Mol Microbiol The emerging oral pathogen, Filifactor alocis, extends the functional lifespan of human neutrophils. | ||
Ann Transl Med Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) inhibit the expression of anti-apoptosis proteins through up-regulation of ATF4 on breast cancer cells. |