Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-MMP14 / MT1-MMP
MMP14 / MT1-MMP Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 29111-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
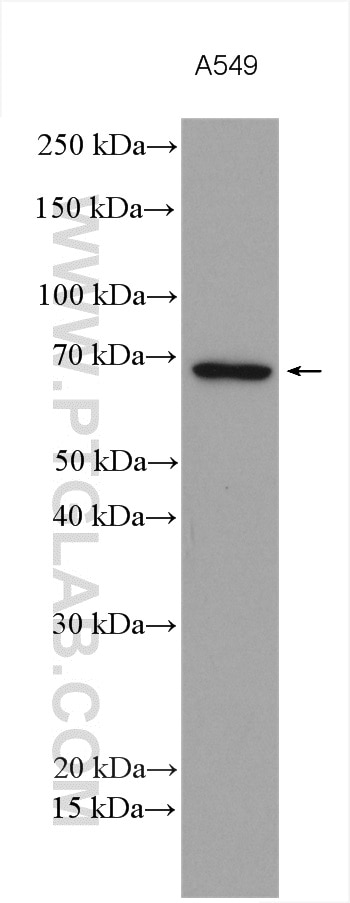
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules A549, |
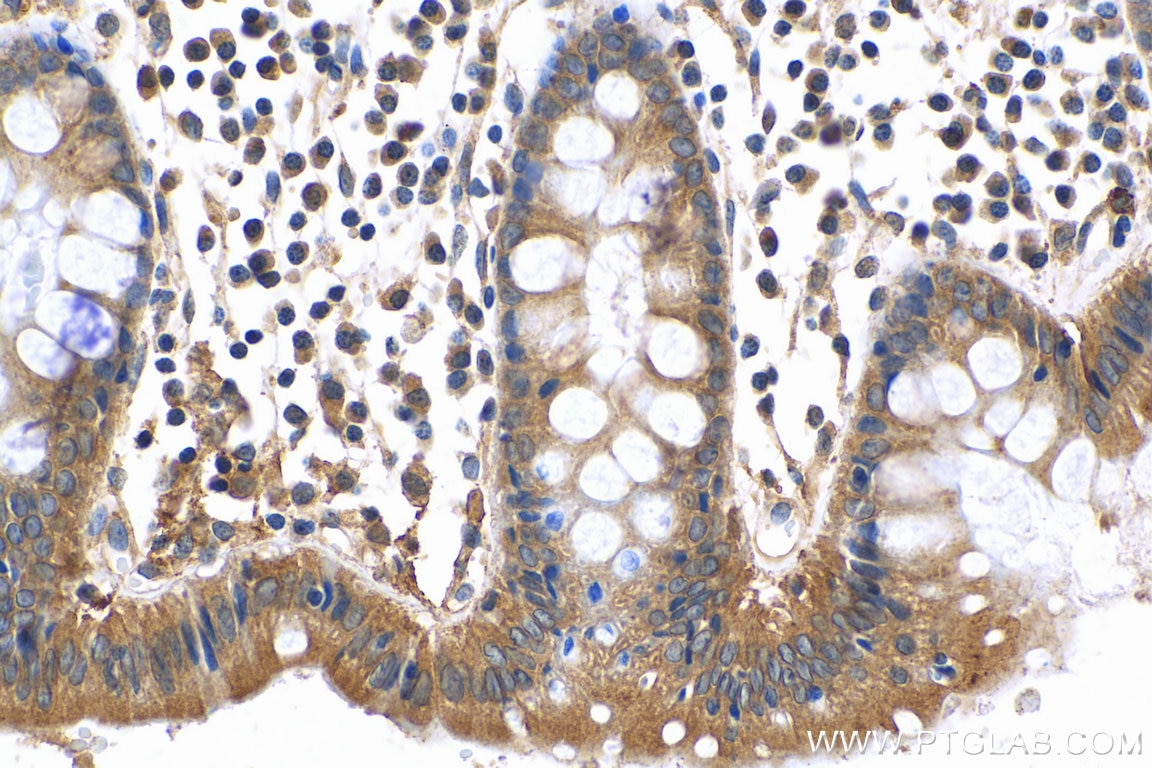
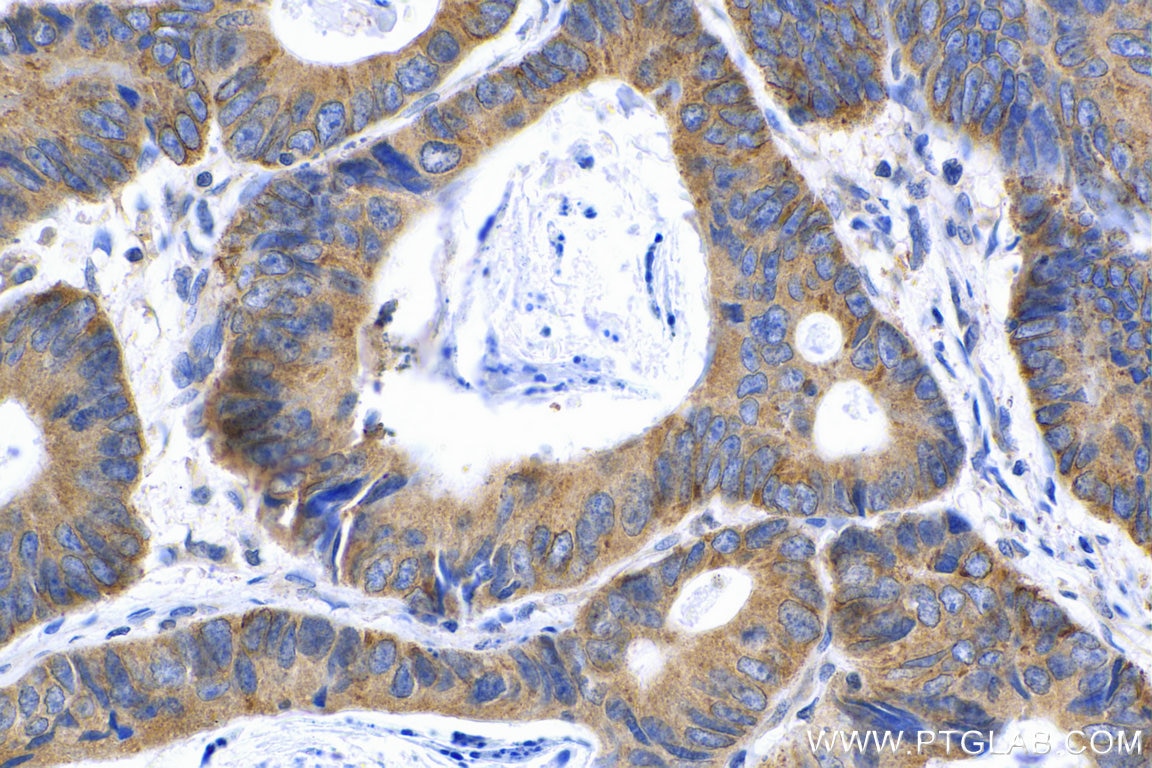
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer du côlon humain, il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
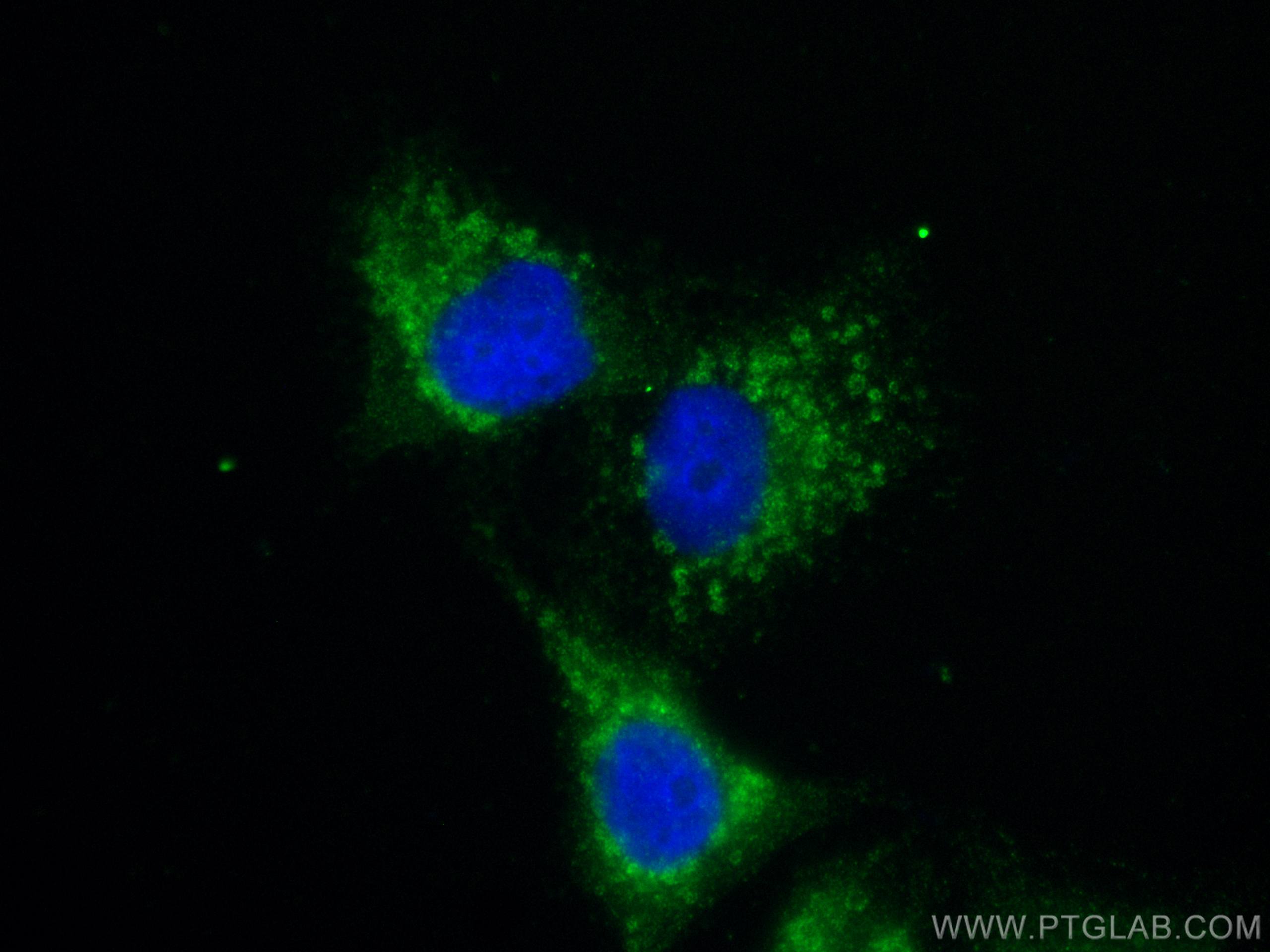
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules A549, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 5 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
29111-1-AP cible MMP14 / MT1-MMP dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Réactivité citée | Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | MMP14 / MT1-MMP Protéine recombinante Ag30755 |
| Nom complet | matrix metallopeptidase 14 (membrane-inserted) |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 66 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 66-70 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC064803 |
| Symbole du gène | MMP14 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 4323 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
MMP14, also named as MT1-MMP, is a key matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family member which plays a crucial role in tumor growth, invasion and metastasis. MT1-MMP is a cell membrane-bound proteinase, and it enhances degradation of collagen IV, a major component of the basement membrane, by forming a complex with tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2) to activate pro-MMP-2. MT1-MMP can influence venous invasion, intrahepatic metastasis , and patient outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). MT1-MMP was reported to be present in centromere and could lead to chromosome instability in MDCK cells, indicating that MT1-MMP may have more novel functions in the intracellular compartments. In western blotting, pro-MMP14 (65 kDa) and MMP14 (51 kDa) bands showed with the truncated MMP14 (45, 42, 35, 20 kDa) forms (PMID:12097451).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for MMP14 / MT1-MMP antibody 29111-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for MMP14 / MT1-MMP antibody 29111-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for MMP14 / MT1-MMP antibody 29111-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Bioact Mater Biomimetic nanoparticles drive the mechanism understanding of shear-wave elasticity stiffness in triple negative breast cancers to predict clinical treatment | ||
Appl Biochem Biotechnol Kunzea Ericoides (Kanuka) Leaf Extracts Show Moisturisation, Antioxidant, and UV Protection Effects in HaCaT Cells and Anti-melanogenesis Effects in B16F10 Cells | ||
Cancer Lett Distinct Immunophenotypic Profiles and Neutrophil Heterogeneity in Colorectal Cancer | ||
Front Oncol Overexpression of MMP14 is associated with poor prognosis and immune cell infiltration in colon cancer | ||
JCI Insight LRP1 regulates asthmatic airway smooth muscle proliferation through FGF2/ERK signaling |