Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-NFKB1,p105
NFKB1,p105 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ChIP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 23576-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
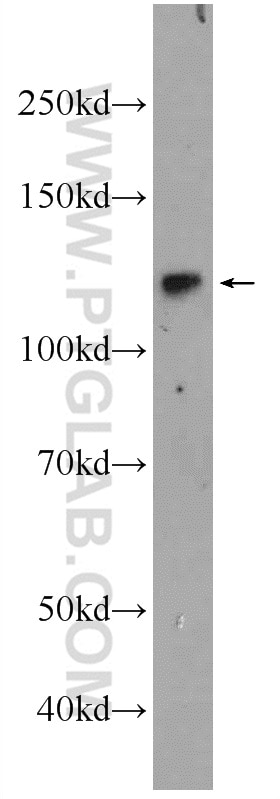
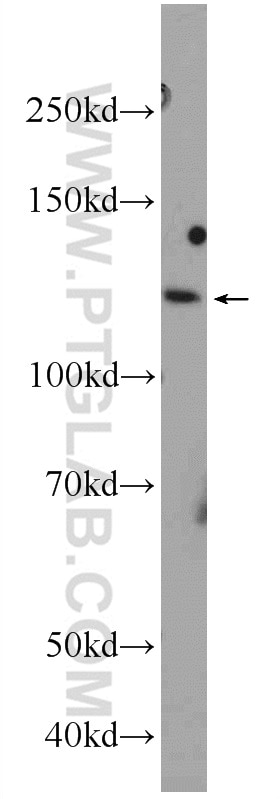
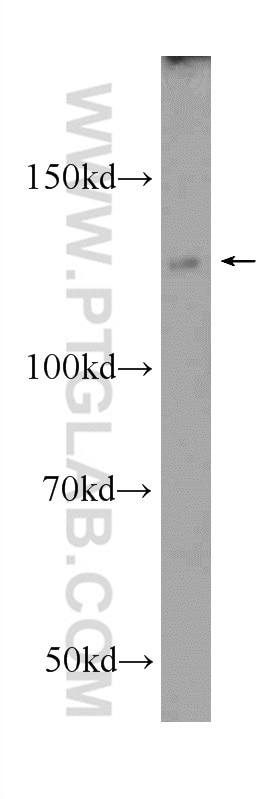
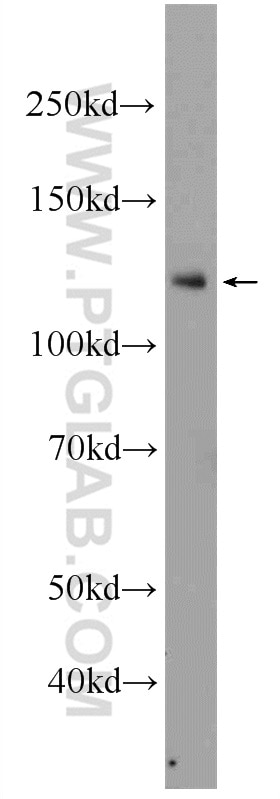
Applications testées
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules SH-SY5Y, cellules HeLa, cellules Jurkat, cellules K-562, cellules Raji |
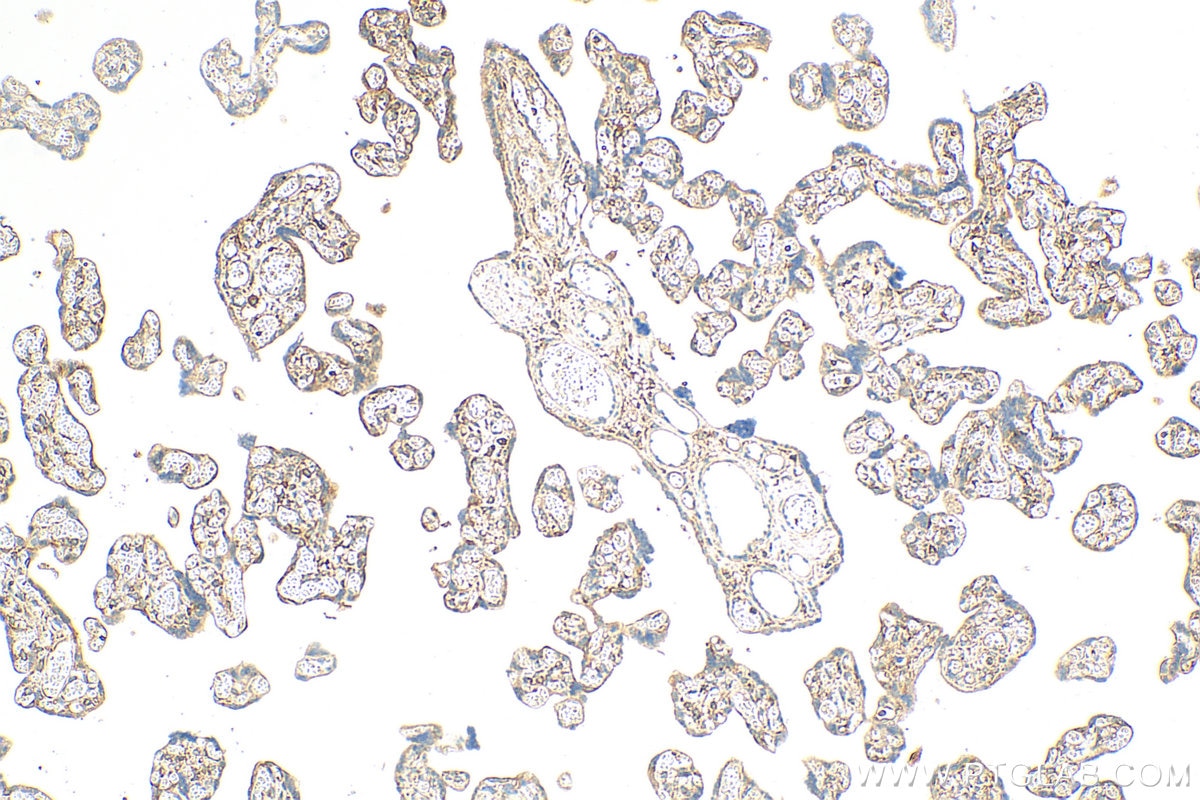
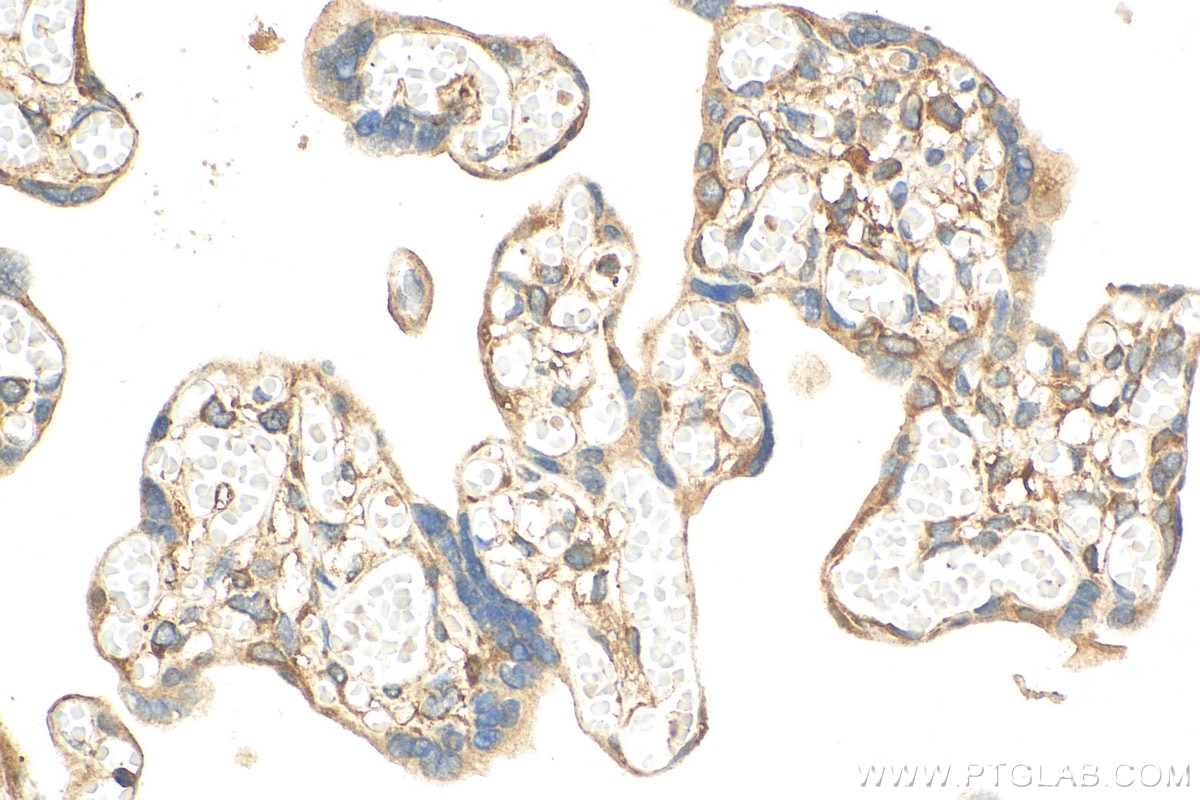
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu placentaire humain, il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
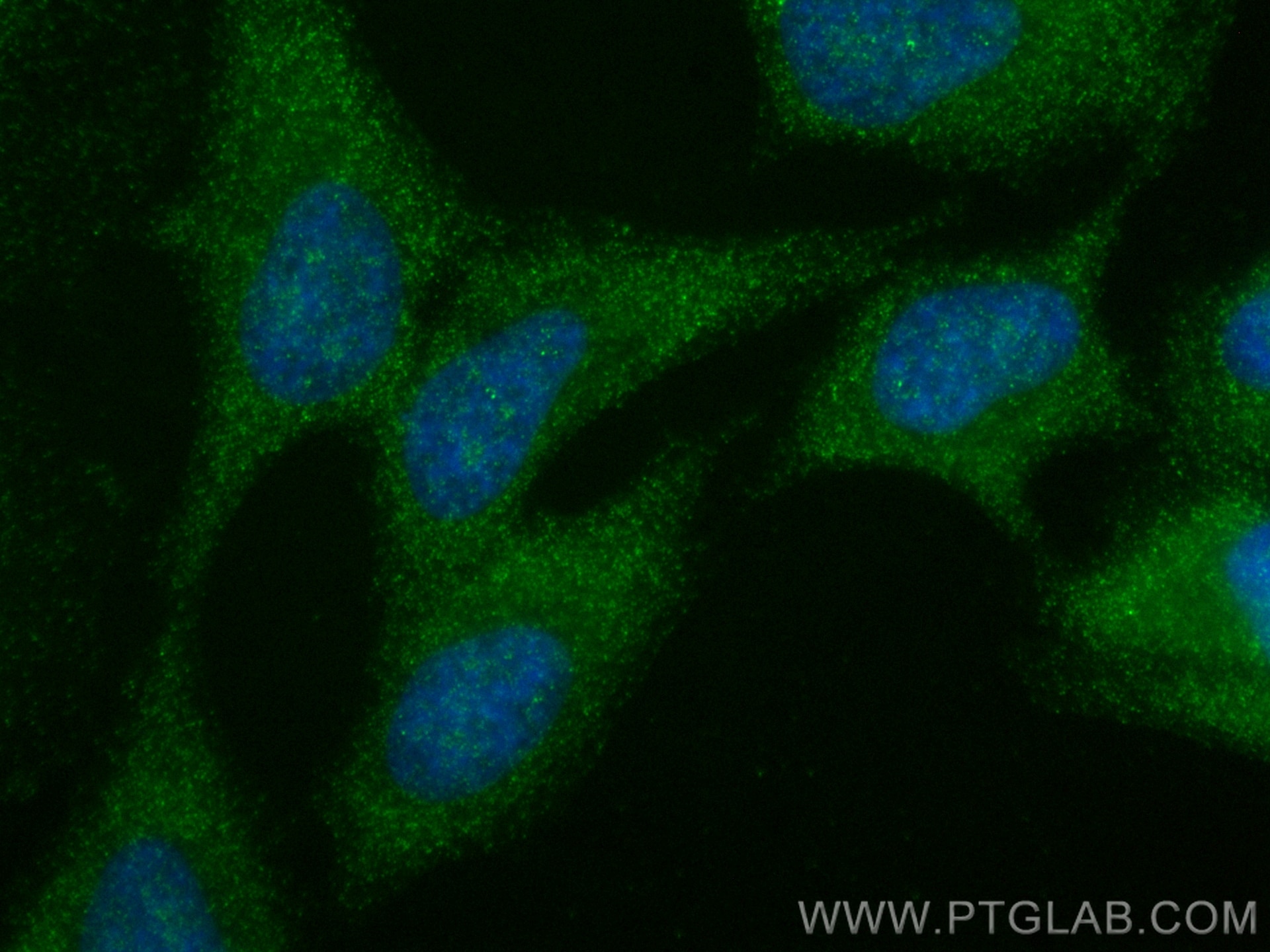
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules HeLa, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 1 publications below |
| ChIP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
23576-1-AP cible NFKB1,p105 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ChIP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain
| Réactivité | Humain |
| Réactivité citée | Humain |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | NFKB1,p105 Protéine recombinante Ag20297 |
| Nom complet | nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 105 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 105 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC051765 |
| Symbole du gène | NFKB1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 4790 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
NFkB is a pleiotropic transcription factor which is present in almost all cell types and is involved in many biological processed such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NFkB is activated by various intra- and extracellular stimuli such as cytokines, oxidant free radicals, ultraviolet irradiation, and bacterial or viral products. NFkB is a family of transcription factors that consists of homo- and heterodimers of NFkB1/p50 and RelA/p65 subunits, and controls a variety of cellular events including development and immune responses. All members share a conserved amino terminus domain that includes dimerization, nuclear localization, and DNA binding regions, and a carboxy terminal transactivation domain. Serines 529 and 536 in the transactivation domain of RelA/p65 are phosphorylated in response to several stimuli including phorbol ester, IL1 alpha and TNF alpha as mediated by IkB kinase and p38 MAPK. Phosphorylation of serines 529 and 536 is critical for RelA/p65 transcriptional activity. Activated NFkB translocates into the nucleus and stimulates the expression of genes involved in a wide variety of biological functions. Inappropriate activation of NFkB has been associated with a number of inflammatory diseases while persistent inhibition of NFkB leads to inappropriate immune cell development or delayed cell growth. NFKB1 appears to have dual functions such as cytoplasmic retention of attached NF-kappa-B proteins by p105 and generation of p50 by a cotranslational processing. This antibody can bind p105 isoforms of NFKB1.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for NFKB1,p105 antibody 23576-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for NFKB1,p105 antibody 23576-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for NFKB1,p105 antibody 23576-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Oncotarget Single cell whole genome sequencing reveals that NFKB1 mutation affects radiotherapy sensitivity in cervical cancer. | ||
In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim NFKB1-miR-612-FAIM2 pathway regulates tumorigenesis in neurofibromatosis type 1. |