- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-SMCR7L/MID51
SMCR7L/MID51 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris et plus (2)
Applications
WB, IHC, IF, IP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 20164-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
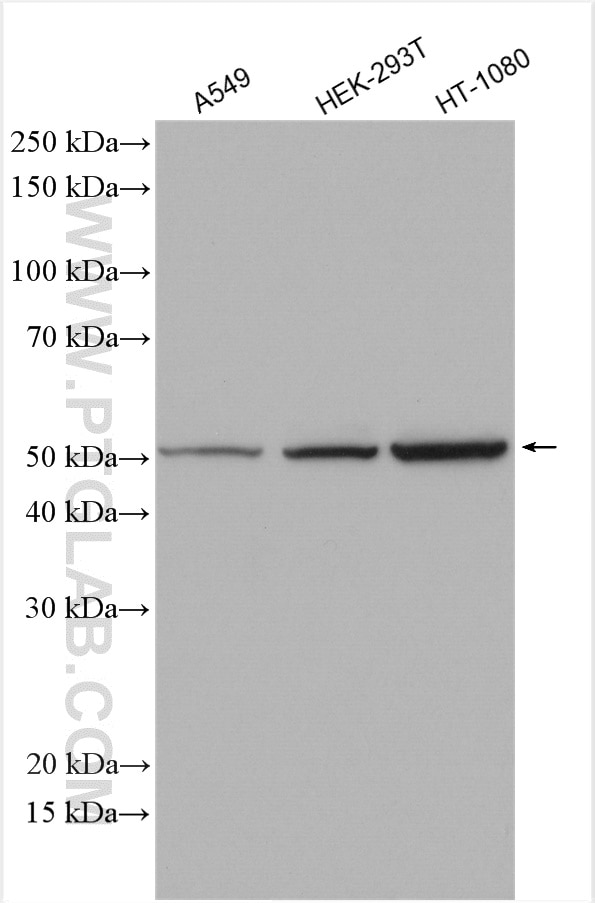
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules A549, cellules HEK-293T, cellules HT-1080, cellules NIH/3T3, RAW264.7, tissu testiculaire de souris |
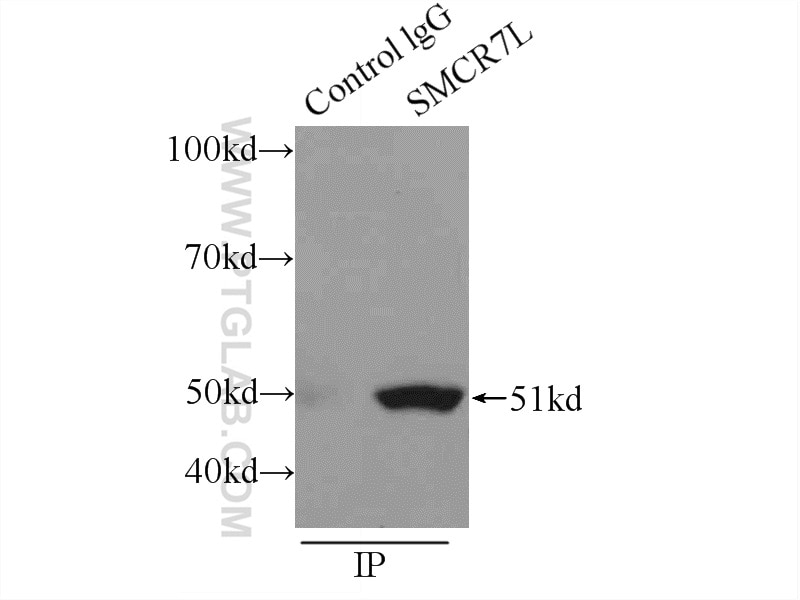
| Résultats positifs en IP | cellules RAW 264.7 |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 10 publications below |
| WB | See 73 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 3 publications below |
| IP | See 2 publications below |
| FC | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
20164-1-AP cible SMCR7L/MID51 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF, IP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, porc, singe, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | SMCR7L/MID51 Protéine recombinante Ag13775 |
| Nom complet | Smith-Magenis syndrome chromosome region, candidate 7-like |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 463 aa, 51 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 48-51 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC002587 |
| Symbole du gène | SMCR7L |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 54471 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Human SMCR7L gene encodes, MID51, the mitochondrial dynamic protein of 51 kDa (also called mitochondrial elongation factor 1, MIEF1). MID51 is a single-pass membrane protein anchored to the mitochondrial outer membrane and regulates mitochondrial morphology. Mitochondrial morphology is controlled by two opposing processes: fusion and fission. Elevated MID51 levels induce extensive mitochondrial fusion, whereas depletion of MID51 causes mitochondrial fragmentation. MID51 interacts with and recruits Drp1 to mitochondria, suggesting a critical role of MID51 in regulation of mitochondrial fusion-fission machinery in vertebrates.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for SMCR7L/MID51 antibody 20164-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for SMCR7L/MID51 antibody 20164-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Science Golgi-derived PI(4)P-containing vesicles drive late steps of mitochondrial division. | ||
Cell Metab Mitochondrial Dynamics Is Critical for the Full Pluripotency and Embryonic Developmental Potential of Pluripotent Stem Cells. | ||
Nat Cell Biol MIROs and DRP1 drive mitochondrial-derived vesicle biogenesis and promote quality control.
| ||
Mol Cell Triaging of α-helical proteins to the mitochondrial outer membrane by distinct chaperone machinery based on substrate topology | ||
Autophagy Loss of MIEF1/MiD51 confers susceptibility to BAX-mediated cell death and PINK1-PRKN-dependent mitophagy.
| ||
Sci Adv Oligodendroglial glycolytic stress triggers inflammasome activation and neuropathology in Alzheimer's disease. |