Recombinant Human CSPG4 protein (Myc Tag, His Tag)
Species
Human
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
Myc Tag, His Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg0201
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human CSPG4 protein Ser1583-Ser2224 (Accession# Q6UVK1) with a Myc tag and a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 1464 |
| Accession | Q6UVK1 |
| PredictedSize | 73.2 kDa |
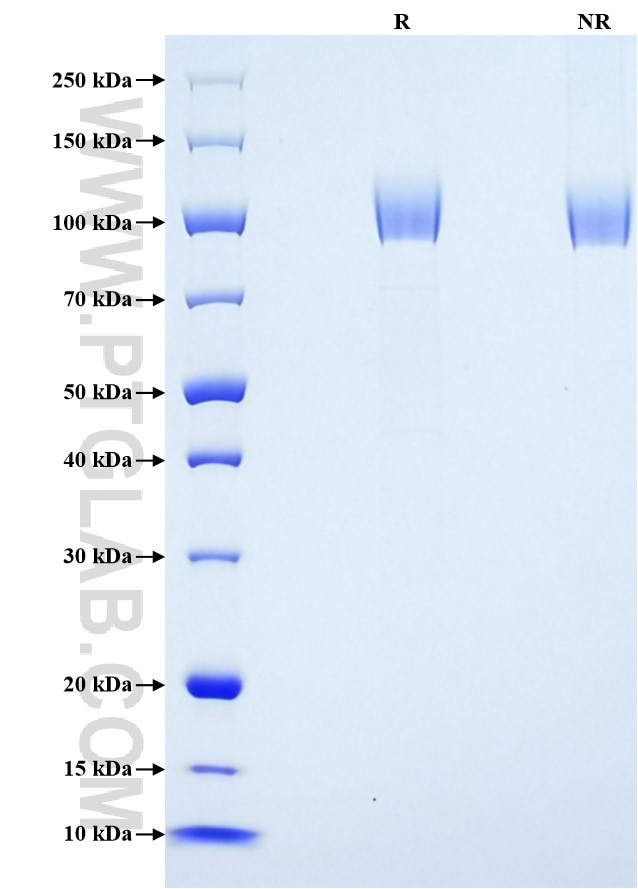
| SDS-PAGE | 90-125 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
CSPG4, also named as HMW-MAA, MCSP, MCSPG, MEL-CSPG, MSK16 and NG2, is a proteoglycan playing a role in cell proliferation and migration which stimulates endothelial cells motility during microvascular morphogenesis. CSPG4 may inhibit neurite outgrowth and growth cone collapse during axon regeneration. It is cell surface receptor for collagen alpha 2(VI) which may confer cells ability to migrate on that substrate. CSPG4 is also a signal-transducing protein by binding through its cytoplasmic C-terminus scaffolding and signaling proteins. It is a target of specific diagnosis and immunotherapy with antiidiotypic antibodies due, in part, to its roles in growth control, adhesion, cell-substratum interactions, and cell-cell contacts.
References:
1. Matthew A Price, et al. (2011) Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 24(6):1148-57. 2. J Iida, et al. (2001) J Biol Chem. 276(22):18786-94. 3. Jianbo Yang, et al. (2004) J Cell Biol. 165(6):881-91. 4. K M Eisenmann, et al. (1999) Nat Cell Biol. 1(8):507-13. 5. Valeria Rolih, et al. (2017) J Transl Med. 15(1):151.