Recombinant Human DLK1 protein (rFc Tag)
Species
Human
Purity
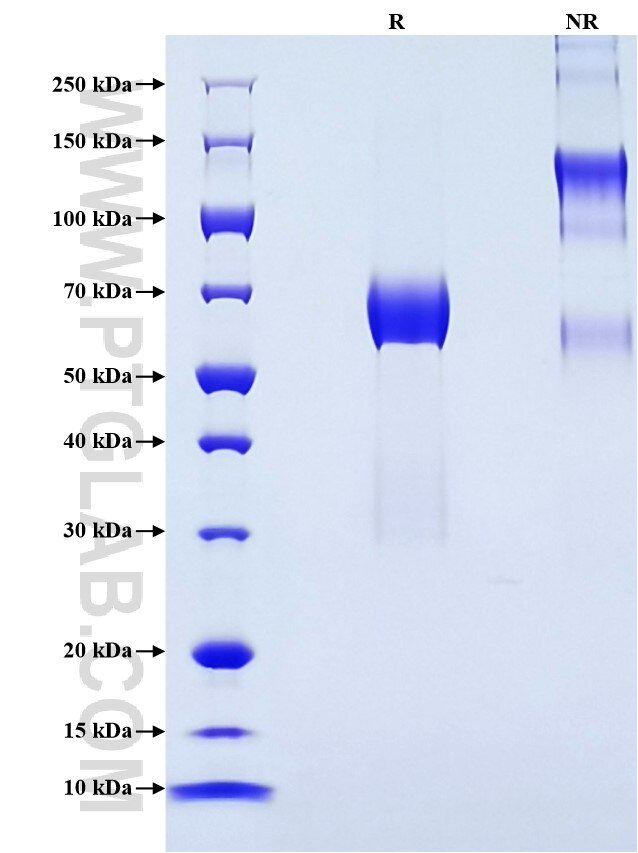
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg2909
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human DLK1 protein Ala24-Pro297 (Accession# P80370-1) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 8788 |
| Accession | P80370-1 |
| PredictedSize | 55.2 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 60-70 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
DLK1, also named PREF1, FA1, or pG2, is a transmembrane protein belonging to the epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like superfamily. It contains six EGF-like repeats in the extracellular region. DLK1 is abundant in preadipocytes and regulate adipocyte differentiation negatively. Deficiency of DLK1 gives rise to growth retardation and accelerated adiposity in mouse model. Expression of DLK1 is found in tumors with neuroendocrine features that implies DLK1 may be involved in neuroendocrine differentiation. It has been reported overexpression of DLK1 could lead to the development of metabolic abnormalities by impairment of adipocyte function in mice. The gene of DLK1 maps to chromosome 14q32, and encodes a 383-amino acid protein with a calculated molecular mass of 41 kDa. In preadipocytes, multiple discrete forms of DLK1 protein of 45-60 kDa are present, owing in part to N-linked glycosylation.
References:
1. Smas CM, Sul HS. (1993) Cell. 73(4):725-34. 2. Laborda J, et al. (1993) J Biol Chem. 268(6):3817-20. 3. Lee K, et al. (2003) J Clin Invest. 111(4):453-61.