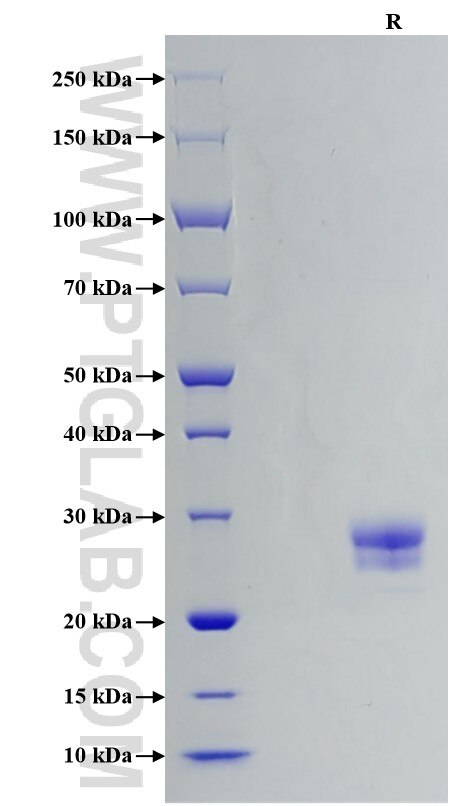
Recombinant Human TL1A/TNFSF15 protein (His Tag)
Species
Human
Purity
>95 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
His Tag
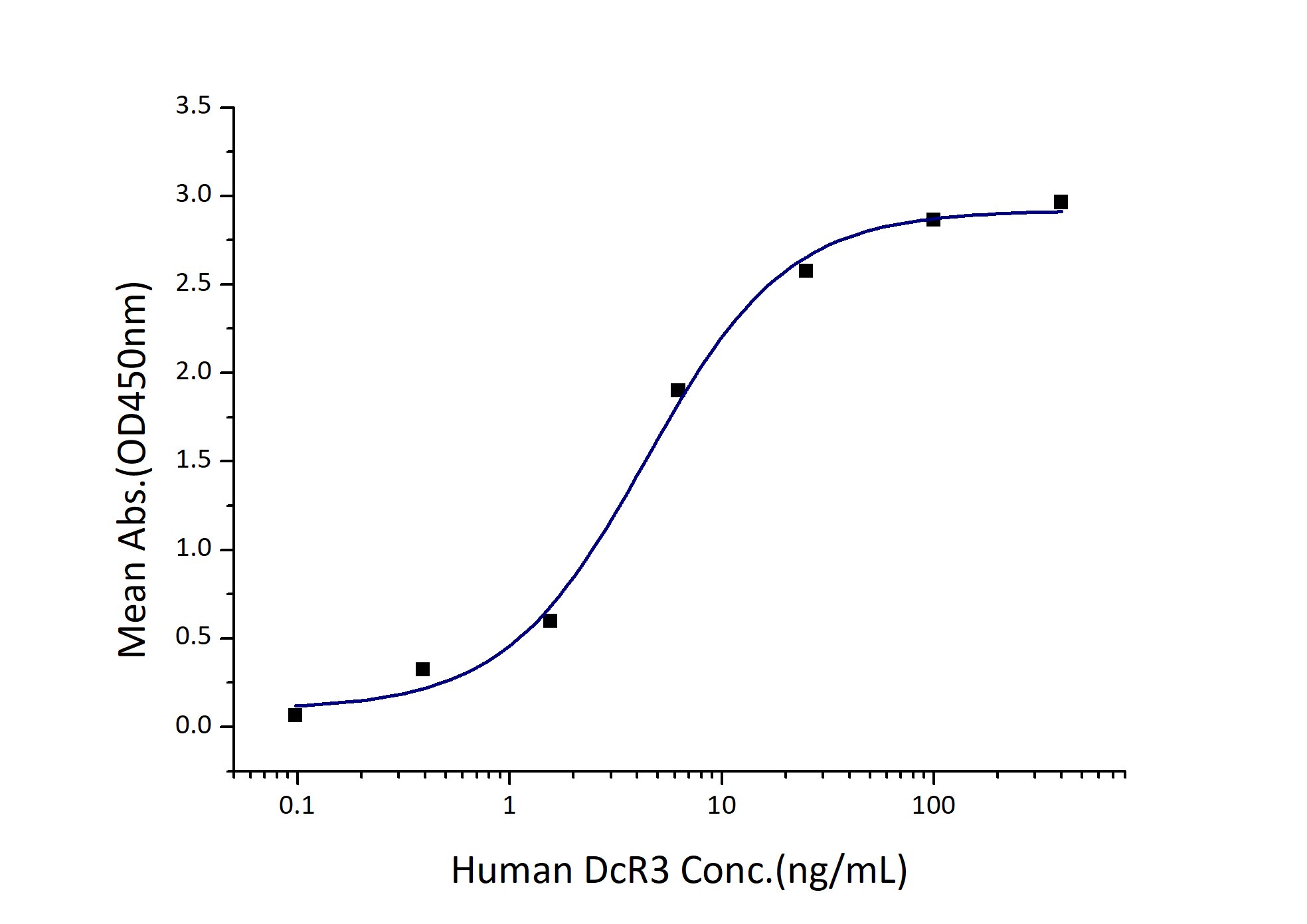
Activity
EC50: 2-9 ng/mL
Cat no : Eg32092
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >95 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Immobilized Human TL1A (His tag) at 0.5 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human DcR3 (His tag) with a linear range of 2-9 ng/mL. |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human TL1A protein Leu72-Leu251 (Accession# O95150-1) with a His tag at the N-terminus. |
| GeneID | 9966 |
| Accession | O95150-1 |
| PredictedSize | 21.3 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 25-29 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15 (TNFSF15) is also named as TL1 and VEGI. And it belongs to the tumor necrosis factor family. It is a receptor for TNFRSF25 and TNFRSF6B. VEGI induced degradation of IκB alpha, and nuclear translocation of p65 subunit of NFκB by activating NFκB. TL1A mediates activation and apoptosis of NFκB in DR3-expressing cell lines. Overexpression by cancer cells of a secretable VEGI fusion protein resulted in abrogation of xenograft tumor progression. The isoforms show endothelial cell-specific expression and are generated from a 17 kb human gene by alternative splicing. In addition, VEGI can inhibit vascular endothelial growth and angiogenesis (in vitro).
References:
1.Haridas V. et al. (1999). Oncogene. 18(47):6496-504. 2.Migone TS. et al. (2002). Immunity. 16(3):479-92 3. Chew LJ. et al. (2002). FASEB J. 16(7):742-4. 4. Zhai Y. et al. (1999). FASEB J. 13(1):181-9.