ASH2L antibody (pAb)
Host / Isotype
Rabbit / Serum
Reactivity
Human, Wide Range Predicted
Applications
ChIP, ChIP-Seq, WB
Cat No : 39099,39100 39099
Synonyms
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Tested Applications |
ChIP, ChIP-Seq, WB
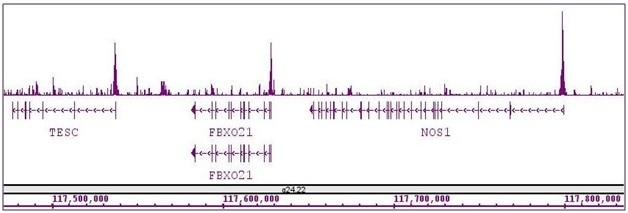
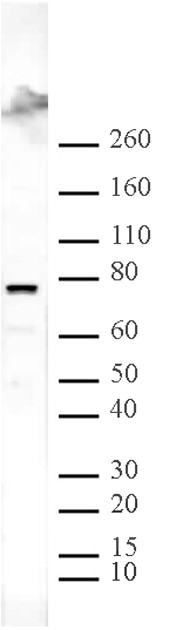
Applications Validated by Active Motif: ChIP: 10 ul per ChIP ChIP-Seq: 10 ul each WB*: 1:500 - 1:2,000 dilution ChIP-Seq validation was performed by Active Motif's Epigenetics Services; the complete data set is available in the UCSC Genome Browser by clicking here. *Note: many chromatin-bound proteins are not soluble in a low salt nuclear extract and fractionate to the pellet. Therefore, we recommend a High Salt / Sonication Protocol when preparing nuclear extracts for Western blot. |
| Tested Reactivity | Human, Wide Range Predicted |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / Serum |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | This ASH2L antibody was raised against full-length recombinant human ASH2L protein. |
| Full Name | ASH2L antibody (pAb) |
| Synonyms | ASH2, ash2l, ash2l1, ash2l2, bre2, set1, set1/ash2, pAb, polyclonal, absent small or homeotic discs, antibody, antibodies, sample, stem cell, stem cells |
| Molecular weight | 77 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NP_004665 |
| RRID | AB_2615057 |
| Purification Method | None |
| Buffer | Rabbit serum containing 30% glycerol and 0.035% sodium azide. Sodium azide is highly toxic. |
| Storage | Some products may be shipped at room temperature. This will not affect their stability or performance. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles by aliquoting items into single-use fractions for storage at -20°C for up to 2 years. Keep all reagents on ice when not in storage. |
Background Information
ASH2L (absent, small or homeotic discs 2) is a trithorax protein and is a component of different protein complexes, including i.e. mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL) oncoproteins, which contain histone methyltransferase activity. These complexes trimethylate the lysine 4 of histone H3. Histone H3 trimethyl Lys4 is one of histone modifications that are part of elaborate mechanisms that evolved to control the structure of the chromatin.