Published Applications
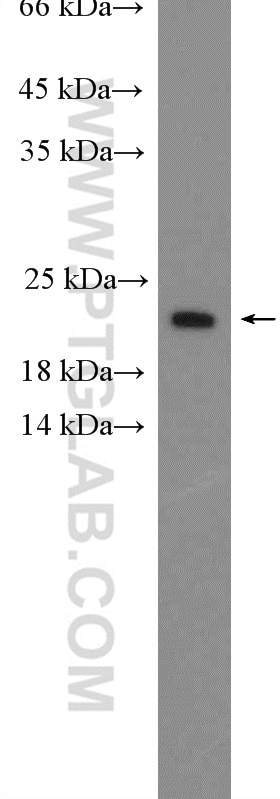
| WB | See 45 publications below |
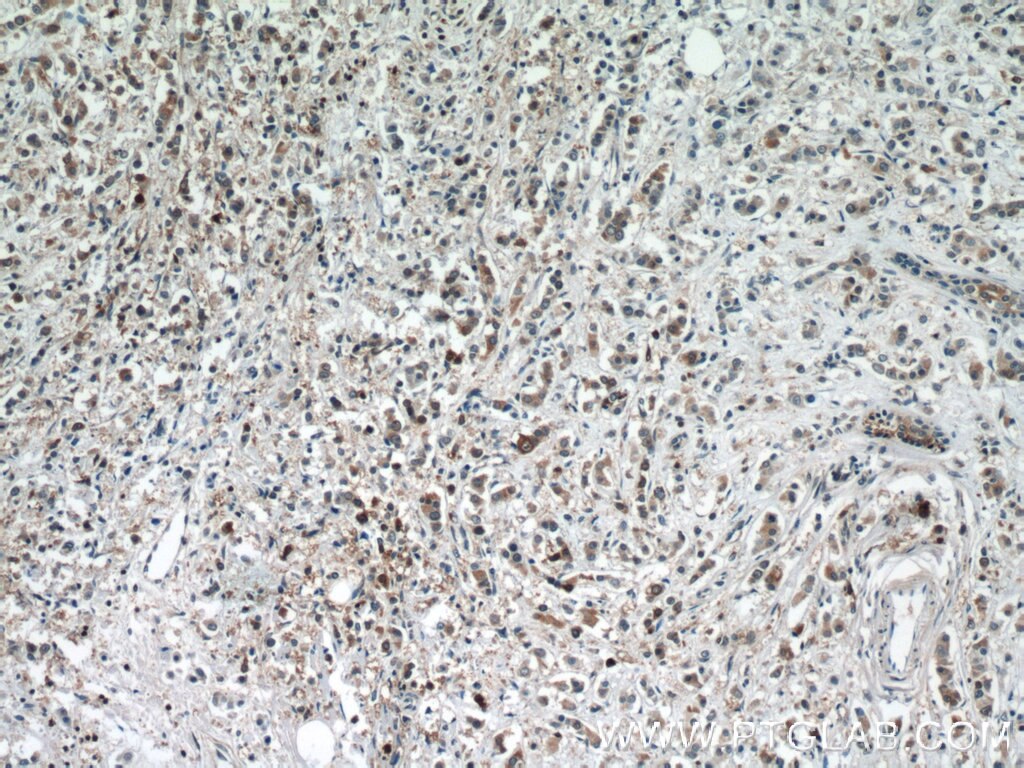
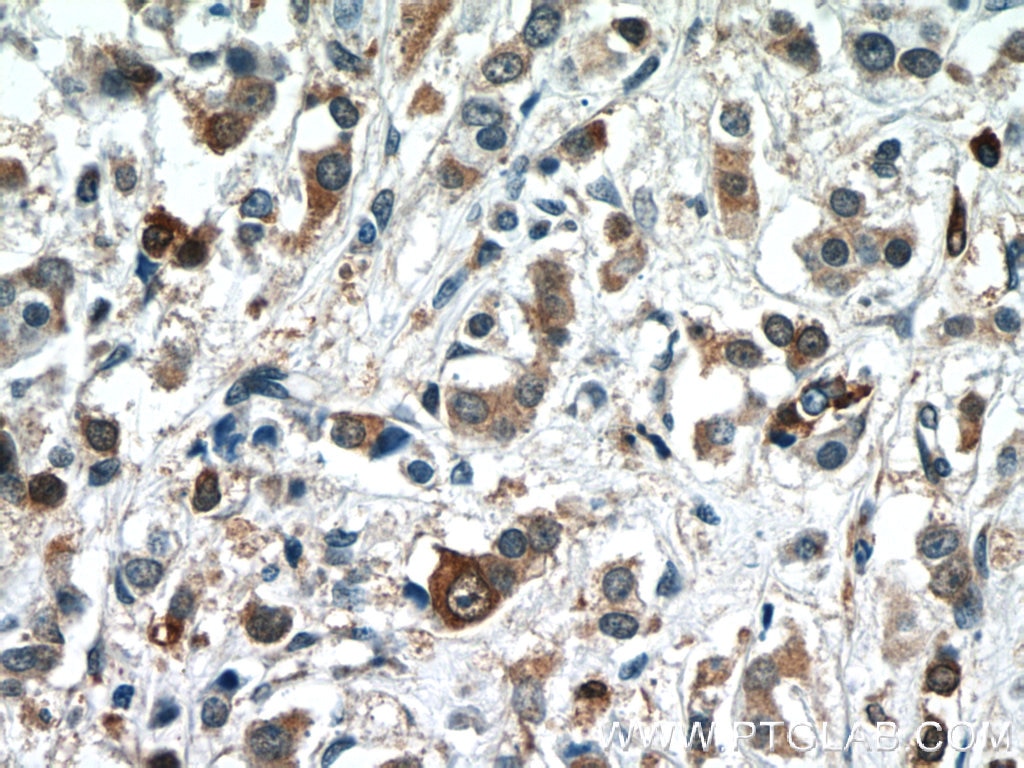
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
Product Information
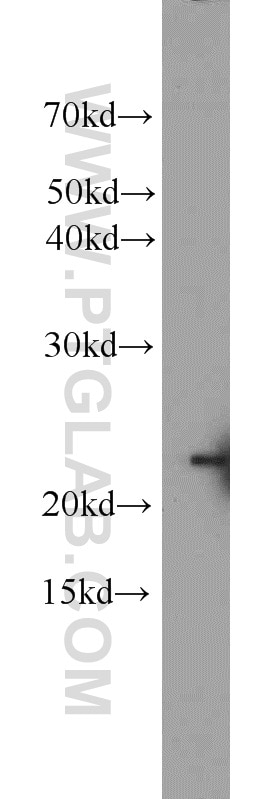
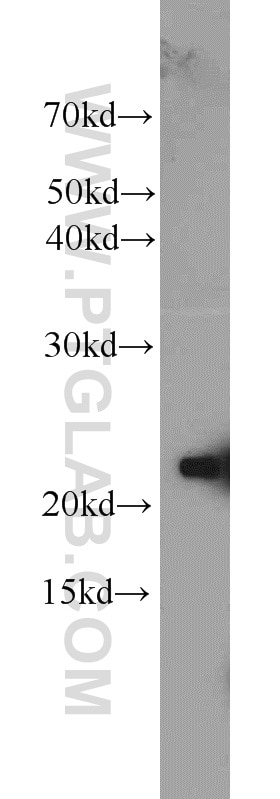
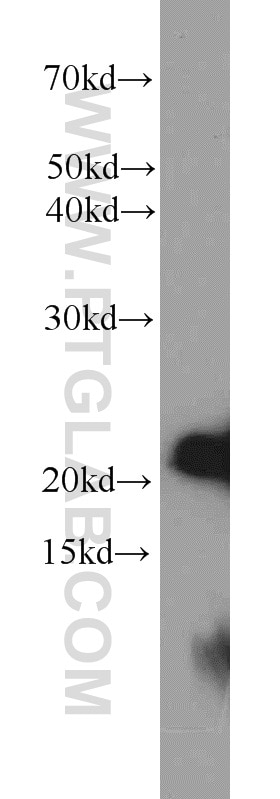
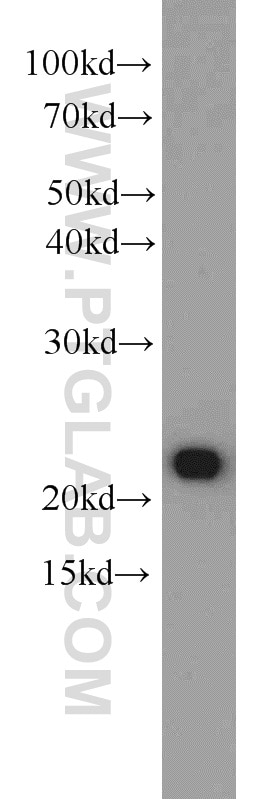
23931-1-AP targets BAX in WB, IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, bovine |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag21068 Product name: Recombinant human BAX protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-192 aa of BC014175 Sequence: MDGSGEQPRGGGPTSSEQIMKTGALLLQGFIQDRAGRMGGEAPELALDPVPQDASTKKLSECLKRIGDELDSNMELQRMIAAVDTDSPREVFFRVAADMFSDGNFNWGRVVALFYFASKLVLKALCTKVPELIRTIMGWTLDFLRERLLGWIQDQGGWDGLLSYFGTPTWQTVTIFVAGVLTASLTIWKKMG Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | BCL2-associated X protein |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 21 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC014175 |
| Gene Symbol | BAX |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 581 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q07812 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
BAX, also named as BCL2L4, is a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 protein family, which plays a pivotal role in controlling cell life and death. Bax largely localizes to the cytoplasm of healthy cells, but accumulates on the outer mitochondrial membrane upon apoptosis induction (PMID: 9108035). BAX can commit a cell to apoptosis by translocation from the cytosol to the mitochondria and permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane, which leads to the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria (PMID: 21763611). The expression of BAX is upregulated by the tumor suppressor protein p53, and BAX has been shown to be involved in p53-mediated apoptosis (PMID: 8183579).
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Br J Pharmacol Astaxanthin attenuates hepatic damage and mitochondrial dysfunction in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by up-regulating the FGF21/PGC-1α pathway. | ||
Oncotarget By reducing hexokinase 2, resveratrol induces apoptosis in HCC cells addicted to aerobic glycolysis and inhibits tumor growth in mice. | ||
Int J Oncol NT21MP negatively regulates paclitaxel-resistant cells by targeting miR‑155‑3p and miR‑155-5p via the CXCR4 pathway in breast cancer. | ||
Nanoscale Res Lett Cytotoxicity induced by nanobacteria and nanohydroxyapatites in human choriocarcinoma cells. | ||
Oncotarget AMPK activation-dependent autophagy compromises oleanolic acid-induced cytotoxicity in human bladder cancer cells. |