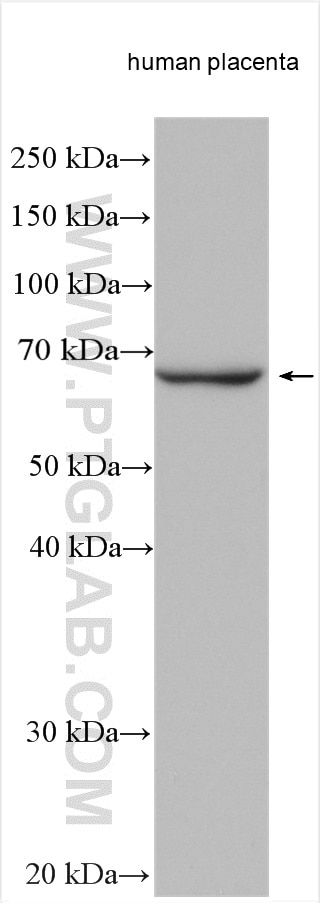
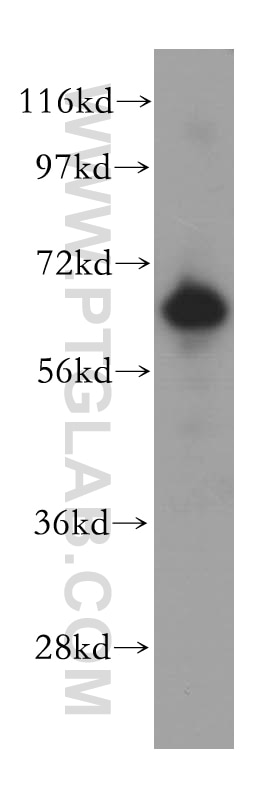
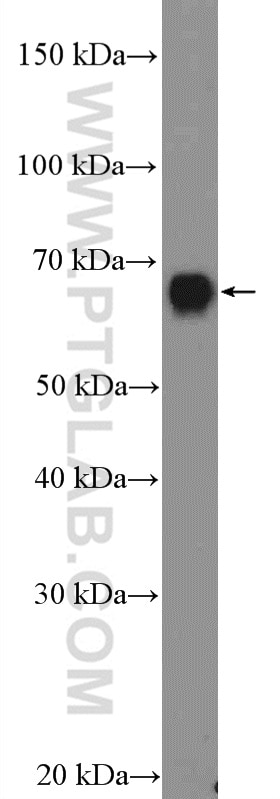
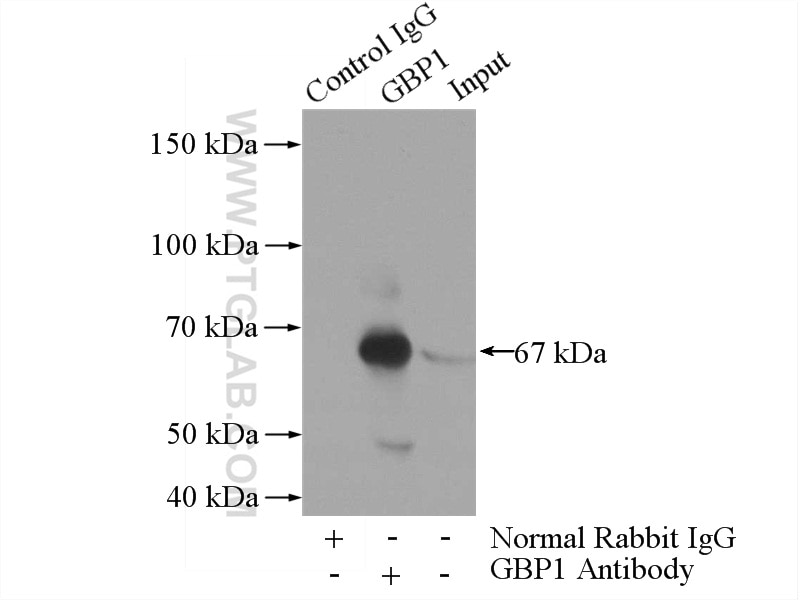
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | human placenta tissue, human brain tissue, HUVEC cells |
| Positive IP detected in | human placenta tissue |
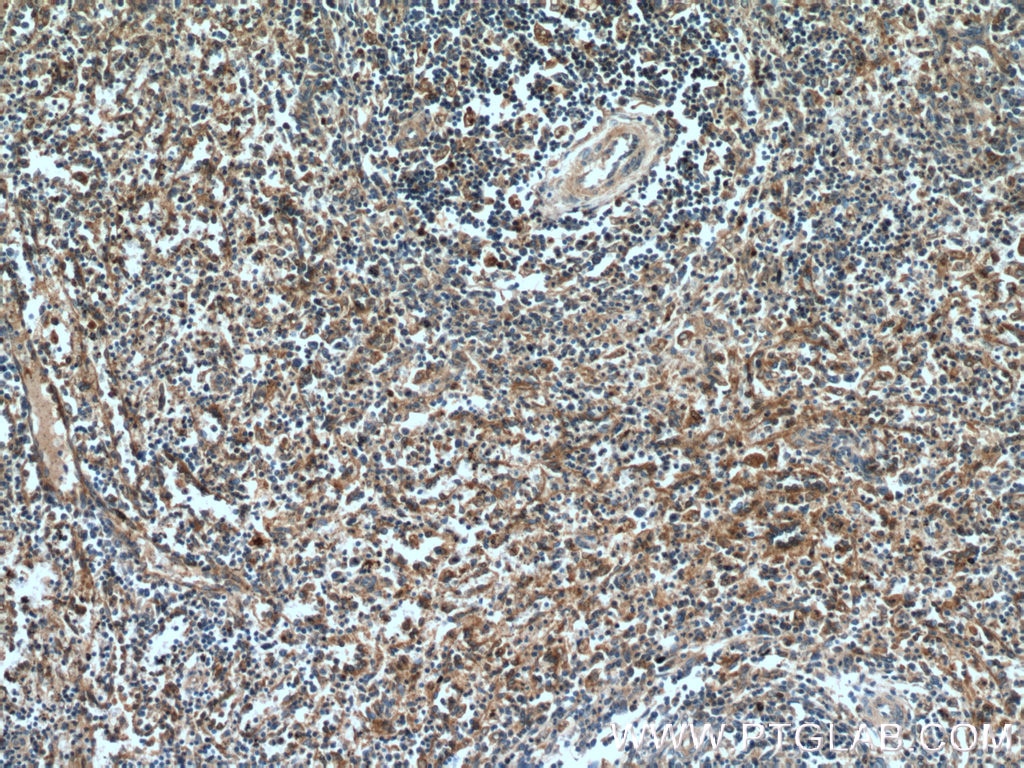
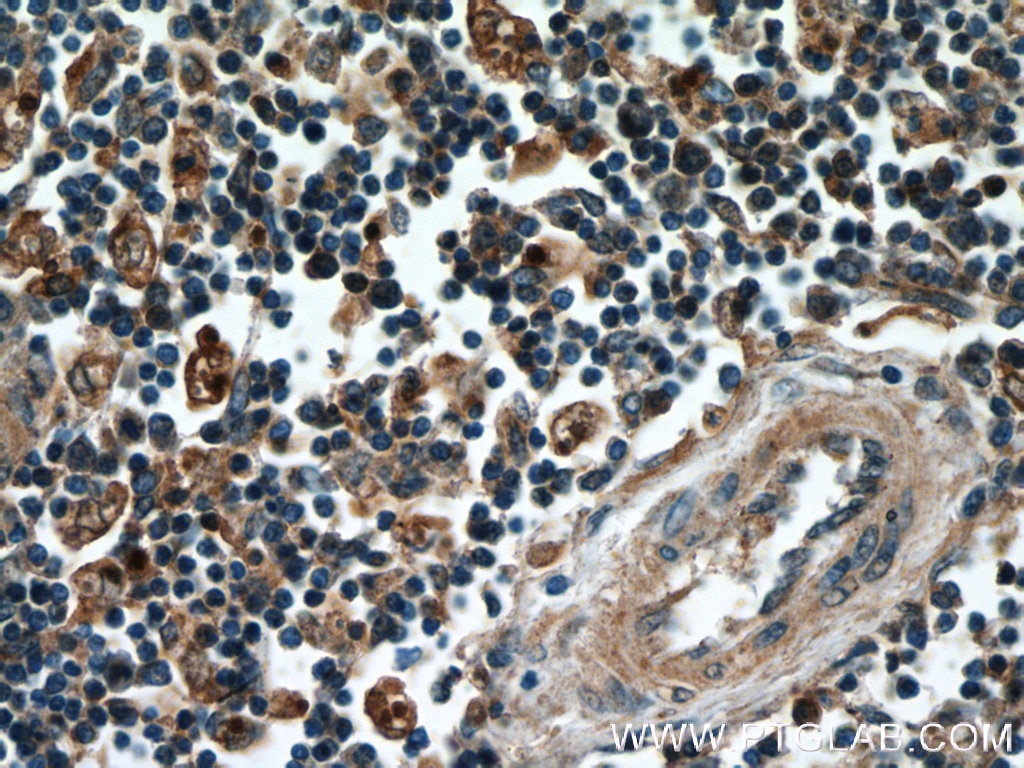
| Positive IHC detected in | human spleen tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
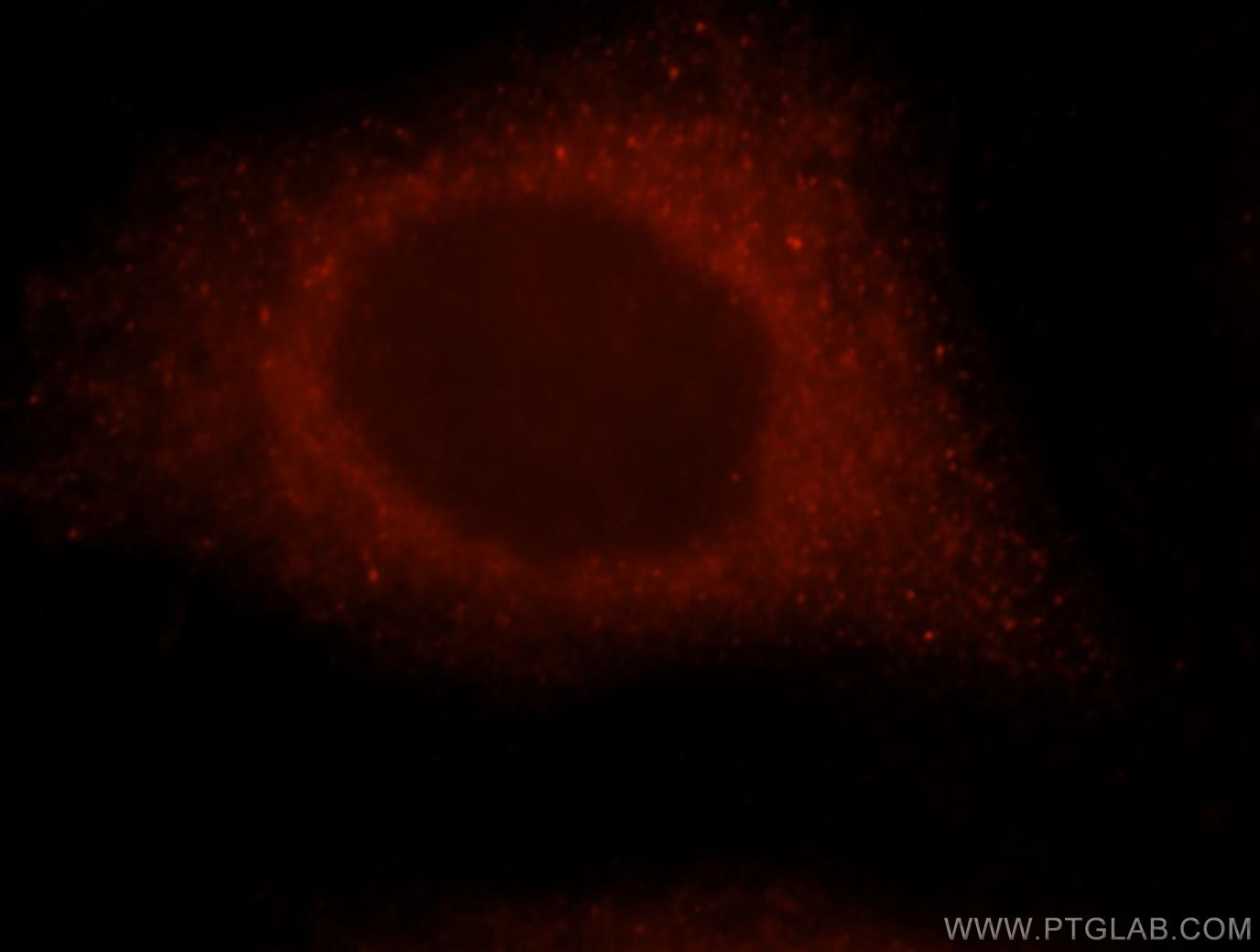
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | MCF-7 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:10-1:100 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 8 publications below |
| WB | See 27 publications below |
| IHC | See 6 publications below |
| IF | See 8 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
| RIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
15303-1-AP targets GBP1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, RIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, pig, chicken |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag7562 Product name: Recombinant human GBP1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 242-592 aa of BC002666 Sequence: VHRRKLAQLEKLQDEELDPEFVQQVADFCSYIFSNSKTKTLSGGIQVNGPRLESLVLTYVNAISSGDLPCMENAVLALAQIENSAAVQKAIAHYEQQMGQKVQLPTESLQELLDLHRDSEREAIEVFIRSSFKDVDHLFQKELAAQLEKKRDDFCKQNQEASSDRCSGLLQVIFSPLEEEVKAGIYSKPGGYRLFVQKLQDLKKKYYEEPRKGIQAEEILQTYLKSKESMTDAILQTDQTLTEKEKEIEVERVKAESAQASAKMLQEMQRKNEQMMEQKERSYQEHLKQLTEKMENDRVQLLKEQERTLALKLQEQEQLLKEGFQKESRIMKNEIQDLQTKMRRRKACTIS Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | GTP binding protein 1 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 68 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 67 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC002666 |
| Gene Symbol | GBP1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2633 |
| RRID | AB_2247448 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P32455 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Guanylate binding protein 1 (GBP1) belongs to the dynamin superfamily of large GTPases. The expression of GBP1 is induced by IFN and GBP1 is characterized by its ability to specifically bind guanine nucleotides such as GMP, GDP, and GTP and its ability to hydrolyze GTP to GDP and GMP.
What is the molecular weight of GBP1?
The molecular weight of GBP1 is 68kDa.
What is the cellular localization of GBP1?
GBP1 is predominantly cytosolic, but under certain conditions is farnesylated and associated with intracellular membranes such as the Golgi (PMID: 15937107).
What is the role of GBP1 in immunity?
GBP1 is induced in response to type I and type II IFN and as such plays a role in protective immunity against a spectrum of intracellular pathogens ranging from viruses to bacteria to protozoa, such as negative-strand RNA Rhabdovirus, vesicular stomatitis virus and the positive-strand RNA Picornovirus, encephalomyocarditis virus in cultured cells, the inhibition of Chlamydia trachomatis, Toxoplasma gondii, and Salmonella enterica (PMID: 21142871). These anti-pathogenic functions involve the recruitment to vacuolar compartments for the destruction of the pathogen, the assembly of innate immune complexes such as the inflammasome, or the initiation of autophagy.
What is the role of GBP-1 in colorectal carcinoma?
In colorectal carcinoma (CRC), the presence of tumor-infiltrating T helper type 1 (Th1) cells participates in anti-tumoral responses and an improved clinical outcome (PMID: 17008531, 20927778). IFN promote the Th1 immune response, as well as GBP-1 expression. In CRC, GBP-1 expression acts as a tumor suppressor, where inhibition of tumor growth by GBP-1 is the result of its strong antiangiogenic activity as well as its direct anti-tumorigenic effect on tumor cells and is correlated with a better outcome (PMID: 23042300).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for GBP1 antibody 15303-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for GBP1 antibody 15303-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for GBP1 antibody 15303-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for GBP1 antibody 15303-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Immunol Guanylate-binding proteins convert cytosolic bacteria into caspase-4 signaling platforms.
| ||
Cell Host Microbe GBPs Inhibit Motility of Shigella flexneri but Are Targeted for Degradation by the Bacterial Ubiquitin Ligase IpaH9.8. | ||
J Med Virol Guanylate-binding protein 1 inhibits Hantaan virus infection by restricting virus entry | ||
J Transl Med Function and mechanism of GBP1 in the development and progression of cervical cancer
|