Recombinant Human CD3 delta protein (rFc Tag)
Species
Human
Purity
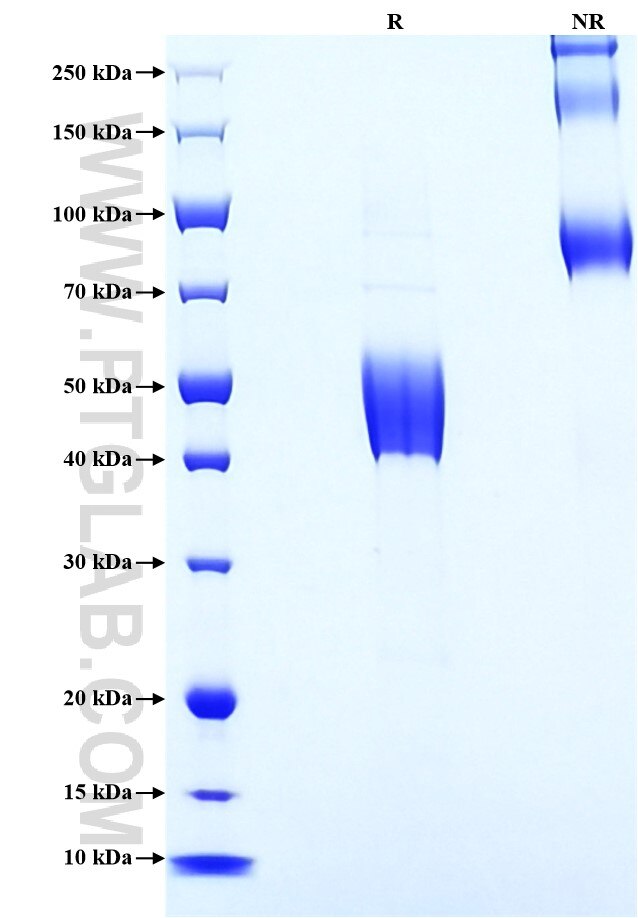
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg2288
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human CD3 delta protein Phe22-Ala105 (Accession# P04234-1) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 915 |
| Accession | P04234-1 |
| PredictedSize | 35.8 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 40-55 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
CD3 is a complex of proteins that directly associates with the T cell receptor (TCR). The TCR/CD3 complex of T-lymphocytes consists of either a TCR alpha/beta or TCR gamma/delta heterodimer coexpressed at the cell surface with the invariant subunits of CD3 labeled gamma, delta, epsilon, zeta, and eta. The TCR recognizes antigens bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. TCR-mediated peptide-MHC recognition is transmitted to the CD3 complex, leading to the intracellular signal transduction. CD3 delta/CD3D is a single-pass type I membrane protein which consists of an extracellular domain of 84 amino acids, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic domain of 45 amino acids. Defects in CD3 delta are a cause of severe combined immunodeficiency.
References:
1. E A Padlan, et al. (1997) Curr Biol. 7(1):R17-20. 2. Geneviève de Saint Basile (2004) J Clin Invest. 114(10):1512-7. 3. Clifford S Guy, et al. (2009) Immunol Rev. 232(1):7-21.