Recombinant Human PD-1/CD279 protein (His Tag)
Species
Human
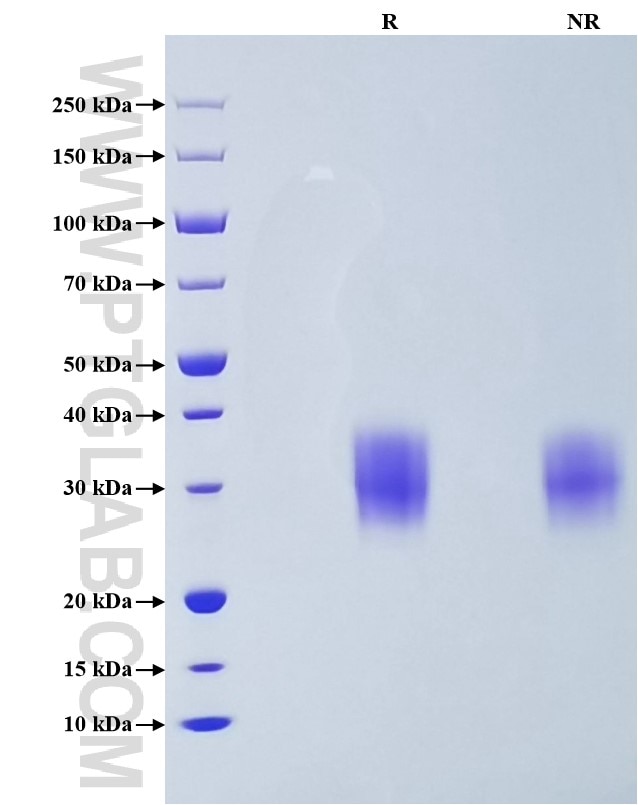
Purity
>95 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
His Tag
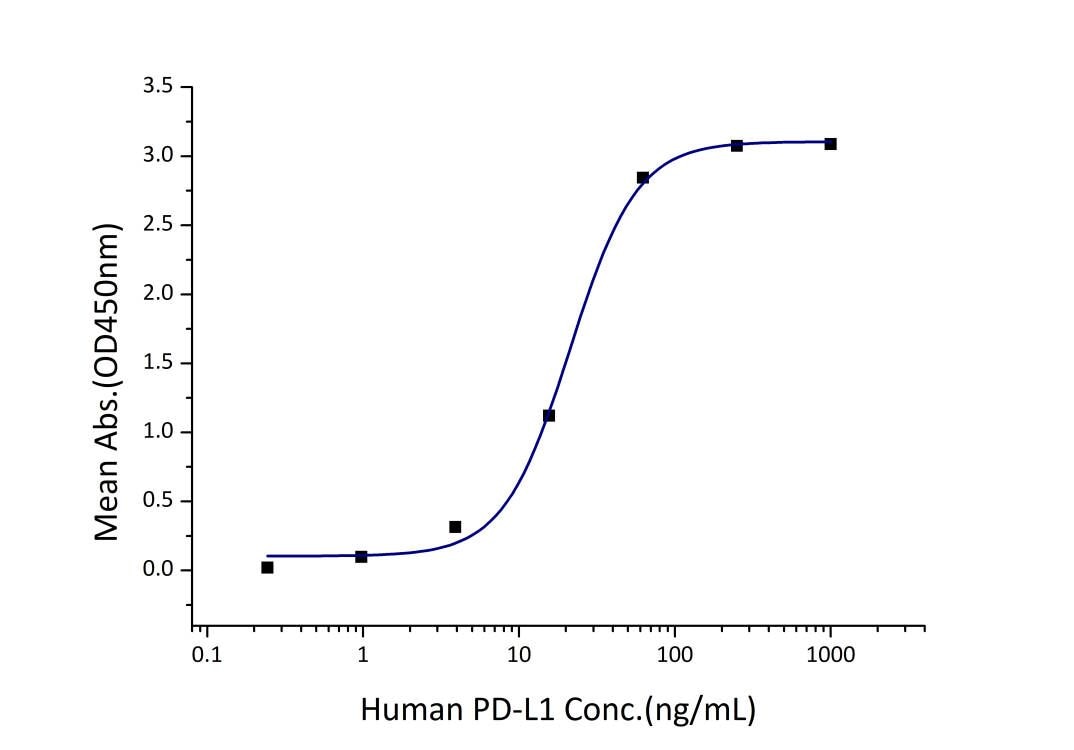
Activity
EC50: 11-43 ng/mL
Cat no : Eg0974
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >95 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Immobilized Human PD-1 (His tag) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human PD-L1 (hFc tag) with a linear range of 11-43 ng/mL. |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human PD-1 protein Phe24-Gln167 (Accession# Q15116) with His tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 5133 |
| Accession | Q15116 |
| PredictedSize | 16.9 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 26-38 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1, also known as CD279) is an immunoinhibitory receptor that belongs to the CD28/CTLA-4 subfamily of the Ig superfamily. It is a 288 amino acid (aa) type I transmembrane protein composed of one Ig superfamily domain, a stalk, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular domain containing an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) as well as an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM). PD-1 is expressed during thymic development and is induced in a variety of hematopoietic cells in the periphery by antigen receptor signaling and cytokines. Engagement of PD-1 by its ligands PD-L1 or PD-L2 transduces a signal that inhibits T-cell proliferation, cytokine production, and cytolytic function. It is critical for the regulation of T-cell function during immunity and tolerance. Blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway has been developed for cancer immunotherapy.
References:
1. Mary E Keir, et al. ( 2008) Annu Rev Immunol. 26:677-704. 2. James L Riley. (2009) Immunol Rev. 229(1):114-25. 3. Loise M Francisco, et al. (2010) Immunol Rev. 236:219-42. 4. Suzanne L Topalian, et al. (2012) N Engl J Med. 366(26):2443-54. 5. Yanyan Han, et al. (2020) Am J Cancer Res. 10(3):727-742.