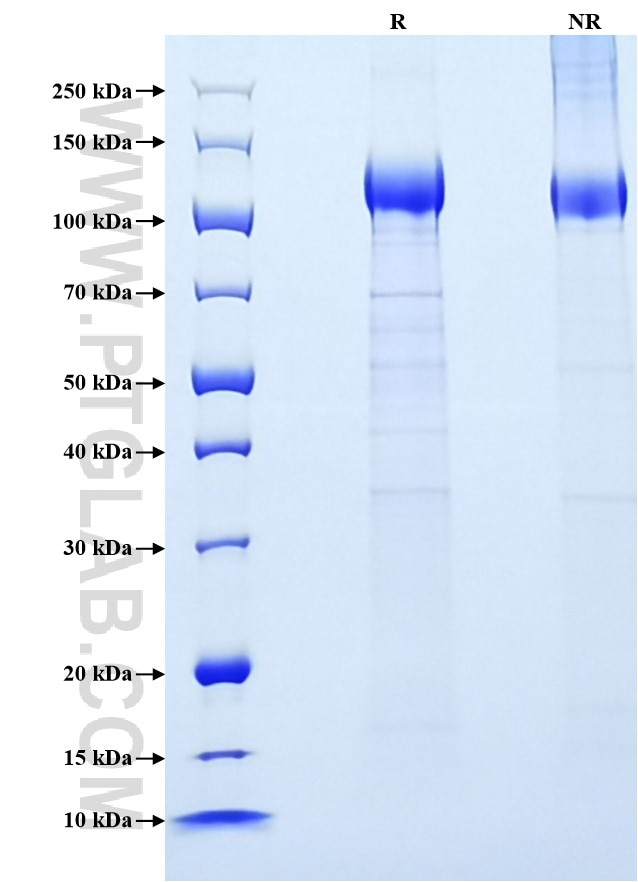
Recombinant Human VEGFR1/FLT-1 protein (His Tag)
Species
Human
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
His Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg0438
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human VEGFR1 protein Ser27-Asn756 (Accession# P17948-1) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 2321 |
| Accession | P17948-1 |
| PredictedSize | 86 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 100-140 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (VEGFR-1, FLT-1) is a receptor tyrosine kinase belonging to the VEGFR family. VEGF is a key regulator of physiological angiogenesis and has also been implicated in pathological angiogenesis associated with tumors, intraocular neovascular disorders and other conditions. The biological effects of VEGF are mediated by VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2. Both the two receptors have seven immunoglobulin-like repeats in the extracellular domain, a single transmembrane region and a tyrosine kinase domain. VEGFR-1 binds VEGFA, PIGF and VEGFB, and plays an essential role in the development of embryonic vasculature, the regulation of angiogenesis, cell survival, cell migration, macrophage function, chemotaxis, and cancer cell invasion. Soluble VEGF receptor-1 (sVEGFR-1, sFlt-1), a truncated version of the cell membrane-spanning VEGFR-1, has the potential to act as a decoy receptor for VEGFA. Elevated serum sVEGFR-1 have been found in women with preeclampsia. Excess placental sVEGFR-1 may contribute to endothelial dysfunction, hypertension, and proteinuria in preeclampsia.
References:
1. Kendall, R L et al. (1996) Biochem Biophys Res Commun.226(2):324-328. 2. Koga, Kaori et al. (2003) J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 88(5):2348-2351. 3. Shibuya, Masaubmi. (2006) Angiogenesis.9(4):225-231. 4. Wu, Florence T H et al. (2010) J Cell Mol Med.14(3):528-552.