Product Information
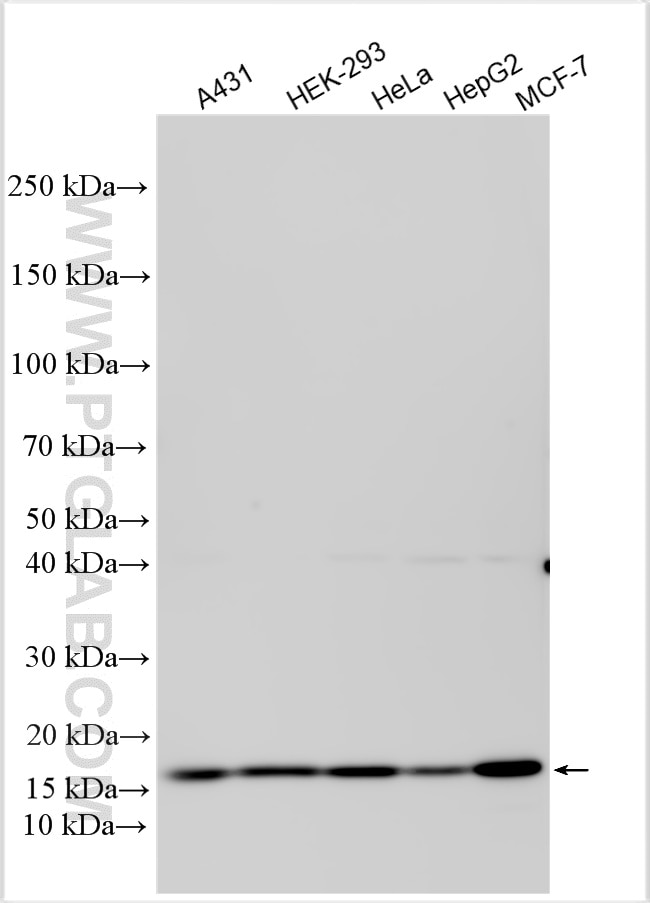
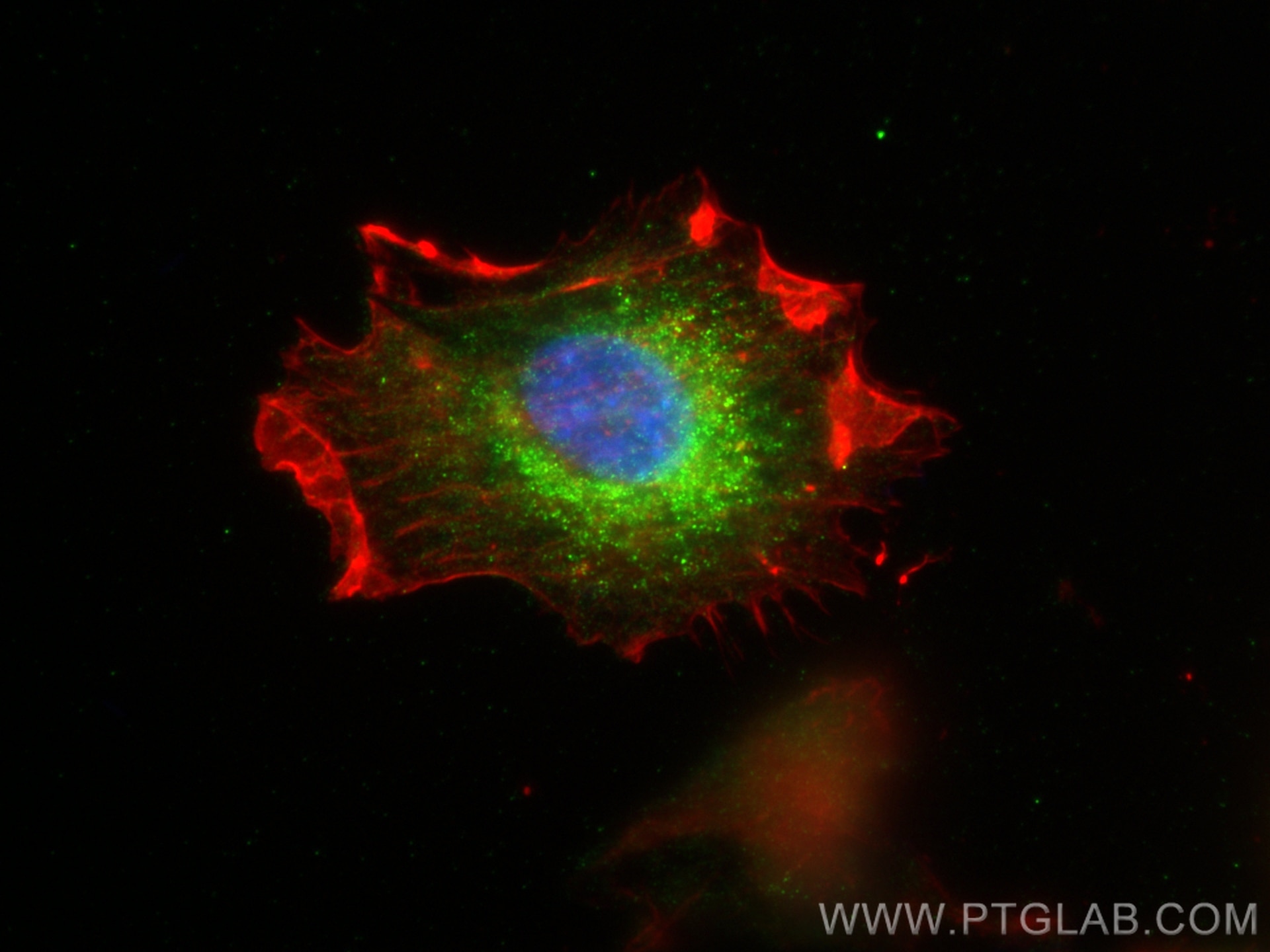
29611-1-PBS targets LAMTOR1 in WB, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | LAMTOR1 fusion protein Ag31215 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | chromosome 11 open reading frame 59 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 161 aa, 18 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 18 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC001706 |
| Gene Symbol | LAMTOR1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 55004 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q6IAA8 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
LAMTOR1 (Late Endosome/Lysosome-Associated Membrane Protein 1) is a membrane protein specifically localized to the surface of late endosomes/lysosomes and is involved in lysosomal transport and maturation. LAMTOR1 is a key component of the lysosomal articulating protein complex Ragulator, which is required for the localization of the Ragulator complex to lysosomes. LAMTOR1 is a key component of the lysosomal bridging protein complex Ragulator and is required for the localization of the Ragulator complex to the lysosome. LAMTOR1 is involved in autophagy, cell growth, immune regulation, cancer development, and regulatory pathways of glucose metabolism. Recent studies have shown that in calorie restriction, lithocholic acid activates AMPK through the glucose-sensing pathway ( the lysosomal pathway ) and the body senses the metabolic signals induced by calorie restriction and exerts its role in slowing down the effects of aging and prolonging the lifespan, whereas deletion of LAMTOR1 results in the inability of AMPK to be activated in order to play its role.