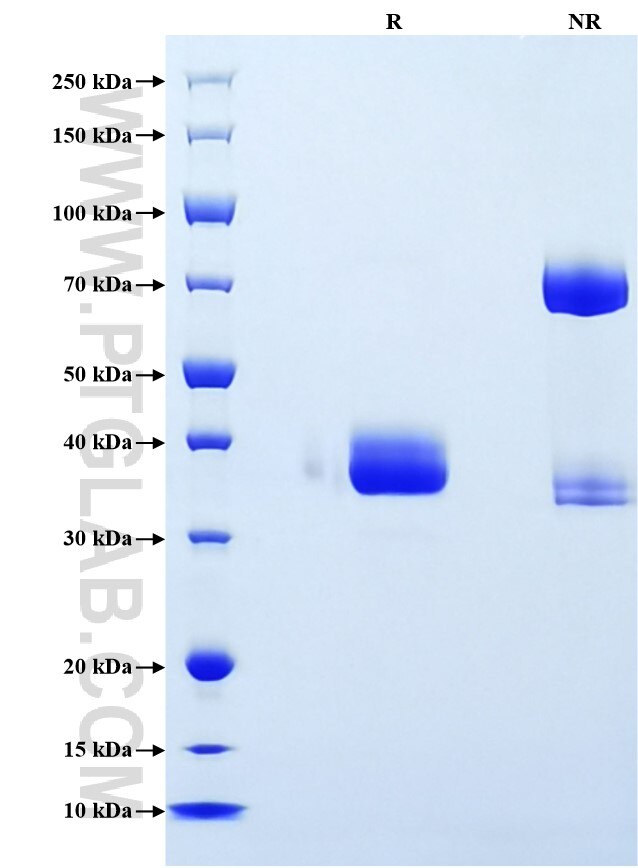
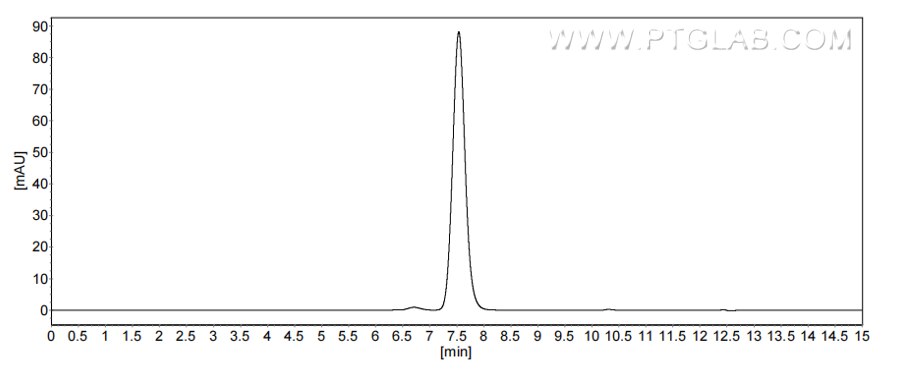
Recombinant Mouse ACBP/DBI protein (rFc Tag) (HPLC verified)
Species
Mouse
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
>90%, SEC-HPLC
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg2462
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE >90%, SEC-HPLC |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Mouse ACBP protein Met1-Ile87 (Accession# P31786) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the N-terminus. |
| GeneID | 13167 |
| Accession | P31786 |
| PredictedSize | 37.2 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 35-40 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Acyl coenzyme A binding protein (ACBP), also known as diazepam-binding inhibitor (DBI), is a phylogenetically ancient protein present in some eubacteria and the entire eukaryotic radiation. In several eukaryotic phyla, ACBP/DBI transcends its intracellular function in fatty acid metabolism because it can be released into the extracellular space.Indeed, autophagy is tied to the atypical secretion of this leaderless protein that is predominantly present in the cytosol of nucleated cells. Once released into the extracellular space, ACBP/DBI then acts on gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors to inhibit autophagy via autocrine, paracrine, and neuroendocrine pathways.
References:
1.Montégut, Léa et al. (2023) Aging Cell.22(9):e13910. 2.Motiño, Omar et al. (2022) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 119(41):e2207344119. 3.Alquier, Thierry et al. (2021) Trends Endocrinol Metab. 32(11):890-903.